What Are The 4 Stages Of The Business Cycle
The economy, much like the seasons, ebbs and flows through predictable stages. Understanding these stages, known as the business cycle, is crucial for businesses, investors, and individuals alike to make informed decisions about spending, saving, and investing.
The business cycle describes the recurring pattern of expansion and contraction in economic activity. It's vital to grasp these cyclical movements to anticipate potential economic shifts and adapt accordingly. This article explores the four distinct stages of the business cycle, examining their characteristics and potential impacts.
The Four Stages of the Business Cycle
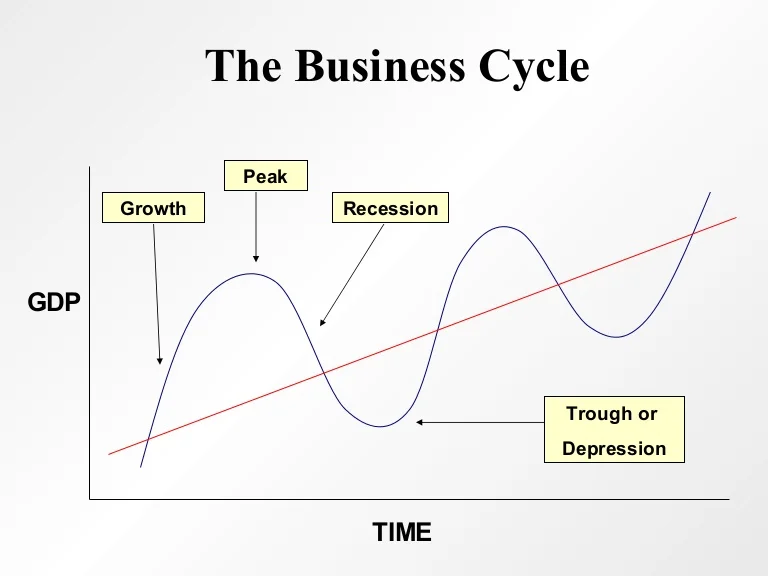
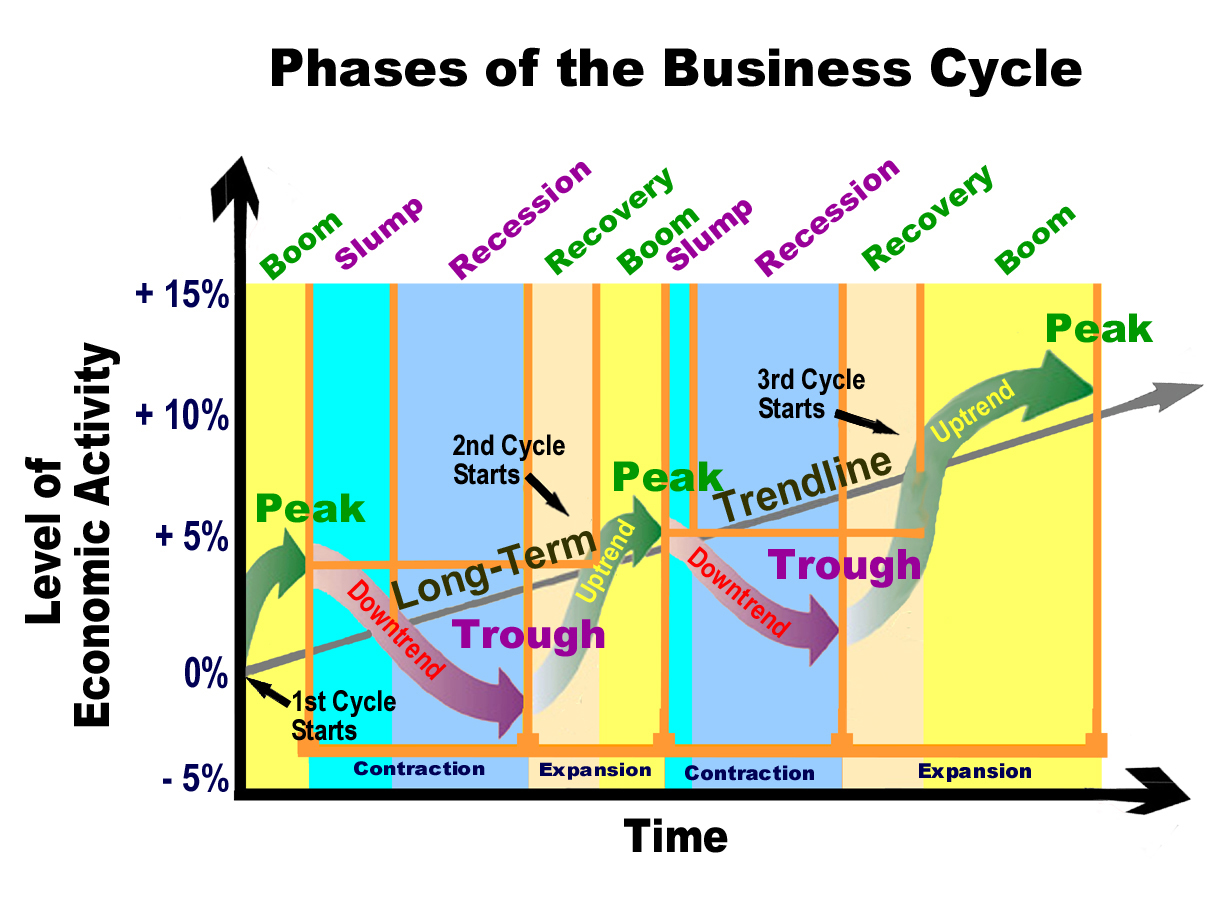
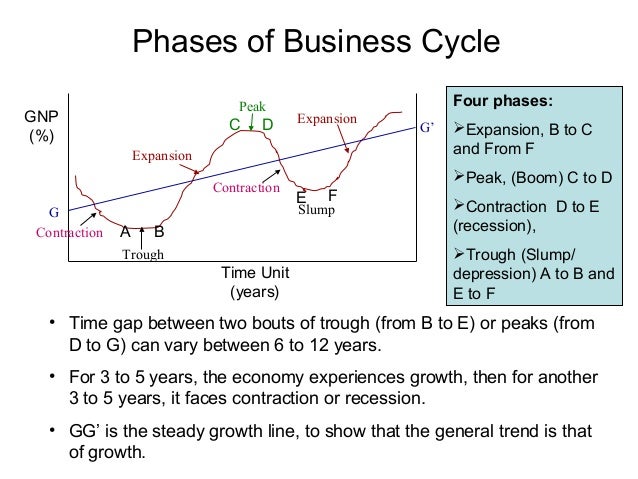
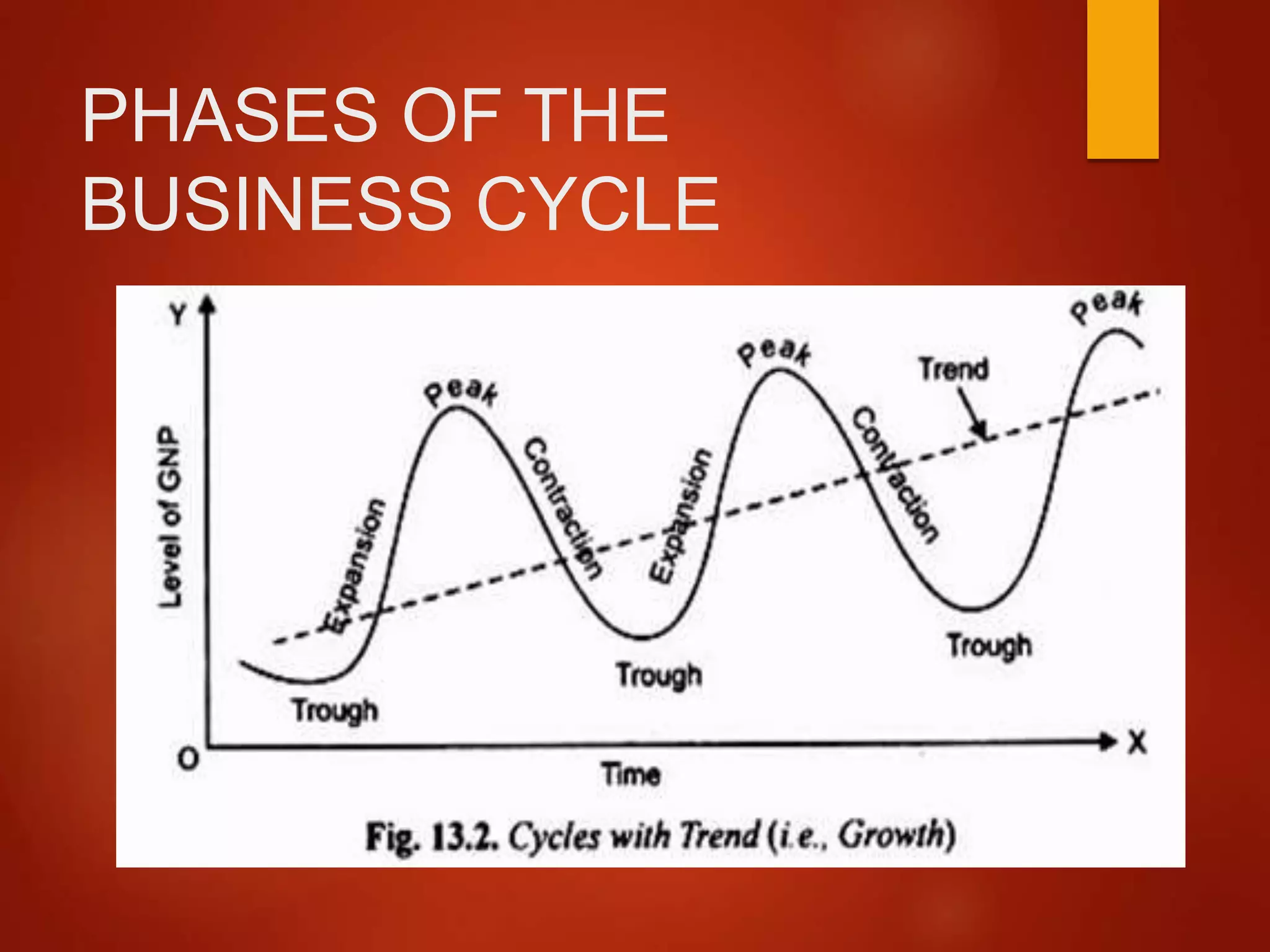
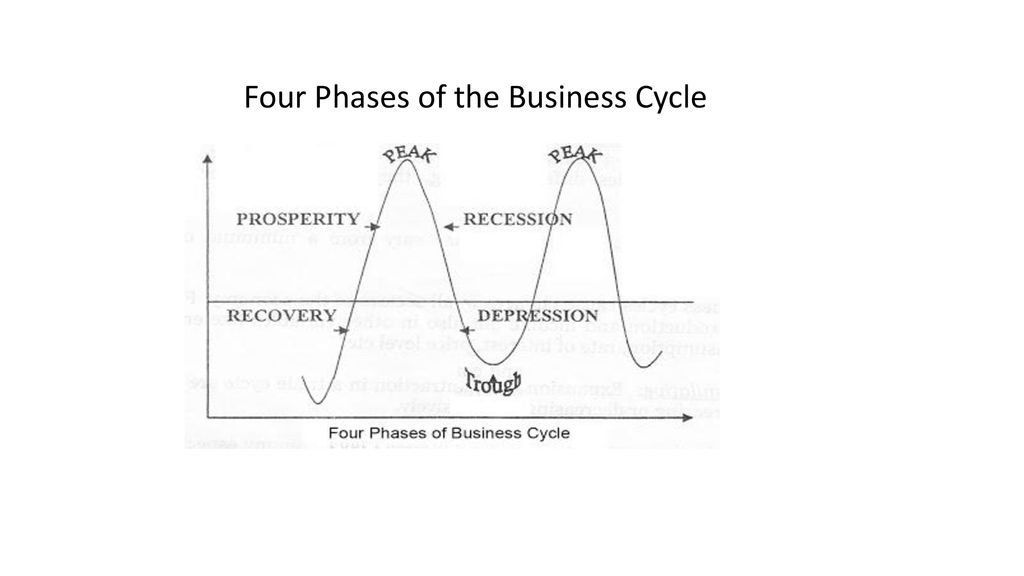
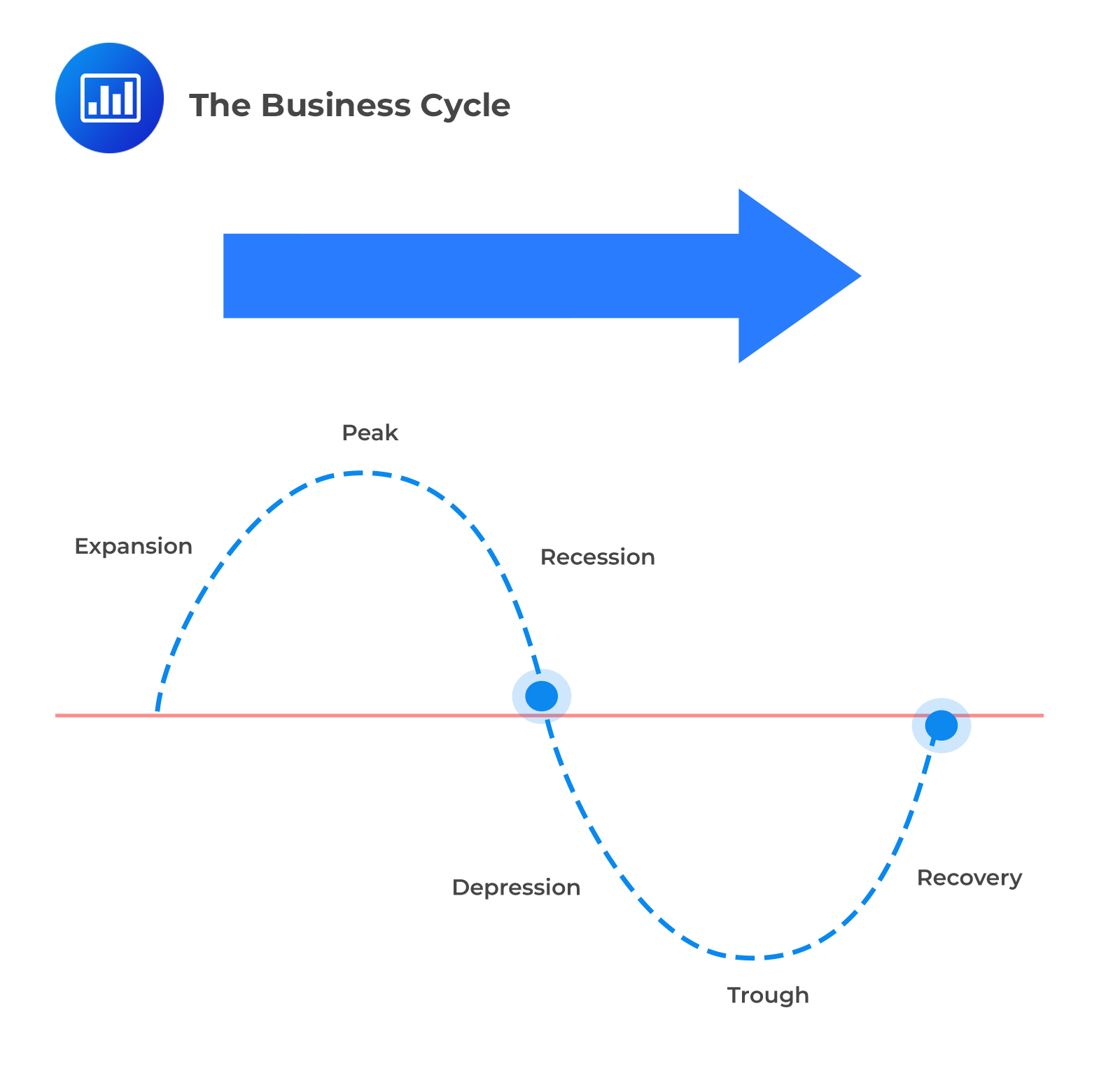
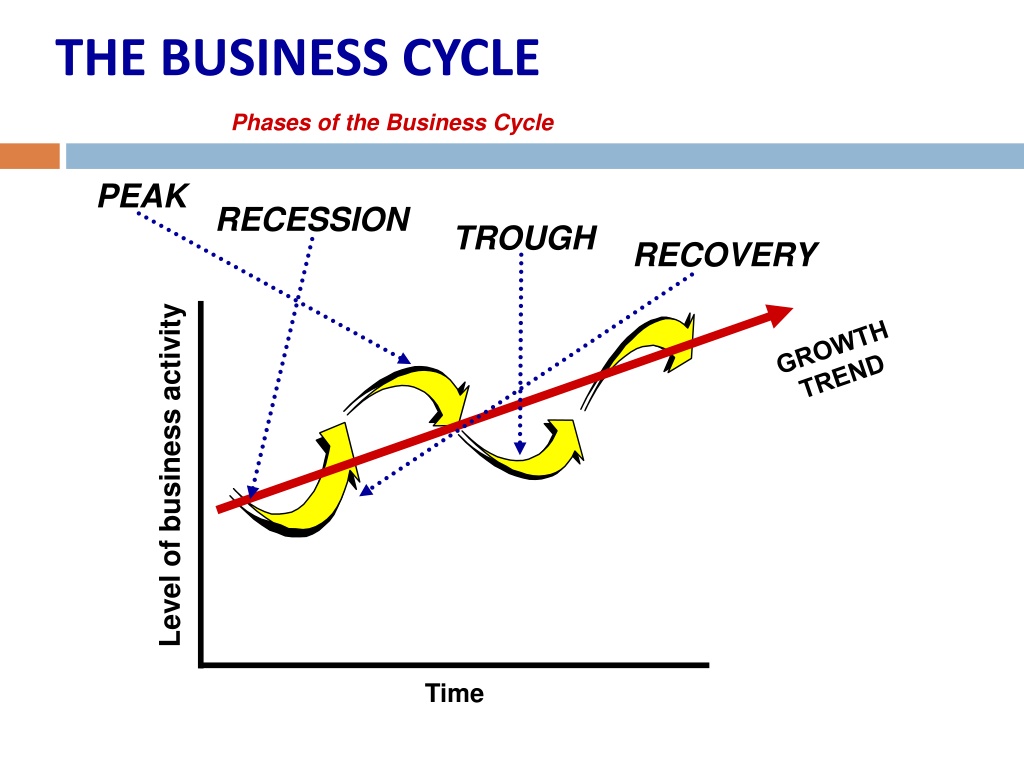
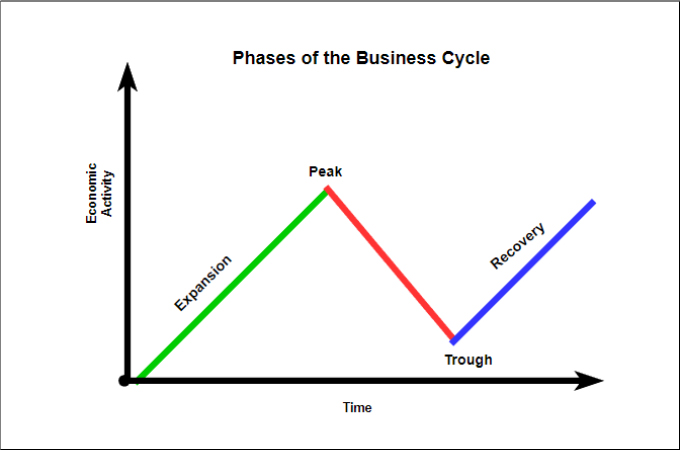
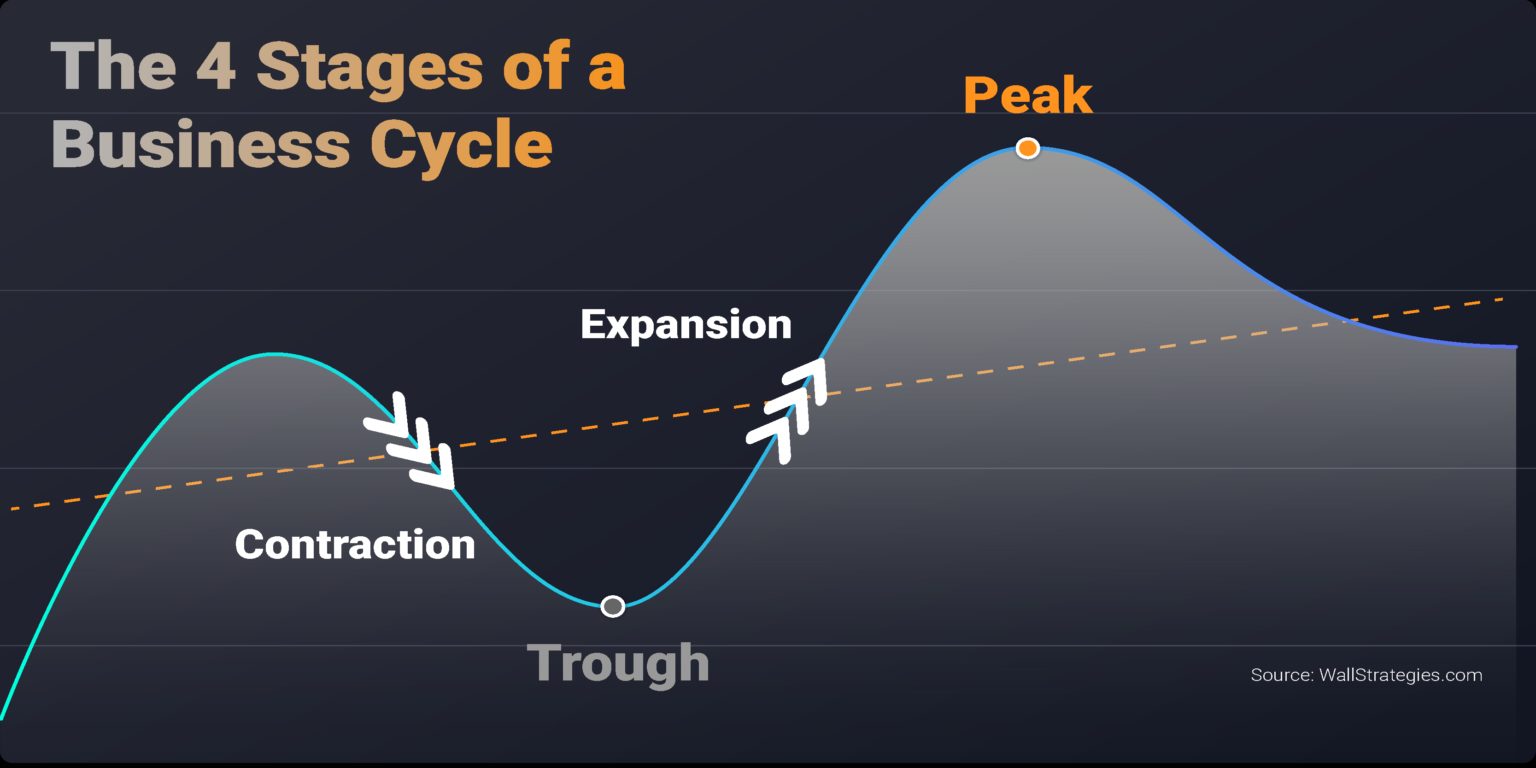
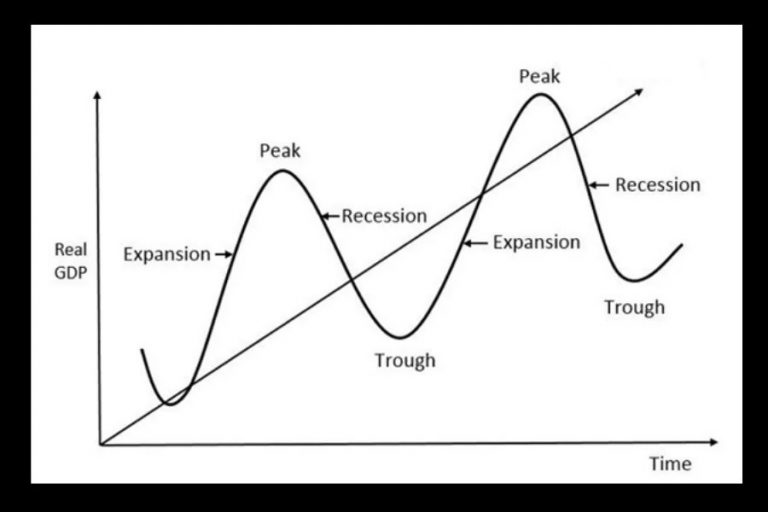
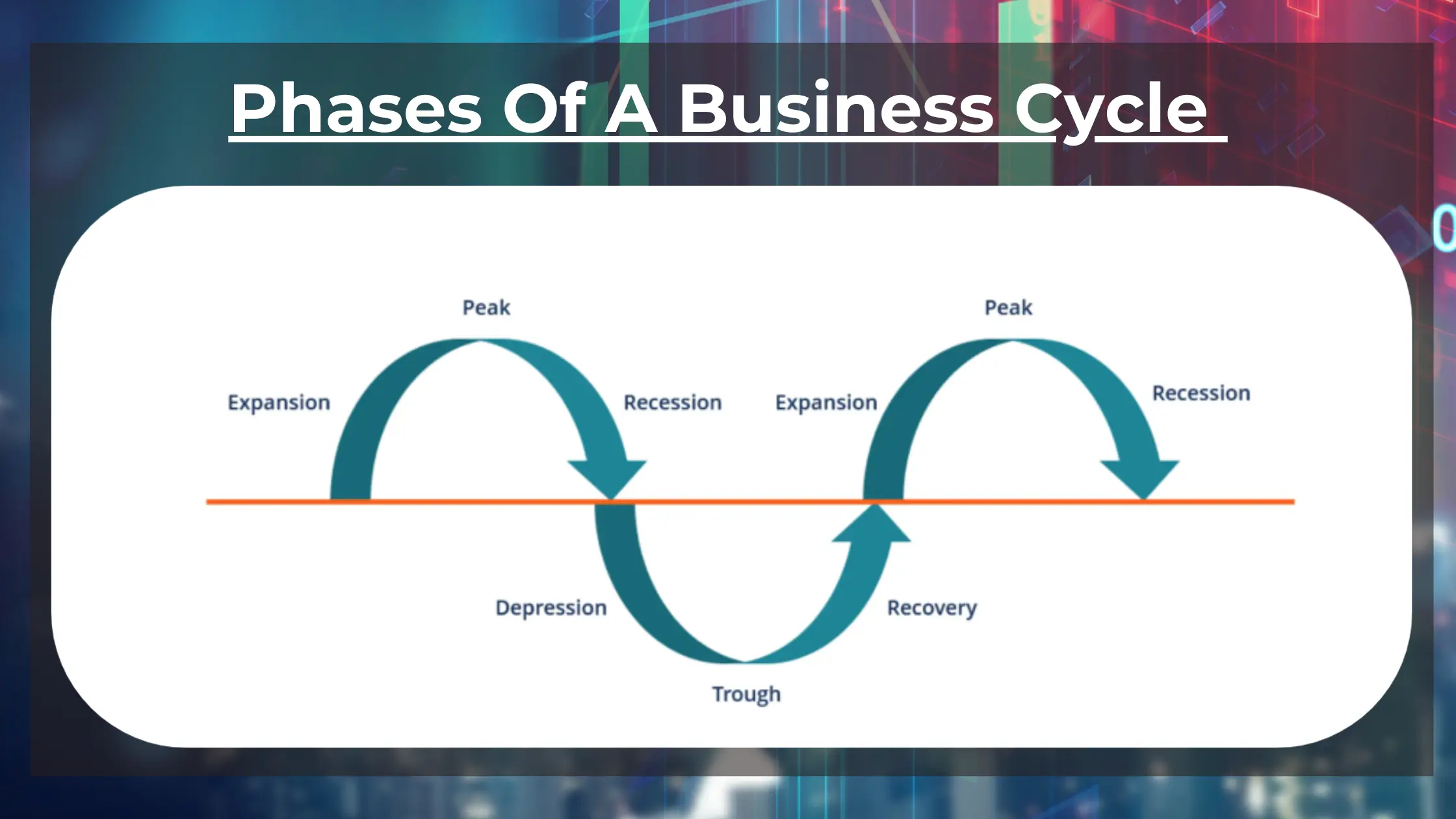
Economists generally identify four distinct phases in the business cycle: expansion, peak, contraction, and trough. Each phase presents