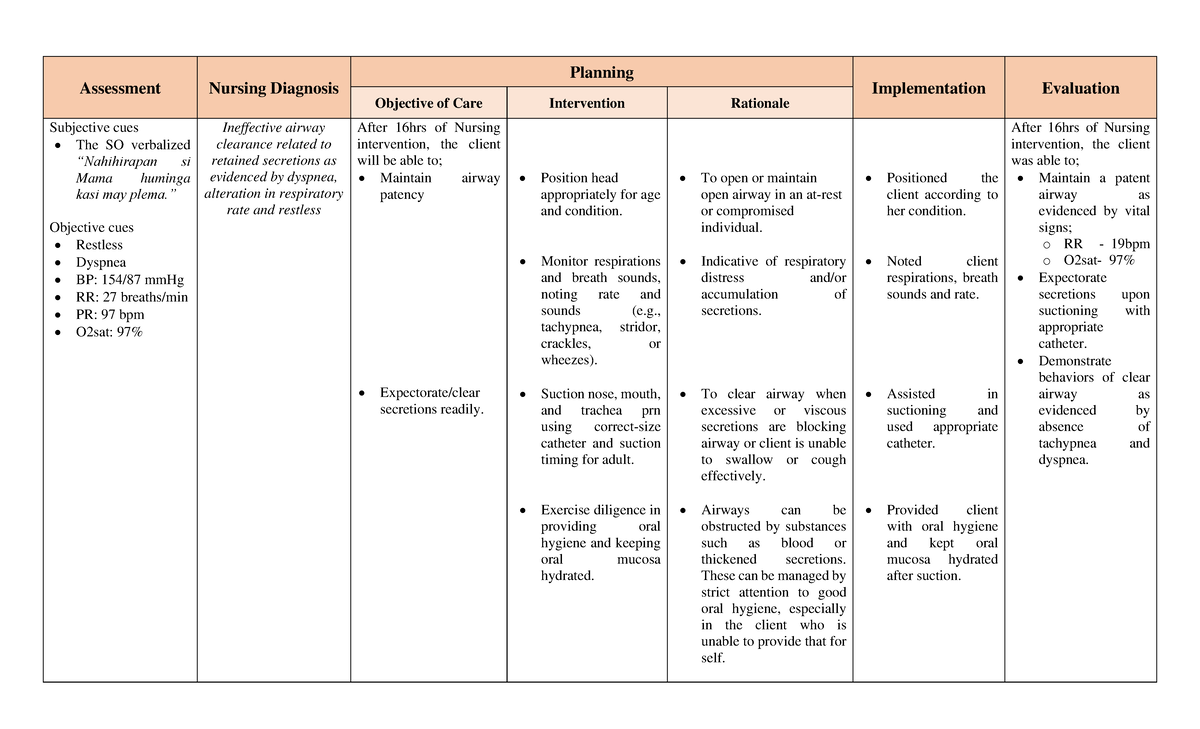
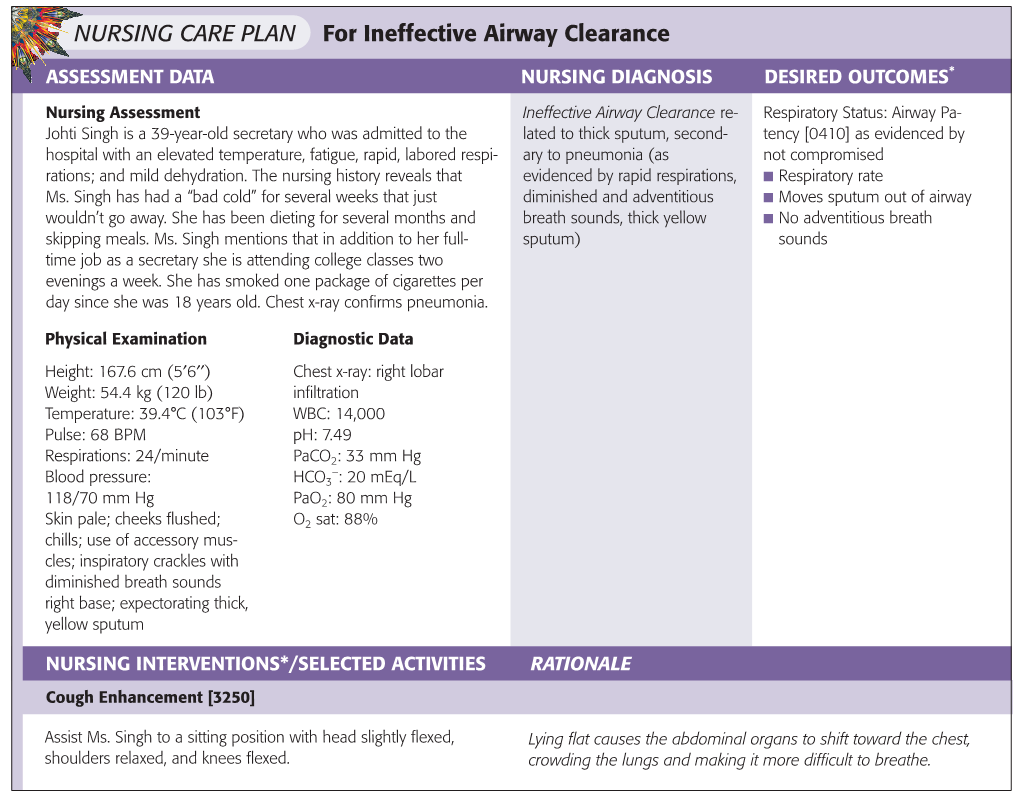
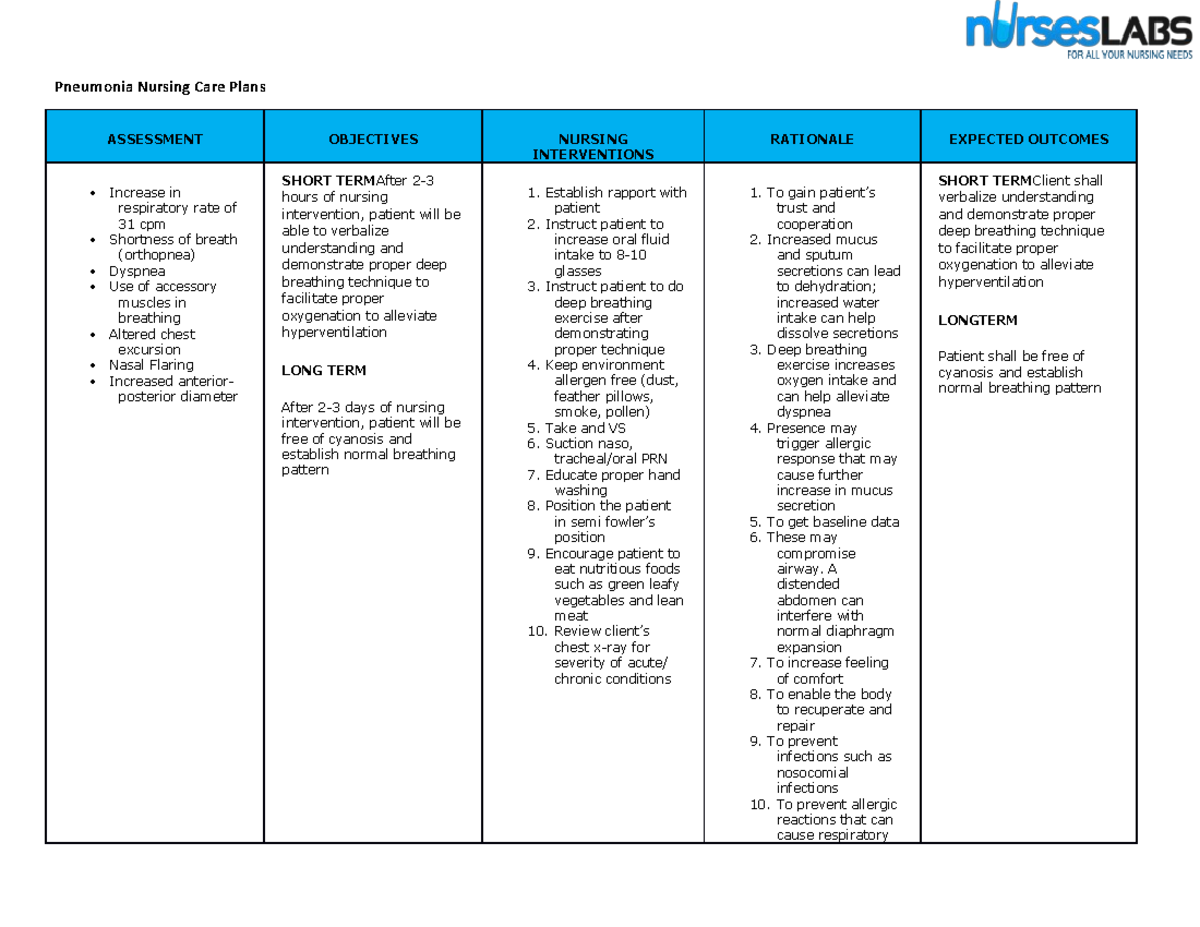
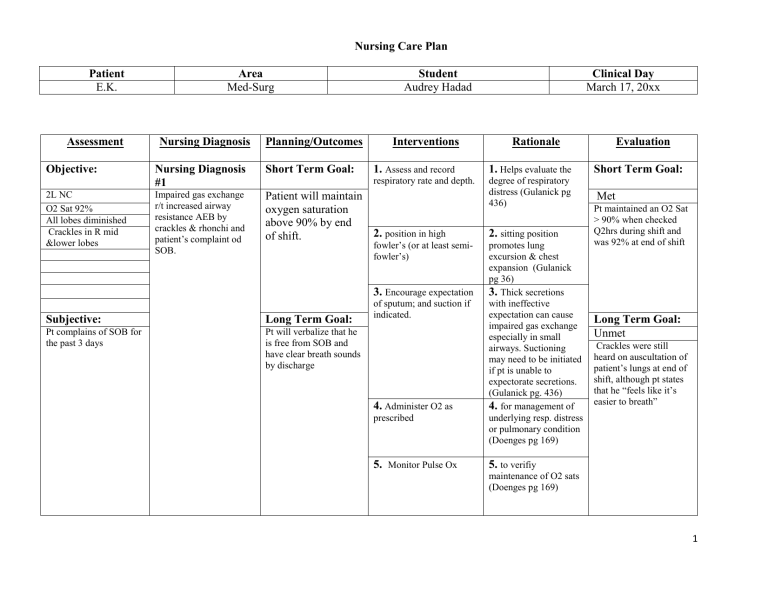
Nursing Diagnosis For Ineffective Airway Clearance
