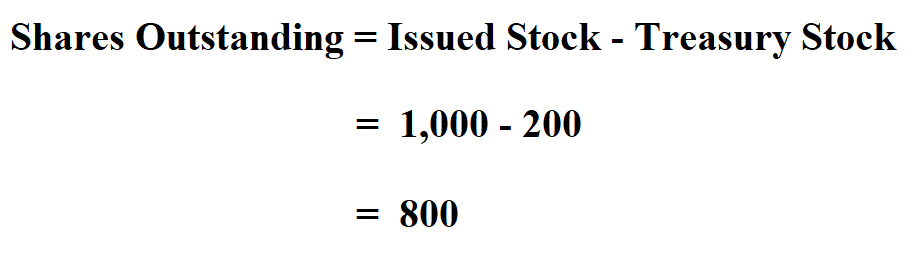Outstanding Common Stock Refers To The Total Number Of Shares
.jpg)
Imagine a bustling town square, not made of brick and mortar, but of numbers and symbols. Here, fortunes are made and lost, ownership shifts hands, and the collective pulse of companies big and small beats strong. At the heart of this financial hub lies a seemingly simple, yet profoundly important concept: outstanding common stock. It's a term often heard, but perhaps not always fully understood.
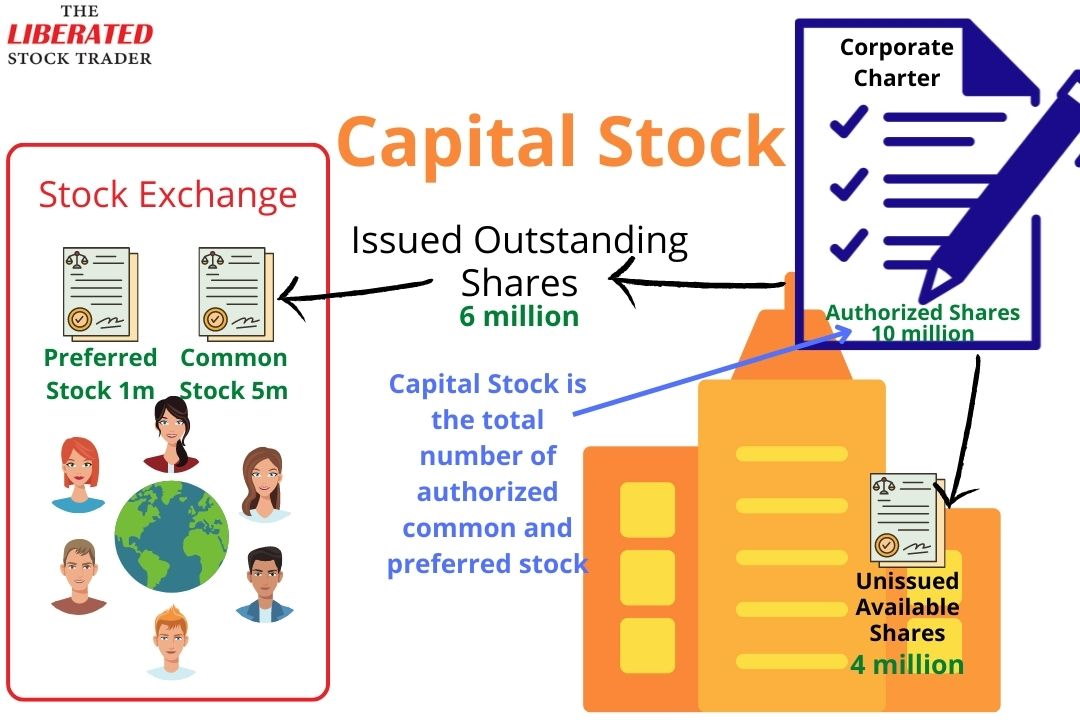
Outstanding common stock refers to the total number of shares of a company's stock that are held by investors, including individuals and institutional investors. This excludes any shares that the company has repurchased and are holding as treasury stock. Understanding this number is crucial because it provides a key insight into a company's value, ownership structure, and potential earnings per share, directly impacting investment decisions.
A Foundation of Ownership
To understand outstanding common stock, we must first revisit the basics of stock itself. When a company decides to go public or needs to raise capital, it often issues shares of stock. These shares represent fractional ownership of the company.
Common stock, specifically, gives shareholders the right to vote on company matters and to receive dividends, if declared by the company. These rights solidify the investor's stake in the organization's future.
