Mp Husky Cable Tray Cable Bus

The landscape of electrical power distribution is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by increasing demands for efficiency, safety, and adaptability. At the heart of this evolution lies the ongoing debate and implementation of various cabling solutions, most notably the comparison between traditional cable tray systems and the increasingly popular cable bus technology. This shift presents both opportunities and challenges for industries reliant on robust and reliable power infrastructure.
This article delves into the nuances of MP Husky cable tray and cable bus systems, examining their individual characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages. We'll explore how these systems are being deployed in various sectors, assess their impact on project costs and timelines, and consider the future trajectory of power distribution technologies.
Understanding Cable Tray Systems
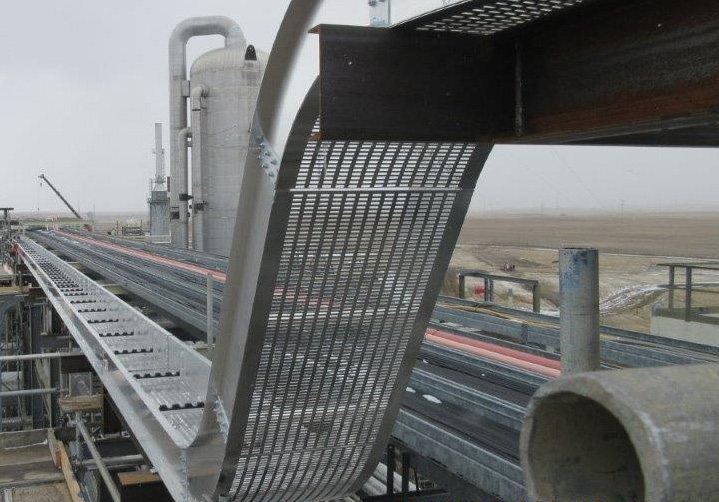
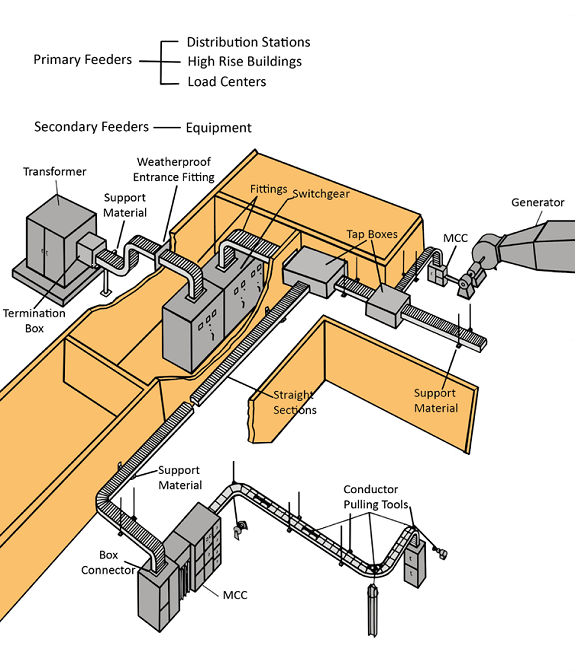
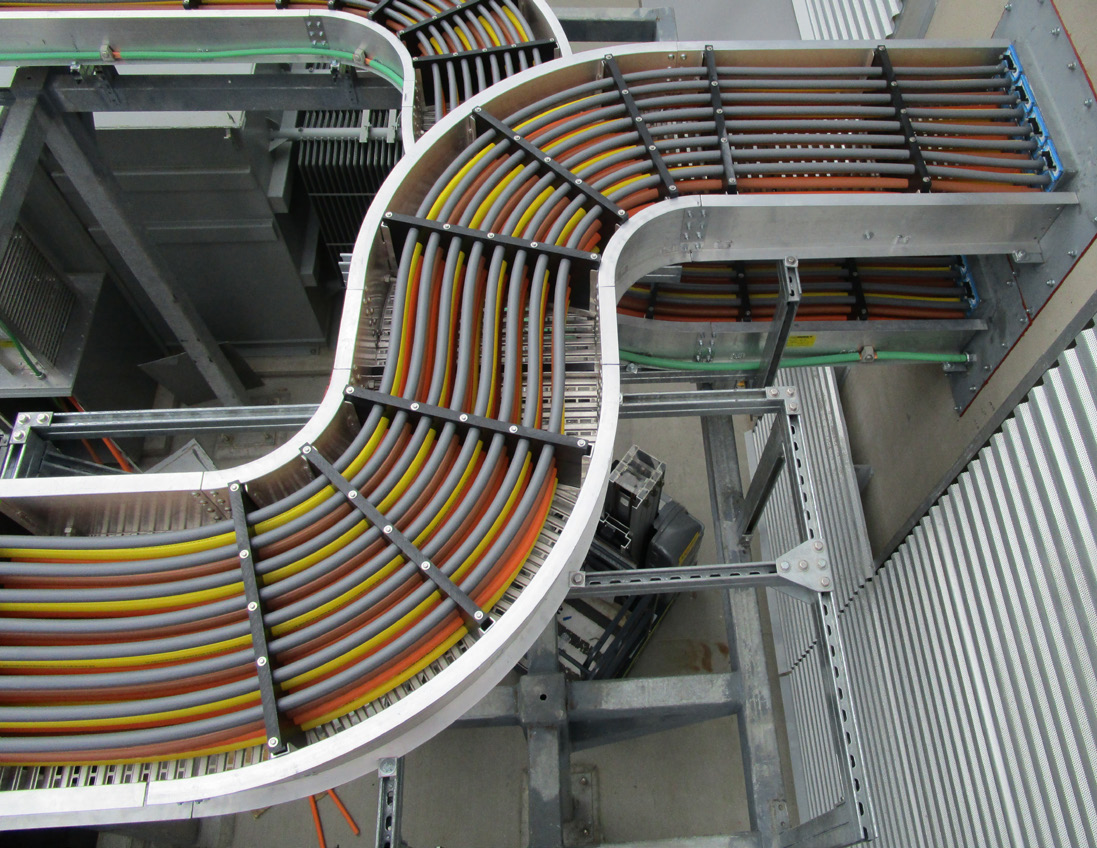
Cable tray systems, a long-standing and widely used solution, consist of a rigid structure designed to support insulated electrical cables used for power distribution, control, and communication. They offer a flexible and accessible pathway for managing large quantities of cables within a facility.
Traditional cable trays are available in a variety of materials, including steel, aluminum, and fiberglass, each offering different levels of corrosion resistance and load-bearing capacity. Their open design allows for easy inspection, maintenance, and future modifications, making them a versatile choice for many applications.
Advantages of Cable Tray
Cost-Effectiveness: Generally, cable tray systems have a lower initial material cost compared to cable bus systems, particularly for smaller installations. The widespread availability of cable tray components and installation expertise also contributes to lower upfront expenses.
Flexibility and Accessibility: The open design of cable trays allows for easy access to cables for maintenance, repairs, and modifications. Adding or removing cables is a relatively straightforward process, providing flexibility for future expansion or reconfiguration.
Versatility: Cable trays can accommodate a wide range of cable sizes and types, making them suitable for various applications, from low-voltage control cables to high-voltage power cables.
Disadvantages of Cable Tray
Labor-Intensive Installation: Installing individual cables within a cable tray can be a time-consuming and labor-intensive process, especially for large-scale installations. This can increase overall project costs and timelines.
Space Requirements: Cable tray systems often require more space compared to cable bus systems, particularly when accommodating multiple layers of cables. This can be a limiting factor in facilities with limited space.
Susceptibility to Damage: The open design of cable trays can make cables more susceptible to damage from environmental factors, such as moisture, dust, and physical impact. Additional protection measures may be required in harsh environments.
