What Happens If You Inject Glp1 Into Muscle

The increasing popularity of GLP-1 receptor agonists, such as semaglutide (Ozempic, Wegovy) and tirzepatide (Mounjaro), for weight management and diabetes treatment has led to widespread discussion about their proper administration. While these medications are typically prescribed for subcutaneous injection, some individuals are exploring alternative injection sites, raising concerns about the potential consequences of injecting GLP-1 agonists into muscle tissue.
This article examines the potential effects and safety considerations associated with intramuscular (IM) injection of GLP-1 receptor agonists, drawing upon available scientific literature, expert opinions, and manufacturer guidelines. Understanding the implications of administering these medications incorrectly is crucial for ensuring patient safety and optimizing treatment outcomes.
Understanding GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and Their Intended Use
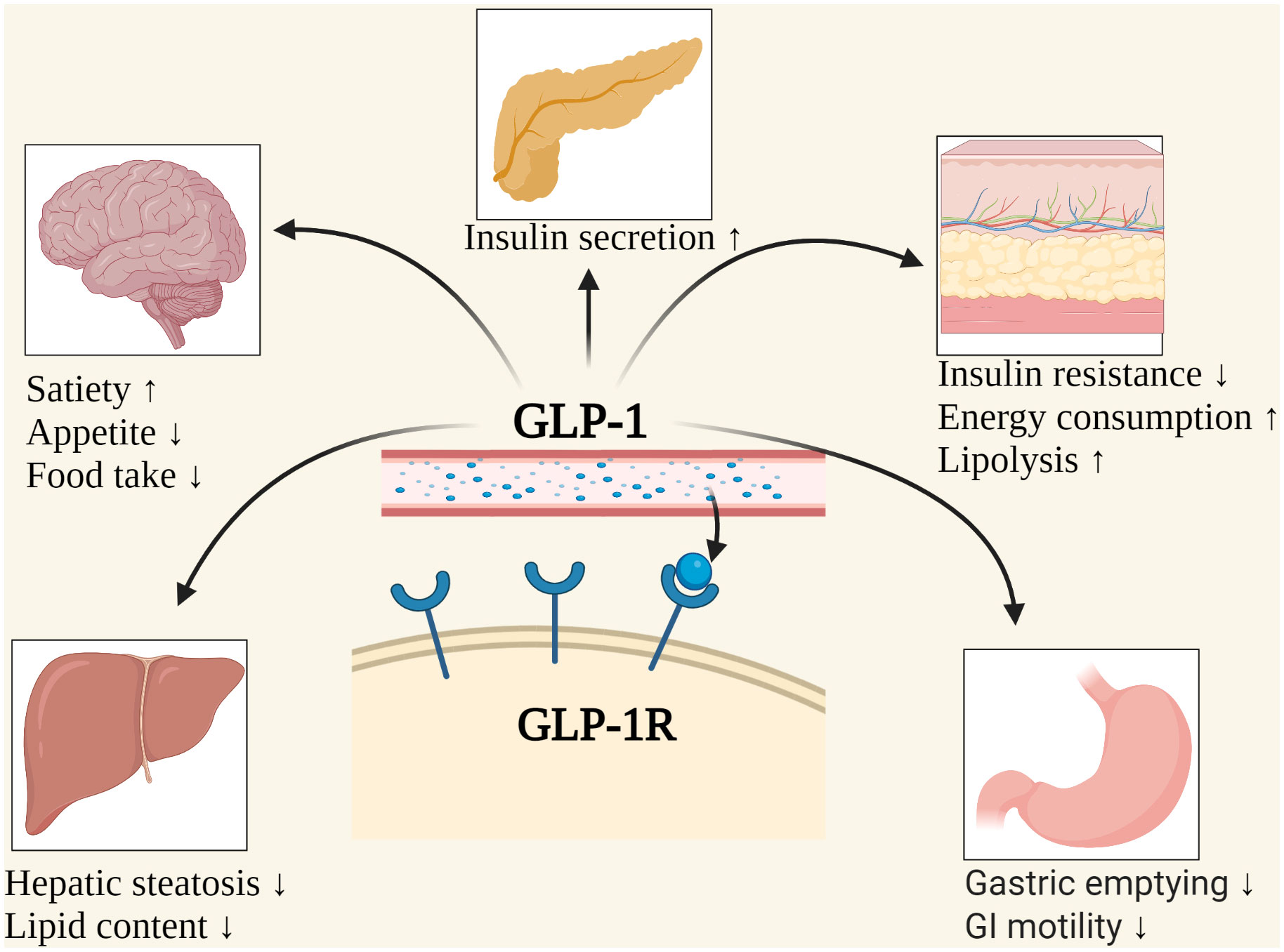
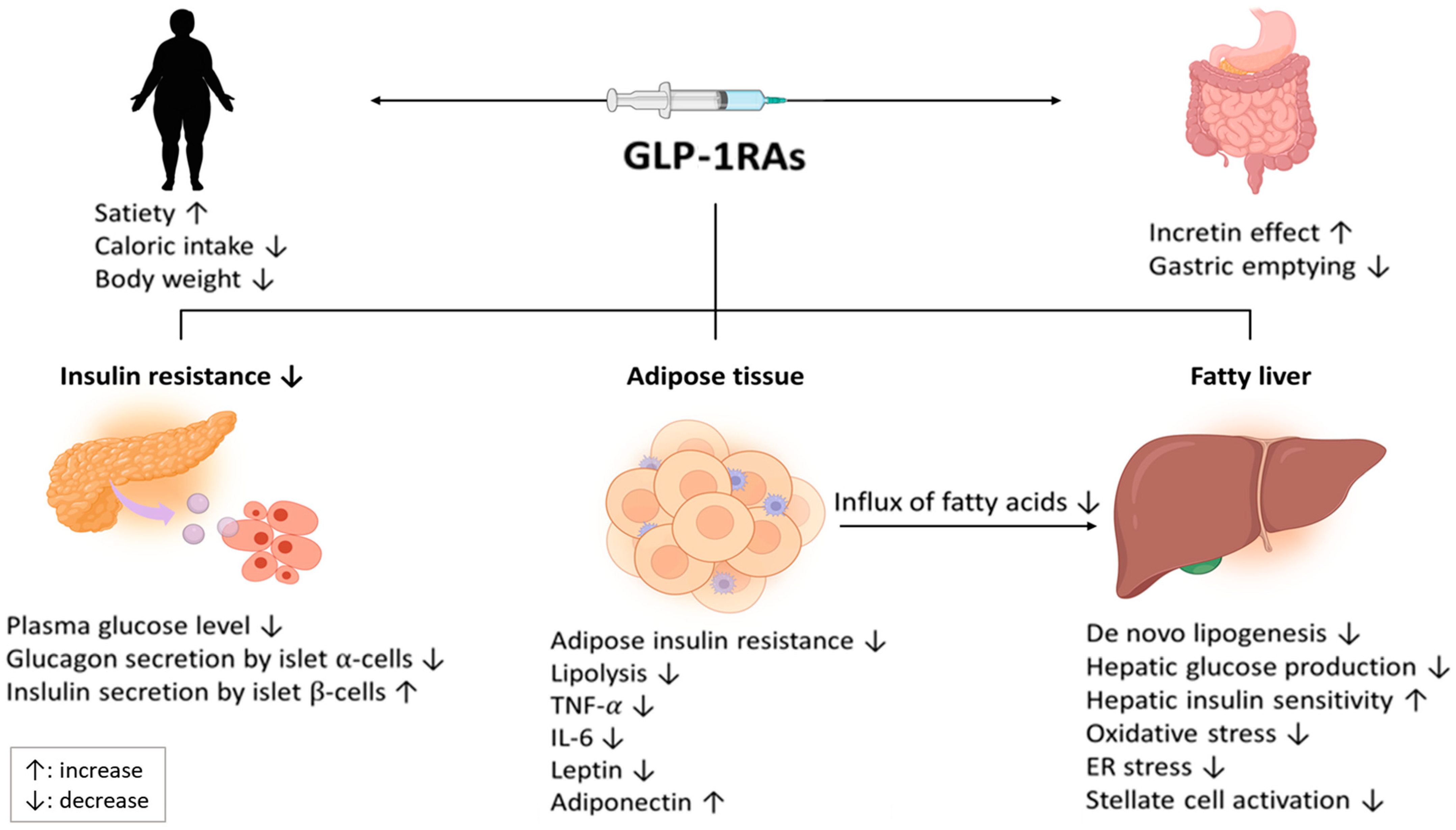
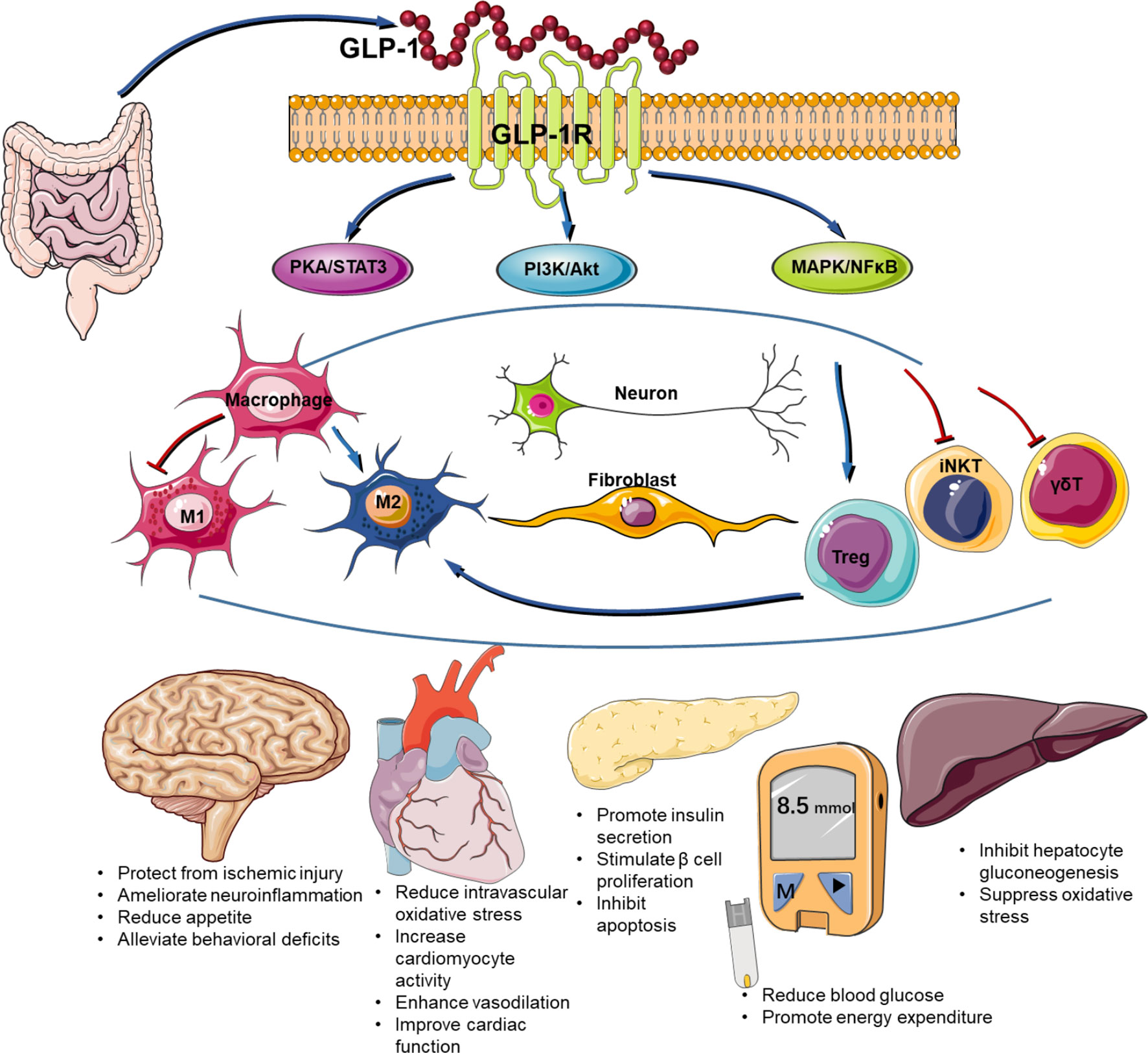