unique challenges and opportunities, influencing everything from employment rates to consumer spending.
Expansion
The expansion phase, also known as recovery, is characterized by a period of economic growth. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) increases, employment rises, and consumer confidence improves. Businesses invest more, and the stock market generally performs well.
During expansion, interest rates are typically low, encouraging borrowing and investment. This increased activity fuels further growth, creating a positive feedback loop. It's a period of general optimism and increased prosperity.
Peak
The peak represents the highest point of economic activity in the cycle. It signifies the end of the expansion phase and the beginning of a potential downturn. At the peak, the economy is operating at or near its full capacity.
Inflation often becomes a concern at the peak, as demand exceeds supply. Businesses may struggle to keep up with orders, and prices rise. This is a signal that the economy may be overheating.
Contraction
The contraction phase, also known as recession, is marked by a decline in economic activity. GDP falls, unemployment rises, and consumer spending decreases. Businesses may reduce investment and lay off workers.
During a contraction, businesses often postpone expansion plans. Consumer confidence declines, leading to further reductions in spending. The National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER) is typically responsible for declaring the start and end dates of recessions in the United States.
Trough
The trough represents the lowest point of economic activity in the cycle. It signifies the end of the contraction phase and the beginning of a potential recovery. This is when the economy "bottoms out," and the cycle begins anew.
