The Market Portfolio Has Which Of These Characteristics

In the complex world of finance, understanding the market portfolio is crucial for investors seeking to optimize their returns and manage risk effectively. The market portfolio, a theoretical concept representing the collection of all assets in the world, weighted by their market capitalization, possesses several defining characteristics. These attributes dictate its role as a benchmark for investment performance and a foundation for modern portfolio theory.
At its core, the market portfolio embodies diversification and efficiency. It raises fundamental questions about portfolio construction, risk assessment, and the nature of investment returns. This article delves into the essential characteristics of the market portfolio, exploring its significance and implications for investors and the broader financial landscape.
What Defines a Market Portfolio?
The market portfolio, in its purest form, includes every conceivable asset available for investment. This spans stocks, bonds, real estate, commodities, and even esoteric assets like art or collectibles. Each asset's weight within the portfolio is determined by its market capitalization: the larger the company or asset, the greater its representation.
Its real-world applications provide a crucial benchmark for evaluating the performance of individual investment portfolios and investment managers. By comparing a portfolio's returns against those of the market portfolio, investors can gauge its relative success or failure.
Key Characteristics
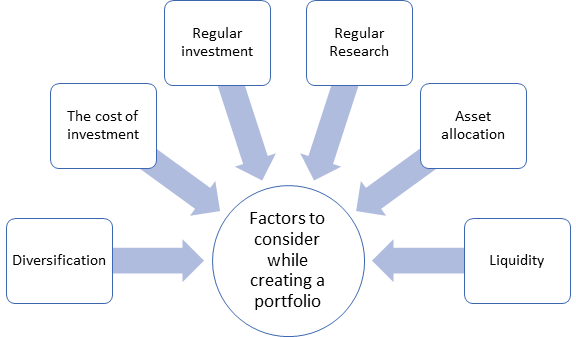
One of the defining characteristics of the market portfolio is its diversification. Because it encompasses all available assets, it inherently minimizes unsystematic risk, also known as company-specific or idiosyncratic risk.
This type of risk can be mitigated by holding a wide variety of assets. However, the market portfolio cannot eliminate systematic risk, or market risk, which affects all assets to some degree.
The market portfolio is considered to be efficient in terms of risk and return. Modern Portfolio Theory suggests that the market portfolio lies on the efficient frontier, representing the optimal trade-off between risk and return. This implies that, given the available assets and their associated risks, no other portfolio can offer a higher expected return for the same level of risk, or a lower risk for the same expected return.
Another key characteristic is its passivity. Because the market portfolio represents the entire market, it requires no active management or security selection.
Investors can replicate the market portfolio through index funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that track broad market indices. This passive investment approach typically results in lower management fees compared to actively managed portfolios.
Significance and Implications
The market portfolio serves as a crucial benchmark for evaluating investment performance. Investment managers are often judged by their ability to outperform the market portfolio, with performance measured by metrics like Sharpe Ratio and Treynor Ratio.
Furthermore, it serves as a foundation for asset pricing models. The Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), for instance, uses the market portfolio as a reference point for determining the expected return of an asset, based on its beta – a measure of its sensitivity to market movements.
Understanding the market portfolio has significant implications for risk management. By recognizing the presence of systematic risk that cannot be diversified away, investors can make informed decisions about their asset allocation and risk tolerance.
"The market portfolio is a cornerstone of modern finance, providing a framework for understanding risk, return, and diversification," said Dr. Anya Sharma, a finance professor at the University of Metropolitan.
Real-World Applications
While the theoretical market portfolio is impossible to fully replicate, investors can approximate it through broad market index funds. These funds offer exposure to a wide range of assets and track the performance of market indices like the S&P 500 or the MSCI World Index.
These funds enable investors to achieve a degree of diversification similar to that of the market portfolio at a relatively low cost. They serve as a core building block for many investment portfolios, providing broad market exposure and a benchmark for performance evaluation.
Consider a retail investor, John Smith, seeking long-term growth. Instead of trying to pick individual stocks, John invests in an S&P 500 index fund. He can effectively capture the returns of the broad market, while benefiting from diversification and low management fees.
Conclusion
The market portfolio is characterized by its diversification, efficiency, and passivity. It serves as a benchmark for investment performance, a foundation for asset pricing models, and a tool for managing risk.
While the theoretical market portfolio is impossible to perfectly replicate, investors can approximate it through broad market index funds and ETFs. These investment vehicles offer a cost-effective way to achieve broad market exposure and build a diversified portfolio.
Understanding the characteristics of the market portfolio is essential for investors of all levels. By embracing diversification and recognizing the role of systematic risk, investors can improve their chances of achieving their financial goals and navigate the complexities of the financial markets more effectively.