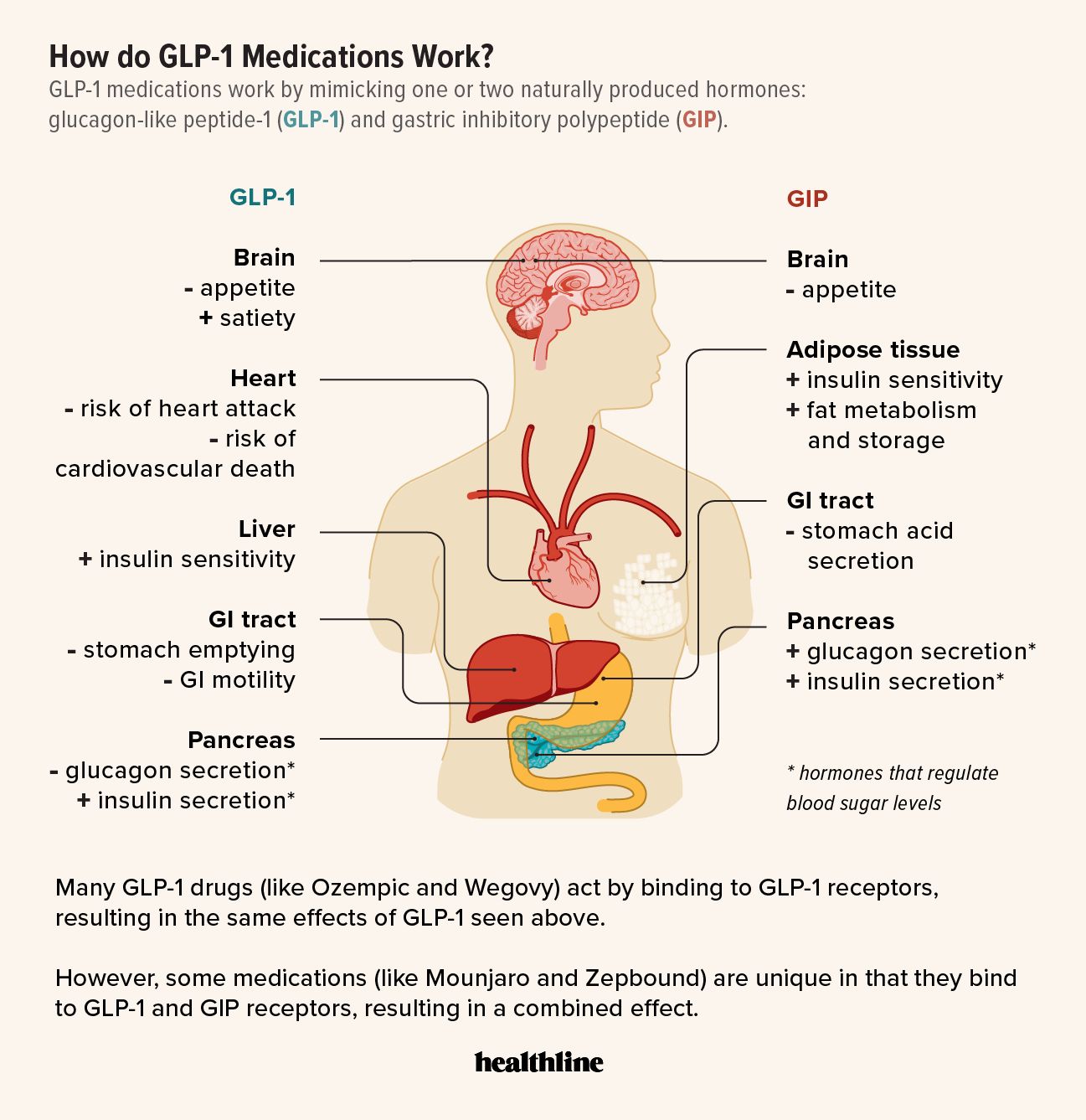
GLP-1 receptor agonists are a class of medications that mimic the effects of the naturally occurring incretin hormone glucagon-like peptide-1. They work by stimulating insulin release, suppressing glucagon secretion, and slowing gastric emptying, ultimately leading to improved blood sugar control and weight loss.
