What Is A Self Grounding Outlet

In the realm of electrical safety, ensuring proper grounding is paramount. One component often encountered in residential and commercial settings is the self-grounding outlet. But what exactly is a self-grounding outlet, and how does it contribute to the overall safety of an electrical system?
The following explores the purpose, mechanism, and potential benefits of these outlets. This article also examines their impact on electrical safety standards.
Understanding Grounding in Electrical Systems
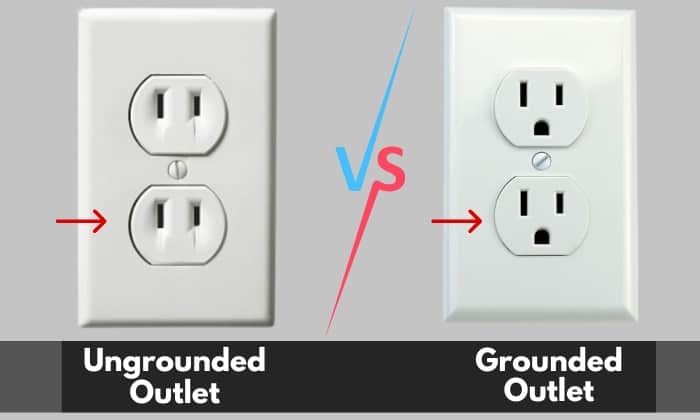
Before delving into the specifics of self-grounding outlets, it's crucial to understand the fundamental concept of grounding. Grounding, in electrical terms, refers to a deliberate connection between the electrical circuit and the earth.
This connection provides a low-resistance path for fault current to flow back to the source, tripping a circuit breaker or fuse and cutting off power to the affected circuit.
Without a proper ground, a fault current could energize metal enclosures or other conductive surfaces, creating a shock hazard.
The Role of the Grounding Conductor
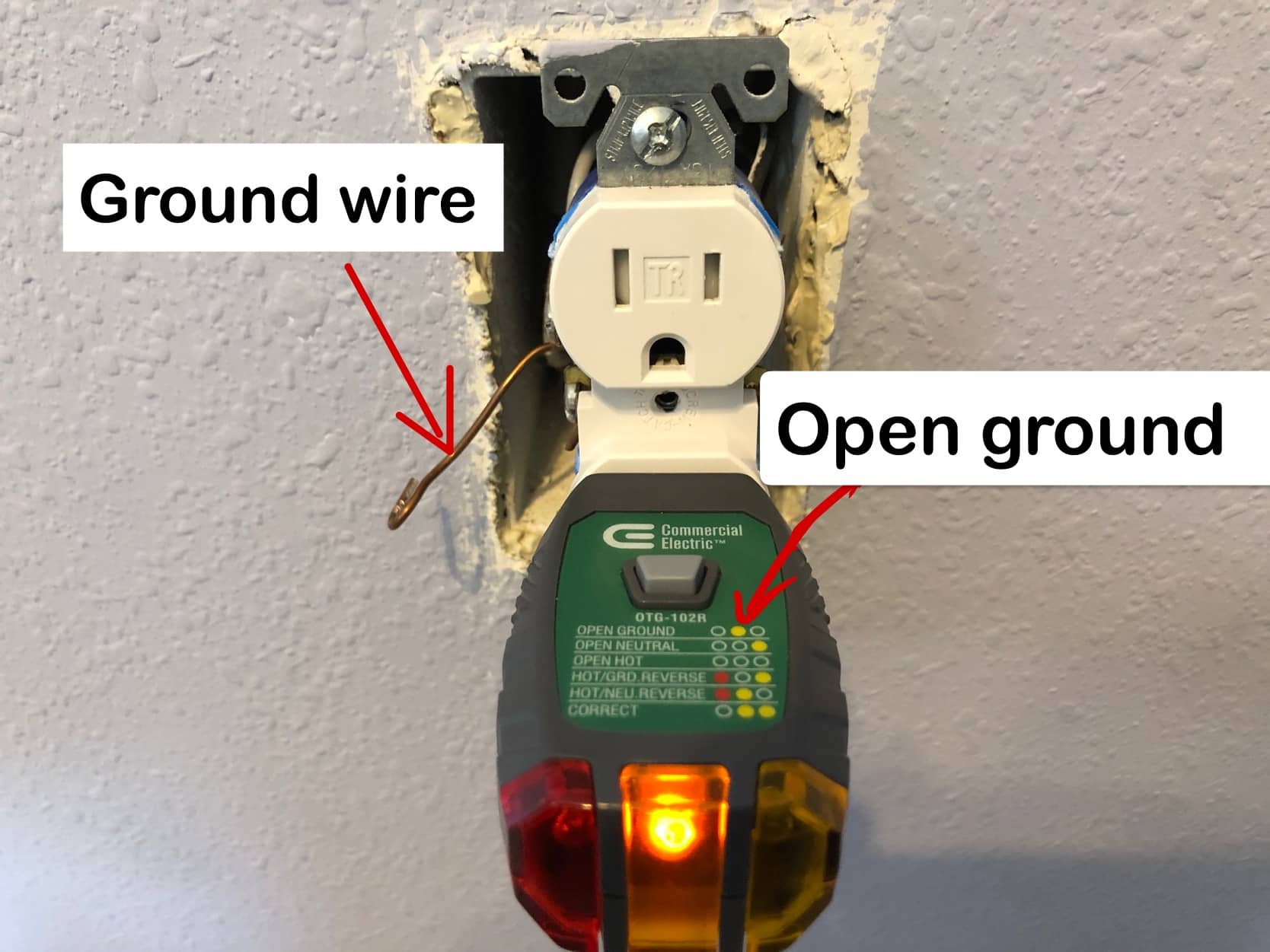
The grounding conductor, typically a bare or green-insulated wire, plays a critical role in the grounding system. It provides the pathway for fault current to return to the source, triggering the overcurrent protection device (breaker or fuse).
