Savings Account Interest Rates In India
In India, savings account interest rates are currently navigating a complex landscape influenced by inflation, central bank policies, and competitive pressures among various banking institutions. These rates, which directly impact the returns on individuals' savings, have seen fluctuations in recent months, prompting both concern and strategic adjustments from savers.
Understanding the current state of savings account interest rates is crucial for Indian consumers. It allows them to make informed decisions about where to park their funds, maximizing their returns while balancing liquidity and risk.
Current Scenario
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) plays a vital role in shaping the overall interest rate environment. The repo rate, the rate at which the RBI lends to commercial banks, directly influences the interest rates offered on savings accounts and other deposit products.
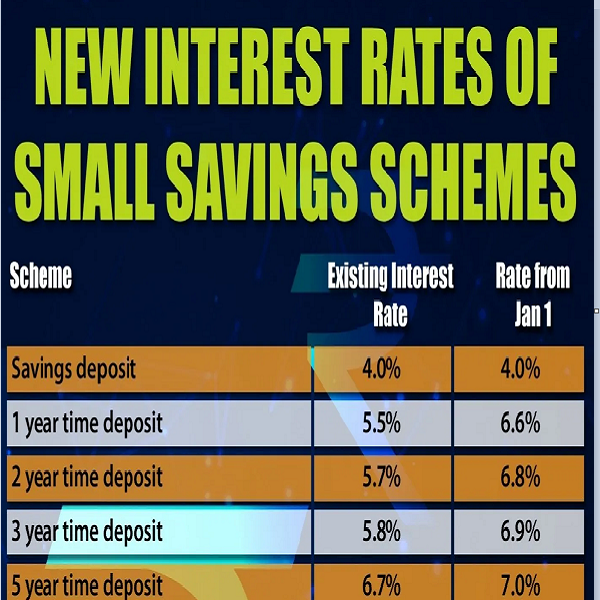
Following periods of aggressive rate hikes to combat inflation, the RBI has adopted a more cautious stance, holding the repo rate steady in recent policy meetings. This has led to a stabilization, albeit at elevated levels, of savings account interest rates across different banks.
