Risk For Electrolyte Imbalance Nursing Diagnosis
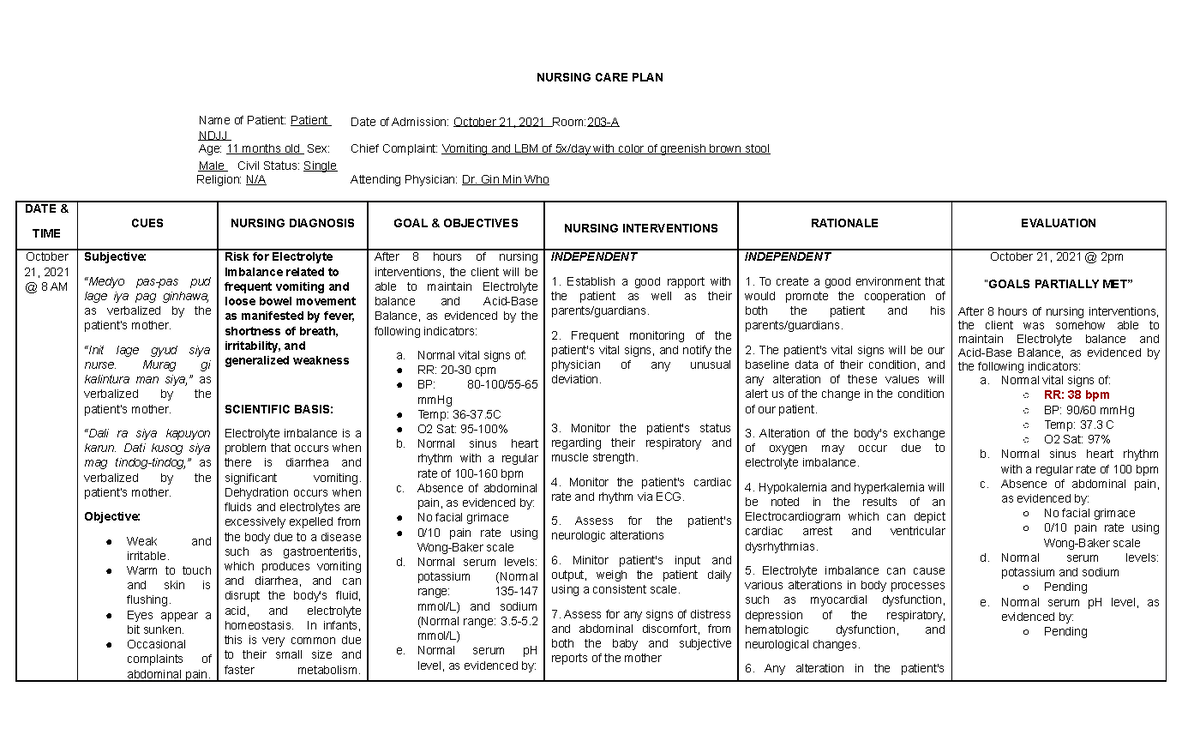
Hospitals nationwide are facing a surge in cases requiring intervention for 'Risk for Electrolyte Imbalance,' placing immense strain on nursing staff and resources. This urgent situation demands immediate attention to prevent severe complications and ensure patient safety.
The increase in this nursing diagnosis, "Risk for Electrolyte Imbalance," signals a growing vulnerability among patient populations, requiring vigilant monitoring and proactive management by healthcare providers. Understanding the contributing factors and implementing effective preventative measures are now critical.
Who is Affected?
The "Risk for Electrolyte Imbalance" affects a broad spectrum of patients. This includes elderly individuals, those with chronic kidney disease, heart failure patients, and individuals undergoing diuretic therapy.
Infants and children are also particularly vulnerable due to their smaller body size and immature kidney function. Oncology patients undergoing chemotherapy are at heightened risk due to treatment side effects.
What are Electrolyte Imbalances?
Electrolyte imbalances occur when the levels of crucial minerals like sodium, potassium, calcium, and magnesium in the body are disrupted. These minerals play vital roles in nerve function, muscle contraction, and fluid balance.
Significant imbalances can lead to a range of complications, including cardiac arrhythmias, seizures, muscle weakness, and even death. Early identification and prompt correction are paramount.