Initial Public Offerings (IPOs) and Beyond
The journey of outstanding common stock typically begins with an Initial Public Offering (IPO). During an IPO, a private company offers shares to the public for the first time. The number of shares offered, and consequently the initial outstanding common stock, is determined by the company and its underwriters.
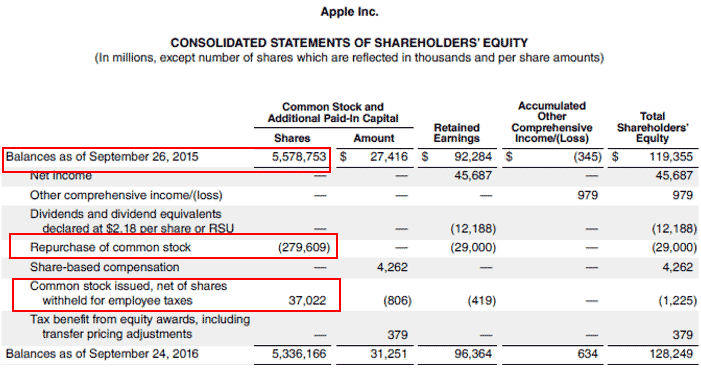
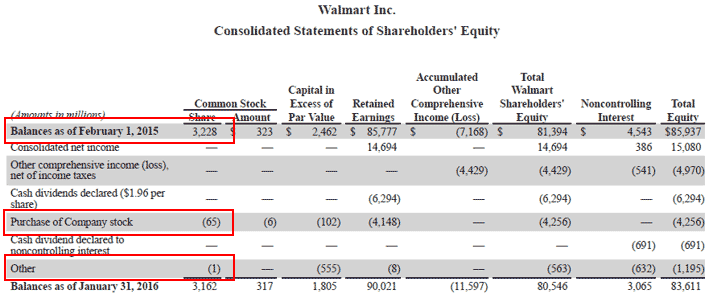
However, the number of outstanding shares is not static. Companies can issue new shares through secondary offerings to raise additional capital. Conversely, they can repurchase their own shares, reducing the number of outstanding shares.
Share buybacks are often seen as a sign that the company believes its stock is undervalued. This strategic move demonstrates confidence in their future prospects.
Calculating and Interpreting Outstanding Common Stock
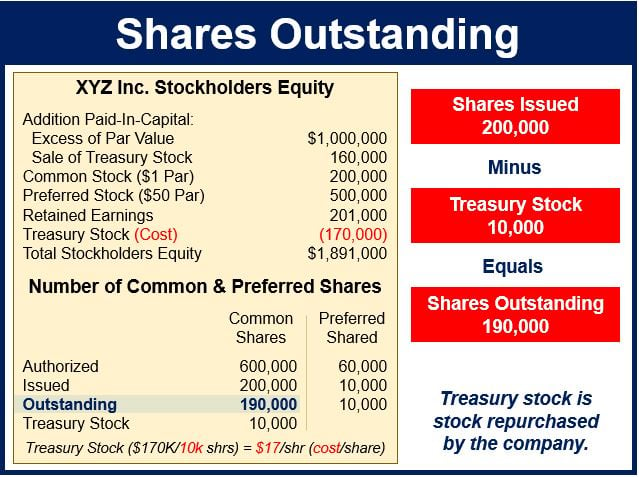
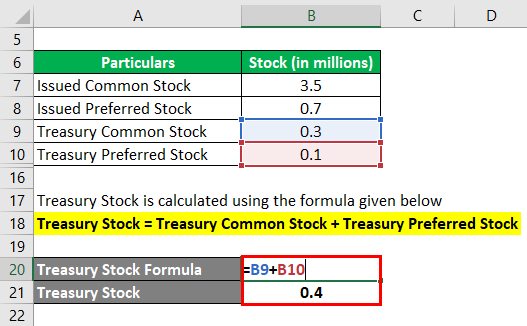
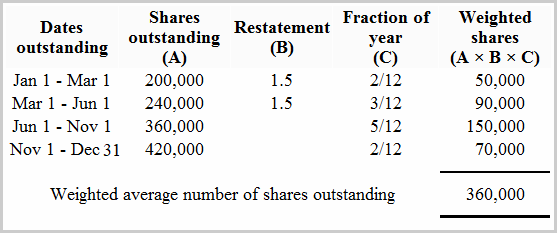
The calculation of outstanding common stock seems deceptively simple: it’s the total number of issued shares minus treasury stock. However, understanding the nuances requires careful attention to a company's financial statements.
The number of issued shares can be found in the company's balance sheet or equity section of their annual or quarterly reports. Treasury stock, representing repurchased shares, is also disclosed in the same financial documents.
