Prior To The Adjusting Process Accrued Revenue Has
The often-overlooked world of accrual accounting is under increased scrutiny as discrepancies between reported revenues and actual earnings, before the adjusting process, spark debate among auditors and financial analysts.
This has led to a growing concern about the accuracy of preliminary financial statements. The core issue revolves around accrued revenue, specifically how it's estimated and reported before the standard end-of-period adjustments are made. This article delves into the intricacies of this financial practice, examining the potential pitfalls, regulatory considerations, and the measures being taken to ensure greater transparency and reliability in financial reporting.
Understanding Accrued Revenue Before Adjustments
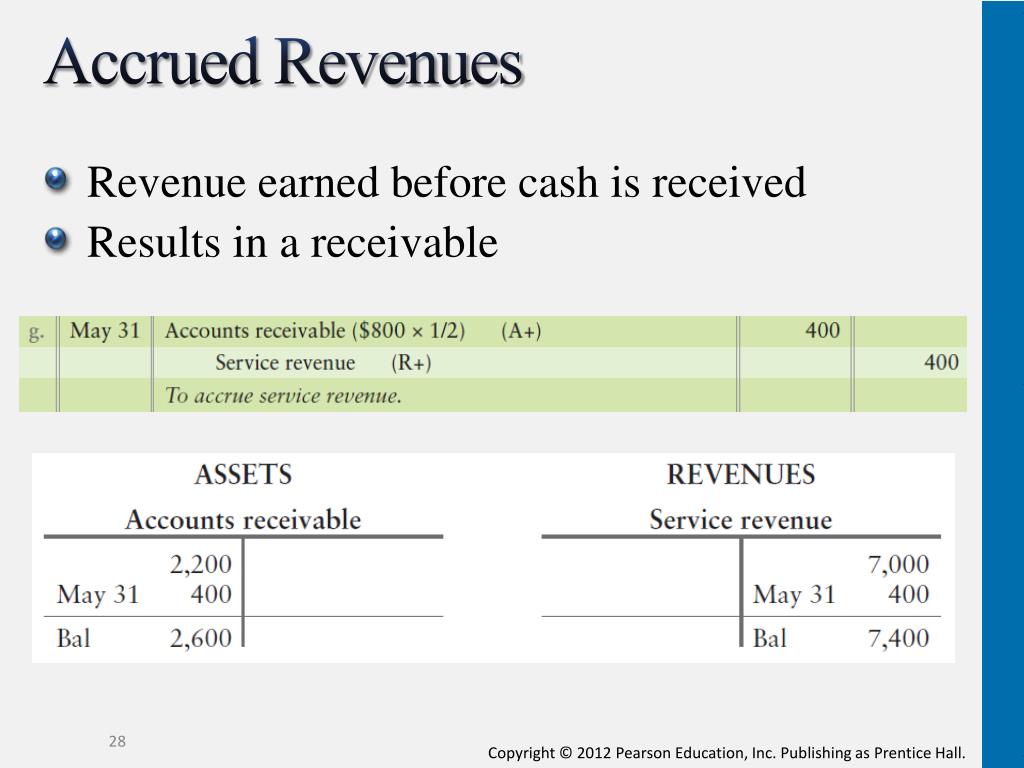
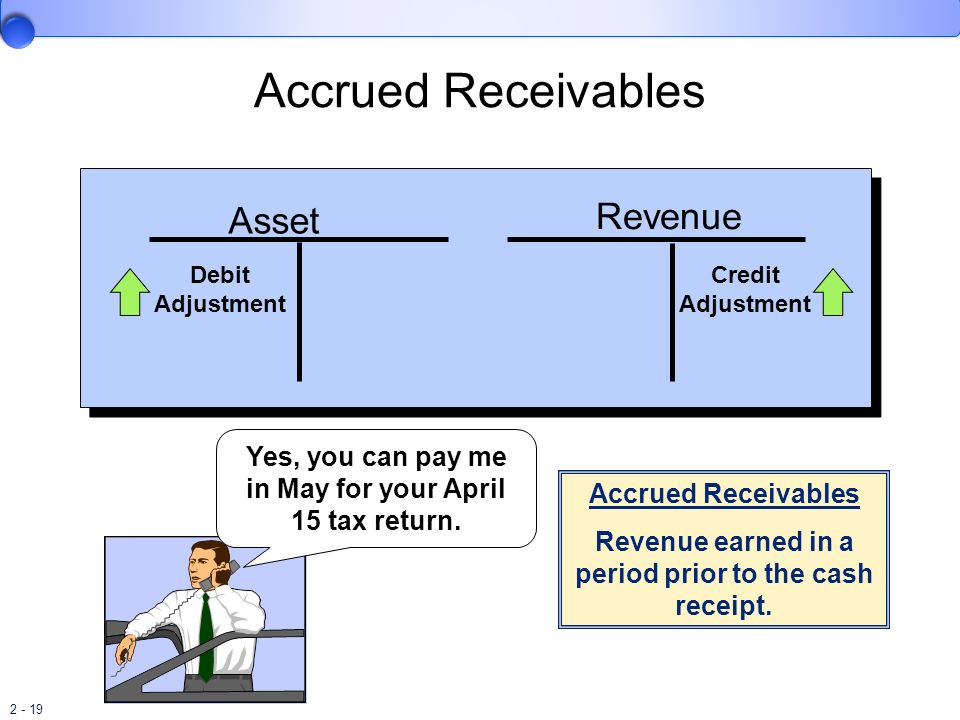
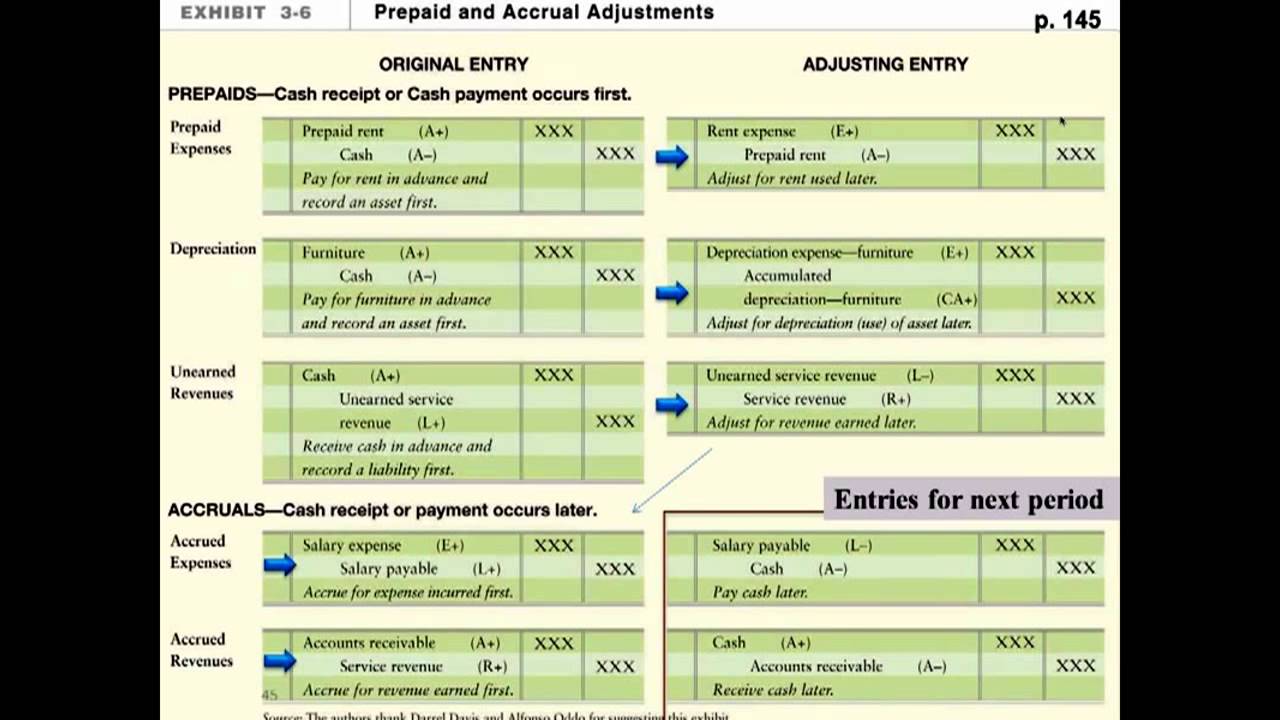
Accrued revenue represents revenue that has been earned but for which cash payment has not yet been received.