Exploring Cable Bus Systems
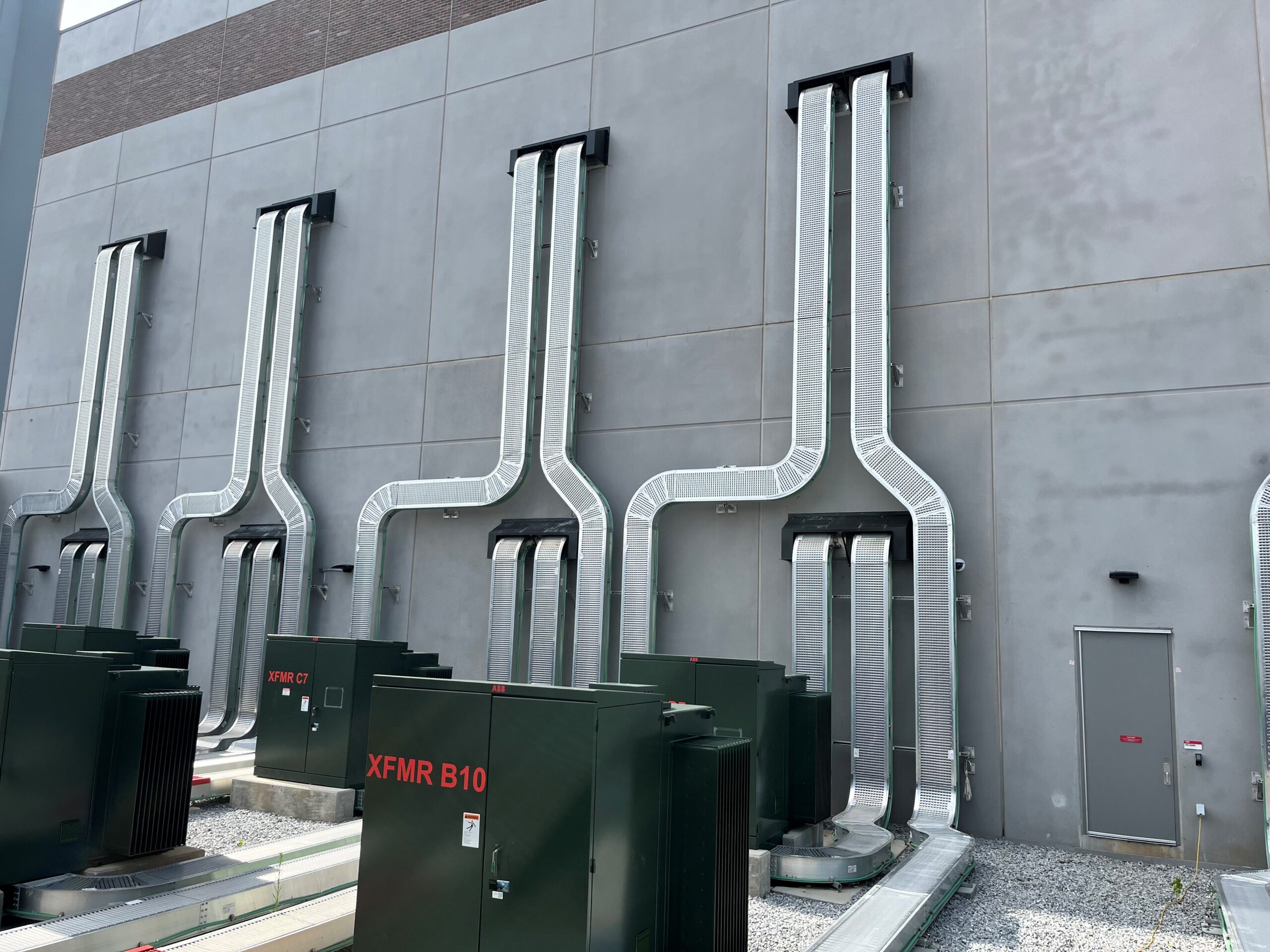
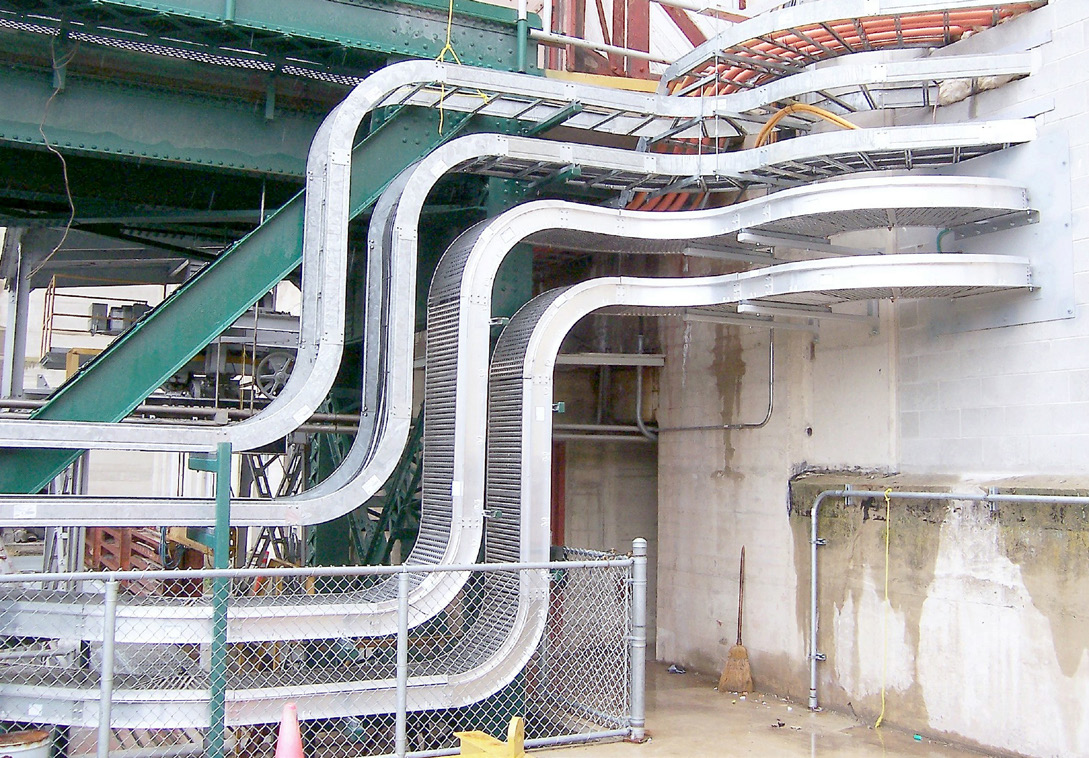
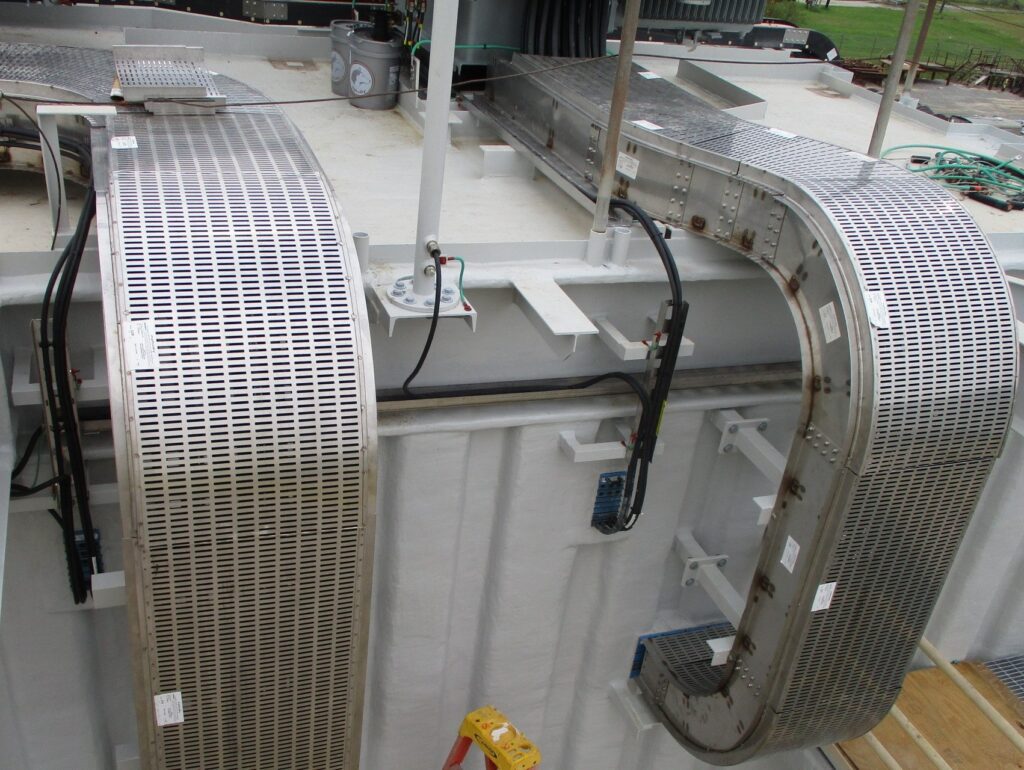
