Outsourcing Benefits And Disadvantages
In an increasingly interconnected global economy, the practice of outsourcing has become a common strategy for businesses seeking to optimize operations and reduce costs. But this practice, involving the delegation of specific business processes to external providers, presents a complex equation with both significant advantages and considerable drawbacks. The trend continues to shape industries worldwide, impacting employment, economic development, and the competitive landscape.
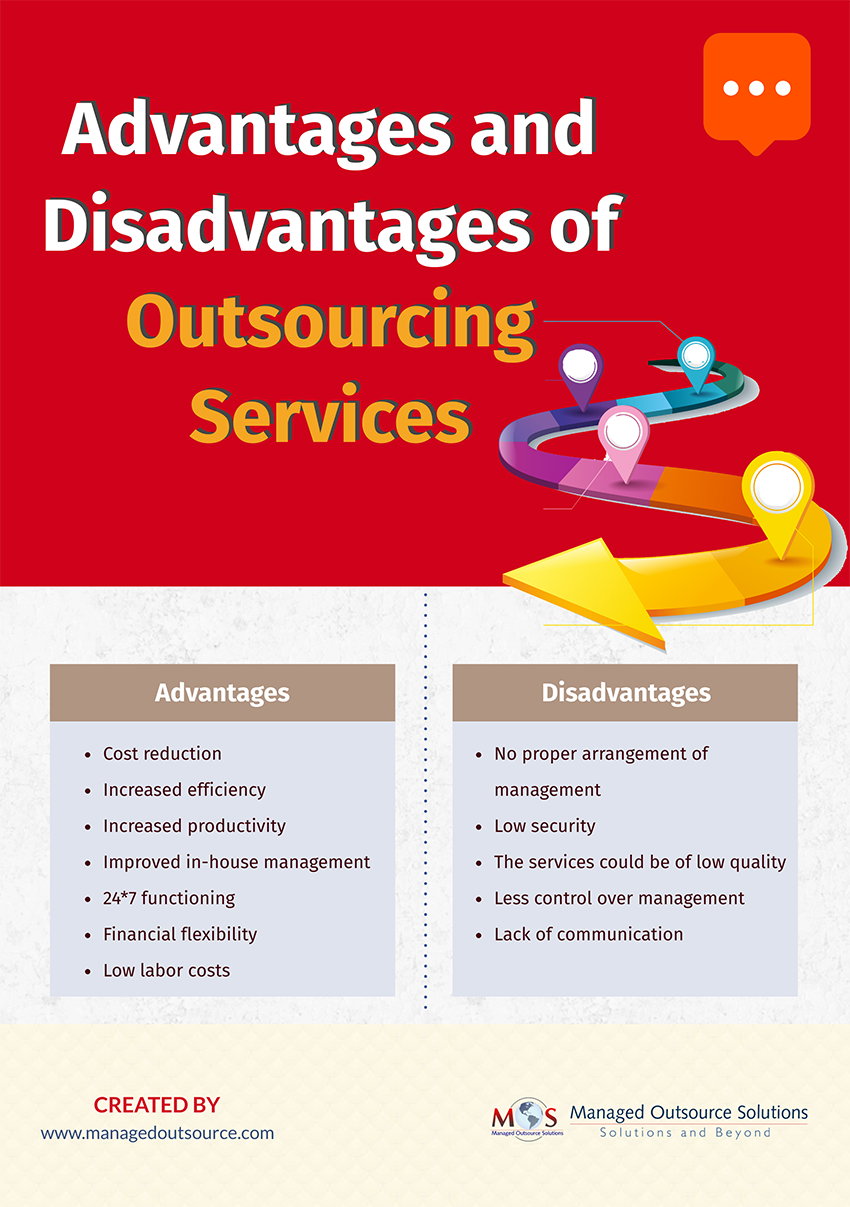
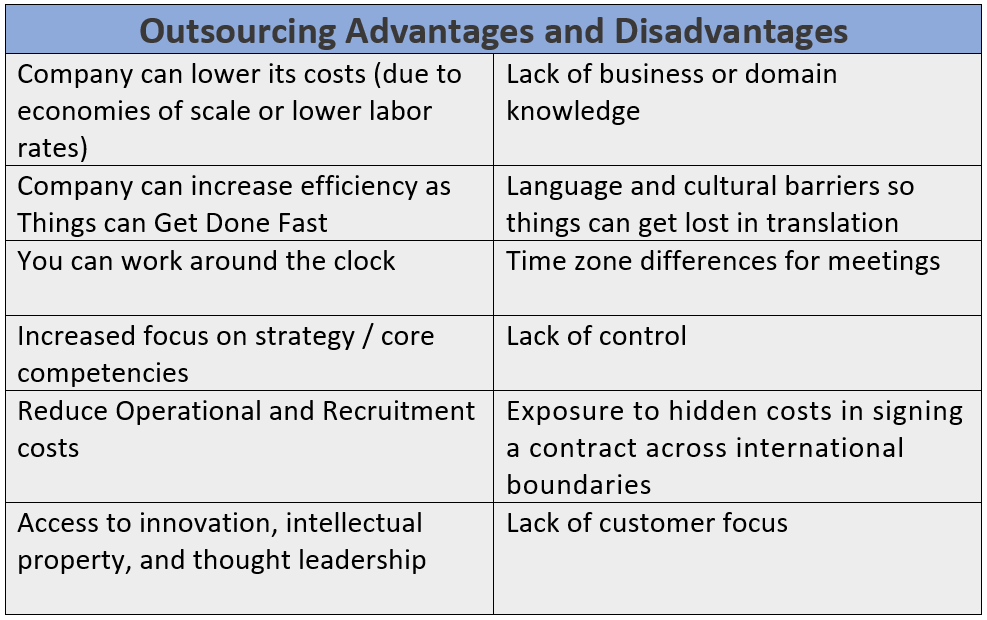
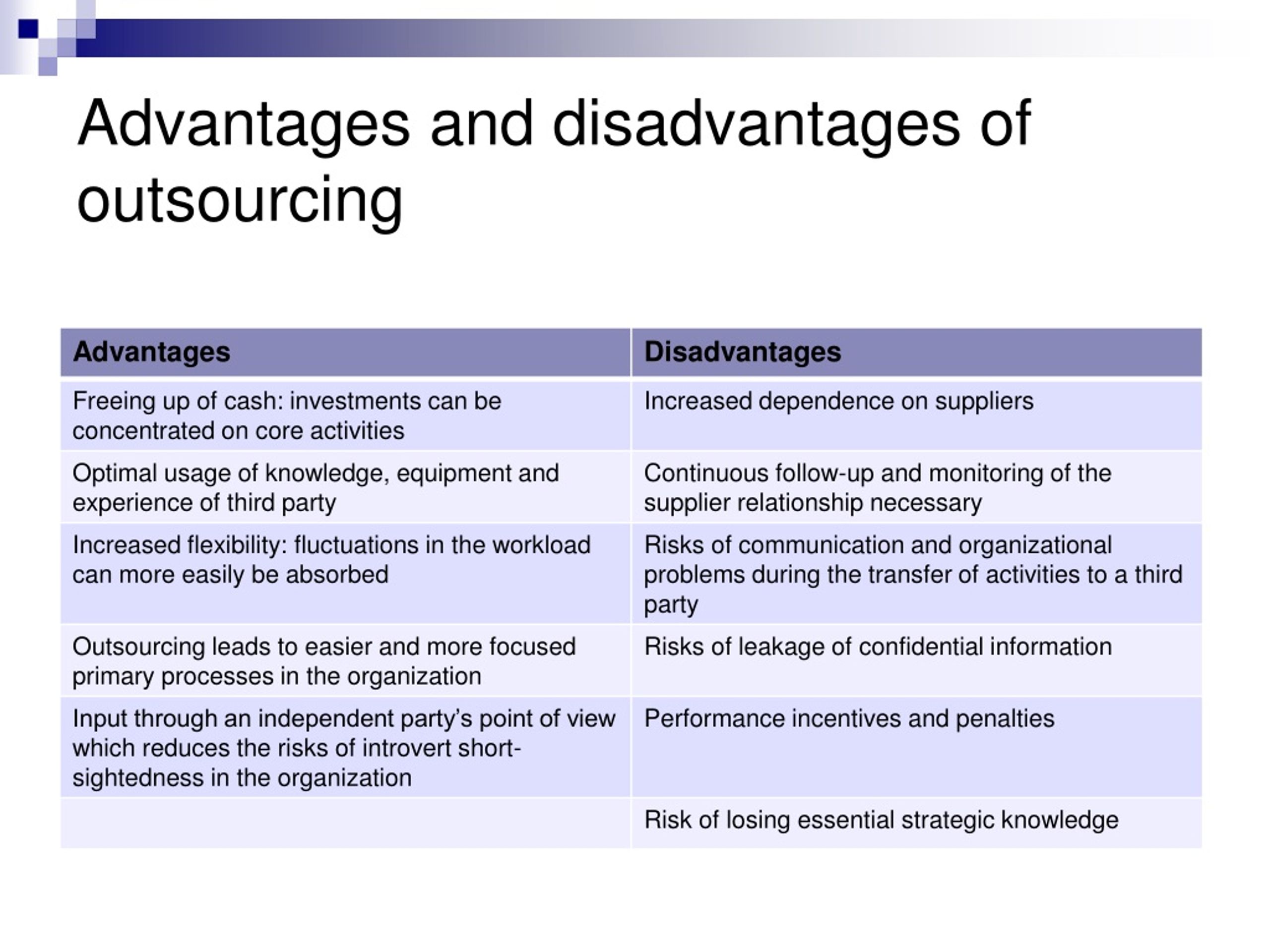
Outsourcing, at its core, is the contracting of non-core business activities to specialized external providers, often located in countries with lower labor costs. This strategy offers businesses the potential for cost reduction, increased efficiency, and access to specialized skills. However, it also raises concerns about job displacement, quality control, and potential security risks.