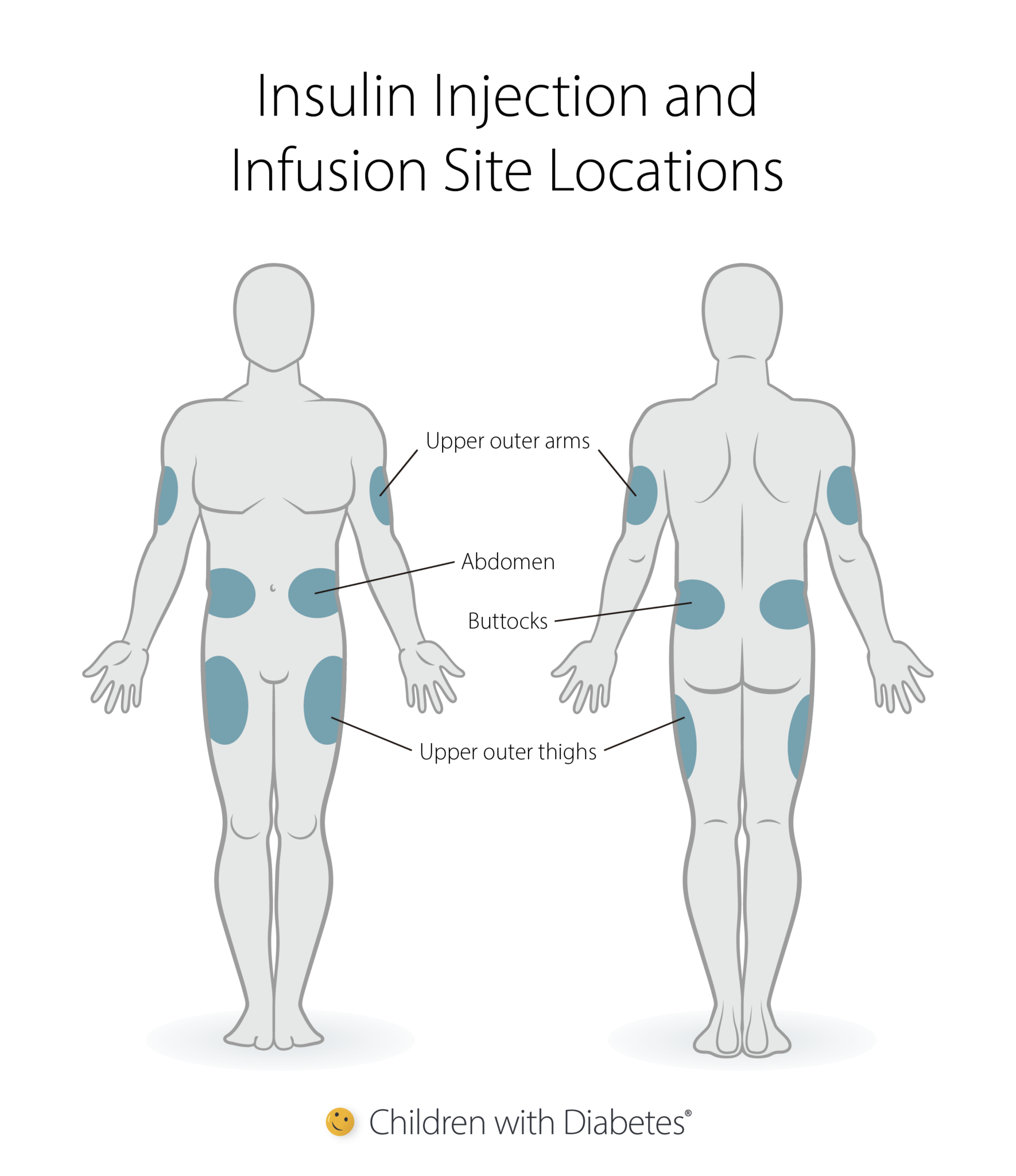
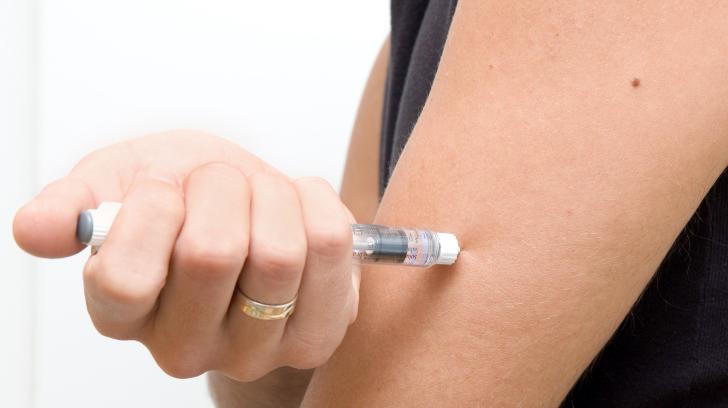
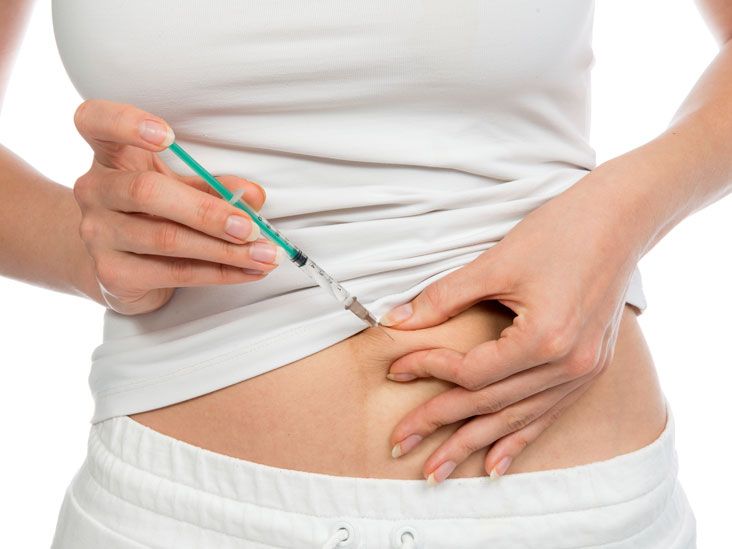
These medications are specifically formulated for subcutaneous injection, meaning they are intended to be injected into the fatty tissue just beneath the skin. The subcutaneous route allows for slow and sustained absorption of the medication into the bloodstream, providing a consistent therapeutic effect.