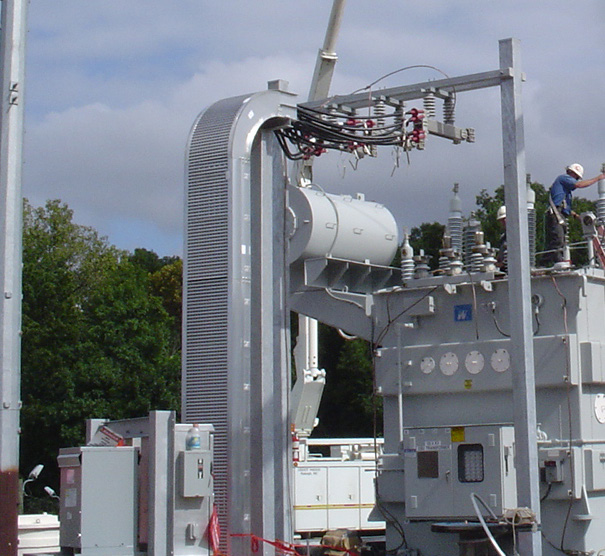
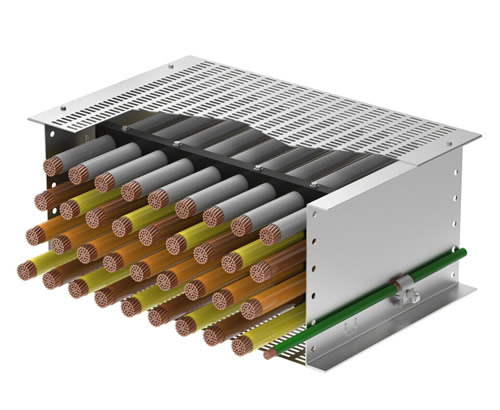
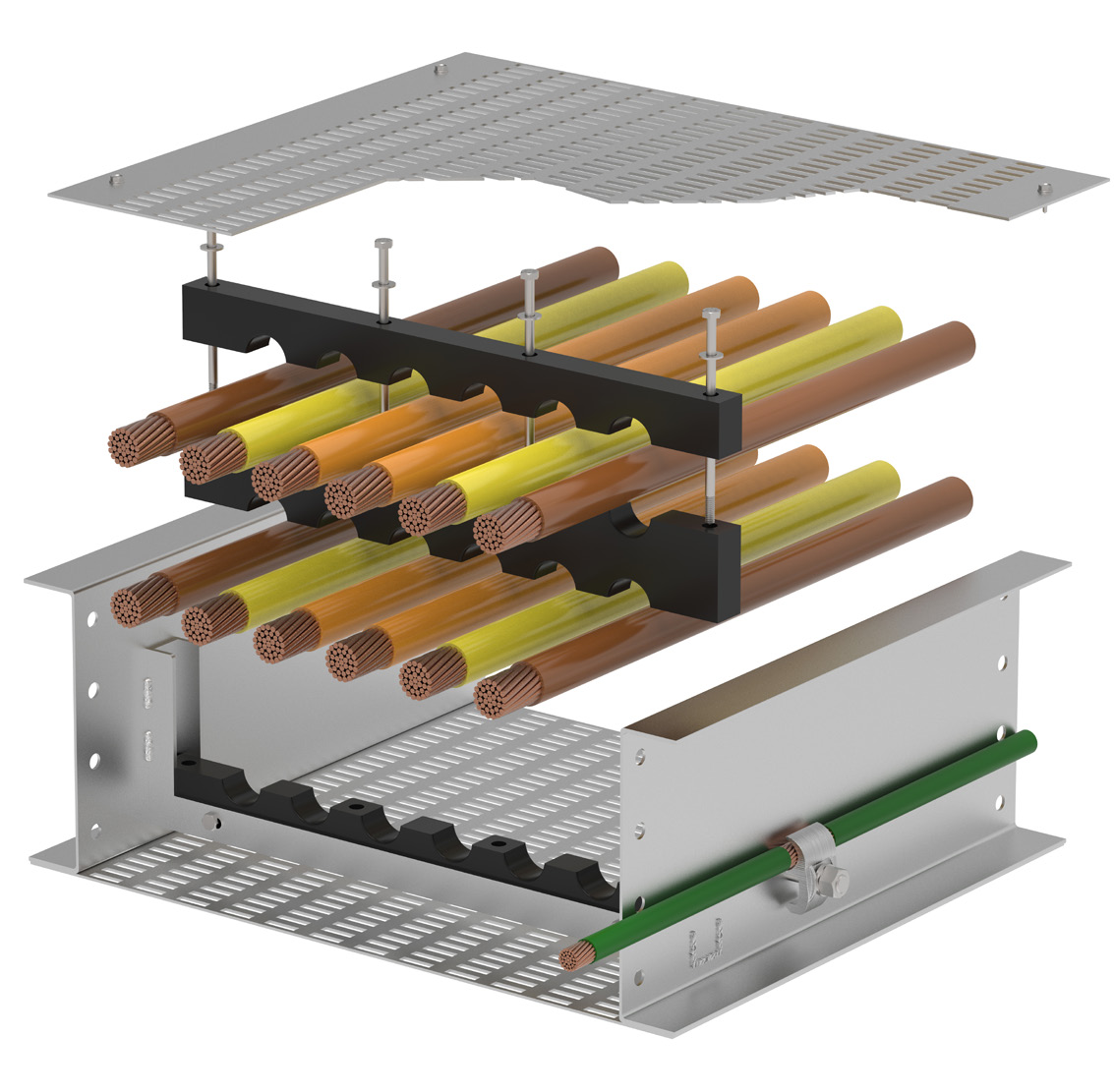
