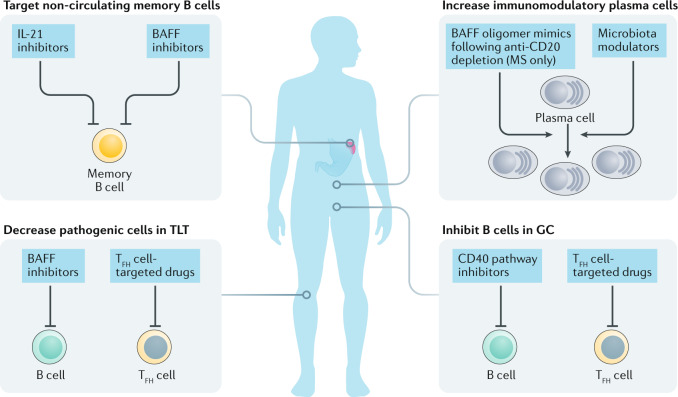
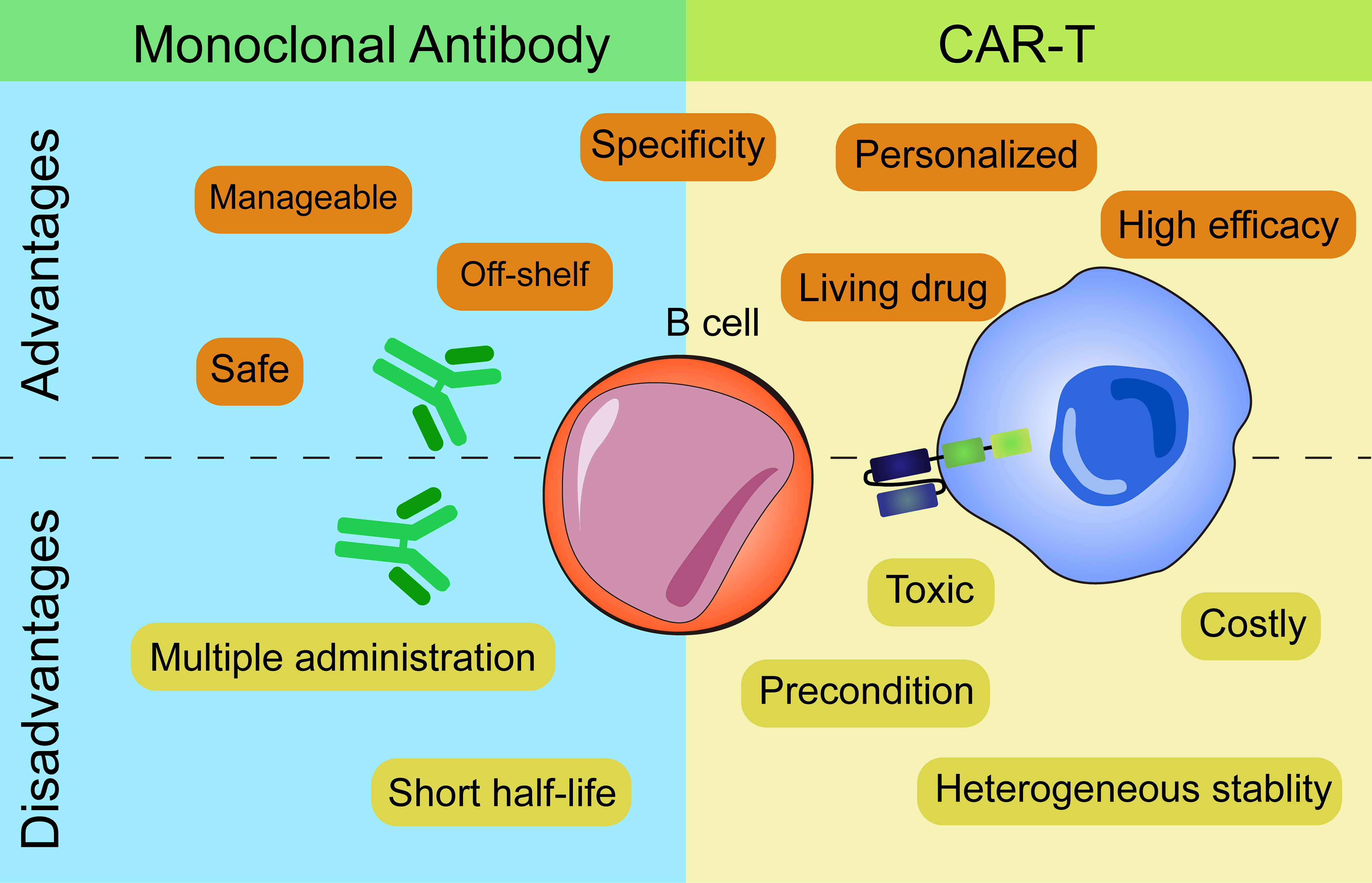
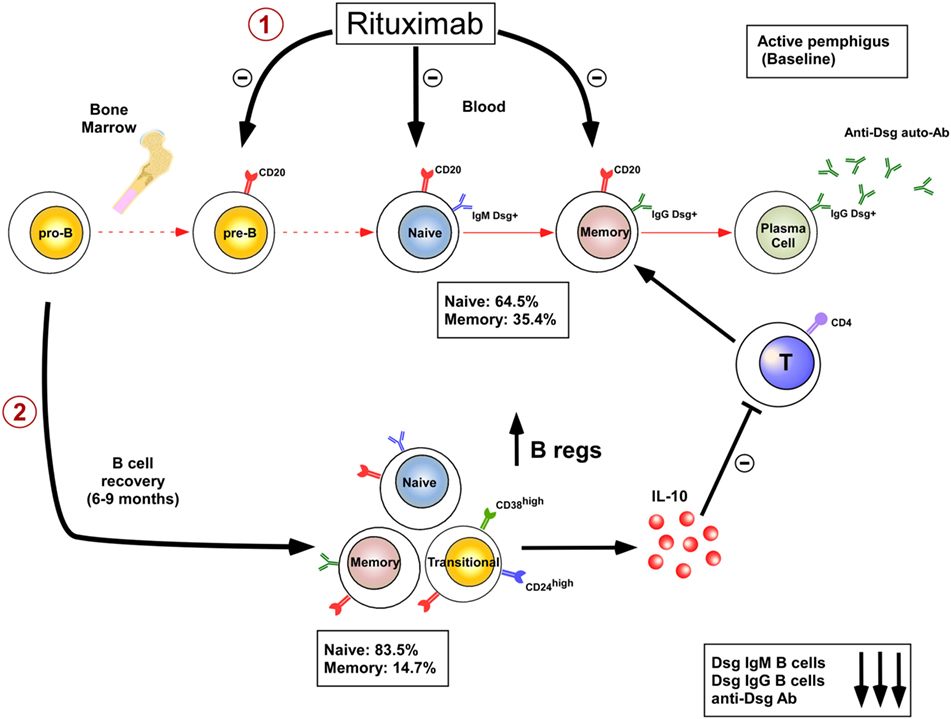
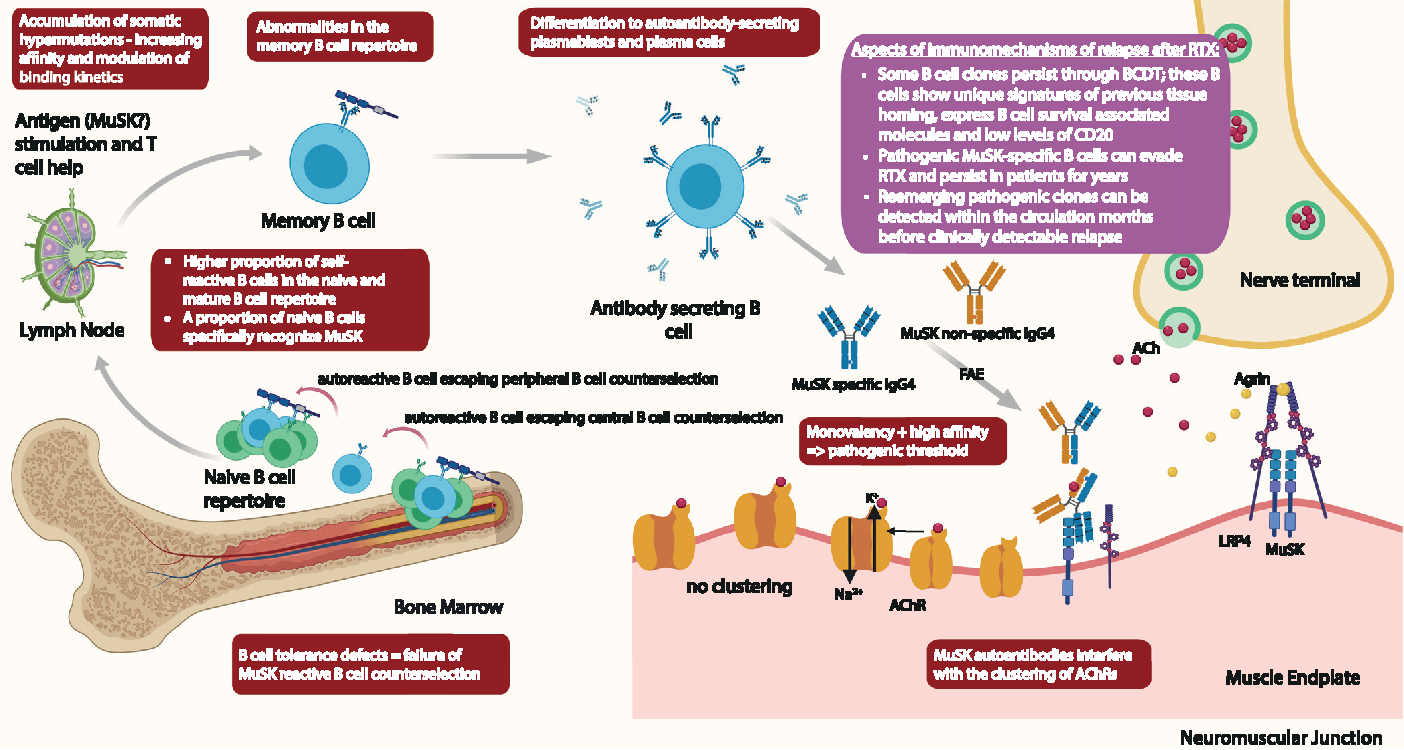
Side Effects Of B Cell Depletion
B cell depletion therapies, a class of drugs increasingly used to treat autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis, have