The Most Important Metabolic Fuel Molecule In The Body Is

Glucose, the seemingly simple sugar, is now unequivocally confirmed as the most important metabolic fuel molecule in the human body. New research solidifies its central role in powering everything from brain function to muscle activity.
This isn't just academic trivia; understanding glucose's dominance is crucial for tackling widespread health issues like diabetes, obesity, and even neurodegenerative diseases. Its intricate dance within our cells dictates our energy levels and overall well-being.
The Centrality of Glucose
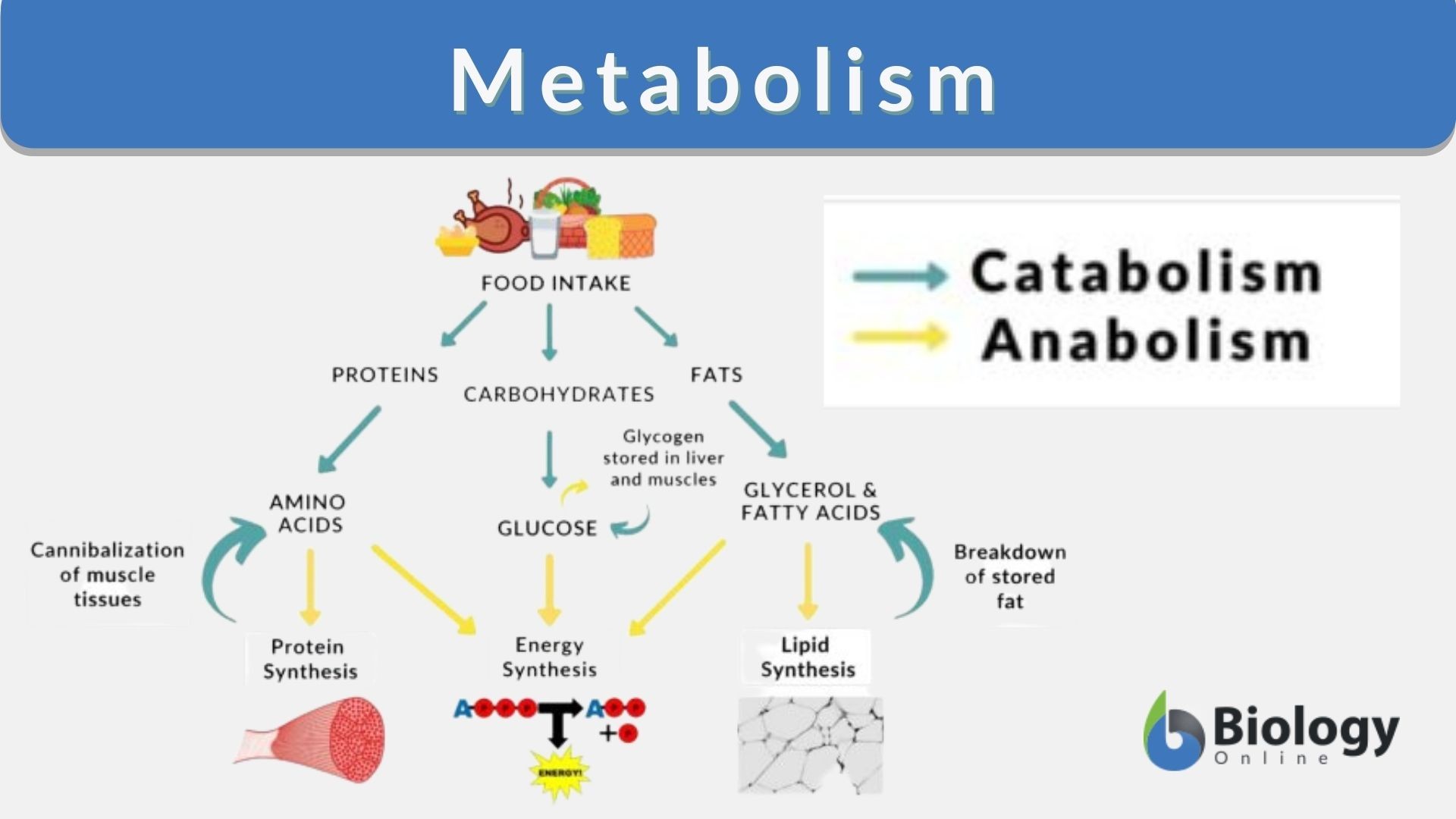
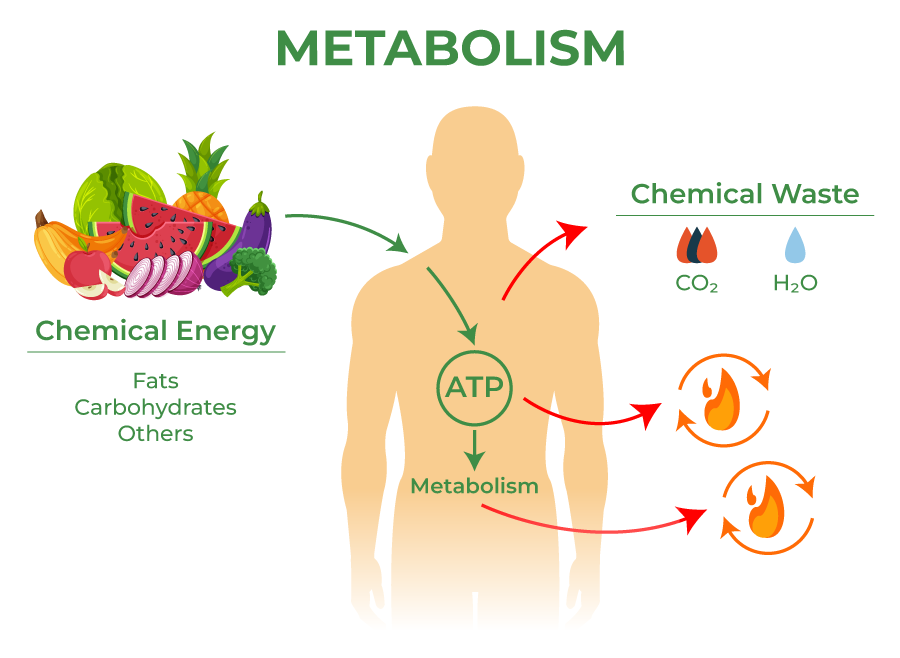
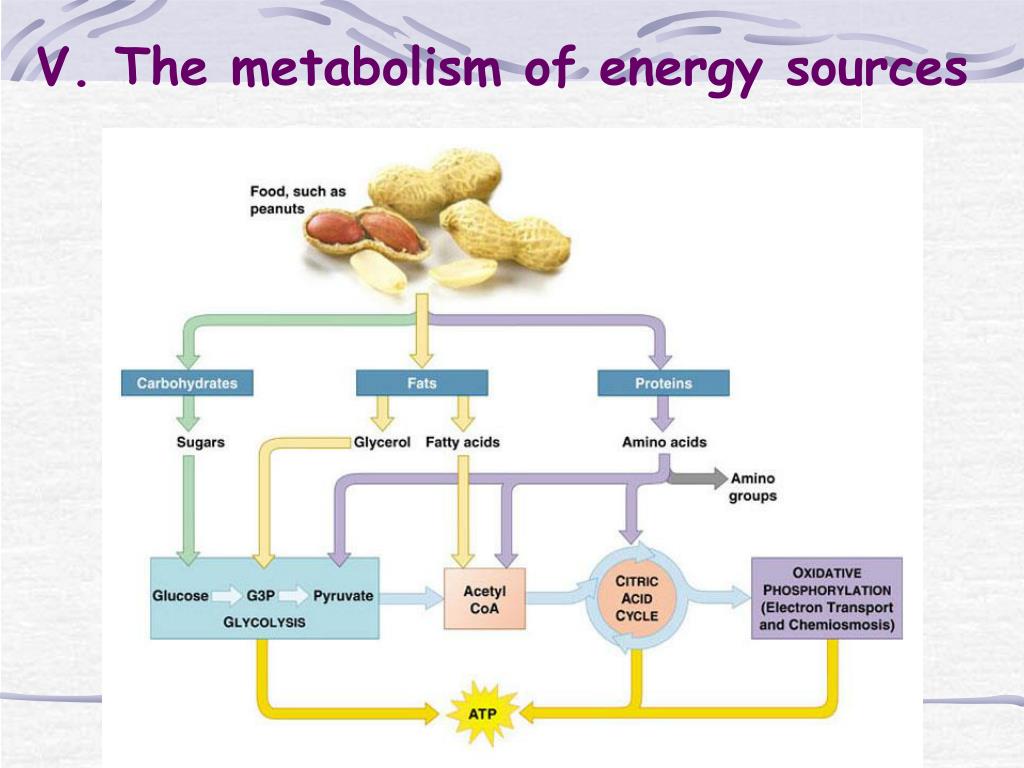
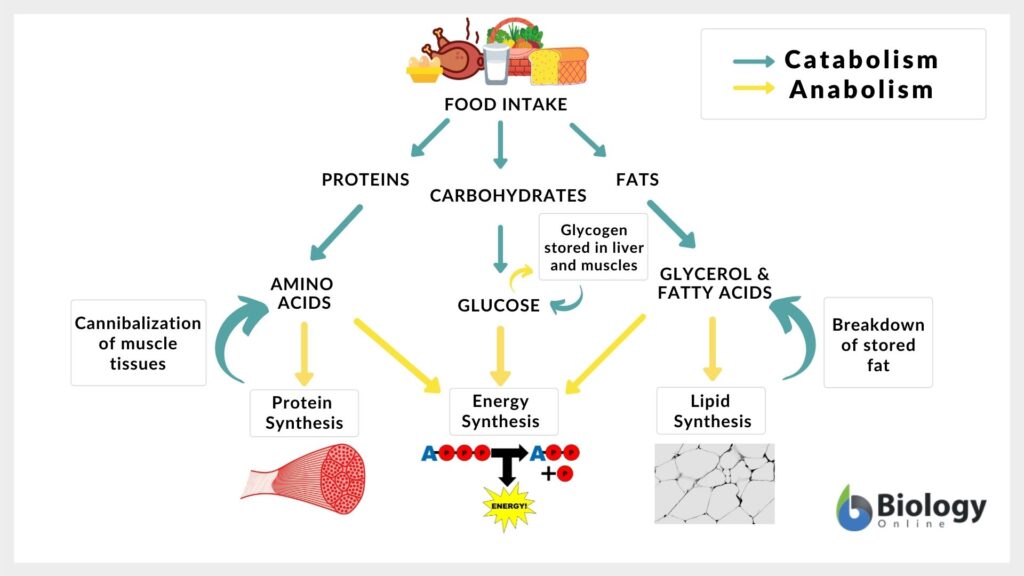
Glucose, a monosaccharide, is primarily obtained from the breakdown of carbohydrates we consume. This breakdown starts in the mouth with salivary amylase and continues in the small intestine.