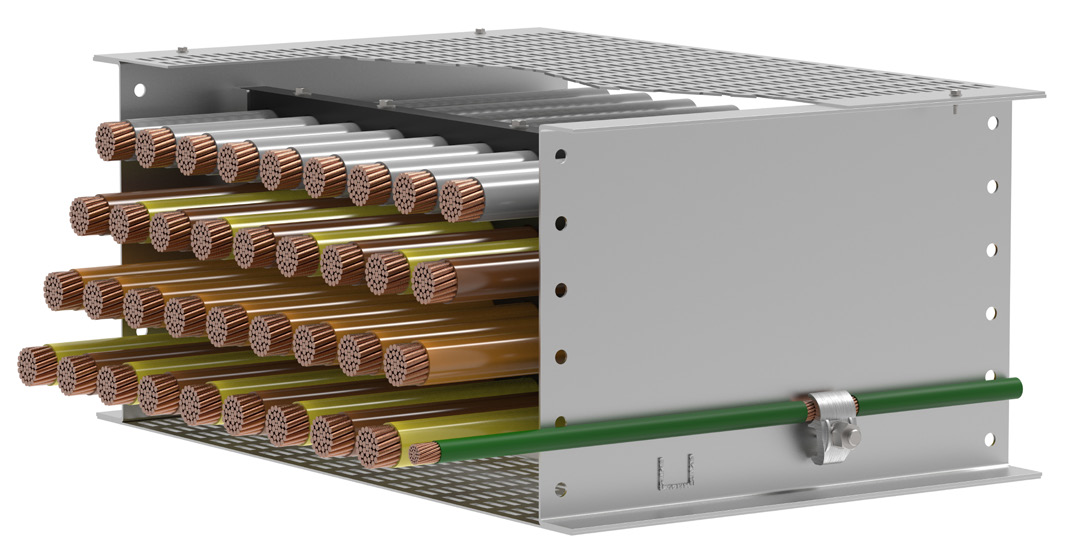
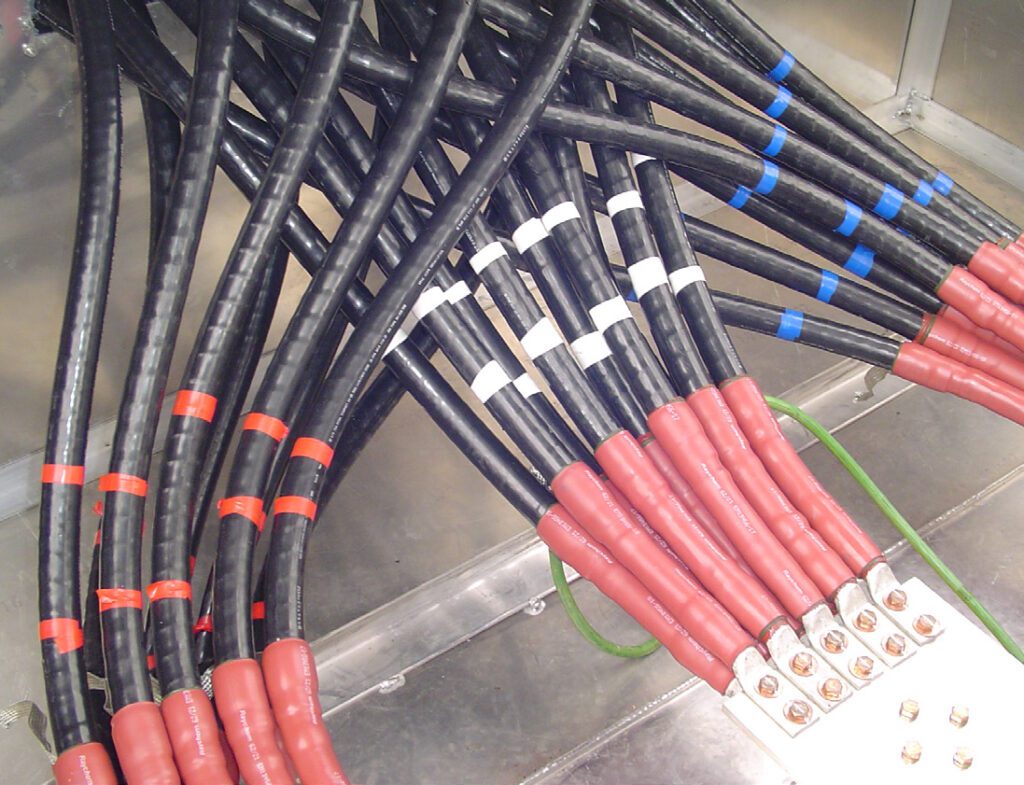
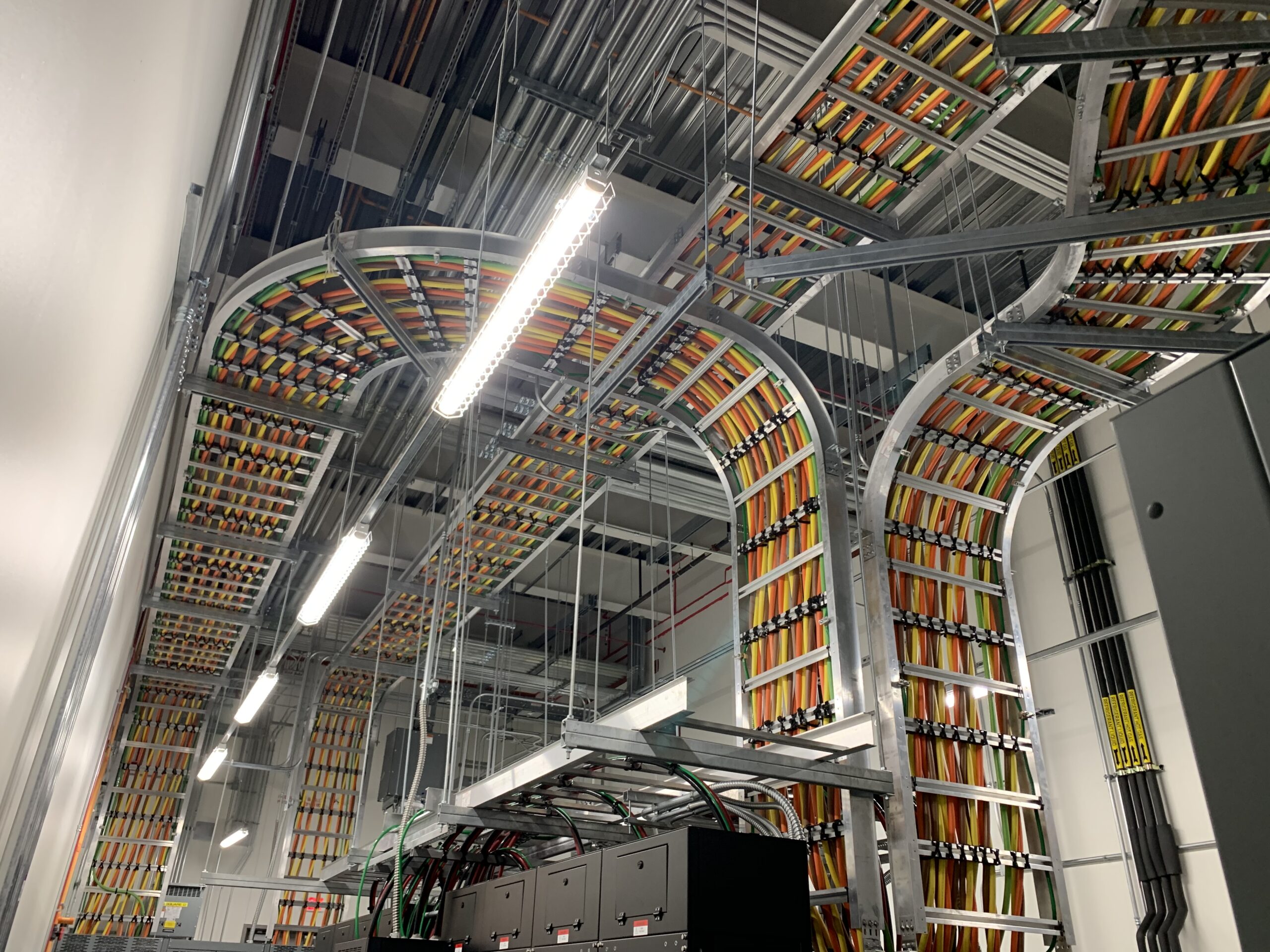
Cable bus systems, a more recent innovation in power distribution, consist of factory-assembled conductors within a ventilated enclosure. This integrated design offers several advantages over traditional cable tray systems, including increased efficiency, reduced installation time, and improved safety.
