Label The Stages That Characterize Progression Of Infectious Disease.

Understanding how infectious diseases progress is crucial for effective diagnosis, treatment, and public health interventions. The course of an infection isn't a single event, but rather a series of distinct phases, each characterized by specific biological events and clinical manifestations. Properly identifying these stages can improve patient care and limit disease spread.
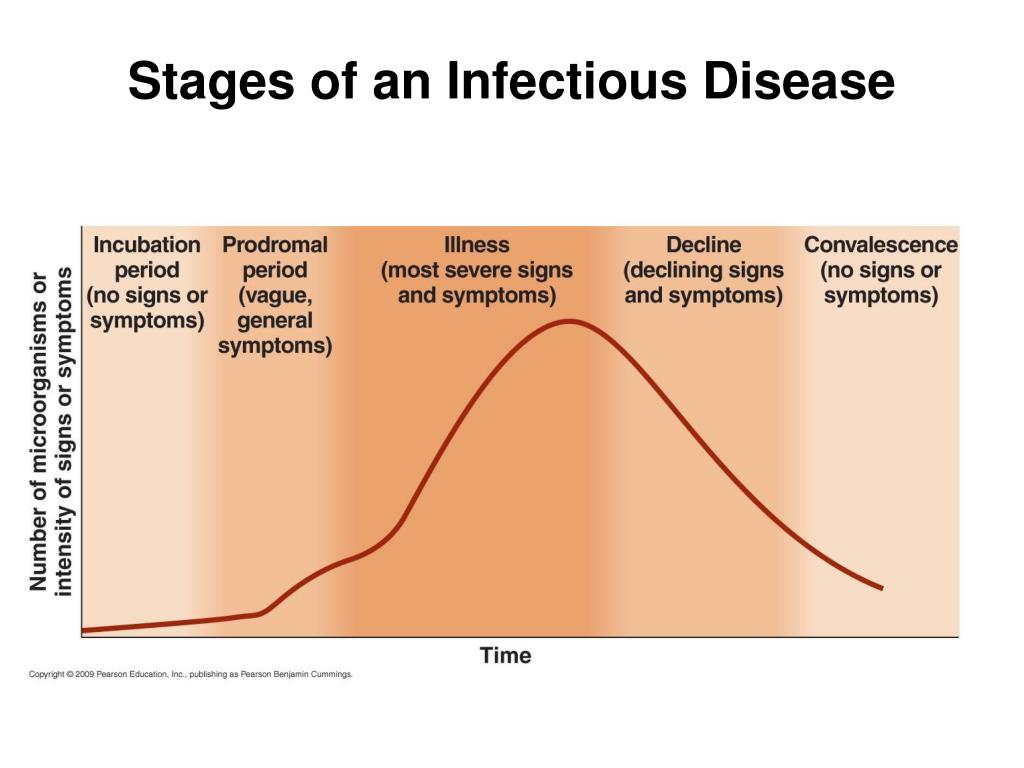
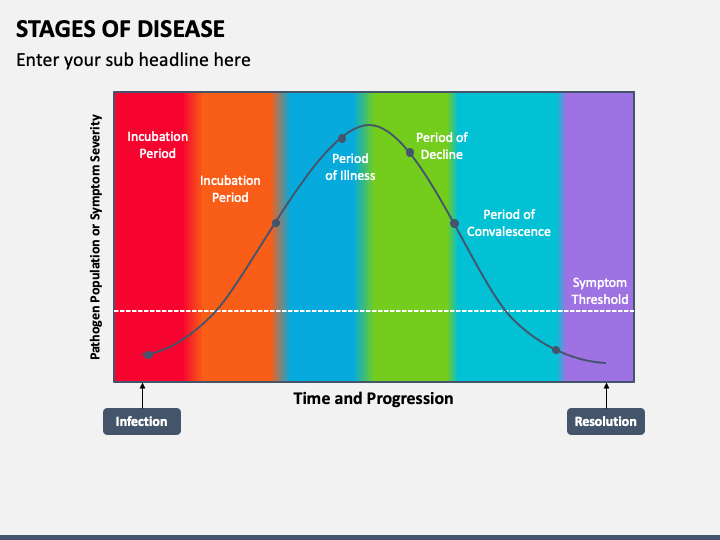
The progression of an infectious disease can be broadly categorized into five key stages: the incubation period, the prodromal period, the illness stage, the decline stage, and the convalescence stage. Each stage plays a vital role in the overall trajectory of the disease and impacts the patient's experience and potential for transmission. Knowing these stages allows healthcare professionals to tailor their approach to patient care, prevention strategies, and research.