By subtracting treasury stock from the total issued shares, one arrives at the number of outstanding common shares. This information is essential for various financial metrics.
Earnings Per Share (EPS) and Market Capitalization
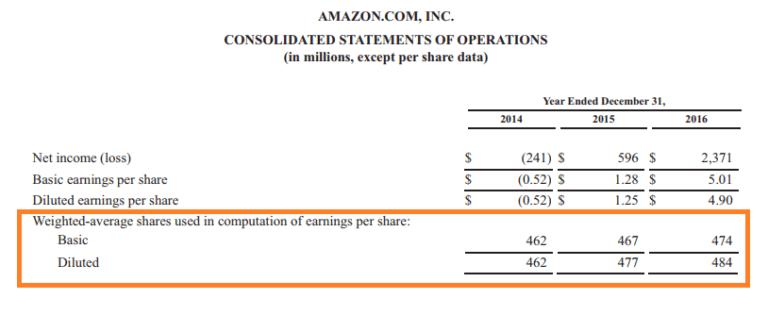
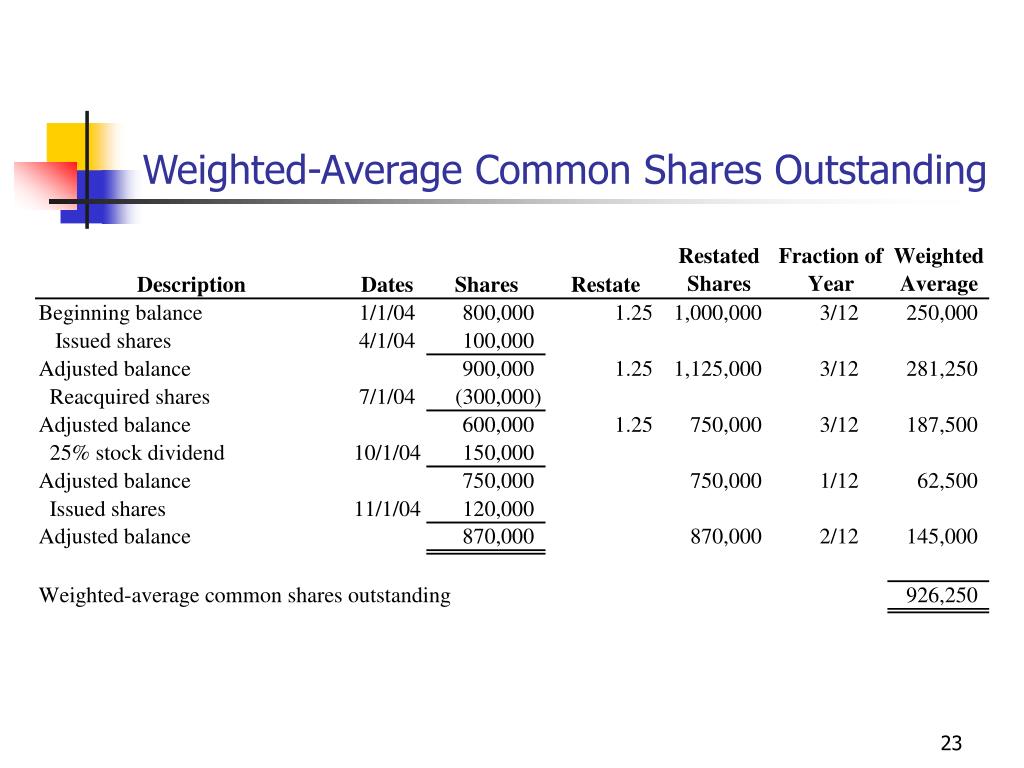
One of the most critical uses of outstanding common stock is in the calculation of Earnings Per Share (EPS). EPS is a key indicator of a company's profitability and is calculated by dividing the company's net income by the number of outstanding shares.
A higher EPS generally indicates greater profitability for each share of stock. This is a crucial data point for investors.
Outstanding common stock is also used to calculate a company's market capitalization, which is the total market value of its outstanding shares. Market capitalization is calculated by multiplying the number of outstanding shares by the current market price per share.
Market capitalization provides a sense of the company's overall size and market value. This metric is often used to categorize companies as small-cap, mid-cap, or large-cap.
The Significance for Investors
For investors, understanding outstanding common stock is paramount. It allows them to evaluate a company's financial health, potential for growth, and the value of their investment.
Tracking changes in outstanding shares can provide valuable insights into a company's strategic decisions. An increase in outstanding shares might dilute earnings per share, while a decrease due to share buybacks could boost EPS.