Cable bus systems are typically constructed with copper or aluminum conductors, insulated with high-quality materials and enclosed in a rigid, grounded enclosure. The enclosure provides protection from environmental factors and physical damage, ensuring reliable and safe operation.
Advantages of Cable Bus
Reduced Installation Time: Cable bus systems are pre-engineered and factory-assembled, significantly reducing installation time compared to cable tray systems. This can lead to substantial cost savings and faster project completion.
Compact Design: Cable bus systems have a more compact design compared to cable tray systems, requiring less space and allowing for greater flexibility in facility layout. This is particularly beneficial in facilities with limited space.
Improved Safety: The enclosed design of cable bus systems provides superior protection against environmental factors, physical damage, and electrical hazards. This enhances safety for personnel and equipment.
Disadvantages of Cable Bus
Higher Initial Cost: Cable bus systems typically have a higher initial material cost compared to cable tray systems. However, the reduced installation time and other benefits can often offset the higher upfront expense.
Limited Flexibility: Modifying a cable bus system after installation can be more challenging compared to cable tray systems. Careful planning is essential to ensure the system meets current and future needs.
Repair Complexity: Repairs to cable bus systems may require specialized expertise and equipment. This can increase downtime and maintenance costs.
MP Husky: A Leading Provider
MP Husky is a well-regarded manufacturer of both cable tray and cable bus systems, offering a comprehensive range of solutions for various industries. Their products are known for their quality, durability, and adherence to industry standards.
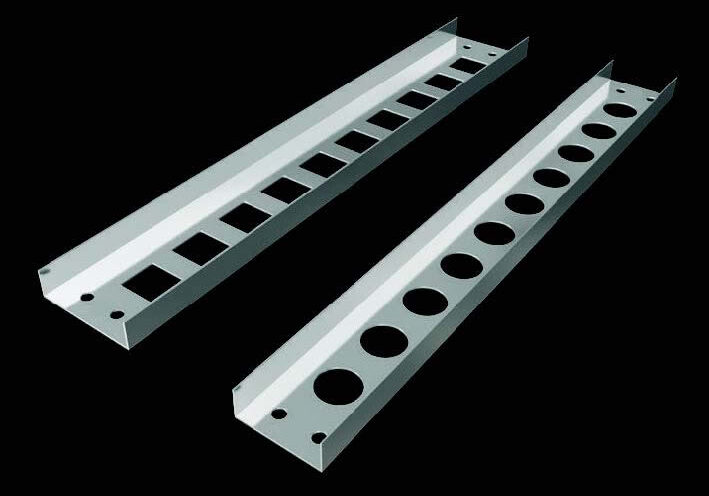
MP Husky provides cable tray systems in a variety of materials and configurations, including ladder, trough, and channel types. They also offer a range of accessories and support components to ensure a complete and reliable installation.
Their cable bus systems are designed for high-current applications and offer superior performance and safety. MP Husky's cable bus solutions are custom-engineered to meet specific project requirements, ensuring optimal efficiency and reliability.
Real-World Applications and Considerations
Cable tray systems are commonly used in commercial buildings, industrial facilities, and data centers for general power distribution and control cabling. Their flexibility and accessibility make them a suitable choice for applications where frequent modifications or expansions are anticipated.
Cable bus systems are often preferred for high-current applications, such as power plants, substations, and large industrial facilities. Their compact design, reduced installation time, and improved safety make them a cost-effective and reliable solution for critical power distribution.
When selecting between cable tray and cable bus systems, it is essential to consider factors such as project budget, space limitations, installation timelines, environmental conditions, and future expansion needs. Consulting with qualified engineers and contractors is crucial to ensure the optimal solution is selected for each specific application.
The Future of Power Distribution
The future of power distribution is likely to see continued advancements in both cable tray and cable bus technologies. Innovations in materials, design, and installation methods will further enhance the efficiency, safety, and sustainability of these systems.
Smart cable management systems, incorporating sensors and data analytics, are emerging as a promising trend. These systems can monitor cable performance, detect potential problems, and optimize power distribution, leading to improved reliability and reduced downtime.
As industries continue to demand more efficient and reliable power infrastructure, the choice between cable tray and cable bus systems will remain a critical decision. A thorough understanding of the advantages and disadvantages of each technology, coupled with careful planning and execution, is essential to ensure the success of any power distribution project.