It arises when a company provides goods or services before billing the client. Prior to the adjusting process, these figures are often preliminary estimates based on various factors.
These factors can include project milestones, service delivery completion rates, or even subjective assessments of work performed. The initial estimate may be based on internal company data, project management reports, or even preliminary communications with clients.
Potential Issues and Concerns
The reliance on preliminary estimates before adjustments raises several red flags. One primary concern is the potential for overestimation of revenue. This overestimation can inflate reported earnings in the short term, potentially misleading investors and stakeholders.
Another issue is the subjective nature of some preliminary accrual estimates. Without rigorous documentation and verification processes, these figures could be manipulated to present a more favorable financial picture. This can be particularly problematic in industries where revenue recognition is complex.
The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has been actively monitoring cases involving inaccurate or misleading accrual accounting. Cases of inflated accrued revenue, prior to adjustments, can result in severe penalties, including fines, restatements of financial statements, and even legal action against company executives.
The Auditor's Perspective
Auditors play a critical role in scrutinizing accrued revenue estimates. They are responsible for verifying the reasonableness and accuracy of these figures before the adjusting entries are made. This involves reviewing supporting documentation, assessing the company's estimation methodologies, and conducting independent testing.
According to the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (PCAOB), auditors must exercise a high degree of professional skepticism when evaluating accrued revenue. This requires auditors to be alert to potential biases and inconsistencies in the information provided by management. They should carefully evaluate the underlying assumptions and judgments used to develop the accrued revenue estimates.
Increased scrutiny by auditors can lead to more conservative accrual estimates and a more accurate portrayal of a company's financial performance. This includes a thorough review of contracts, invoices, and project completion reports.
The Impact on Financial Reporting
The accuracy of accrued revenue estimates has a direct impact on the reliability of financial statements. If the estimates are materially inaccurate, it can distort a company's reported revenues, earnings, and assets.
This can have significant consequences for investors, creditors, and other stakeholders who rely on financial statements to make informed decisions. Investors might make poor decisions based on inflated earnings figures.
Creditors might extend loans to companies that appear financially stronger than they actually are. The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) is actively working on developing clearer guidelines for revenue recognition, which may reduce the potential for manipulation.
Best Practices and Mitigation Strategies
To mitigate the risks associated with accrued revenue, companies should implement robust internal controls. These controls should include well-defined policies and procedures for estimating and recording accrued revenue. Clear documentation requirements and independent review processes should be implemented.
Companies should also invest in training for their accounting and finance teams to ensure they are knowledgeable about the latest accounting standards and best practices. Utilizing technology and data analytics can also improve the accuracy and efficiency of accrued revenue estimation.
For instance, sophisticated software can track project progress, automatically generate invoices, and provide real-time insights into revenue recognition. This can minimize the risk of errors and inaccuracies.
Technological Solutions
Many software providers now offer solutions designed to streamline and improve the accuracy of revenue recognition. These solutions automate various aspects of the process, from contract management to invoice generation to revenue allocation. They provide audit trails and facilitate compliance with accounting standards.
Furthermore, advanced analytics tools can be used to identify patterns and anomalies in revenue data, which can help detect potential errors or fraud. Data analytics can provide valuable insights into customer behavior, sales trends, and other factors that influence revenue.
The adoption of such technologies can lead to more reliable financial reporting and reduce the risk of costly restatements.
Looking Ahead
The focus on accrued revenue and its pre-adjustment implications is likely to intensify in the coming years. Regulators, auditors, and investors are all becoming more aware of the potential risks associated with inaccurate or misleading accrual accounting.
Companies that prioritize accuracy and transparency in their financial reporting will be best positioned to maintain investor confidence and avoid regulatory scrutiny. Continuing improvements in accounting standards, auditing practices, and technology will further enhance the reliability of financial information.
Ultimately, the goal is to ensure that financial statements provide a fair and accurate representation of a company's financial performance, fostering trust and confidence in the capital markets. Companies are expected to be held accountable for their accrual practices.