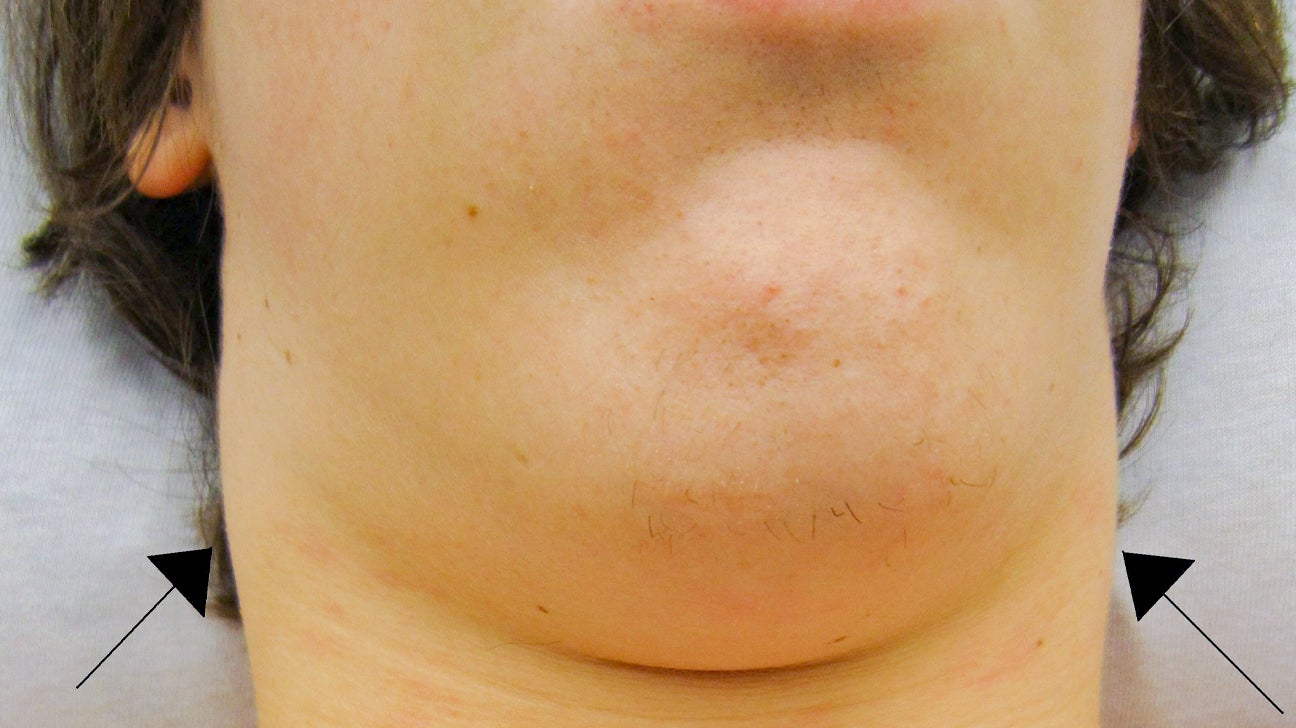
Swollen Lymph Nodes 12 Months After Covid Vaccine

A year after the initial rollout of COVID-19 vaccines, reports of persistent side effects, while rare, are prompting ongoing investigation and raising questions about long-term immunological responses. Specifically, some individuals are experiencing swollen lymph nodes, known medically as lymphadenopathy, which have persisted for months, even a year, after vaccination. This phenomenon, though not widely publicized, is triggering a deeper look into the potential delayed or prolonged reactions to the vaccines.
This article delves into the documented cases of persistent lymph node swelling following COVID-19 vaccination, exploring the available data, expert opinions, and ongoing research efforts to understand the underlying mechanisms and implications. We aim to provide a balanced perspective, acknowledging the overwhelming safety and efficacy of COVID-19 vaccines while addressing the legitimate concerns of individuals experiencing prolonged side effects. Furthermore, this exploration is critical for informing future vaccine development and refining post-vaccination monitoring protocols.
Lymphadenopathy: A Known, Typically Transient, Side Effect
Swollen lymph nodes are a recognized side effect of many vaccines, including those against COVID-19. This reaction typically signifies the body's immune system responding to the vaccine, a sign that the immune system is learning to recognize and fight the virus. In most cases, the swelling subsides within a few weeks.