proven remarkably effective for many patients. However, alongside their benefits, these treatments carry a spectrum of potential side effects that are drawing increased scrutiny from researchers and clinicians alike.
This article explores the known side effects associated with B cell depletion, examining their frequency, severity, and the ongoing research aimed at mitigating these risks and improving patient outcomes. Understanding these potential complications is crucial for both healthcare professionals and patients considering or undergoing these therapies.
Understanding B Cell Depletion
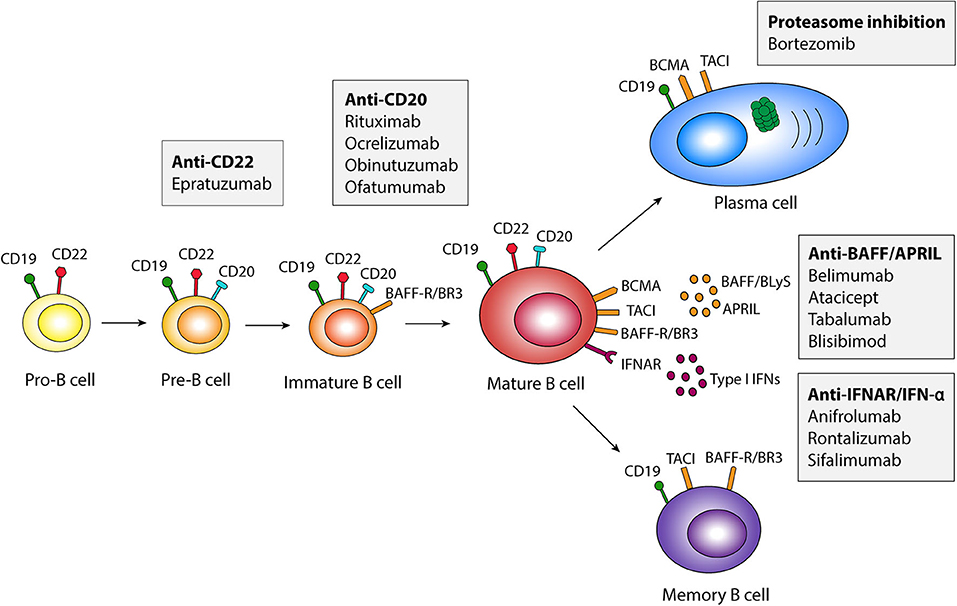
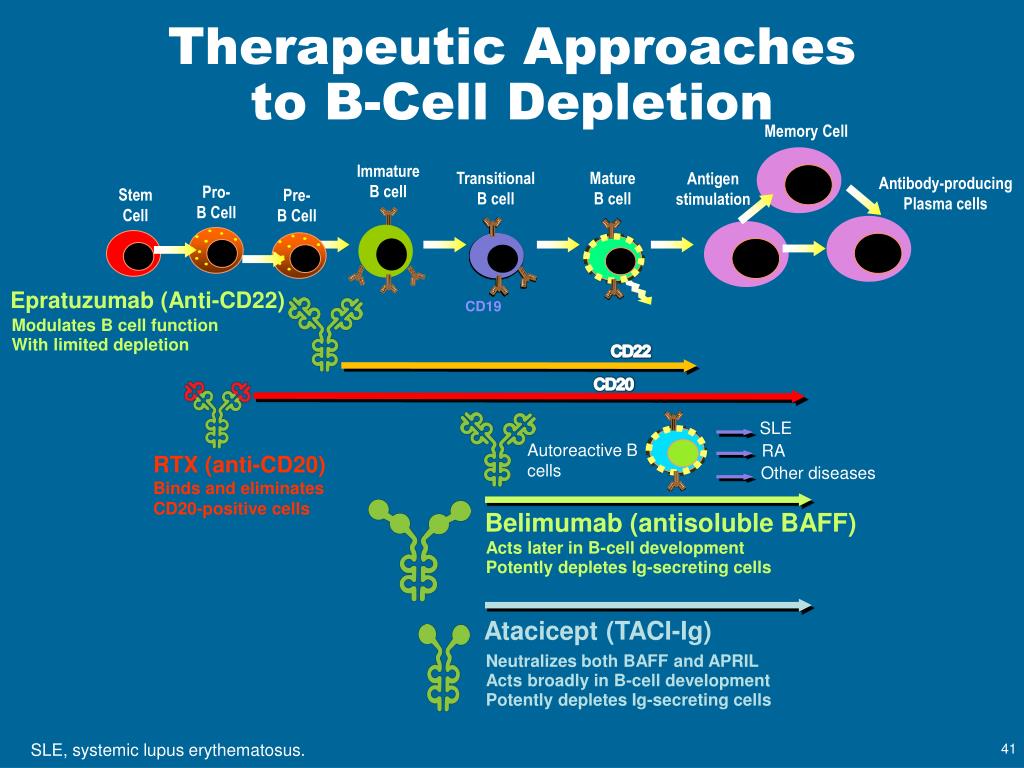
B cells are a type of white blood cell responsible for producing antibodies. In autoimmune diseases, these antibodies can mistakenly attack the body's own tissues, leading to inflammation and damage.
