What Can Result From A Functional Decline

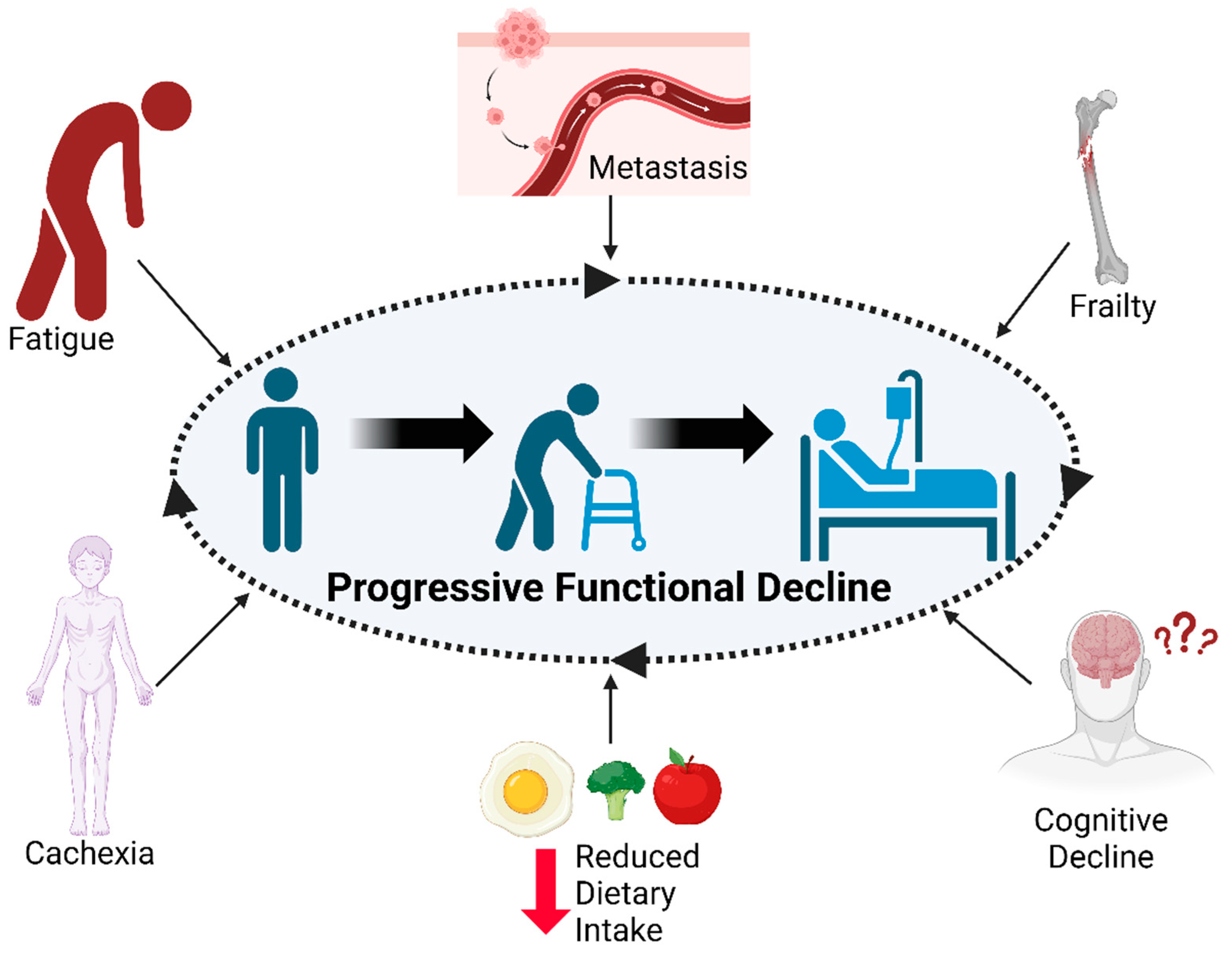
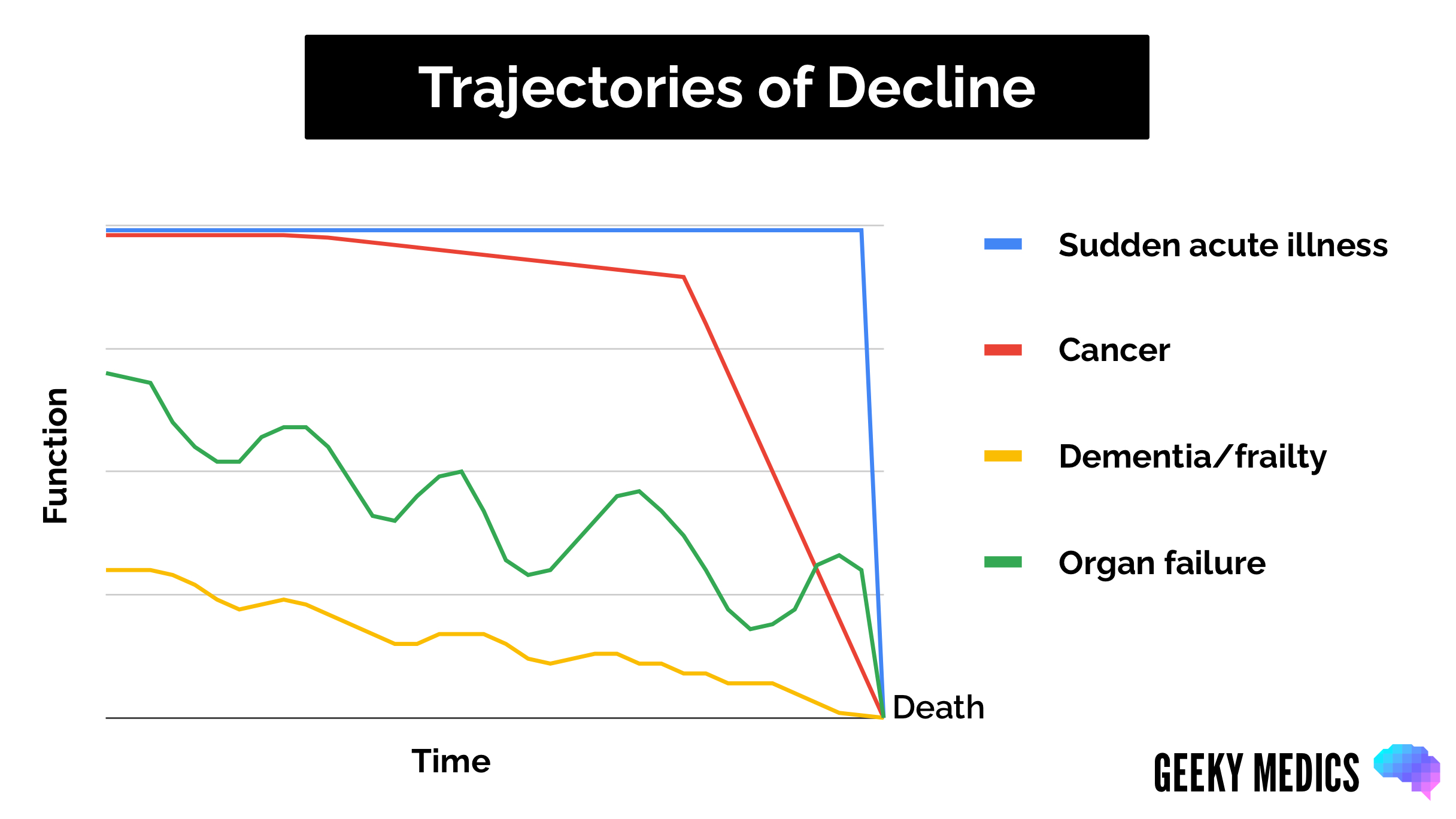
For many, the subtle slowing down that comes with age or the unexpected consequence of illness can trigger a cascade of challenges, often stemming from a gradual functional decline. This decline, characterized by a loss of physical or cognitive abilities needed for daily living, can dramatically reshape an individual's life and require significant adjustments in care and support systems.
