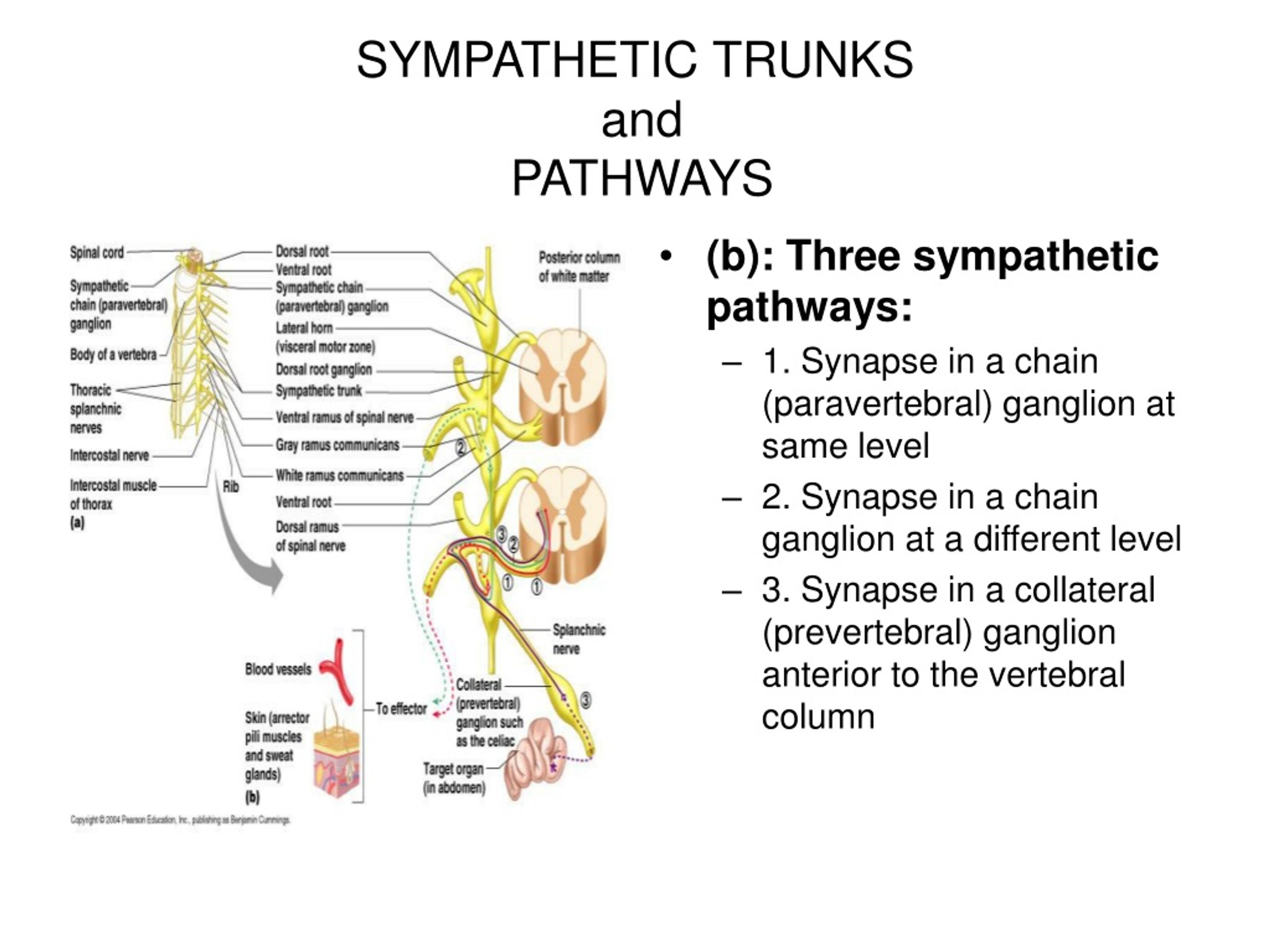
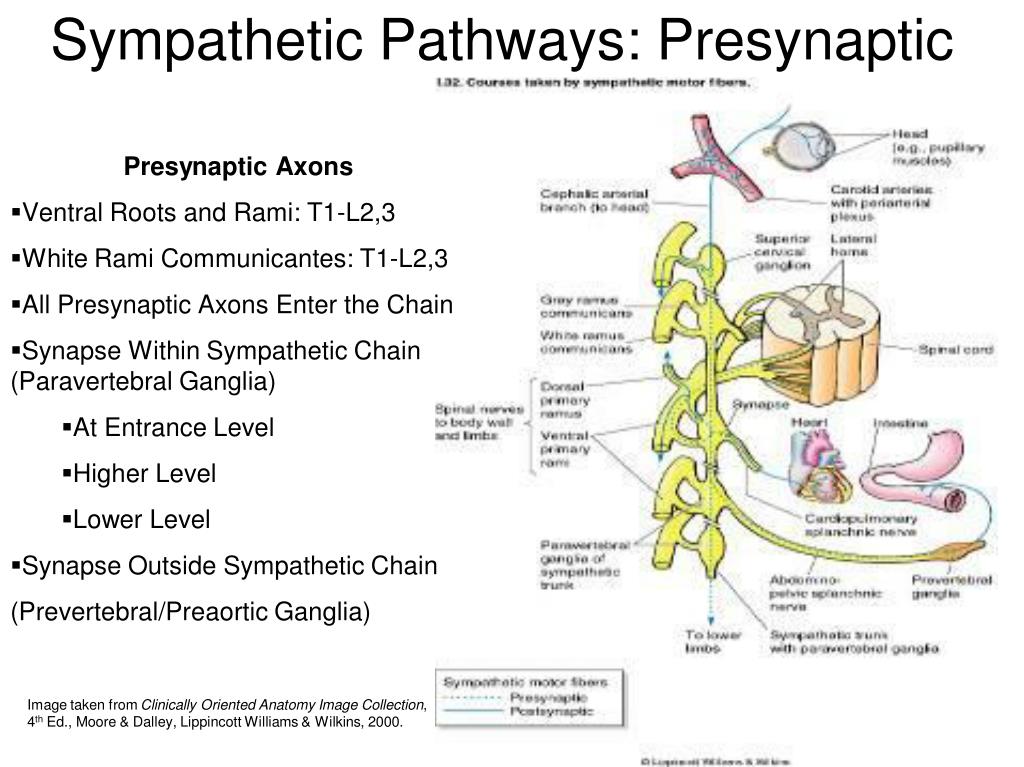
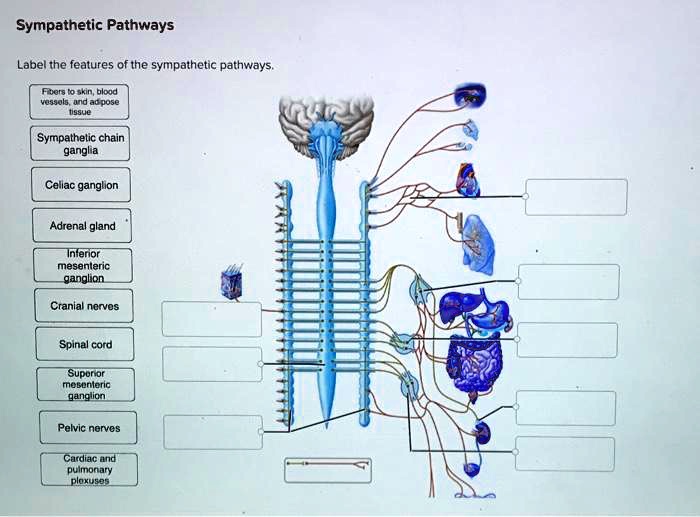
Label The Features Of The Sympathetic Pathways.