The Allure of Cost Savings and Efficiency
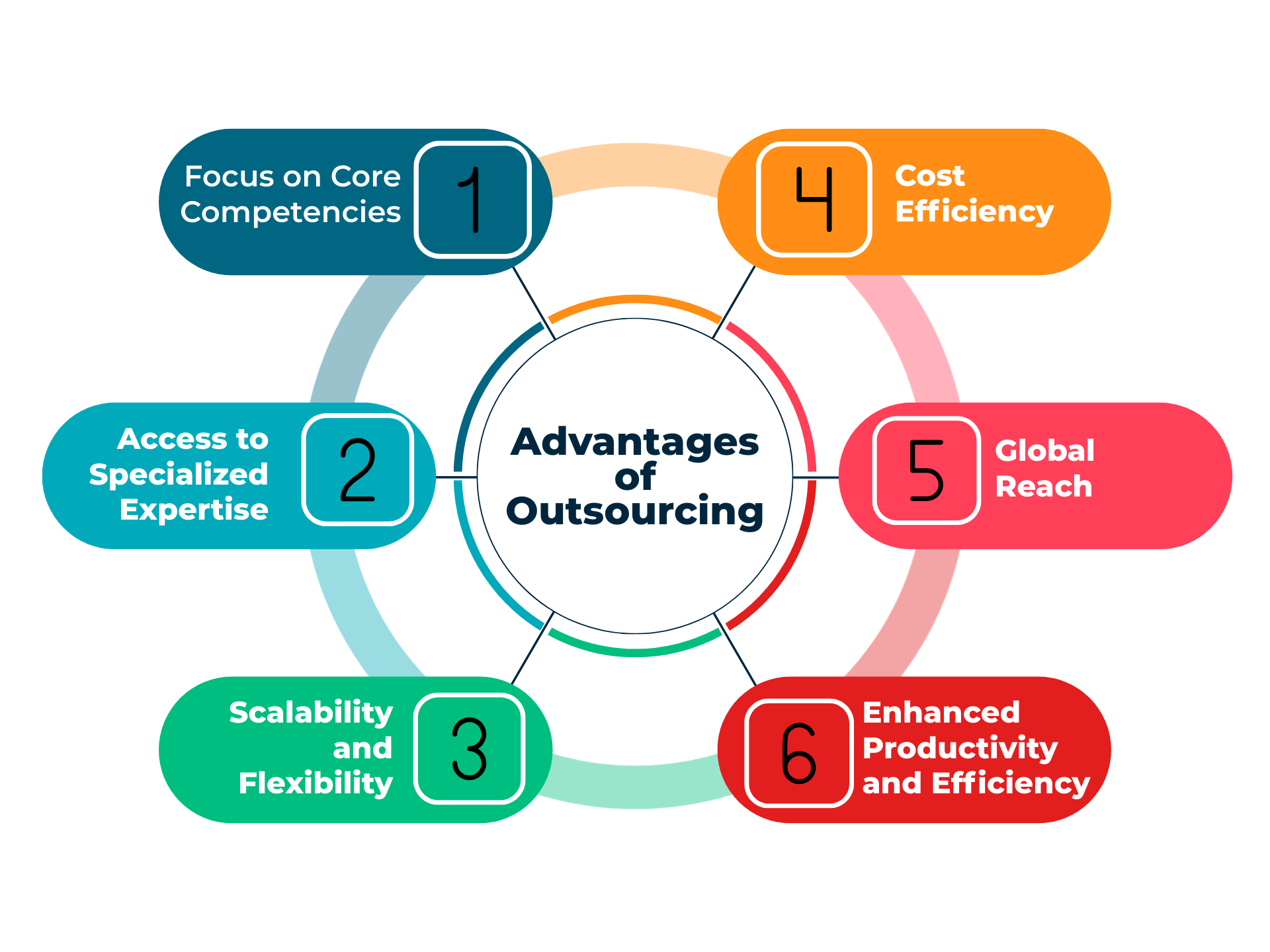
One of the most compelling benefits of outsourcing is the potential for substantial cost savings. By leveraging lower labor costs in countries like India, the Philippines, and China, companies can significantly reduce operational expenses.
