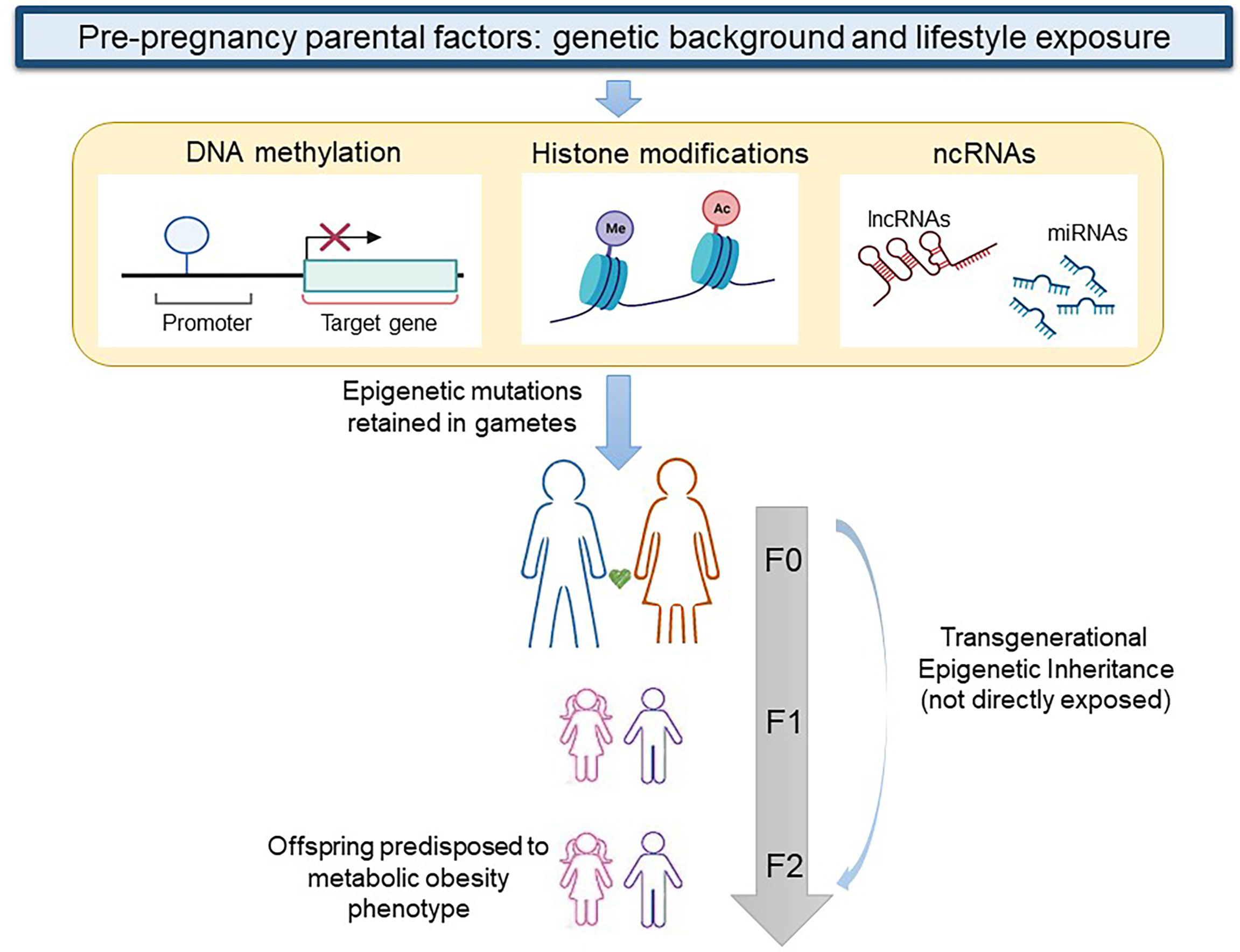
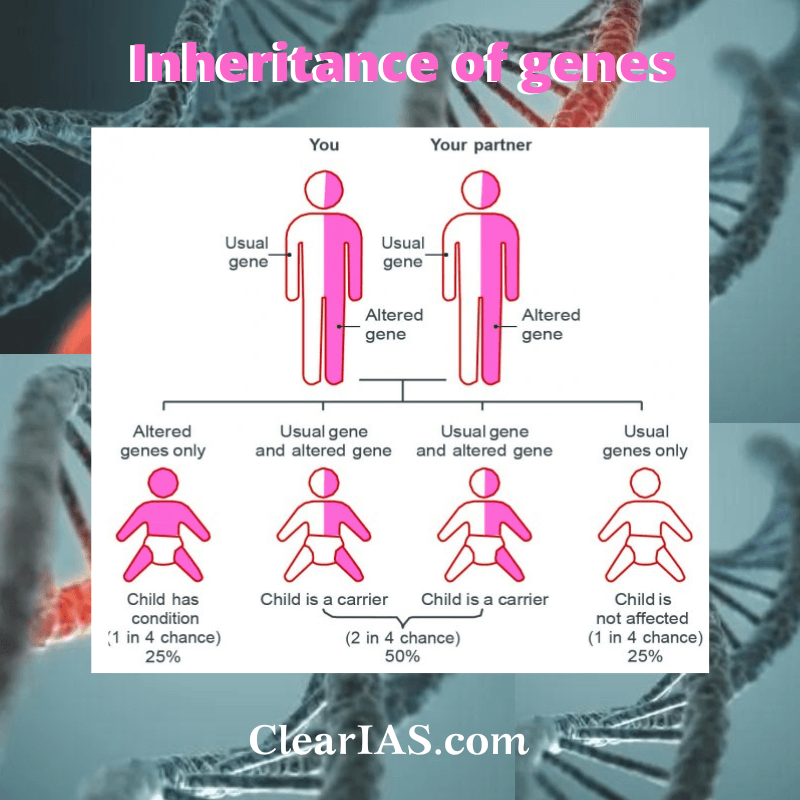
Risks Associated With Genetics Research Are Best Described As

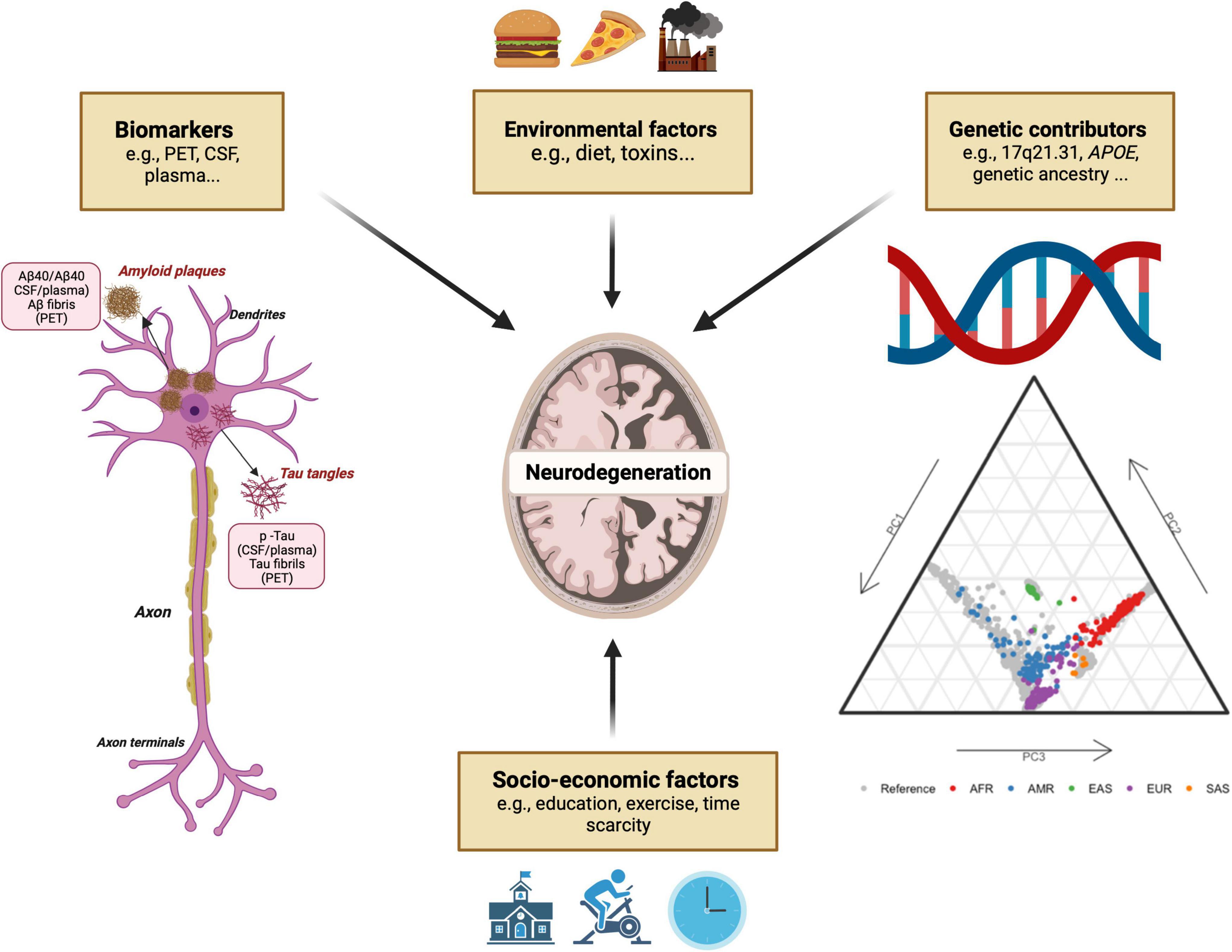
Genetic research, while promising revolutionary medical breakthroughs, carries inherent risks impacting individual privacy, societal equity, and even biosecurity. The potential misuse of genetic information