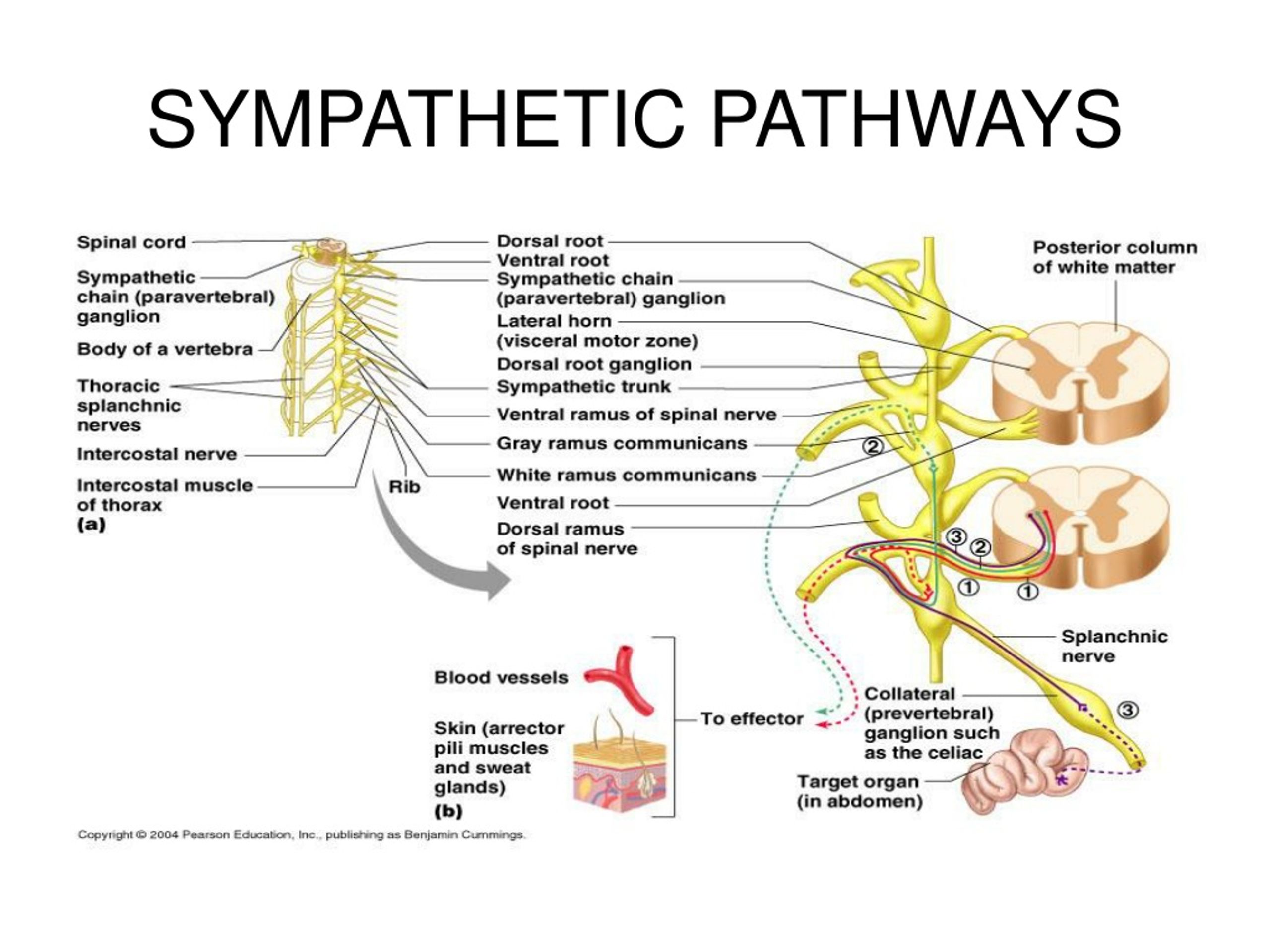
The intricate network of the sympathetic nervous system, often referred to as the “fight or flight” system, has long been a subject of intense scientific scrutiny. Researchers are increasingly focused on clearly labeling the distinct features of its pathways. This renewed emphasis aims to unlock a deeper understanding of its role in human health and disease.
This comprehensive effort involves identifying and mapping the specific components of the sympathetic pathways, including the preganglionic neurons, ganglia, and postganglionic neurons. Understanding these features is crucial for developing targeted therapies for conditions ranging from hypertension to anxiety disorders. The initiative brings together neuroscientists, physiologists, and clinicians from across the globe.