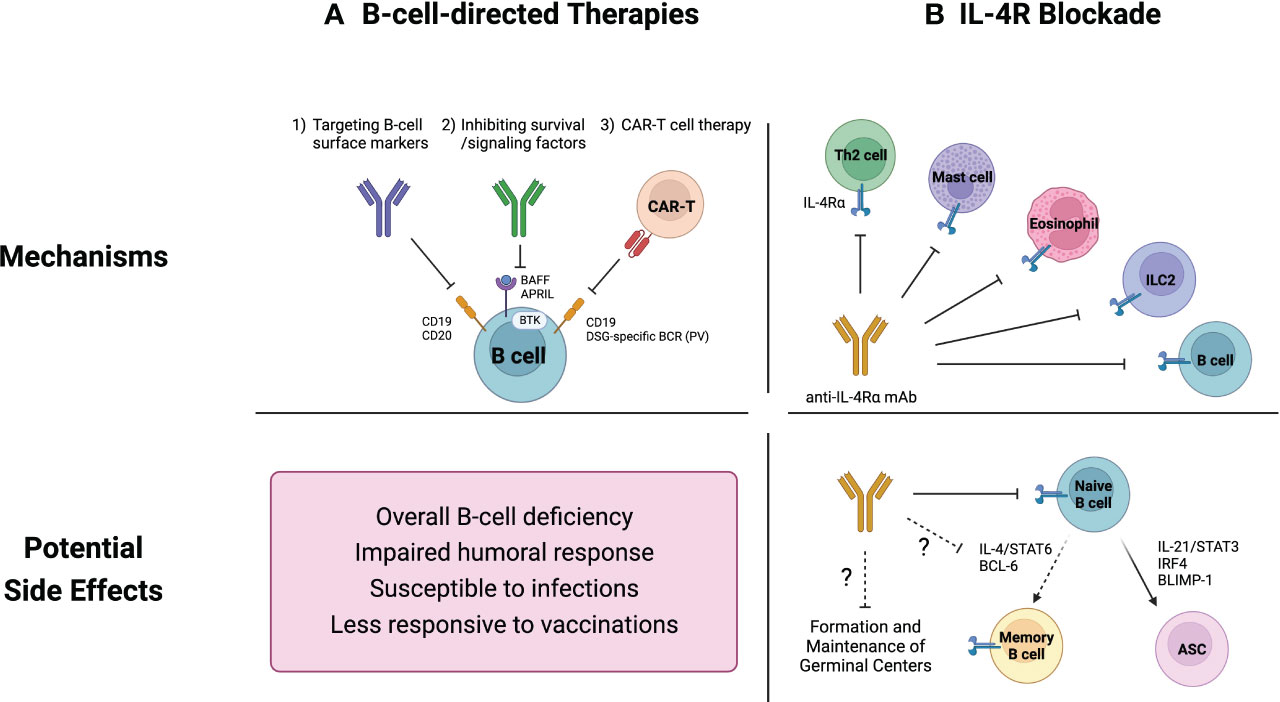
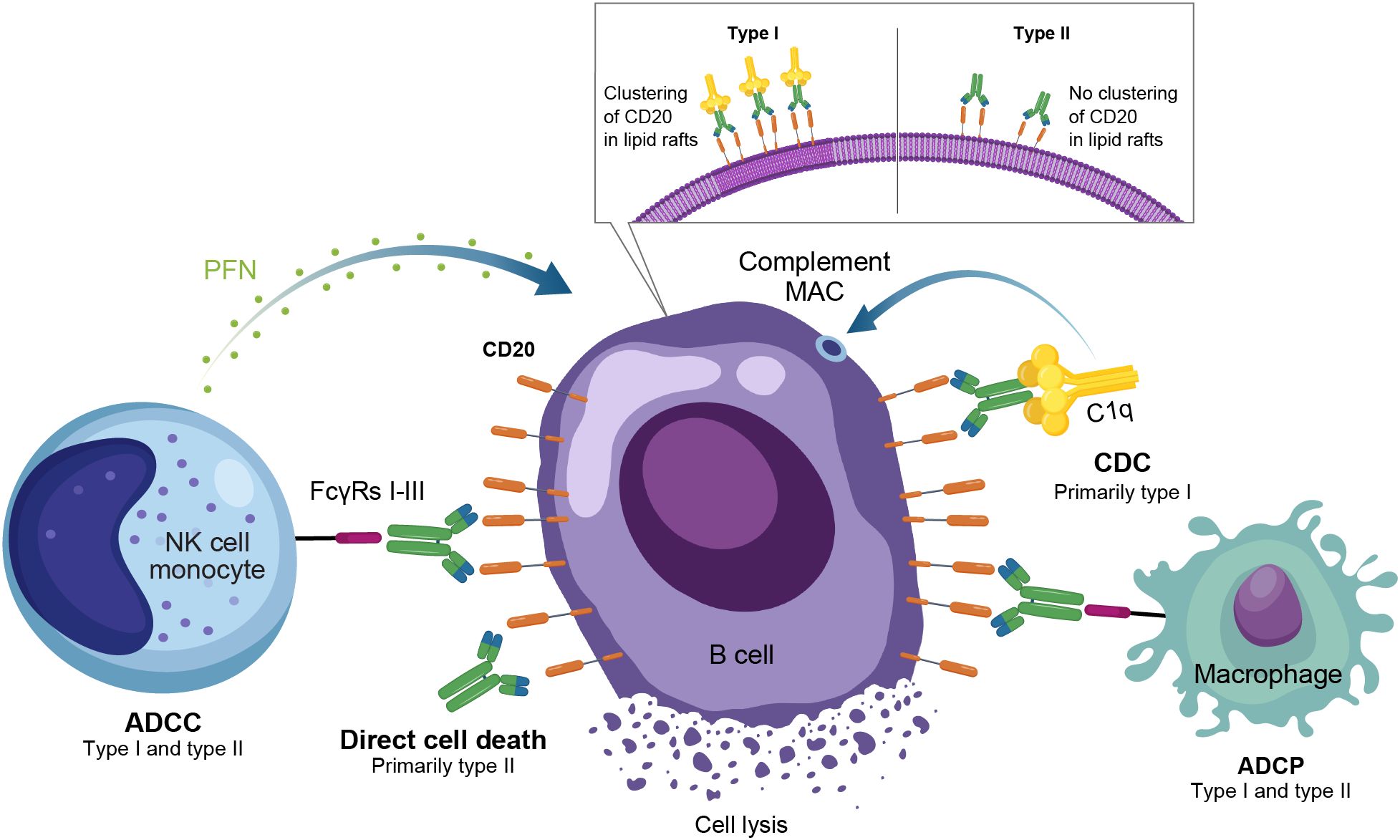
B cell depletion therapies work by targeting and eliminating B cells, thereby reducing the production of these harmful antibodies. Rituximab, ocrelizumab, and ofatumumab are among the most commonly used drugs in this category.