Where is This Happening?
Reports indicate that this trend is widespread across various healthcare settings. Emergency departments, intensive care units, and long-term care facilities are particularly impacted.
Urban hospitals and rural clinics are reporting similar challenges in managing patients at risk. The nationwide scope of this issue requires a coordinated public health response.
When Did This Start?
While electrolyte imbalances have always been a concern, healthcare providers have noted a significant increase in recent months. Initial observations suggest a correlation with changing patient demographics and increased use of certain medications.
A retrospective analysis of patient data is underway to pinpoint the exact timeline and identify any contributing seasonal factors. Preliminary findings point towards a potential link with the ongoing heatwaves across the country.
Why is This a Concern?
The increasing prevalence of "Risk for Electrolyte Imbalance" poses a direct threat to patient well-being. Unaddressed imbalances can lead to life-threatening complications and increased hospital readmissions.
Furthermore, the additional workload strains already overburdened nursing staff, potentially compromising the quality of care. Efficient protocols and enhanced training are crucial to mitigate these risks.
How Can This Be Addressed?
Healthcare providers are urged to implement proactive strategies for identifying and managing patients at risk. This includes thorough medication reviews, frequent electrolyte monitoring, and patient education.
Standardized protocols for electrolyte replacement and fluid management are essential. Telehealth and remote monitoring technologies can play a vital role in tracking high-risk patients outside of hospital settings.
Immediate Actions