Understanding the Sympathetic Pathways
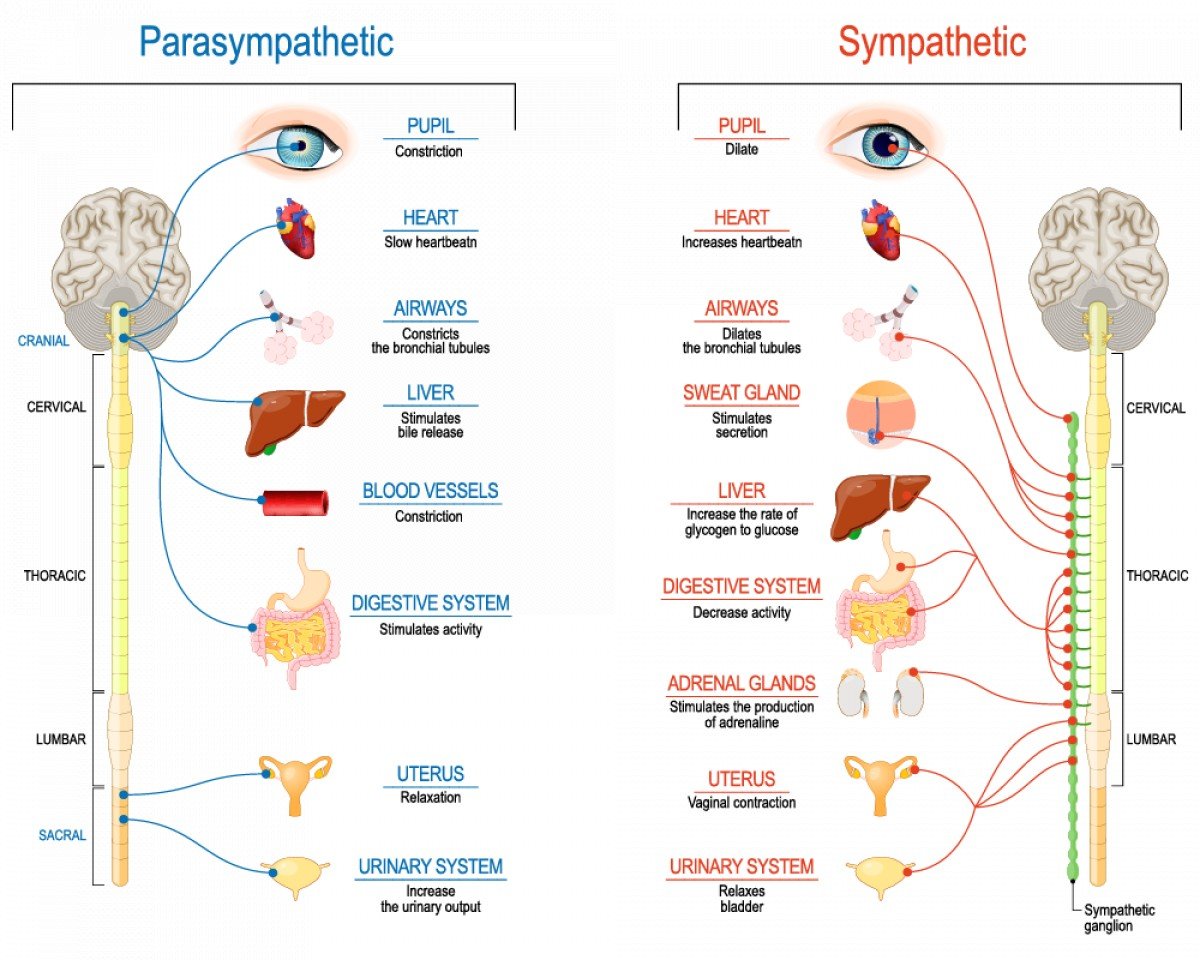
The sympathetic nervous system is a division of the autonomic nervous system, responsible for regulating involuntary bodily functions during times of stress or danger. It prepares the body for action by increasing heart rate, dilating pupils, and diverting blood flow to muscles. A clear understanding of its architecture is essential for appreciating its impact on human physiology.