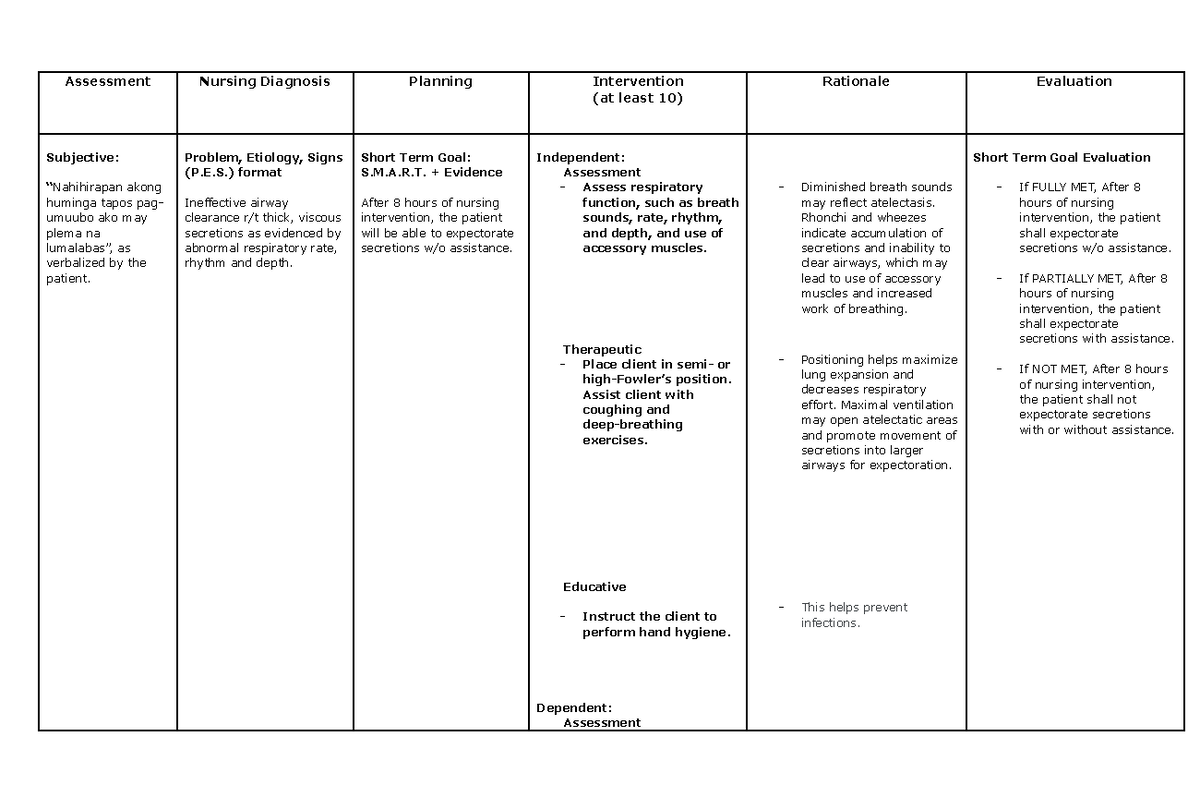
Healthcare professionals are increasingly focused on the intricacies of ineffective airway clearance, a nursing diagnosis that signifies a patient's struggle to maintain a clear and open passage for breathing. Understanding the nuances of this condition is crucial for effective patient care, especially within the context of rising respiratory illnesses and complex medical conditions.
