Is Spiritual Health A Part Of Mental Emotional Health

In an era defined by unprecedented rates of anxiety, depression, and burnout, a growing number of individuals and mental health professionals are looking beyond traditional therapeutic models. They are seeking a deeper understanding of well-being, one that encompasses not only the psychological and emotional, but also the spiritual. But is spiritual health truly a component of mental and emotional health, or is it a separate, albeit related, aspect of human experience?
This question sparks a complex and often nuanced debate within the fields of psychology, healthcare, and spirituality. While some consider spirituality an integral part of a holistic approach to mental and emotional well-being, others view it as a distinct domain, potentially offering complementary benefits but not directly impacting mental health. Understanding the interplay between these facets of our lives is crucial for developing more effective and personalized strategies for promoting overall well-being.
Defining Spiritual Health
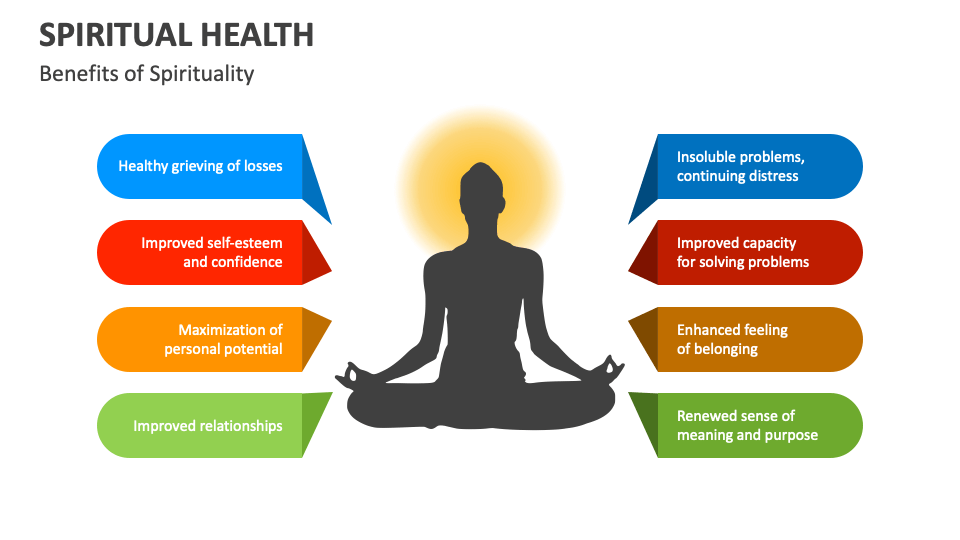
The term "spiritual health" often conjures images of religious practices, but its definition extends far beyond organized religion. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), spirituality encompasses an individual's beliefs, values, and sense of purpose in life. It includes their search for meaning and connection to something larger than themselves, whether that be a higher power, nature, humanity, or a personal set of guiding principles.
This broader understanding emphasizes the subjective and personal nature of spirituality. It acknowledges that individuals can cultivate spiritual well-being regardless of their religious affiliation or lack thereof. This allows space for agnostics and atheists to also cultivate this side of health.
The Argument for Integration
Many researchers and clinicians argue that spiritual health is inextricably linked to mental and emotional health. They posit that a strong sense of purpose and meaning can provide resilience in the face of adversity, buffer against stress, and promote positive emotions. This holistic approach highlights the individual parts that make up a whole person.
Studies have shown that individuals with a strong spiritual foundation often report higher levels of life satisfaction, hope, and optimism. They are better equipped to cope with challenges such as grief, illness, and trauma. Finding purpose has become more important to individuals.
Dr. Kenneth Pargament, a professor of psychology at Bowling Green State University and a leading expert on the psychology of religion and spirituality, has extensively researched the ways in which spirituality can buffer against stress and promote well-being. His work demonstrates that individuals who draw on their spiritual beliefs and practices are more likely to experience post-traumatic growth, finding meaning and purpose in the aftermath of difficult experiences.
The Case for Distinction
Conversely, some experts argue that while spirituality can positively influence mental and emotional health, it is a distinct construct that should not be conflated with psychological well-being. They suggest that focusing solely on spirituality as a means to improve mental health may oversimplify the complexities of mental illness and neglect the importance of evidence-based treatments.
This perspective emphasizes the importance of addressing underlying psychological and emotional issues through traditional therapies such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and medication. While spirituality can be a valuable resource, it should not be considered a replacement for professional mental health care.
Furthermore, some argue that conflating spirituality with mental health could lead to spiritual bypassing. Spiritual bypassing is the use of spiritual beliefs or practices to avoid dealing with painful emotions or unresolved psychological issues. This can hinder personal growth and prevent individuals from seeking the necessary professional help.