Furthermore, outsourcing can improve efficiency by allowing companies to focus on their core competencies while delegating specialized tasks to experts. The Deloitte Global Outsourcing Survey consistently highlights cost reduction and improved efficiency as primary drivers for outsourcing decisions.
Access to a wider talent pool is another key advantage. Companies can tap into specialized skills and expertise that may not be readily available internally, fostering innovation and improving product or service quality.
The Downside: Job Displacement and Quality Concerns
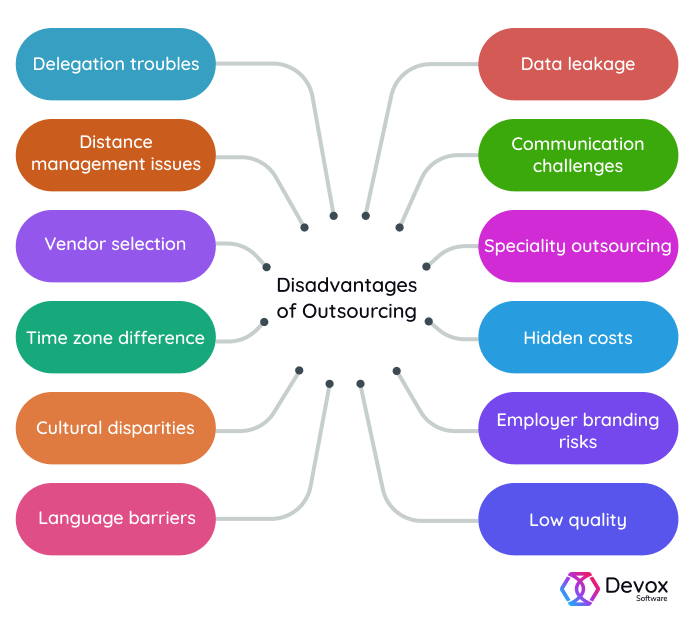
Despite the potential benefits, outsourcing is not without its drawbacks. Job displacement remains a significant concern, particularly in developed countries where companies are moving jobs to lower-cost locations.
According to the Economic Policy Institute, outsourcing has contributed to job losses in sectors such as manufacturing and customer service in the United States. This can lead to economic hardship and social unrest in affected communities.
Maintaining quality control can also be a challenge when outsourcing. Differences in language, culture, and business practices can lead to misunderstandings and errors, impacting the quality of goods or services.
Navigating the Risks: Communication and Security
Effective communication and project management are crucial for successful outsourcing. Establishing clear expectations, providing regular feedback, and fostering strong relationships with external providers are essential for mitigating risks and ensuring quality.
Data security is another critical concern. Outsourcing sensitive information to third-party providers can expose companies to data breaches and cyberattacks. It is essential to implement robust security measures and ensure that providers comply with relevant data protection regulations.
The National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) advises organizations to carefully assess the security risks associated with outsourcing and implement appropriate safeguards.
A Human Perspective
The impact of outsourcing extends beyond the corporate boardroom, affecting the lives of individuals and communities. A former call center worker in Ohio, who lost her job when her company outsourced its customer service operations to India, shared her experience: "It was devastating. I had worked there for 15 years, and suddenly I was out of a job. It's hard to compete with such low wages."
This personal story highlights the human cost of outsourcing and underscores the need for policies that support workers who are displaced by globalization.
Conversely, outsourcing can create employment opportunities in developing countries, providing jobs and contributing to economic growth. In Bangalore, India, a thriving outsourcing industry has transformed the city into a global hub for technology and business services.
The Future of Outsourcing
As technology continues to evolve, the future of outsourcing is likely to be shaped by automation, artificial intelligence (AI), and cloud computing. These technologies will enable companies to automate more complex tasks and further optimize their operations.
However, ethical considerations will become increasingly important. Companies will need to balance the pursuit of cost savings with the need to protect workers' rights, ensure data security, and promote sustainable business practices.
The International Labour Organization (ILO) emphasizes the importance of promoting fair labor standards and protecting workers' rights in the context of globalization and outsourcing.
In conclusion, outsourcing presents a complex set of benefits and disadvantages that businesses must carefully weigh. While it offers the potential for cost savings, increased efficiency, and access to specialized skills, it also raises concerns about job displacement, quality control, and security risks. A strategic and responsible approach is essential for maximizing the benefits of outsourcing while mitigating its potential drawbacks.