Common Side Effects
Infusion reactions are among the most common side effects associated with B cell depletion therapies. These reactions can occur during or shortly after the infusion of the drug and may manifest as fever, chills, nausea, itching, rash, or shortness of breath.
Typically, these reactions are mild to moderate and can be managed with medications like antihistamines or corticosteroids. However, in rare cases, they can be severe and require immediate medical intervention.
An increased risk of infections is another well-documented side effect. B cells play a crucial role in the immune system's ability to fight off infections.
Depleting these cells can weaken the body's defenses, making patients more susceptible to bacterial, viral, and fungal infections. Respiratory infections, such as pneumonia and bronchitis, are particularly common.
Less Common but Serious Risks
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) is a rare but potentially fatal brain infection that has been linked to B cell depletion therapies, particularly rituximab. PML is caused by the John Cunningham (JC) virus, which is common but usually harmless in individuals with healthy immune systems.
However, in patients with weakened immune systems, the JC virus can reactivate and attack the brain, leading to severe neurological damage. Symptoms of PML can include weakness, vision problems, difficulty speaking, and cognitive decline.
Reports of hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation have also emerged in patients undergoing B cell depletion therapy. HBV is a liver infection that can cause serious liver damage.
Patients who have a history of HBV infection, even if it is inactive, should be screened for HBV before starting B cell depletion therapy. If HBV reactivation is detected, antiviral treatment should be initiated.
In rare cases, B cell depletion therapies have been associated with severe skin reactions, such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN). These are life-threatening conditions that cause blistering and peeling of the skin.
Ongoing Research and Mitigation Strategies
Researchers are actively investigating ways to minimize the side effects associated with B cell depletion therapies. One area of focus is identifying biomarkers that can predict which patients are at higher risk of developing specific complications.
For example, studies are exploring whether certain genetic markers or pre-existing immune conditions can increase the risk of PML or HBV reactivation. Understanding these risk factors could allow clinicians to tailor treatment strategies and monitor patients more closely.
Another research area involves optimizing the dosing and duration of B cell depletion therapy. Some studies suggest that lower doses or shorter treatment courses may be effective in controlling autoimmune diseases while reducing the risk of side effects.
"Finding the right balance between efficacy and safety is a key goal,"explains Dr. Emily Carter, a rheumatologist at the Mayo Clinic.
Prophylactic measures, such as vaccination and antiviral medications, are also being used to mitigate the risk of infections. Patients undergoing B cell depletion therapy are typically advised to receive vaccinations against influenza and pneumococcal pneumonia.
Furthermore, patients at high risk of HBV reactivation may be prescribed antiviral medications before or during treatment. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) provides specific guidelines on screening and managing HBV in patients receiving immunosuppressive therapies.
The Patient Perspective
For patients with debilitating autoimmune diseases, B cell depletion therapies can offer significant relief and improve their quality of life. However, the potential side effects can be a source of anxiety and uncertainty.
Sarah Miller, a patient with rheumatoid arthritis who has been treated with rituximab, shares, "The medication has been life-changing, but I worry about getting sick. I make sure to wash my hands frequently and avoid crowded places."
Open communication between patients and their healthcare providers is essential. Patients should be fully informed about the potential risks and benefits of B cell depletion therapy, and they should feel comfortable discussing any concerns or symptoms they experience.
Conclusion
B cell depletion therapies remain a valuable tool in the treatment of autoimmune diseases. While these therapies are associated with a range of potential side effects, ongoing research is helping to identify and mitigate these risks.
Careful patient selection, proactive monitoring, and appropriate prophylactic measures are essential to ensure that the benefits of B cell depletion therapy outweigh the potential harms. As our understanding of the immune system and autoimmune diseases continues to evolve, the use of these therapies will likely become even more refined and personalized.