The Role of Research and Evidence
The debate surrounding the relationship between spiritual health and mental emotional health highlights the need for more rigorous research in this area. While numerous studies have explored the correlation between spirituality and well-being, further investigation is needed to establish causal relationships and identify the specific mechanisms through which spirituality impacts mental health.
Research is also needed to explore the potential negative effects of spirituality, such as spiritual abuse or the use of religion to justify harmful beliefs and behaviors. A balanced approach is essential to understanding the complex interplay between spirituality and mental health.
Integrating Spirituality into Mental Healthcare
Despite the ongoing debate, a growing number of mental health professionals are recognizing the importance of addressing spirituality in their practice. They are incorporating spiritual assessments into their evaluations and tailoring treatment plans to meet the unique spiritual needs of their clients. This can include encouraging clients to engage in spiritual practices that they find meaningful, such as meditation, prayer, or spending time in nature.
However, it is crucial for mental health professionals to approach spirituality with sensitivity and respect. They must be mindful of their own biases and avoid imposing their beliefs on their clients. The goal is to support clients in exploring their own spirituality in a way that promotes their overall well-being.
"The integration of spirituality into mental healthcare requires cultural competence and a deep understanding of diverse spiritual traditions," explains Dr. Anu Sharma, a psychiatrist specializing in integrative mental health. "It's about creating a safe space for clients to explore their beliefs and values, and helping them to harness the power of their spirituality to promote healing and resilience."
Moving Forward: A Holistic Approach
Ultimately, the question of whether spiritual health is a part of mental and emotional health may not have a definitive answer. The relationship between these aspects of human experience is complex and multifaceted, varying from individual to individual.
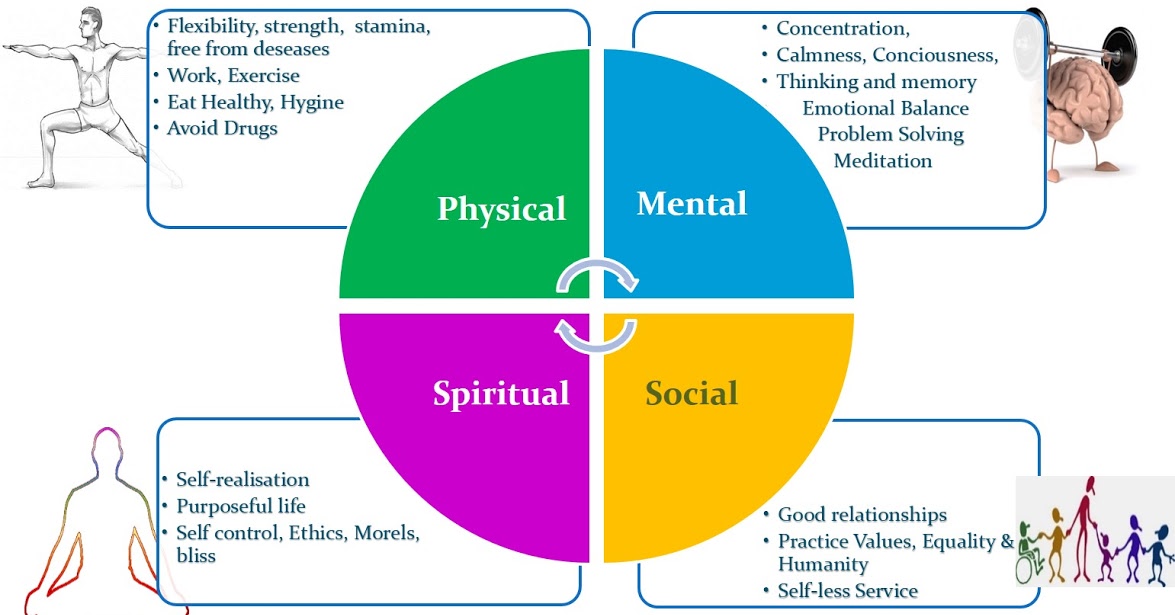
What is clear is that a holistic approach to well-being must acknowledge the importance of both mental/emotional and spiritual dimensions. By integrating spirituality into mental healthcare and promoting research in this area, we can develop more comprehensive and personalized strategies for supporting individuals in their journey towards overall well-being. This can potentially make people more at peace.
As the mental health landscape continues to evolve, it is essential to remain open to new perspectives and approaches. Embracing the potential of spirituality as a resource for healing and growth can lead to a more nuanced and compassionate understanding of the human experience.