necessitates immediate and stringent ethical and regulatory frameworks.
This article examines the risks associated with genetics research, focusing on the potential for discrimination, psychological distress, and unintended consequences arising from advanced technologies like CRISPR gene editing.
Data Privacy and Discrimination
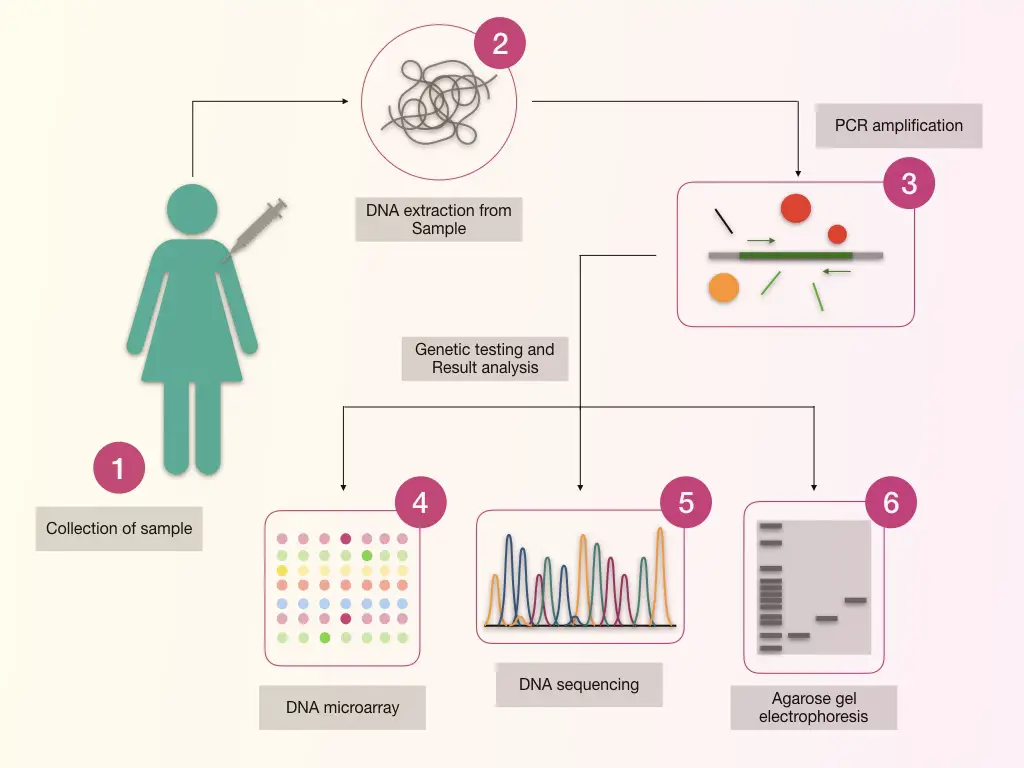
Genetic data is profoundly personal, revealing predispositions to diseases, ancestry, and other sensitive information. The unauthorized access or misuse of this data could lead to discrimination in employment, insurance, and even social interactions. The Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act (GINA) in the U.S. offers some protection, but gaps remain, particularly in long-term care insurance.
