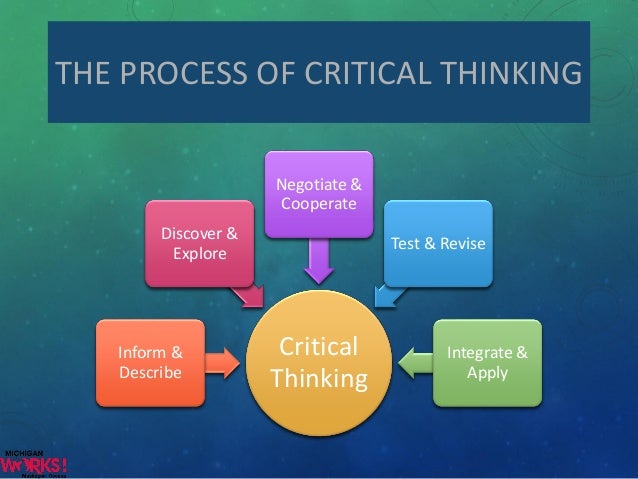
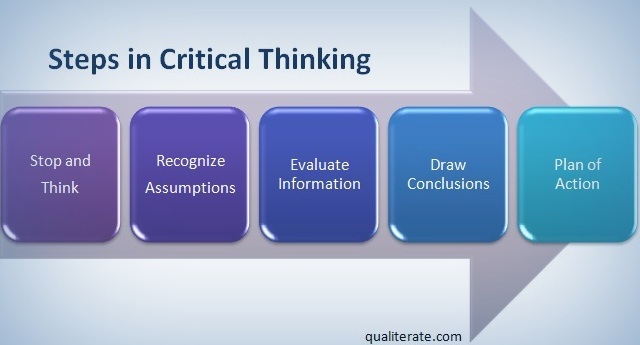
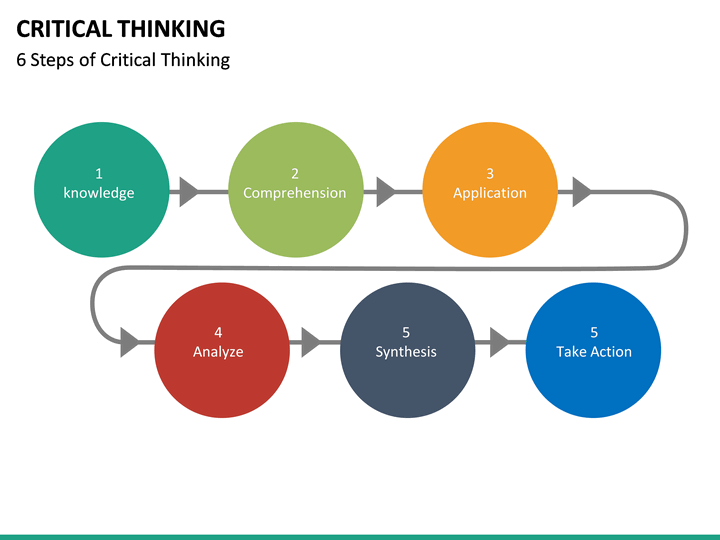
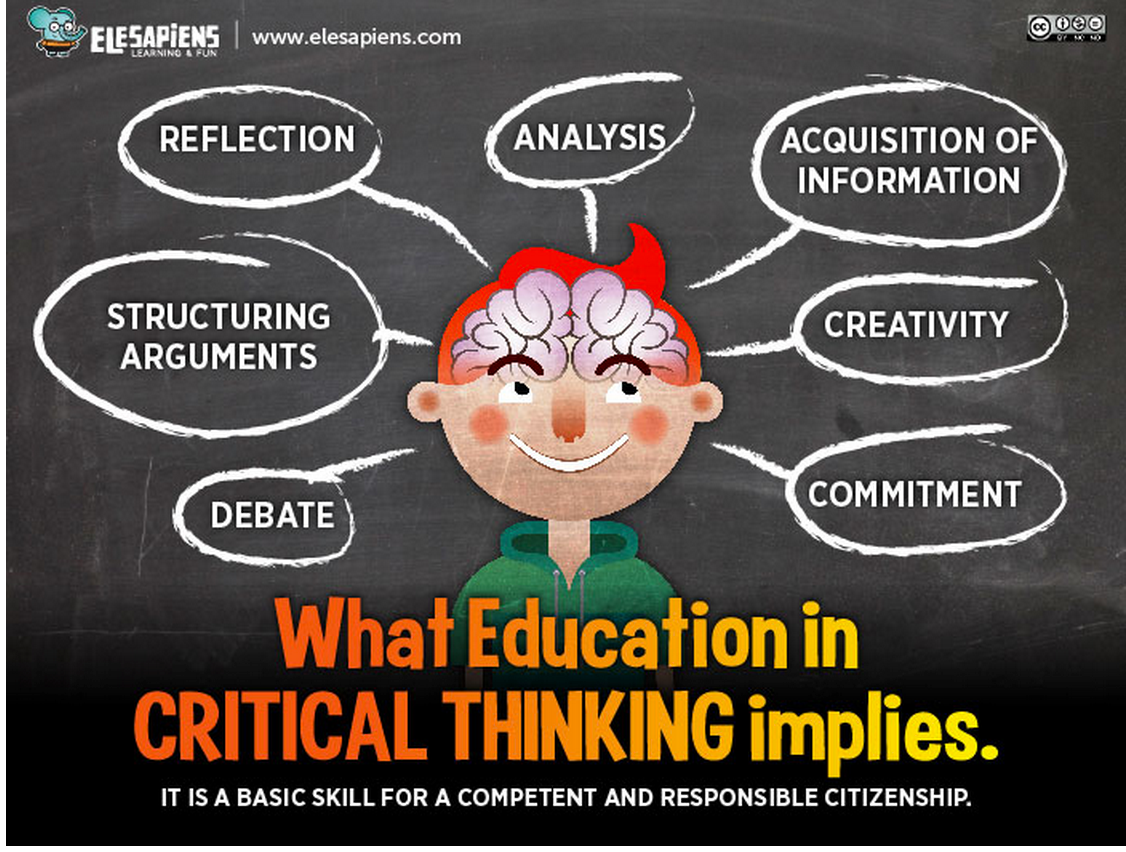
Steps In Critical Thinking Process
Critical thinking failures are costing businesses and individuals dearly. A structured approach is essential to navigate the complexities of modern decision-making.
This article outlines the vital steps in the critical thinking process, enabling readers to enhance their analytical skills and avoid costly mistakes.
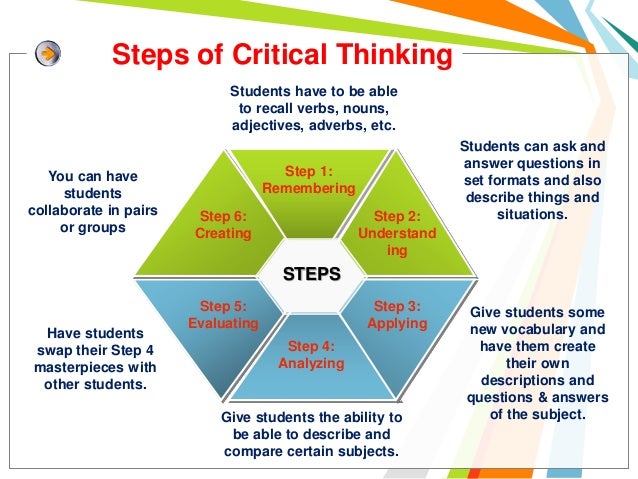
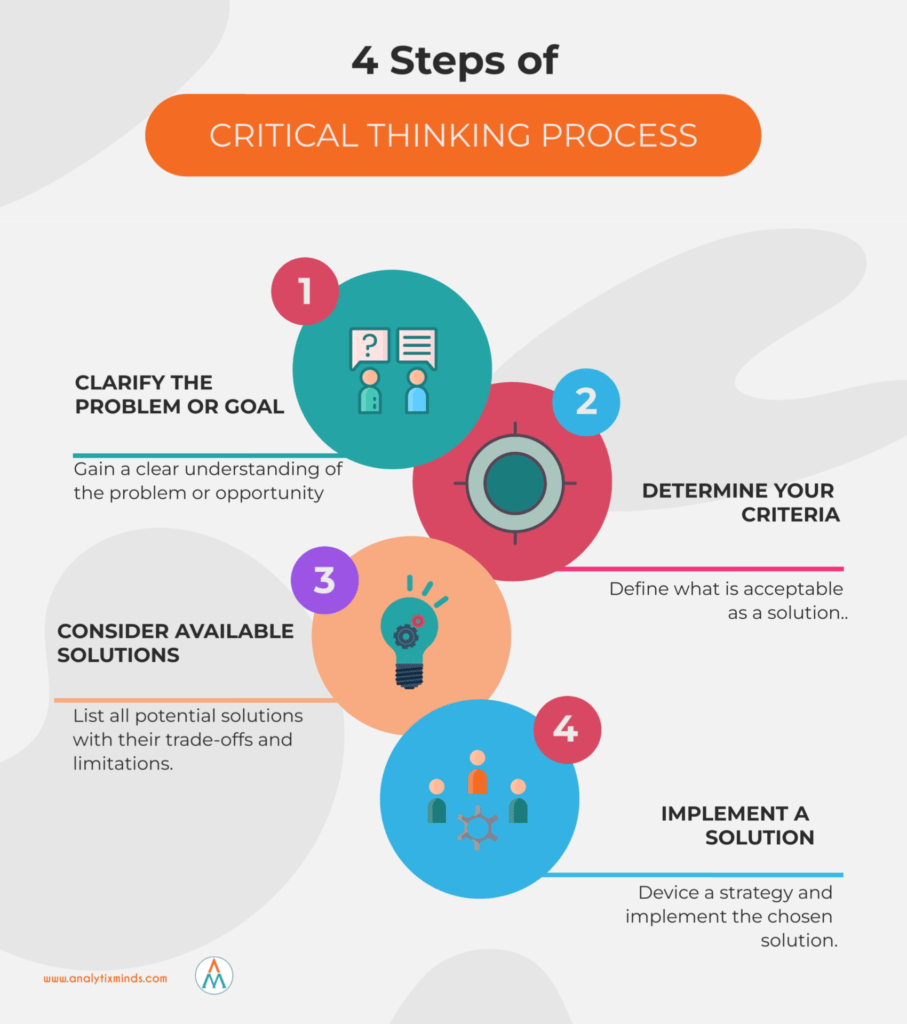
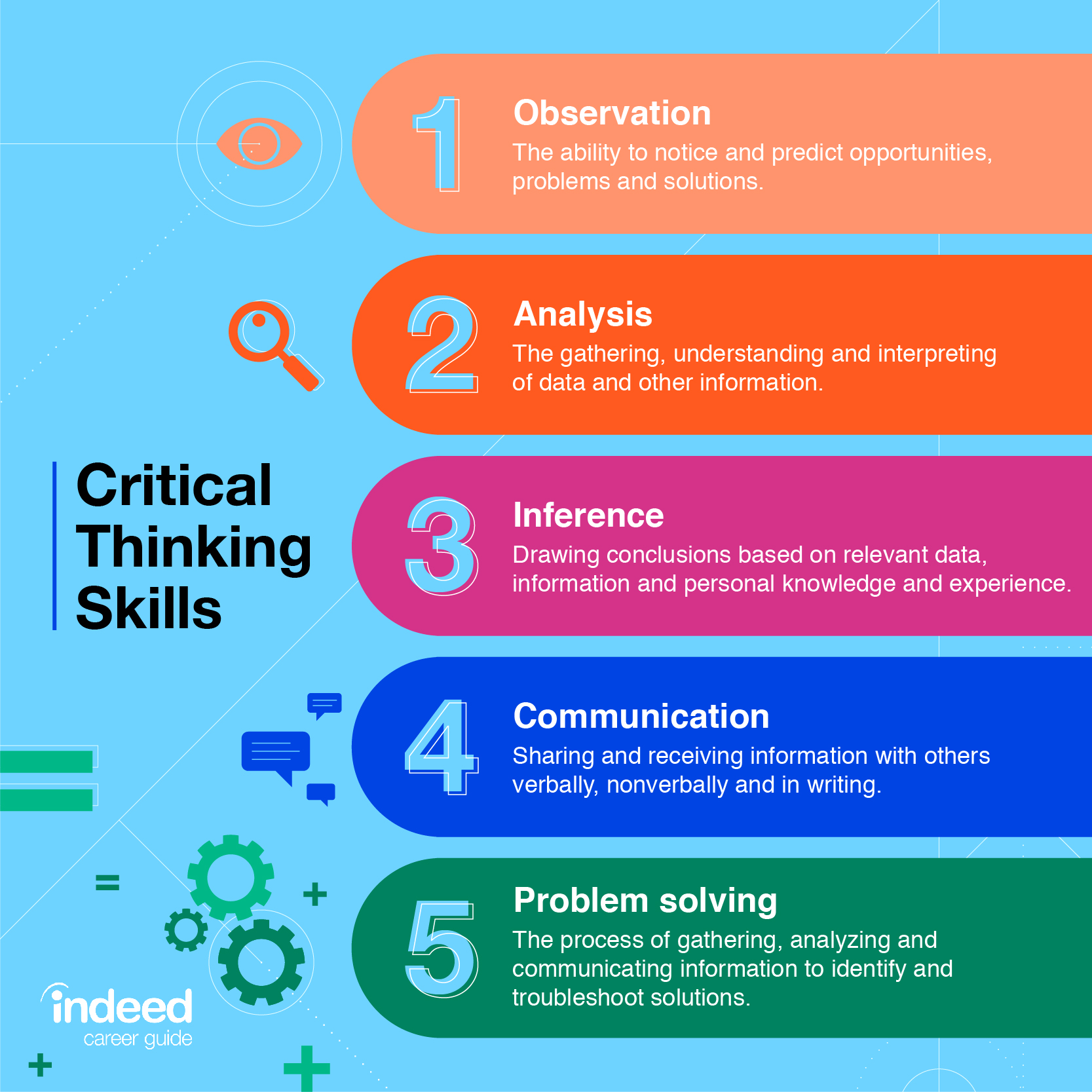
Step 1: Identification of the Problem or Question
First, you must pinpoint the exact issue. What is the core problem that needs solving?
Clearly defining the problem prevents wasted effort on addressing the wrong concerns. A precise problem statement is the foundation.
Step 2: Gathering Information and Research