Understanding the potential repercussions of this decline is crucial for individuals, families, and healthcare providers alike. Early recognition and proactive intervention can mitigate the severity of these outcomes and improve quality of life.
What is Functional Decline?
Functional decline refers to a loss of independence in performing activities of daily living (ADLs) and instrumental activities of daily living (IADLs). ADLs encompass basic self-care tasks such as bathing, dressing, eating, toileting, and transferring (moving from one place to another).
IADLs are more complex tasks that enable an individual to live independently in their community, including managing finances, cooking, cleaning, shopping, and using transportation.
Risk Factors and Causes
Numerous factors can contribute to functional decline. Age is a primary risk factor, as the body naturally undergoes changes that can impact physical and cognitive abilities.
Chronic diseases such as arthritis, heart disease, stroke, dementia, and Parkinson's disease can significantly impair function. Acute illnesses like pneumonia or influenza, hospitalization, and surgery can also trigger a decline, particularly in older adults.
Other factors include poor nutrition, lack of physical activity, social isolation, and mental health conditions such as depression.
Potential Outcomes of Functional Decline
The consequences of functional decline are far-reaching, impacting various aspects of an individual's life. Loss of independence is a major outcome.
As individuals struggle with daily tasks, they may become increasingly reliant on others for assistance, which can lead to feelings of frustration, helplessness, and loss of dignity.
Increased risk of falls is another significant concern. Impaired mobility and balance can increase the likelihood of falls, resulting in injuries such as fractures, head trauma, and hospitalizations.
Cognitive decline can also contribute to falls, as it affects judgment and awareness of surroundings.
Social isolation and loneliness are common consequences of functional decline. Individuals may find it difficult to participate in social activities, maintain relationships, and engage with their community.
This isolation can lead to depression, anxiety, and a further decline in cognitive and physical function.
Furthermore, functional decline often results in increased healthcare costs. Individuals may require more frequent medical appointments, hospitalizations, and long-term care services.
The financial burden can be substantial, impacting both the individual and their family.
Cognitive decline also often impacts decision-making capacity.
"Loss of decision-making capacity is a serious consequence, as individuals may be unable to manage their finances, make healthcare decisions, or protect themselves from exploitation," explains Dr. Emily Carter, a geriatric specialist.
Caregiver burden is a critical consideration. Family members and friends who provide care for individuals experiencing functional decline often face significant physical, emotional, and financial strain.
This burden can lead to burnout, depression, and a decline in their own health and well-being.
Mitigating the Effects of Functional Decline
Early detection and intervention are essential to mitigating the negative outcomes of functional decline. Regular screenings for cognitive and physical function can help identify individuals at risk.
Physical therapy and occupational therapy can improve mobility, strength, and balance, while cognitive training can enhance memory and attention. Lifestyle modifications, such as a healthy diet and regular exercise, can also play a crucial role.
Assistive devices, such as walkers, grab bars, and medication organizers, can promote independence and safety.
Social support and engagement are vital for maintaining mental and emotional well-being. Encouraging participation in social activities, connecting with support groups, and utilizing technology to stay connected can combat isolation and loneliness.
Caregiver support programs can provide education, resources, and respite care to alleviate caregiver burden. These programs can help caregivers maintain their own health and well-being while providing quality care for their loved ones.
Advance care planning is crucial for ensuring that an individual's wishes are respected as their functional abilities decline. This involves discussing healthcare preferences, appointing a healthcare proxy, and creating advance directives such as a living will.
By proactively addressing functional decline, individuals and families can navigate these challenges with greater resilience and maintain a higher quality of life.