According to a 2023 report by the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), concerns about data breaches and re-identification of individuals in genetic databases are escalating. Several high-profile breaches involving healthcare providers and research institutions highlight the vulnerability of genetic information.
Furthermore, the cost of genetic testing is falling rapidly, leading to wider availability and greater risk of inappropriate use. Direct-to-consumer (DTC) genetic testing companies collect vast amounts of data, and their privacy policies often allow for sharing anonymized data with third parties, raising concerns about potential commercial exploitation.
Psychological and Emotional Impacts
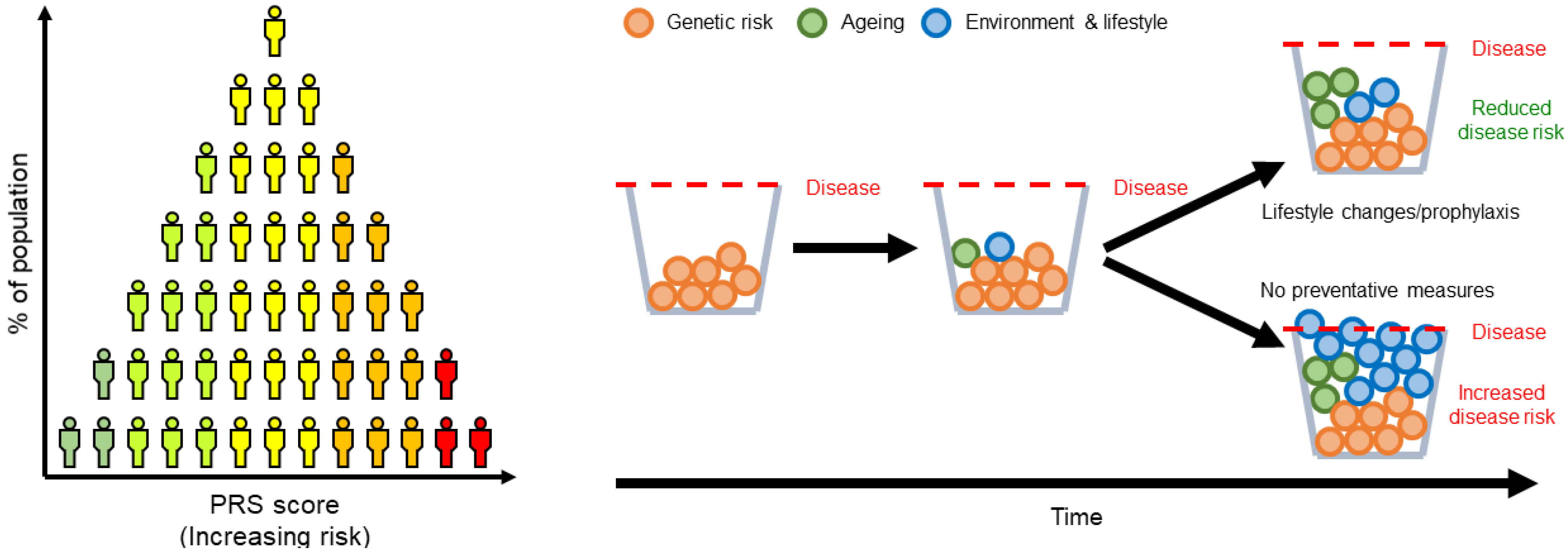
Learning about one's genetic predispositions can have significant psychological and emotional consequences. Discovering a higher risk for a debilitating disease can cause anxiety, depression, and even suicidal ideation. Genetic counseling is essential to help individuals understand and cope with this information.