Key components of the sympathetic pathways are being meticulously labeled and characterized. This involves advanced imaging techniques and molecular biology approaches. The goal is to create a detailed "map" of the sympathetic nervous system.
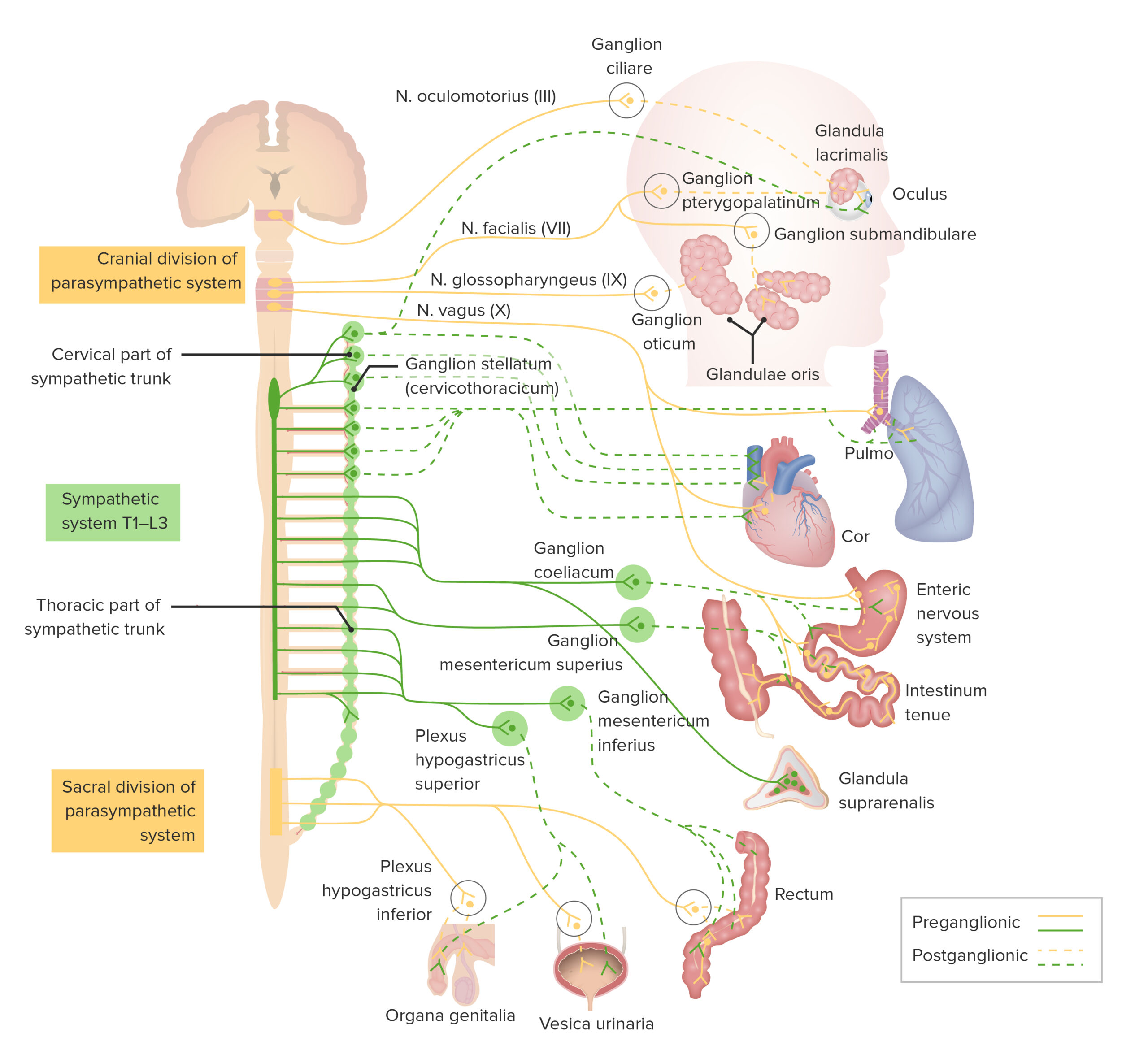
Preganglionic Neurons: The Starting Point
Preganglionic neurons originate in the thoracic and lumbar regions of the spinal cord. Their axons, which are relatively short, extend to the sympathetic ganglia. These neurons release acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that stimulates the postganglionic neurons.