Absorption occurs primarily in the small intestine, where glucose is transported into the bloodstream via specialized carrier proteins. From there, it journeys to various tissues and organs, ready to fuel cellular processes.
Dr. Anya Sharma, lead researcher at the National Institute of Health, stated, "Our findings reinforce glucose's position as the primary energy currency. Its availability and utilization are paramount for life itself."
Glucose's Multifaceted Roles
The brain, despite accounting for only 2% of body weight, consumes approximately 20% of the body's glucose supply. This highlights glucose's critical role in cognitive function, memory, and neuronal communication.
Muscle tissue relies heavily on glucose, especially during physical exertion. Glycogen, the stored form of glucose in muscles, provides a readily available energy source for contractions and movement.
Red blood cells exclusively rely on glucose for energy production. Since they lack mitochondria, they can't utilize other fuels like fatty acids, making glucose absolutely essential for oxygen transport.
The Insulin Connection
Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, plays a vital role in regulating blood glucose levels. It acts like a key, unlocking cells to allow glucose entry for energy production or storage.
Type 2 diabetes arises when cells become resistant to insulin, leading to elevated blood glucose levels. This chronic hyperglycemia can damage various organs and tissues over time.
Dr. Kenji Tanaka, an endocrinologist at Mayo Clinic, emphasized, "Understanding the insulin-glucose relationship is critical for preventing and managing diabetes. Lifestyle interventions and medications are often necessary to maintain healthy glucose levels."
Beyond Energy: Glucose in Cellular Processes
Glucose isn't just a fuel source; it's also a precursor for various essential molecules. It's involved in the synthesis of glycoproteins, glycolipids, and other structural components of cells.
Glucose-derived metabolites participate in crucial signaling pathways that regulate cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis. Dysregulation of these pathways can contribute to cancer development.
Professor Emily Carter, a biochemist at Harvard University, notes, "Glucose metabolism is intricately linked to numerous cellular processes. Manipulating glucose pathways is a promising avenue for therapeutic interventions."
The Dark Side: Glucose Toxicity
While essential, excessive glucose levels can be detrimental. Chronic hyperglycemia can lead to glycation, where glucose molecules bind to proteins and lipids, impairing their function.
This glycation process contributes to the development of advanced glycation end products (AGEs), which are implicated in aging and various chronic diseases. AGEs accumulate in tissues, causing inflammation and oxidative stress.
Dr. David Lee, a cardiologist at Johns Hopkins Hospital, warns, "The long-term consequences of uncontrolled blood glucose can be devastating, affecting the heart, kidneys, eyes, and nerves."
The Future of Glucose Research
Researchers are actively exploring novel strategies to modulate glucose metabolism for therapeutic benefit. This includes developing new drugs that enhance insulin sensitivity or inhibit glucose absorption.
Personalized nutrition plans tailored to individual glucose responses are gaining traction. Continuous glucose monitoring devices are empowering individuals to track their glucose levels in real-time and make informed dietary choices.
Ongoing studies are investigating the role of glucose metabolism in neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. Understanding how glucose utilization affects brain health could lead to new preventive and therapeutic approaches.
Next Steps
Health organizations are ramping up public awareness campaigns emphasizing the importance of balanced diets and regular exercise for maintaining healthy glucose levels. Early detection and management of glucose imbalances are crucial for preventing chronic diseases.
Further research is needed to fully elucidate the complex interplay between glucose metabolism and overall health. Investing in glucose-related research is essential for developing innovative strategies to combat metabolic diseases and promote longevity.