A study published in the American Journal of Medical Genetics found that individuals with a family history of genetic disorders often experience "genetic anxiety" even before undergoing testing. The anticipation of potentially unfavorable results can lead to chronic stress and impact overall well-being.
Prenatal genetic testing raises ethical dilemmas concerning selective abortion based on perceived disabilities. These decisions are intensely personal and can lead to significant emotional distress for parents, regardless of their choice.
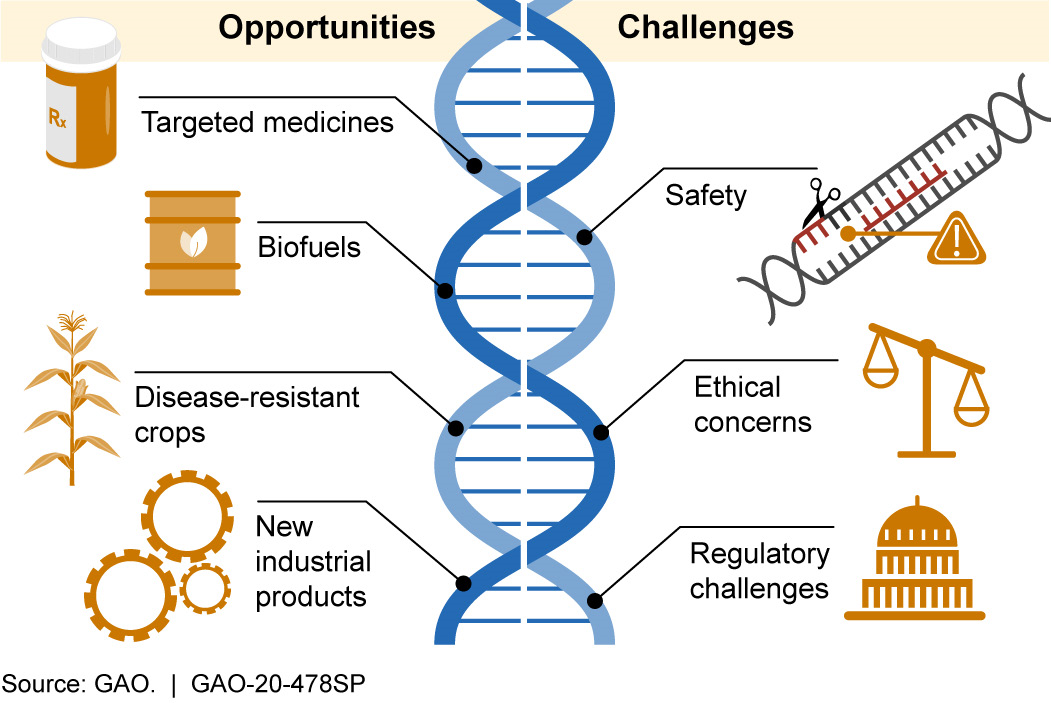
Ethical Concerns with Gene Editing
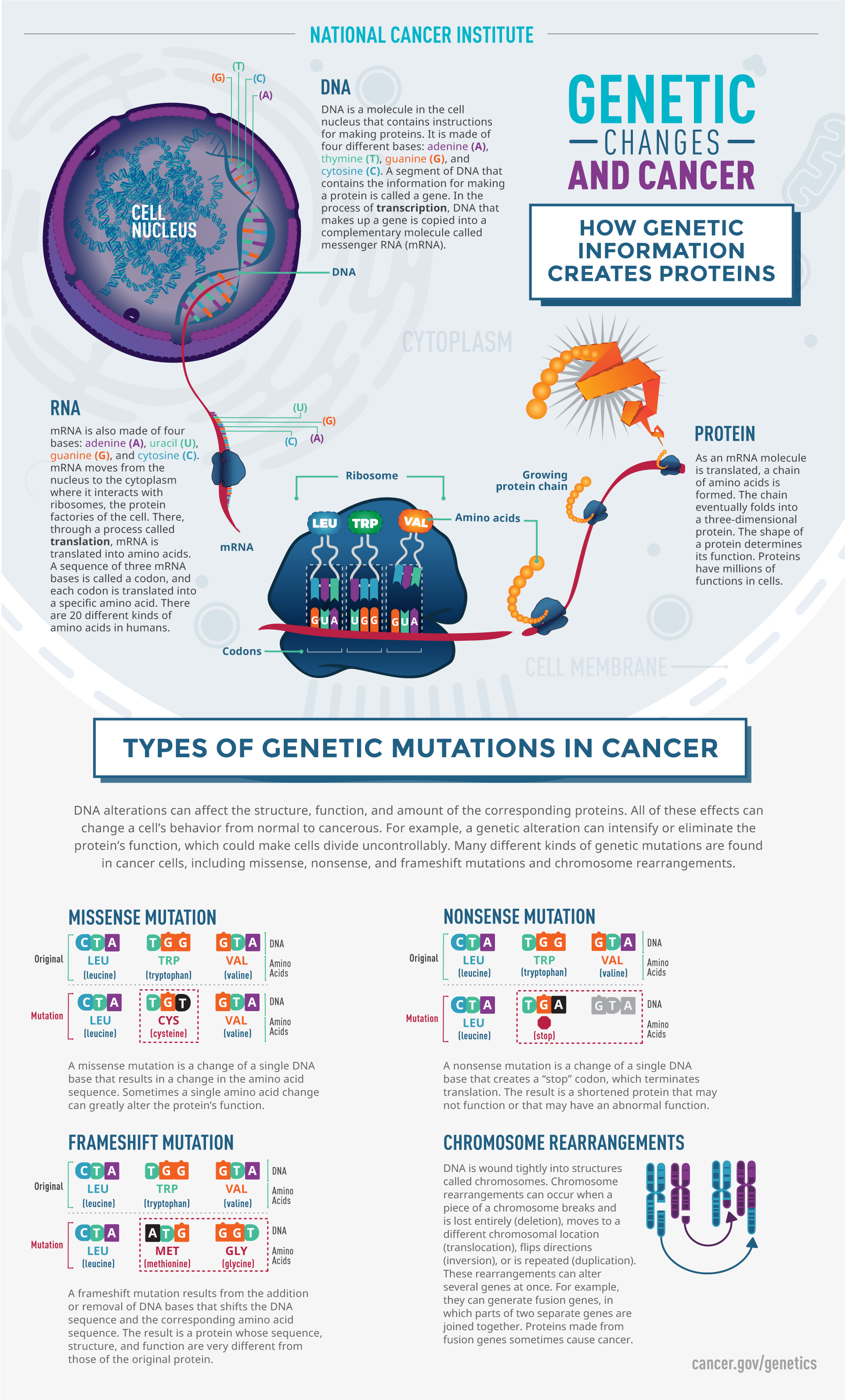
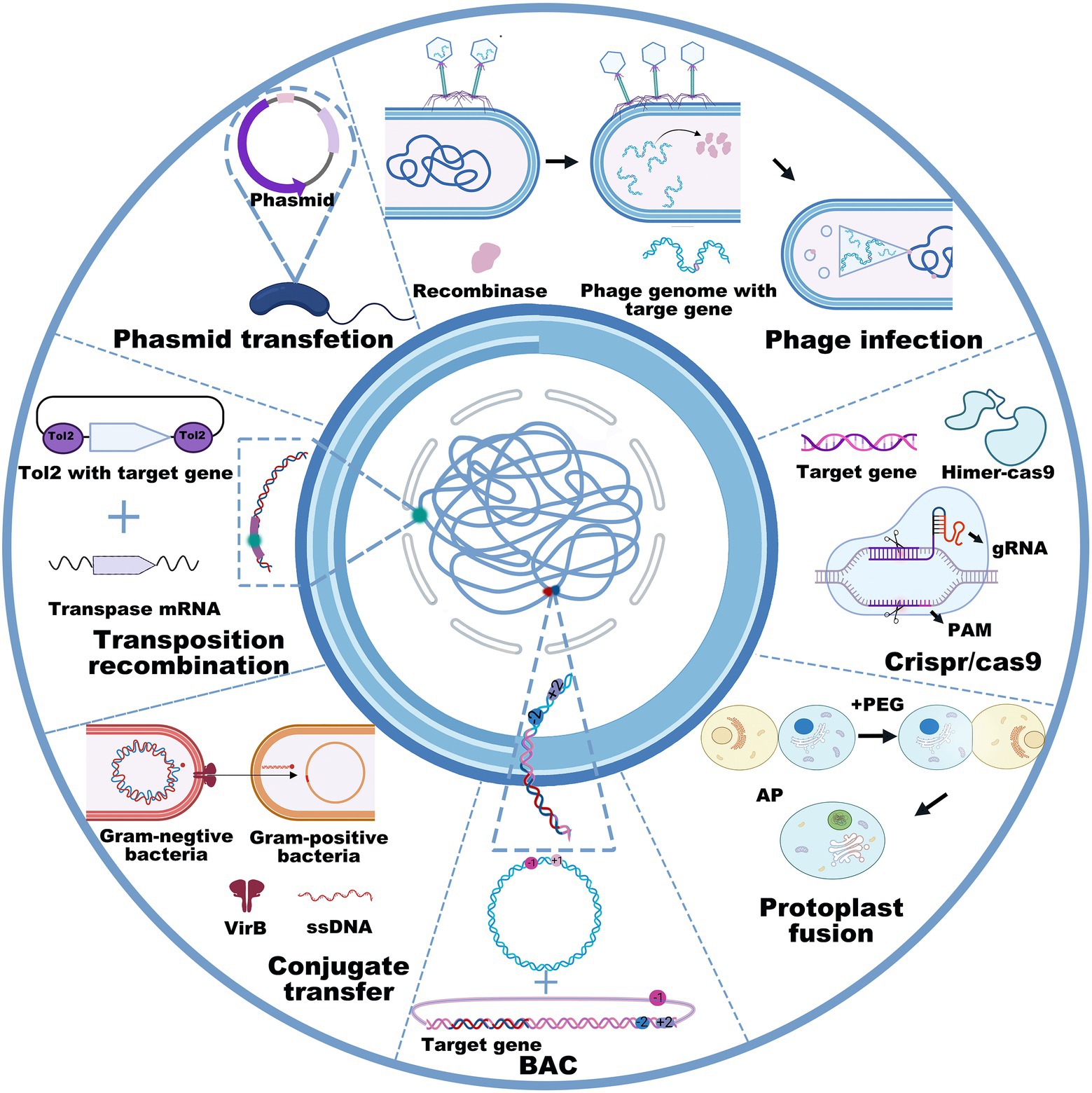
CRISPR-Cas9 technology has revolutionized gene editing, allowing scientists to precisely modify DNA sequences. However, this powerful tool carries significant ethical risks. Off-target effects, where the editing tool unintentionally modifies other genes, are a major concern.