The Stages of Infectious Disease
The incubation period is the time between the initial exposure to the infectious agent and the onset of the first symptoms. During this phase, the pathogen is replicating within the host, but the individual is typically asymptomatic.
The length of the incubation period varies depending on the infectious agent, the host's immune status, and the route of transmission. For example, the incubation period for influenza is typically 1-4 days, while HIV can have an incubation period of several years.
Next is the prodromal period, which follows the incubation stage and is characterized by the appearance of non-specific symptoms. These symptoms, such as fatigue, malaise, and mild fever, indicate the body is beginning to respond to the infection.
It is often difficult to diagnose the specific infection during the prodromal period due to the vague and overlapping nature of the symptoms. However, recognizing these early warning signs can prompt individuals to seek medical attention and take precautions to prevent further spread.
The illness stage is when the disease reaches its peak and characteristic signs and symptoms are most evident. During this phase, the pathogen load is high, and the body's immune response is in full force.
The specific symptoms experienced during the illness stage depend on the type of infection and the organs or systems affected. For instance, a respiratory infection might present with cough, sore throat, and shortness of breath, while a gastrointestinal infection might manifest as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
The decline stage marks the beginning of the end of the acute phase of the infection. As the immune system or medical interventions begin to control the pathogen, the signs and symptoms of the illness start to subside.
It is crucial for individuals to continue following medical advice and completing prescribed treatments during this stage to prevent relapse or complications. Even as symptoms diminish, the body is still recovering and vulnerable.
Finally, the convalescence stage is the period of recovery and return to a pre-disease state. During this phase, the body repairs damaged tissues, restores normal function, and eliminates any remaining pathogens.
Convalescence can be a lengthy process, particularly for severe infections or in individuals with weakened immune systems. Some individuals may experience lingering symptoms or long-term complications even after the infection is cleared.
Impact on Public Health
Understanding these stages is not only critical for individual patient care, but also for public health initiatives. Knowledge of incubation periods can inform quarantine measures and contact tracing efforts.
Recognizing the prodromal period allows for early detection and intervention strategies, reducing the spread of the disease within a community. Accurate identification of the illness stage enables timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment protocols.
Furthermore, monitoring the decline and convalescence stages helps healthcare providers and public health officials assess the overall impact of the infection on the population and plan for long-term care and rehabilitation needs.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), accurate staging of infectious diseases is paramount for effective disease surveillance. The WHO emphasizes that standardized diagnostic criteria and reporting systems are essential for tracking disease trends and implementing targeted public health interventions.
Recent studies published in the New England Journal of Medicine have highlighted the importance of considering individual variability in disease progression. Factors such as age, underlying health conditions, and vaccination status can significantly influence the duration and severity of each stage of an infection.
Looking Ahead
Continued research into the intricacies of infectious disease progression is crucial for developing novel diagnostic tools and therapeutic strategies. A deeper understanding of the interplay between the pathogen, the host immune response, and the environment is essential for improving patient outcomes and preventing future outbreaks.
By recognizing the different stages of infectious disease and their implications, both healthcare professionals and the general public can contribute to a more effective and proactive approach to disease management and prevention. Ultimately, such knowledge helps create a healthier and safer world for everyone.