Collect all relevant data pertaining to the problem. This involves research, analysis, and fact-finding.
Use credible sources. Don't rely on assumptions or hearsay.
Consider diverse viewpoints to gain a comprehensive understanding.
Step 3: Analysis of Data
Examine the gathered information for patterns and biases. Analyze the evidence critically.
Look for inconsistencies. Identify potential errors in reasoning.
Separate fact from opinion to avoid flawed conclusions.
Step 4: Developing Potential Solutions
Brainstorm and create a range of potential solutions. Think outside the box.
Don't settle for the first idea that comes to mind. Explore multiple options.
Consider both conventional and unconventional approaches.
Step 5: Evaluating Solutions
Assess each potential solution based on established criteria. What are the pros and cons?
Consider the potential consequences of each solution. Use tools like cost-benefit analysis.
Eliminate impractical or high-risk options to refine the selection.
Step 6: Choosing the Best Solution
Based on the evaluation, select the most suitable solution. Justify your decision.
Consider factors like feasibility and impact when making your choice. This requires sound judgement.
Be prepared to defend your rationale with evidence.
Step 7: Implementation
Put the chosen solution into action. Develop a clear plan of action.
Allocate resources effectively. Communicate the plan to stakeholders.
Monitor progress and make adjustments as needed.
Step 8: Evaluation of Results
After implementation, evaluate the outcome. Did the solution solve the problem?
Measure the impact and effectiveness of the solution. Collect relevant data.
Identify lessons learned for future problem-solving.
Real-World Application: Case Study
Tesla's recent supply chain issues demonstrate the need for critical thinking. Faced with chip shortages, they re-engineered their software to accommodate alternative chips.
This proactive approach mitigated production delays and kept them competitive. They adapted quickly.
This serves as an example of effective critical thinking in action.
Pitfalls to Avoid
Common pitfalls include confirmation bias and groupthink. Be aware of these risks.
Confirmation bias leads to seeking only information that supports pre-existing beliefs. Challenge your assumptions.
Groupthink stifles dissenting opinions within a group. Encourage diverse viewpoints.
Resources for Further Learning
Numerous resources are available to enhance critical thinking skills. Online courses and workshops are valuable.
Books on logic, reasoning, and decision-making provide insights. Practice applying the principles regularly.
Seek mentorship from experienced problem-solvers. Learn from their expertise.
Next Steps
Individuals and organizations must prioritize critical thinking development. Implement these steps in your decision-making processes.
Ongoing training and assessment are crucial for continuous improvement. Foster a culture of critical thinking.
Mastering these steps can lead to better outcomes and reduced risks.