The 2018 birth of gene-edited babies in China, orchestrated by scientist Dr. He Jiankui, sparked global outrage and highlighted the dangers of premature application of gene-editing technologies. The long-term health consequences for these children remain unknown.
Germline editing, which alters the DNA of sperm, eggs, or embryos, raises the specter of inheritable changes that could affect future generations. This practice is widely condemned due to concerns about unintended consequences and the potential for eugenics.
Biosecurity Risks
The knowledge gained from genetics research can be misused to create biological weapons or to enhance existing pathogens. So-called "gain-of-function" research, which aims to increase the virulence or transmissibility of pathogens, is particularly controversial.
Concerns have been raised that dual-use research, with legitimate scientific purposes but also potential for misuse, could fall into the wrong hands. Robust oversight mechanisms are needed to prevent the weaponization of genetic knowledge.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has established a framework for responsible life sciences research, emphasizing the importance of risk assessments and mitigation strategies. However, effective implementation requires international collaboration and strong national regulations.
Addressing the Risks: Next Steps
Mitigating the risks associated with genetics research requires a multi-faceted approach. Stronger data privacy laws are needed to protect genetic information from unauthorized access and misuse. Public awareness campaigns can educate individuals about the potential risks and benefits of genetic testing.
Increased funding for ethical, legal, and social implications (ELSI) research is crucial to understand and address the complex societal challenges posed by genetics. International collaborations are essential to develop harmonized regulatory frameworks for gene editing and biosecurity.
Ongoing dialogue between scientists, ethicists, policymakers, and the public is necessary to ensure that genetics research is conducted responsibly and benefits all of humanity. The urgency of this task cannot be overstated.