Penn State Entrance To Major Requirements

UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. – Penn State University continues to navigate the complexities of its entrance to major (ETM) policies, a system impacting thousands of students striving to declare their desired field of study. Recent data and ongoing discussions highlight the challenges and opportunities within the current framework.
The ETM process, a critical juncture for Penn State undergraduates, determines whether students can officially enroll in their preferred major. Understanding its mechanisms, impacts, and potential reforms is essential for current and prospective students, as well as faculty and administrators.
The entrance to major requirements vary significantly across Penn State's diverse academic colleges. Generally, students must meet specific GPA thresholds, complete designated prerequisite courses with minimum grades, and, in some cases, undergo a portfolio review or audition.
Key Components of the ETM Process
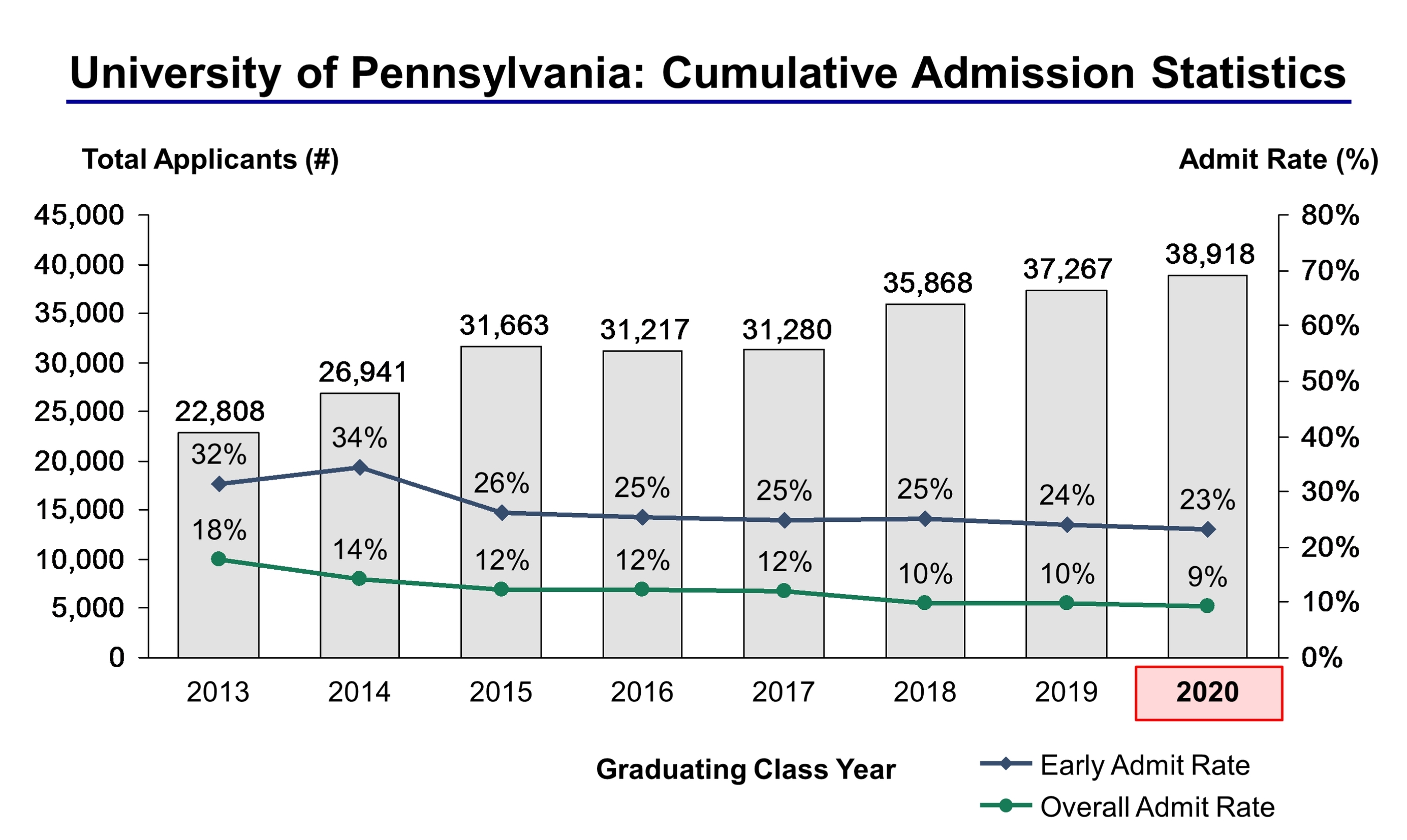
The foundational element is the Grade Point Average (GPA). Many highly competitive majors, particularly within the Smeal College of Business and the College of Engineering, necessitate a GPA significantly above the university's overall average.
Prerequisite courses serve as gateways, ensuring students possess the fundamental knowledge required for advanced study. These courses, often in math, science, or writing, demand a minimum grade, typically a C or higher, to qualify for entrance to the major.
Some programs, especially those in the arts and design disciplines, incorporate portfolio reviews or auditions into the ETM process. These assessments evaluate a student's creative potential and skill level.
Challenges and Concerns
One significant concern is the potential for increased student stress and anxiety. The pressure to maintain a high GPA and excel in prerequisite courses can create a competitive and sometimes overwhelming environment.
Students who are not admitted to their first-choice major may experience discouragement and uncertainty about their academic path. This situation can lead to delays in graduation or changes in career aspirations.
There have been arguments that the current ETM system disproportionately affects students from underrepresented backgrounds. Access to resources and opportunities to prepare for rigorous coursework may vary, potentially impacting GPA and overall academic performance.
University Responses and Potential Reforms
Penn State administrators acknowledge the challenges associated with the ETM process and are actively exploring potential reforms. These efforts aim to create a more equitable and transparent system.
The university is exploring options such as holistic review processes. Holistic review considers a broader range of factors beyond GPA and test scores, including a student's background, experiences, and demonstrated potential.
Increased advising and support services are also being considered. Providing students with comprehensive guidance and resources can help them navigate the ETM process more effectively.
Student Perspectives
“The ETM process felt incredibly stressful,” stated Emily Carter, a junior majoring in Computer Science. “The pressure to get a high GPA in those intro courses was immense, and it definitely impacted my mental health.”
Another student, David Lee, shared his experience. “I didn’t get into my first-choice major, but the advising staff helped me explore other options that aligned with my interests. It was tough, but I eventually found a great fit.”
These student testimonials highlight the emotional and academic impact of the ETM process.
Looking Ahead
The ongoing discussions surrounding Penn State's ETM policies reflect a commitment to improving the undergraduate experience. By addressing the challenges and exploring innovative solutions, the university seeks to create a more equitable and supportive environment for all students.
The evolution of the ETM process at Penn State is a continuous journey, driven by data, feedback, and a shared goal of fostering student success.
Future adjustments to the entrance to major requirements will likely depend on further data analysis and continued dialogue between students, faculty, and administration.