Defining Ineffective Airway Clearance
Ineffective airway clearance, as defined by the North American Nursing Diagnosis Association (NANDA), is the state in which an individual is unable to clear secretions or obstructions from the respiratory tract to maintain a clear airway. This diagnosis encompasses a broad range of conditions and patient populations, demanding a thorough understanding of its underlying causes and appropriate interventions.
Causes and Contributing Factors
The root causes of ineffective airway clearance are varied and can stem from a multitude of medical conditions. These include, but are not limited to, respiratory infections like pneumonia and bronchitis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, cystic fibrosis, and neuromuscular disorders that weaken the muscles responsible for breathing and coughing. Presence of foreign bodies in the airway, excessive mucus production, and impaired cough reflex also significantly contribute.
"Recognizing the specific etiology behind the ineffective airway clearance is paramount," explains Dr. Emily Carter, a pulmonary specialist at Massachusetts General Hospital. "A targeted approach based on the underlying cause will dramatically improve patient outcomes."
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms
Identifying ineffective airway clearance involves careful observation and assessment of the patient. Common signs and symptoms include abnormal breath sounds such as wheezing, crackles, or rhonchi; difficulty breathing (dyspnea); excessive coughing, which may or may not be productive; decreased oxygen saturation levels; cyanosis (bluish discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes); and changes in respiratory rate and depth. Restlessness, anxiety, and altered mental status can also indicate compromised airway function.
Early detection and intervention are critical to prevent further complications, such as respiratory failure or pneumonia. The American Thoracic Society stresses the importance of regular respiratory assessments, particularly for patients at high risk.
Diagnostic Procedures and Assessments
Diagnosing ineffective airway clearance requires a comprehensive assessment that includes a thorough medical history, physical examination, and relevant diagnostic tests. Auscultation of the lungs, monitoring oxygen saturation levels via pulse oximetry, and assessing respiratory rate and effort are fundamental components. Chest X-rays may be ordered to identify underlying lung conditions such as pneumonia or atelectasis. Sputum cultures can help identify infectious agents in cases of respiratory infections, guiding appropriate antibiotic therapy.
In some cases, more advanced diagnostic procedures like bronchoscopy may be necessary to visualize the airway and obtain samples for analysis. Arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis provides critical information about the patient's oxygenation, ventilation, and acid-base balance, aiding in the assessment of respiratory function.
Nursing Interventions and Management
Effective management of ineffective airway clearance involves a multi-faceted approach aimed at clearing secretions, improving ventilation, and addressing the underlying cause. Key nursing interventions include encouraging coughing and deep breathing exercises, providing hydration to thin secretions, and administering medications such as bronchodilators, mucolytics, and expectorants as prescribed. Chest physiotherapy techniques, such as percussion, vibration, and postural drainage, can help loosen and mobilize secretions.
In some cases, more invasive interventions such as suctioning may be necessary to remove secretions from the airway. Oxygen therapy may be required to improve oxygen saturation levels. Patients with severe respiratory compromise may require mechanical ventilation to support breathing. The Respiratory Nursing Society provides detailed guidelines on best practices for managing patients with ineffective airway clearance.
The Impact on Patient Care
The nursing diagnosis of ineffective airway clearance has a significant impact on patient care, guiding nursing interventions and promoting individualized treatment plans. Accurate diagnosis and timely interventions can improve patient outcomes, reduce hospital readmission rates, and enhance overall quality of life. By focusing on the underlying causes and implementing evidence-based strategies, healthcare professionals can effectively manage this common yet complex clinical problem.
"The challenge lies in personalizing care." says Nurse Practitioner, Sarah Jones. "What works for one COPD patient might be completely ineffective for another dealing with cystic fibrosis. Individualized care plans are a necessity, not a luxury."
Looking Ahead: Research and Innovation
Ongoing research efforts are focused on developing new and innovative approaches to managing ineffective airway clearance. Studies are exploring the use of advanced technologies such as high-frequency chest wall oscillation and intrapulmonary percussive ventilation to improve secretion clearance. Researchers are also investigating the role of personalized medicine in tailoring treatments to individual patient needs. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) is funding several projects aimed at improving the understanding and treatment of respiratory conditions that contribute to ineffective airway clearance.
"Future innovations may include non-invasive methods for monitoring mucus viscosity and robotic-assisted airway clearance devices, opening up possibilities for more effective and less invasive treatments," speculates Dr. Carter.
The effective management of ineffective airway clearance requires a collaborative effort between healthcare professionals, patients, and their families. Education plays a crucial role in empowering patients to actively participate in their care and manage their symptoms effectively. This includes teaching patients proper coughing techniques, promoting adherence to medication regimens, and encouraging healthy lifestyle choices such as smoking cessation and regular exercise. With continued research, innovation, and collaboration, healthcare professionals can further improve the lives of individuals affected by ineffective airway clearance.