Moreover, understanding the ownership structure, as indicated by the distribution of outstanding shares, can reveal potential governance issues or shareholder influence.
Dilution and Stock Splits
Dilution occurs when a company issues new shares, increasing the total number of outstanding shares. This can decrease the ownership percentage of existing shareholders and potentially lower the value of their shares, especially if the new shares are issued at a price lower than the current market price.
Stock splits, on the other hand, involve dividing existing shares into multiple shares. While the number of outstanding shares increases, the market capitalization remains the same, and the price per share decreases proportionally.
Stock splits can make a company's stock more accessible to smaller investors. This can potentially increase liquidity.
Real-World Examples
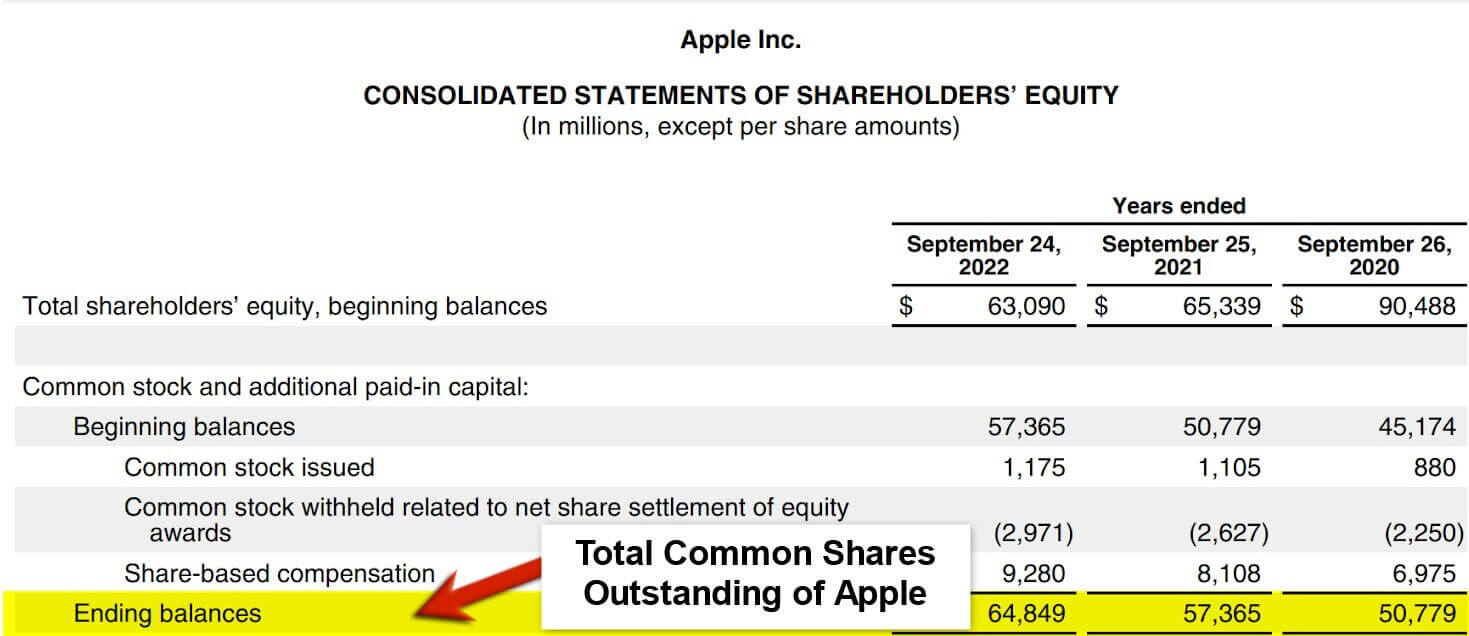
Consider Apple Inc., a global technology giant. By tracking their outstanding common stock over the years, one can see how share buybacks have been used to enhance shareholder value.
Conversely, a rapidly growing tech startup might issue more shares to fuel its expansion. This would lead to an increase in outstanding common stock.
These examples illustrate how companies manage their outstanding shares to achieve specific financial goals.
Conclusion: A Cornerstone of Financial Literacy
Outstanding common stock may seem like a dry, technical term. However, it is actually a fundamental concept that unlocks a deeper understanding of the financial world. It is a cornerstone of financial literacy.
By understanding how it's calculated, what it signifies, and how it impacts various financial metrics, investors can make more informed decisions. The outcome would be better navigating the complexities of the stock market.
So, the next time you hear the term outstanding common stock, remember the bustling town square, the fractional ownership, and the strategic decisions behind the numbers. This knowledge will empower you on your investment journey.