Hospitals are being advised to review and update their electrolyte management protocols. Nurses should receive additional training on recognizing early warning signs of imbalance.
Patients, especially those with pre-existing conditions, should be educated about the importance of hydration and dietary modifications. Clear communication between patients and providers is critical.
Long-Term Strategies
Researchers are investigating the underlying causes of the increased prevalence of electrolyte imbalances. Public health campaigns are needed to raise awareness about the risk factors and preventative measures.
Collaboration between healthcare institutions and government agencies is essential to address this growing concern. Investing in resources and developing best practices will be crucial to protecting patient health.
The American Nurses Association (ANA) and the National Institutes of Health (NIH) have announced joint initiatives to provide further guidance and support to healthcare professionals tackling this challenge. The World Health Organization (WHO) is also monitoring the situation and offering technical assistance.
The situation remains dynamic, with ongoing data collection and analysis. Healthcare providers are encouraged to stay informed and adapt their practices based on the latest evidence-based recommendations. Addressing the "Risk for Electrolyte Imbalance" requires a concerted effort from all stakeholders to ensure optimal patient outcomes.
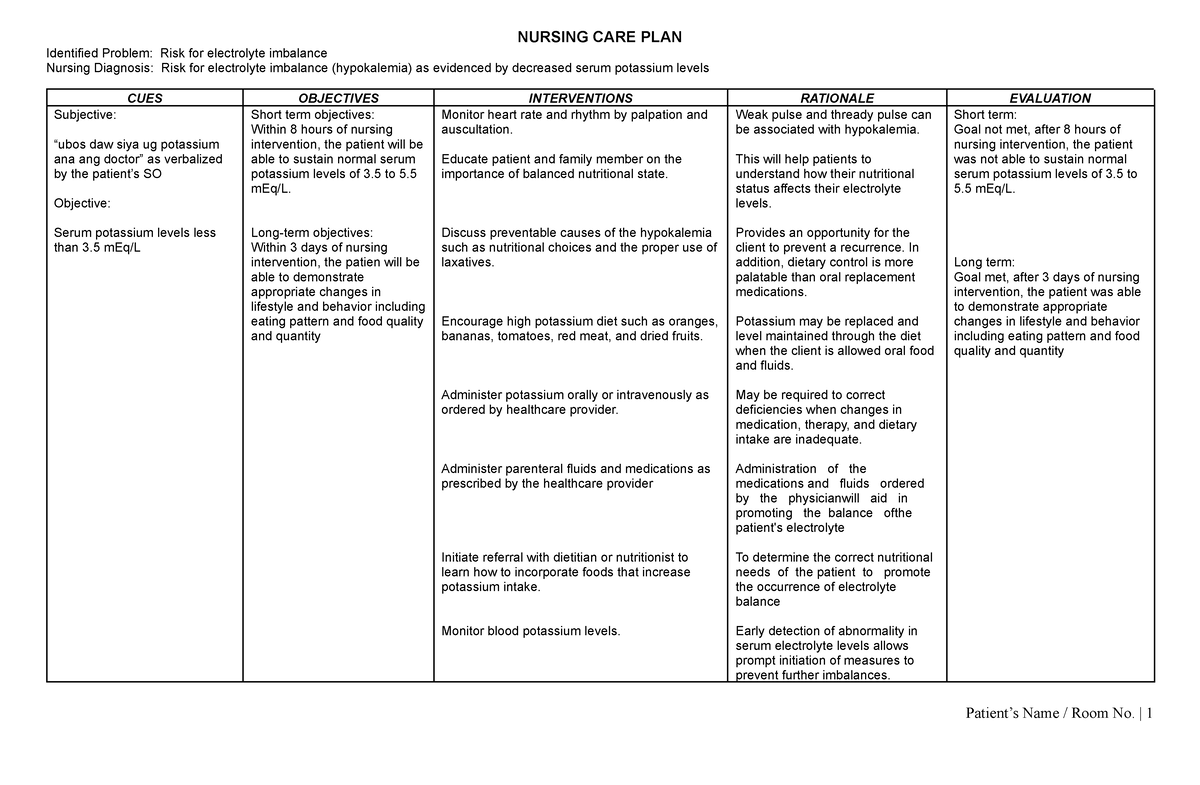



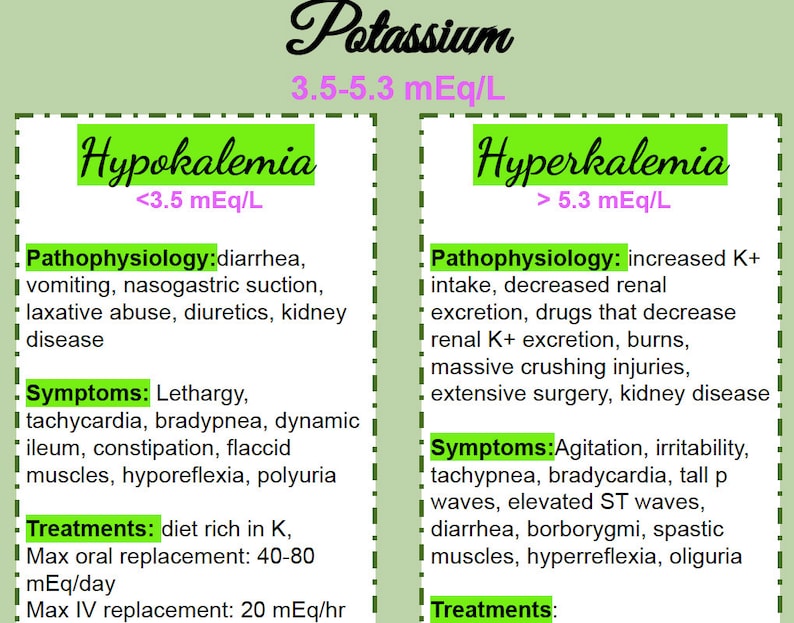



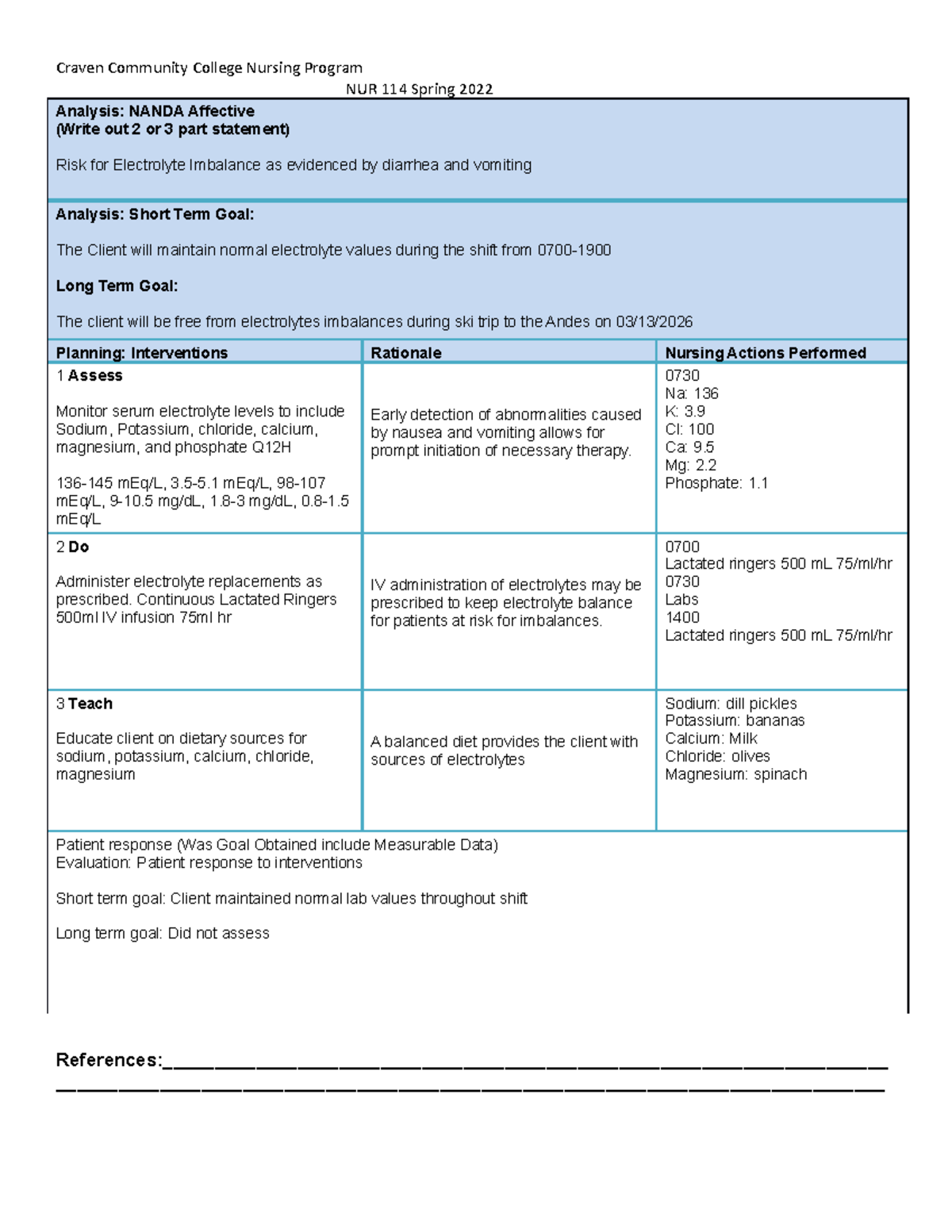
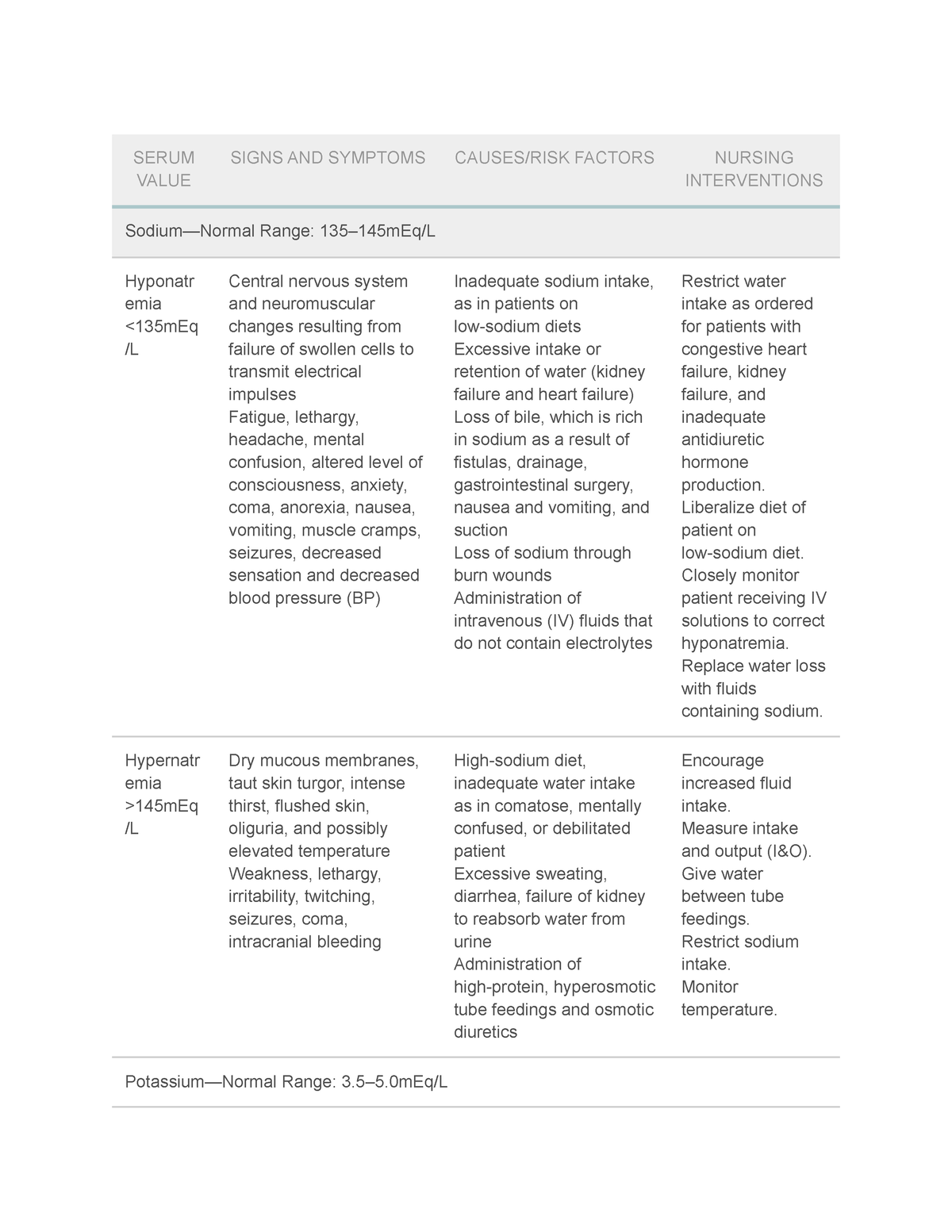

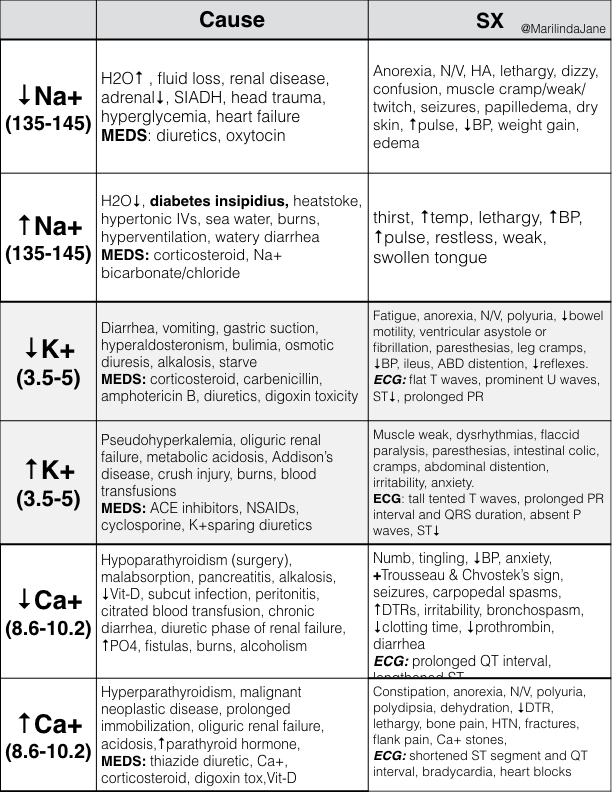





+Indentify+clients+at+risk+for+fluid+volume+imbalances.+Indentify+specific+assessment+findings+in+electrolyte+imbalances..jpg)
