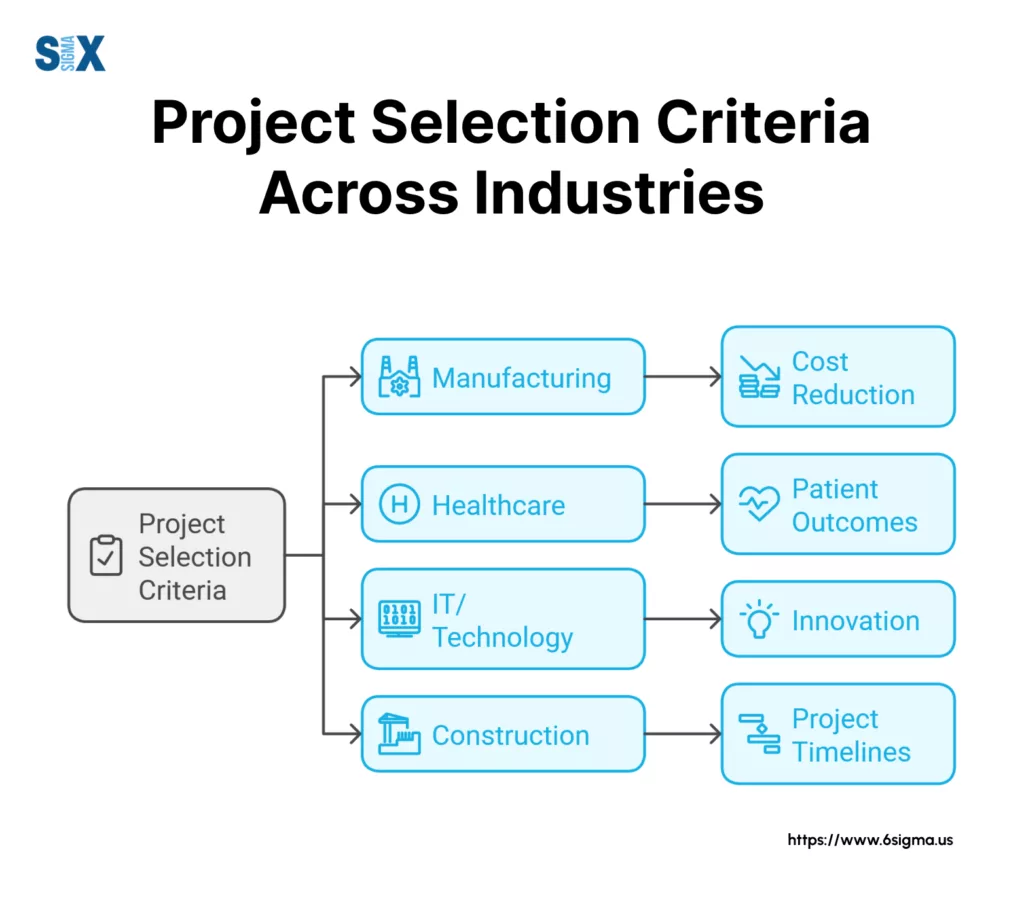
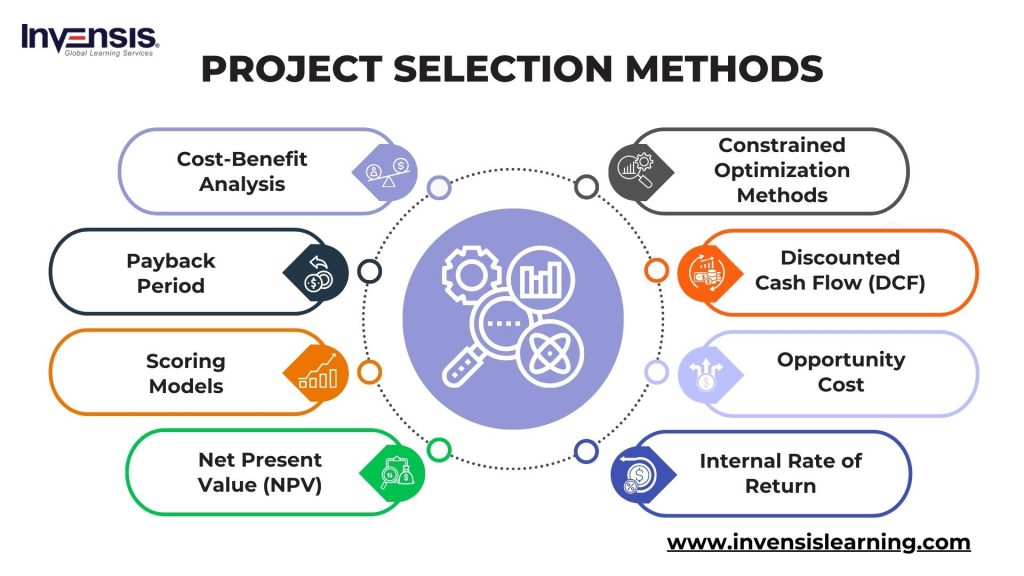
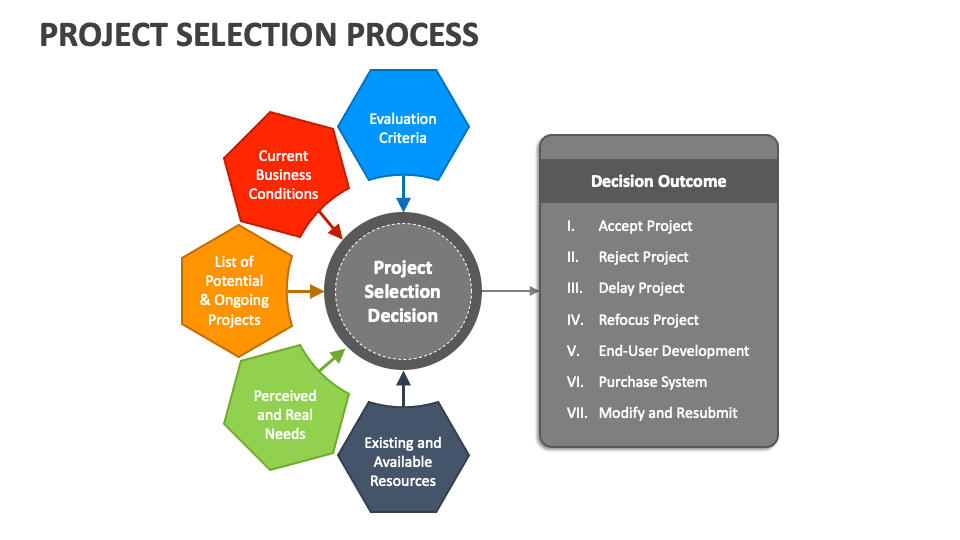
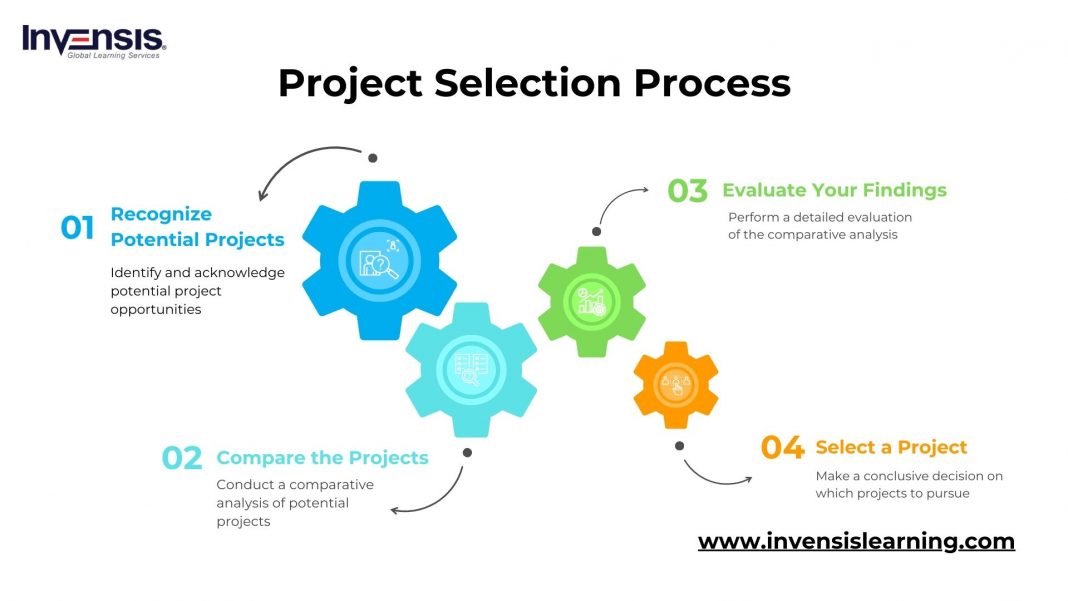
Project Selection Criteria Are Typically Classified As

Organizations across diverse sectors face the constant challenge of choosing the right projects to invest in, balancing potential returns with resource constraints. Effective project selection is paramount, determining not only financial success but also strategic alignment and long-term growth. The criteria used to evaluate projects play a critical role in this process, often falling into distinct categories that guide decision-makers.