Researchers are using tracing techniques to precisely identify the origins and projections of these neurons. This allows for a greater understanding of the specific organs and tissues they influence. The location of these neurons is critical to understand.
Sympathetic Ganglia: Relay Stations
Sympathetic ganglia act as relay stations between the preganglionic and postganglionic neurons. These ganglia are located in two main chains: the paravertebral ganglia (also known as the sympathetic trunk) and the prevertebral ganglia. Here, preganglionic fibers synapse with postganglionic neurons.
The arrangement and organization of neurons within these ganglia are under intense investigation. Scientists are seeking to understand how these ganglia integrate and process signals from the central nervous system. This area of the system is the relay station.
Postganglionic Neurons: The Effectors
Postganglionic neurons have long axons that extend from the ganglia to the target organs, such as the heart, blood vessels, and sweat glands. They primarily release norepinephrine (noradrenaline), a neurotransmitter that produces the characteristic sympathetic effects.
Scientists are studying the expression of receptors for norepinephrine on different target tissues. This information is crucial for understanding the specificity of sympathetic responses in different parts of the body. They release hormones into the body.
The Significance of Accurate Labeling
Accurately labeling the features of the sympathetic pathways has far-reaching implications for medicine and basic science. It can help in the development of more targeted drugs with fewer side effects. It can improve our understanding of the pathophysiology of various diseases.
For instance, understanding the specific sympathetic pathways involved in hypertension could lead to the development of new therapies that selectively block overactive sympathetic signaling to the kidneys. This could reduce the need for broad-acting medications that affect multiple organ systems.
Furthermore, a clearer understanding of the sympathetic nervous system could aid in the development of more effective treatments for anxiety disorders and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). These conditions often involve excessive activation of the sympathetic nervous system. Developing the treatment could help the patient.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite significant progress, challenges remain in fully labeling the sympathetic pathways. The complexity of the nervous system and the variability between individuals pose significant hurdles. The use of advanced technologies, such as optogenetics and chemogenetics, is helping to overcome these challenges.
Researchers are also exploring the interactions between the sympathetic nervous system and other physiological systems, such as the immune system and the endocrine system. This holistic approach is crucial for understanding the full impact of the sympathetic nervous system on overall health and disease.
Future research will likely focus on developing personalized therapies that target specific sympathetic pathways based on an individual's genetic makeup and disease profile. This represents a significant step toward precision medicine.
Conclusion
The effort to precisely label the features of the sympathetic pathways is a significant undertaking with the potential to transform our understanding of human health and disease. By mapping the intricate network of neurons and identifying their specific functions, scientists are paving the way for new and more effective therapies for a wide range of conditions. This research highlights the continued importance of investing in basic science to unlock the secrets of the human body.
The work is ongoing. The data is important and will be used to combat multiple diseases.


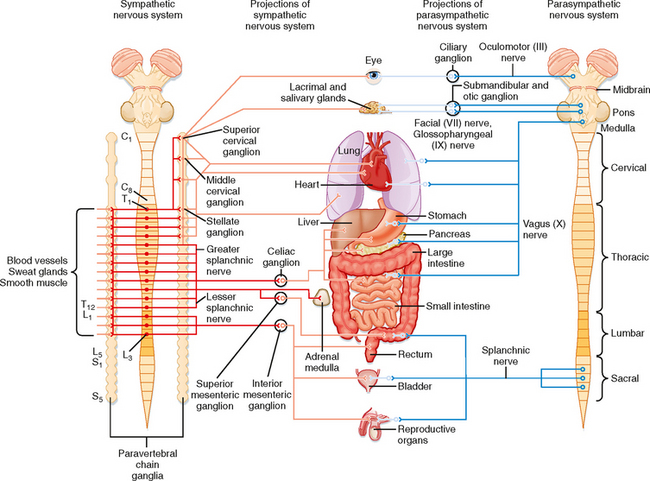







.jpg)