The Potential Consequences of Intramuscular Injection
While limited research directly addresses the effects of injecting GLP-1 agonists into muscle, potential consequences can be inferred based on the pharmacokinetic properties of these drugs and the physiological differences between subcutaneous and intramuscular administration.
Altered Absorption Rates
One of the primary concerns with IM injection is the potential for altered absorption rates. Muscles have a richer blood supply than subcutaneous tissue, leading to faster drug absorption.
This rapid absorption could result in a higher peak concentration of the drug in the bloodstream, potentially increasing the risk of side effects such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Conversely, the faster absorption could also lead to a shorter duration of action, requiring more frequent injections to maintain therapeutic efficacy.
Increased Risk of Local Reactions
Intramuscular injections are generally associated with a higher risk of local reactions compared to subcutaneous injections. These reactions can include pain, swelling, redness, and even muscle damage.
Injecting a GLP-1 agonist into muscle could exacerbate these risks, especially if the injection is performed incorrectly or if the individual has a pre-existing muscle condition.
Unpredictable Drug Response
The unpredictable absorption rates and potential for local reactions associated with IM injection could lead to an inconsistent and unreliable drug response. This inconsistency could make it difficult to manage blood sugar levels and achieve optimal weight loss.
Furthermore, the altered pharmacokinetic profile of the drug could potentially affect its interaction with other medications, leading to unforeseen consequences.
Expert Opinions and Manufacturer Guidelines
Medical professionals and pharmaceutical manufacturers strongly advise against injecting GLP-1 receptor agonists into muscle tissue.
According to the official prescribing information for Ozempic and Wegovy, the medication should be administered subcutaneously in the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm. Similar guidelines apply to other GLP-1 receptor agonists.
Healthcare providers emphasize the importance of following the prescribed injection technique to ensure patient safety and maximize treatment effectiveness. They also advise patients to consult with their doctor or pharmacist if they have any questions or concerns about their medication.
A Human Perspective
Sarah M., a patient using semaglutide for weight management, shared her initial confusion regarding injection sites. "At first, I was unsure about the correct way to inject. I even considered injecting into my arm muscle, thinking it would be more effective," she admitted.
"However, after consulting with my doctor and watching instructional videos, I realized the importance of subcutaneous injection. I'm glad I clarified before making a mistake."
The Importance of Proper Administration
The proper administration of GLP-1 receptor agonists is paramount for ensuring patient safety and maximizing therapeutic benefits. Subcutaneous injection, as recommended by healthcare professionals and pharmaceutical manufacturers, allows for slow and sustained drug absorption, minimizing the risk of side effects and providing consistent blood sugar control and weight loss.
Injecting these medications into muscle tissue could lead to altered absorption rates, increased risk of local reactions, and unpredictable drug response. It is crucial for individuals using GLP-1 receptor agonists to adhere to the prescribed injection technique and consult with their healthcare provider if they have any questions or concerns.
By following these guidelines, patients can safely and effectively manage their diabetes or weight loss journey with GLP-1 receptor agonists.




![What Happens If You Inject Glp1 Into Muscle Intramuscular Injections [+ Free Cheat Sheet] | Lecturio](https://cdn.lecturio.com/assets/Nursing_CS_Intramuscular-medication-administration.jpg)