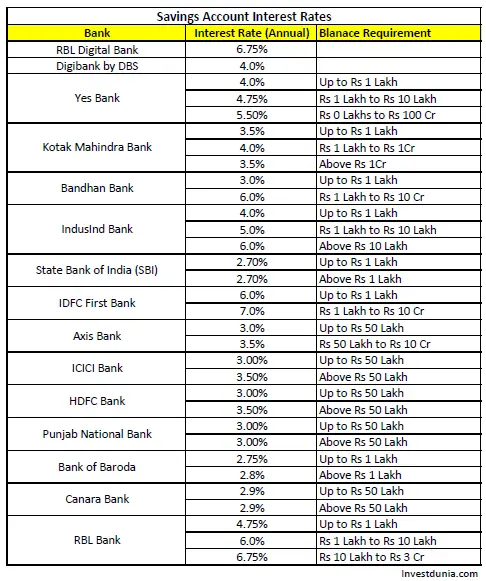
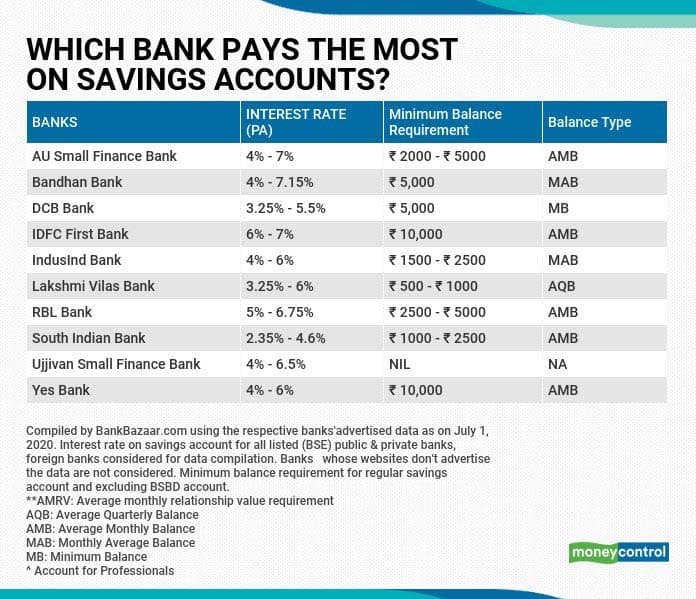
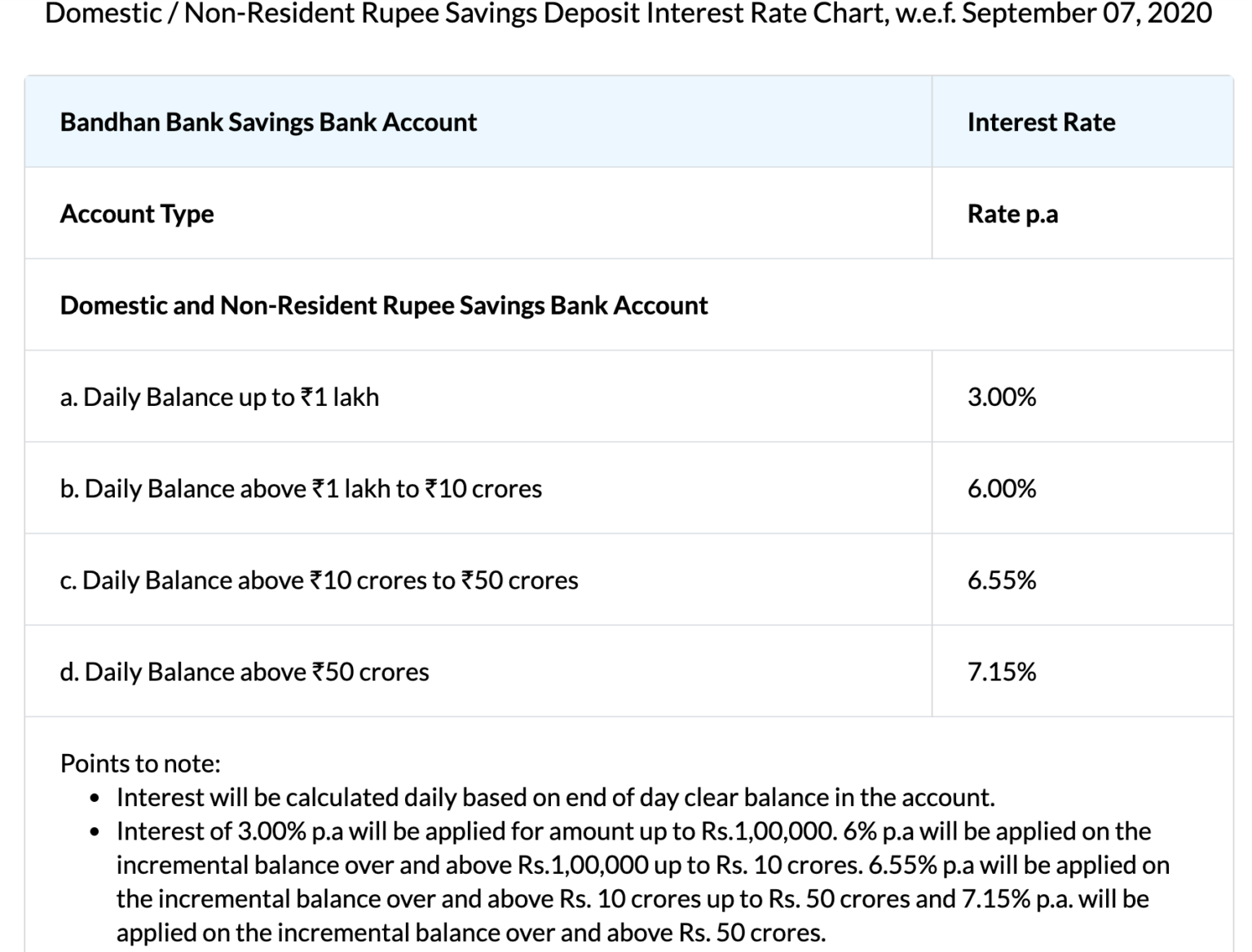
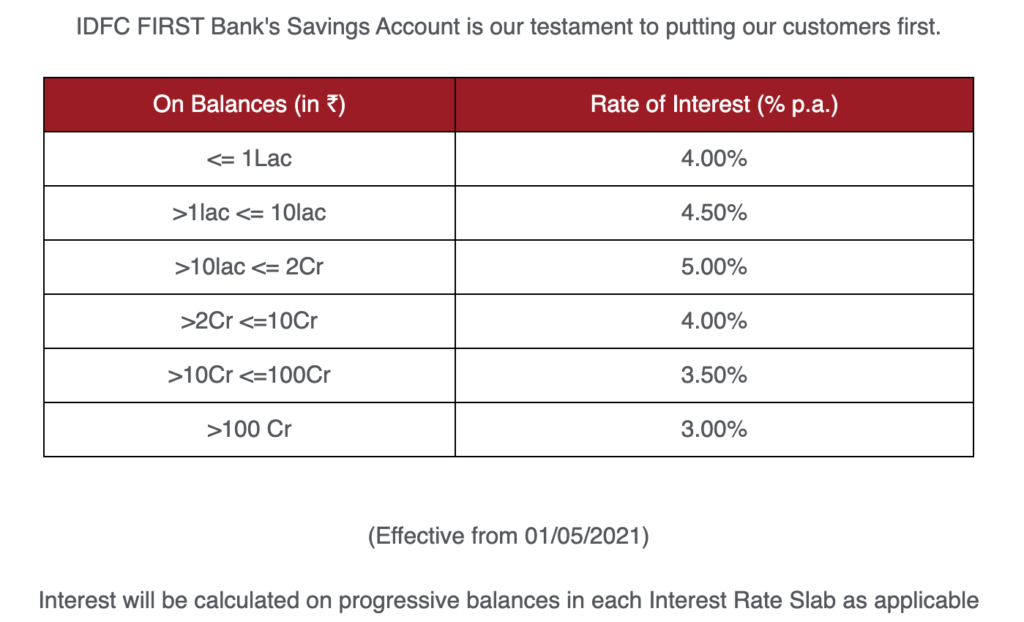
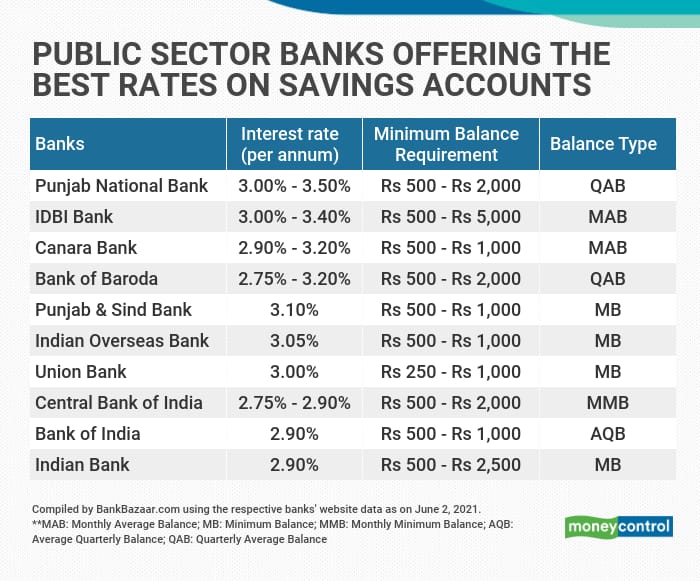
State Bank of India (SBI), for instance, one of the largest public sector banks, offers interest rates on savings accounts that typically range from 2.70% to 3.00% per annum, depending on the account balance. HDFC Bank and ICICI Bank, leading private sector players, offer similar rates, often with slight variations based on specific account types and promotional offers.