This article delves into the classification of project selection criteria, exploring the common types used by businesses and governmental bodies. Understanding these criteria is crucial for anyone involved in project management, portfolio optimization, or strategic planning. Proper selection ensures that resources are allocated effectively and that pursued projects align with organizational goals and objectives.
Classifying Project Selection Criteria
Project selection criteria are typically classified based on their nature and impact on the decision-making process. The classifications help in structuring project evaluations and making informed choices.
Financial Criteria
Financial criteria are among the most commonly used and heavily weighted in project selection. These metrics focus on the expected financial returns and costs associated with a project. Common financial metrics include Return on Investment (ROI), Net Present Value (NPV), and Internal Rate of Return (IRR).
The ROI measures the profitability of an investment relative to its cost, providing a clear indication of potential gains. NPV calculates the present value of expected cash flows, discounted by a specific rate, allowing for comparison of projects with varying timelines. IRR indicates the discount rate at which the project's NPV equals zero, showing the project's profitability threshold.
Organizations use these metrics to prioritize projects that offer the most attractive financial prospects. However, financial metrics alone are insufficient and need to be evaluated along with other non-financial aspects.
Strategic Alignment Criteria
Beyond financial returns, it's important to evaluate how well a project aligns with the organization's overarching strategy and objectives. Strategic alignment criteria assess whether a project supports the company's mission, vision, and long-term goals.
For instance, a project may be selected if it helps the company expand into new markets, improve customer satisfaction, or enhance its competitive advantage. Strategic criteria involve assessing the fit of the project with the company's strategic direction and whether it leverages core competencies.
Consider the case of a software company deciding between developing a new AI-powered tool or upgrading its existing customer support platform. The AI tool might seem innovative, but the platform upgrade could be more strategic if it directly enhances customer retention and reduces churn, aligning better with the company's customer-centric strategy.
Operational Criteria
Operational criteria relate to the practicality and feasibility of executing a project within the organization's current operational capabilities. These criteria assess whether the organization has the resources, skills, and infrastructure to successfully complete the project.
Factors such as the availability of skilled personnel, access to necessary technology, and the presence of adequate infrastructure are critical. Project selection involves determining if the organization can handle the project's operational demands.
For example, a manufacturing company considering a new production line must evaluate whether its current facility has the capacity to house the new equipment and if its workforce is trained to operate it efficiently.
Risk Assessment Criteria
Every project carries some degree of risk, and risk assessment criteria are used to evaluate the potential challenges and uncertainties associated with a project. These criteria consider various risks such as technical, financial, market, and regulatory risks.
Organizations typically use risk assessment tools such as SWOT analysis, Monte Carlo simulations, and sensitivity analysis. These tools help in identifying potential threats and evaluating their impact on the project's success.
A biotech company developing a new drug, for example, will consider the risks associated with clinical trials, regulatory approvals, and market acceptance. Understanding these risks informs decisions about whether to proceed with the project and what mitigation strategies to implement.
Social and Environmental Criteria
Increasingly, organizations are considering social and environmental criteria when selecting projects. These criteria assess the project's impact on society, the environment, and stakeholders beyond the company itself.
This might involve evaluating the project's contribution to community development, its impact on carbon emissions, or its adherence to ethical business practices. Sustainable development initiatives are often evaluated based on their social and environmental benefits.
For instance, a construction company planning a new building might consider its impact on local ecosystems, energy efficiency, and accessibility for people with disabilities. These factors help ensure that projects are both profitable and responsible.
The Impact of Choosing the Right Criteria
Selecting the appropriate project selection criteria has a significant impact on an organization’s success. Using a well-defined set of criteria ensures that the organization invests in projects that are most likely to generate value and align with its strategic objectives.
In contrast, inadequate or poorly chosen criteria can lead to misallocation of resources, project failures, and missed opportunities. The result can be project that do not bring value and impact the bottom line negatively.
The ability to effectively assess and select projects is crucial for long-term sustainability and competitiveness. Organizations that understand the nuances of project selection criteria are better positioned to thrive in dynamic and competitive environments.
Conclusion
Project selection criteria are the foundation of sound project management and strategic planning. By classifying these criteria into categories such as financial, strategic, operational, risk assessment, and social/environmental, organizations can make more informed decisions.
Each category offers unique insights into a project's potential value, feasibility, and impact. Organizations that effectively integrate these diverse criteria into their project selection processes will improve the likelihood of project success.
Ultimately, the right project selection criteria enable organizations to drive innovation, enhance competitiveness, and achieve their strategic goals, contributing to long-term success and sustainability.