Data from the initial vaccine trials and post-authorization monitoring showed that lymphadenopathy was more commonly reported after mRNA vaccines (Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna) than adenovirus vector vaccines (Johnson & Johnson/Janssen and AstraZeneca). These reactions were typically mild and resolved quickly.
The Emergence of Persistent Cases
However, a subset of individuals has reported experiencing lymph node swelling that persists for significantly longer than the expected few weeks. These cases, while relatively infrequent compared to the millions vaccinated, are drawing scrutiny from researchers and clinicians. Reports suggest that the swelling can last for months, even up to a year in some instances.
These longer-lasting cases are more often reported in the armpit on the same side as the vaccination site, suggesting a direct relationship to the vaccine administration. Some individuals have described experiencing pain and discomfort associated with the swollen lymph nodes.
Investigating the Cause: Possible Mechanisms
The precise mechanisms behind this prolonged lymphadenopathy are still under investigation. Several hypotheses are being explored to explain these persistent reactions. The prevailing theories revolve around the nature of the immune response triggered by the vaccines.
One possibility is that the mRNA or viral vector particles are remaining in the lymph nodes for an extended period, continuously stimulating an immune response. This prolonged stimulation could lead to chronic inflammation and persistent swelling. This is supported by some research suggesting that vaccine mRNA can be detected in lymph nodes for several weeks after vaccination.
Another potential explanation involves an overzealous immune response in susceptible individuals. In some cases, the immune system may mount a disproportionately strong reaction to the vaccine, leading to prolonged inflammation. This theory requires further research to identify potential genetic or immunological factors that could predispose individuals to this reaction.
Expert Opinions and Ongoing Research
The medical community acknowledges the existence of these persistent cases of lymphadenopathy and is actively working to understand the phenomenon. Organizations like the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the World Health Organization (WHO) are monitoring vaccine safety data and conducting further investigations.
Many physicians and researchers emphasize the importance of distinguishing between vaccine-related lymphadenopathy and other potential causes of swollen lymph nodes, such as infections or malignancies. A thorough medical evaluation is crucial to rule out other underlying conditions.
Several research groups are conducting studies to characterize the immune responses in individuals with persistent lymphadenopathy following COVID-19 vaccination. These studies aim to identify biomarkers that can predict the likelihood of developing this side effect and to develop strategies for managing it.
Impact on Vaccine Confidence and Public Health
While the vast majority of individuals experience only mild and transient side effects from COVID-19 vaccines, reports of persistent reactions, however rare, can impact vaccine confidence. Transparency and open communication about potential side effects are crucial to maintaining public trust.
It is important to reiterate that the benefits of COVID-19 vaccination far outweigh the risks. The vaccines have been proven highly effective in preventing severe illness, hospitalization, and death from COVID-19. The risk of experiencing a severe adverse reaction is exceedingly low.
Addressing concerns about persistent lymphadenopathy requires a multi-faceted approach, including robust research, clear communication, and individualized medical care. By providing accurate information and addressing patient concerns, we can ensure that individuals make informed decisions about vaccination.
A Path Forward: Monitoring, Research, and Communication
Moving forward, enhanced monitoring of vaccine recipients is essential. This includes tracking the incidence and duration of lymphadenopathy and other potential side effects. This data can inform future vaccine development and help identify individuals who may be at higher risk of experiencing prolonged reactions.
Continued research is also crucial. Understanding the underlying mechanisms of persistent lymphadenopathy will allow for the development of targeted interventions. This may include strategies to modulate the immune response or to reduce inflammation in the lymph nodes.
Finally, open and transparent communication is paramount. Providing accurate information about the benefits and risks of COVID-19 vaccines is essential for maintaining public trust. Healthcare providers should be equipped to address patient concerns and provide individualized care for those experiencing prolonged side effects.
In conclusion, while reports of swollen lymph nodes persisting for an extended period after COVID-19 vaccination are a concern, they remain a rare occurrence within the context of a globally administered vaccine. Ongoing research, enhanced monitoring, and transparent communication are critical to understanding these cases and ensuring continued confidence in vaccination efforts. The overall benefit of widespread vaccination in combating the COVID-19 pandemic continues to be overwhelmingly positive.