Variations Among Banks
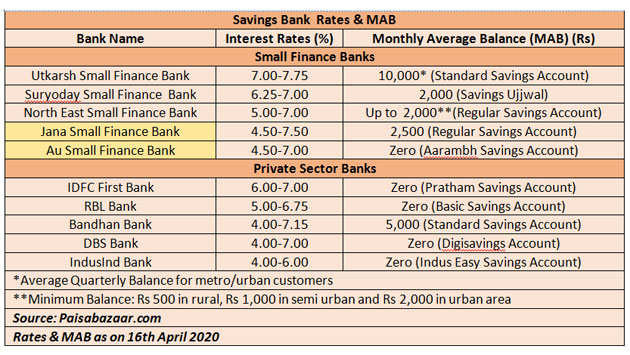
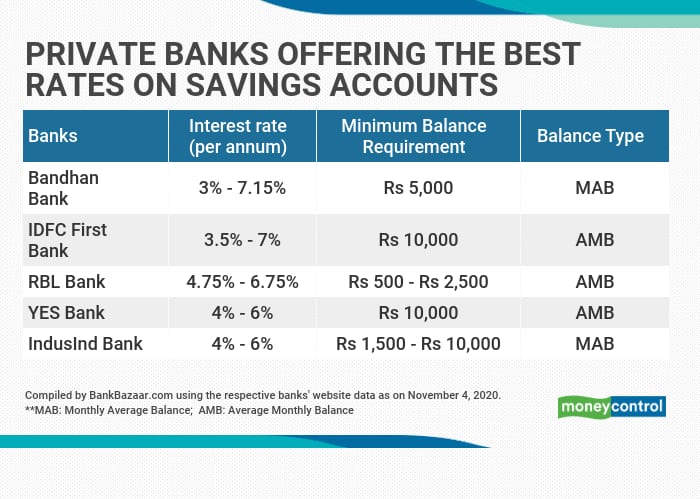
While the broad trend shows a stabilization, significant differences exist. Small finance banks (SFBs) and some cooperative banks often provide higher interest rates on savings accounts, sometimes exceeding 6% per annum.
This is a strategy to attract deposits and build their customer base, particularly in rural and semi-urban areas. However, these higher rates often come with conditions, such as maintaining higher minimum balances or limitations on withdrawals.
It's essential for consumers to compare the rates offered by different banks, considering the associated terms and conditions before making a decision. Look at deposit insurance coverage provided by the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC).
Impact on Savers
The current interest rate scenario presents both challenges and opportunities for Indian savers. High inflation erodes the real value of savings, meaning that returns from savings accounts may not fully compensate for the increase in the cost of living.
This has prompted many individuals to explore alternative investment options, such as mutual funds, stocks, or government bonds, which offer the potential for higher returns but also carry greater risk. Financial advisors suggest diversifying portfolios to balance risk and return.
For risk-averse individuals and those with short-term financial goals, savings accounts remain a safe and convenient option. It provides easy access to funds and a guaranteed return, albeit a modest one.
"In the current environment, it's crucial for savers to be proactive and explore options that align with their risk appetite and financial goals," advises Neha Gupta, a certified financial planner based in Mumbai.
The Road Ahead
The future trajectory of savings account interest rates in India will largely depend on the RBI's monetary policy decisions. Any further adjustments to the repo rate will inevitably impact the rates offered by commercial banks.
Global economic factors, such as fluctuations in crude oil prices and changes in international interest rates, could also influence the RBI's decisions. Monitoring these factors will be essential for predicting future trends in savings account interest rates.
Banks are also increasingly focusing on digital channels and innovative financial products. Fintech companies are emerging that could change the competitive landscape and potentially drive up interest rates as they compete for customers.
In conclusion, the savings account interest rate scenario in India is dynamic, influenced by a combination of macroeconomic factors, regulatory policies, and competitive pressures. While the current rates may not be exceptionally high, savings accounts remain a crucial component of a well-rounded financial strategy for many Indians.