Unemployment is typically high at the trough, and business sentiment is low. However, this phase can also present opportunities for investors and businesses willing to take risks. Government intervention, such as stimulus packages, may be implemented to stimulate economic activity.
Understanding the Impact
The business cycle impacts every facet of the economy, from individual households to large corporations. Recognizing which stage the economy is in allows for better financial planning and decision-making.
For example, during an expansion, individuals may be more willing to take on debt or invest in the stock market. Conversely, during a contraction, they may prioritize saving and reducing debt. Businesses might invest heavily during an expansion, while cutting costs and streamlining operations during a contraction.
Government policies also play a crucial role in mitigating the effects of the business cycle. Central banks, like the Federal Reserve in the United States, use monetary policy to influence interest rates and credit conditions. Fiscal policy, involving government spending and taxation, can also be used to stimulate or cool down the economy.
Understanding the business cycle doesn't guarantee predicting the future with certainty. Economic forecasting is complex and subject to numerous variables. However, awareness of these cyclical patterns provides a valuable framework for navigating the ever-changing economic landscape.
By paying attention to economic indicators and understanding the dynamics of the business cycle, individuals and businesses can be better prepared to adapt to changing conditions and make informed choices to achieve their financial goals.
/businesscycle-013-ba572c5d577c4bd6a367177a02c26423.png)



.png)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/businesscycle-013-ba572c5d577c4bd6a367177a02c26423.png)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/phasesofthebusinesscycle-c7cb7a3ce6894e86a3e44d5b0fe4d5e2.jpg)