In older electrical systems, metal conduit served as the grounding path.
However, modern systems generally rely on a dedicated grounding wire run alongside the circuit conductors.
What is a Self-Grounding Outlet?
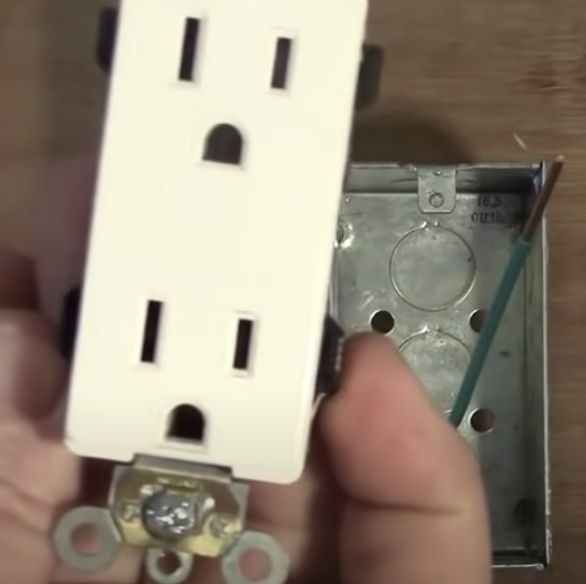
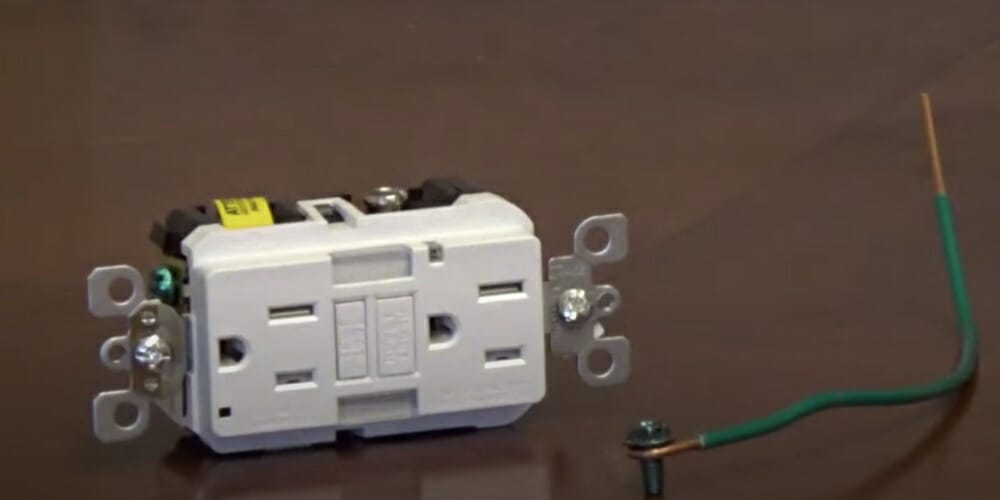
A self-grounding outlet is designed to establish a grounding connection even when the electrical box it's mounted in isn't directly grounded. It achieves this through a specialized design that ensures reliable contact with the mounting screw and, consequently, the metal electrical box.
This design feature provides an alternative grounding path when the electrical box itself is properly grounded to the building's grounding system.
It's important to note that a self-grounding outlet does not *create* a ground; it simply utilizes an existing grounded electrical box.
Key Features of Self-Grounding Outlets
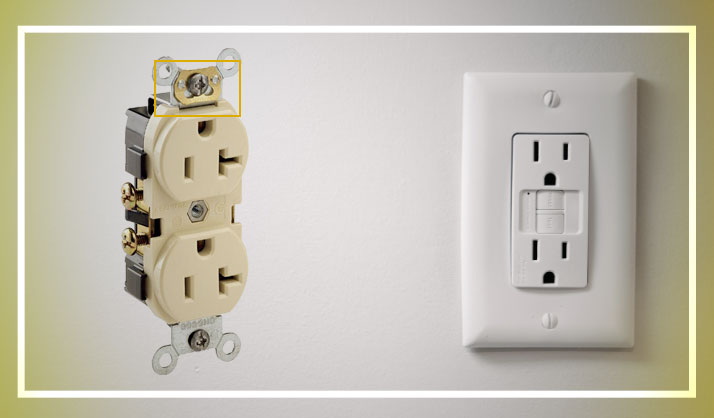
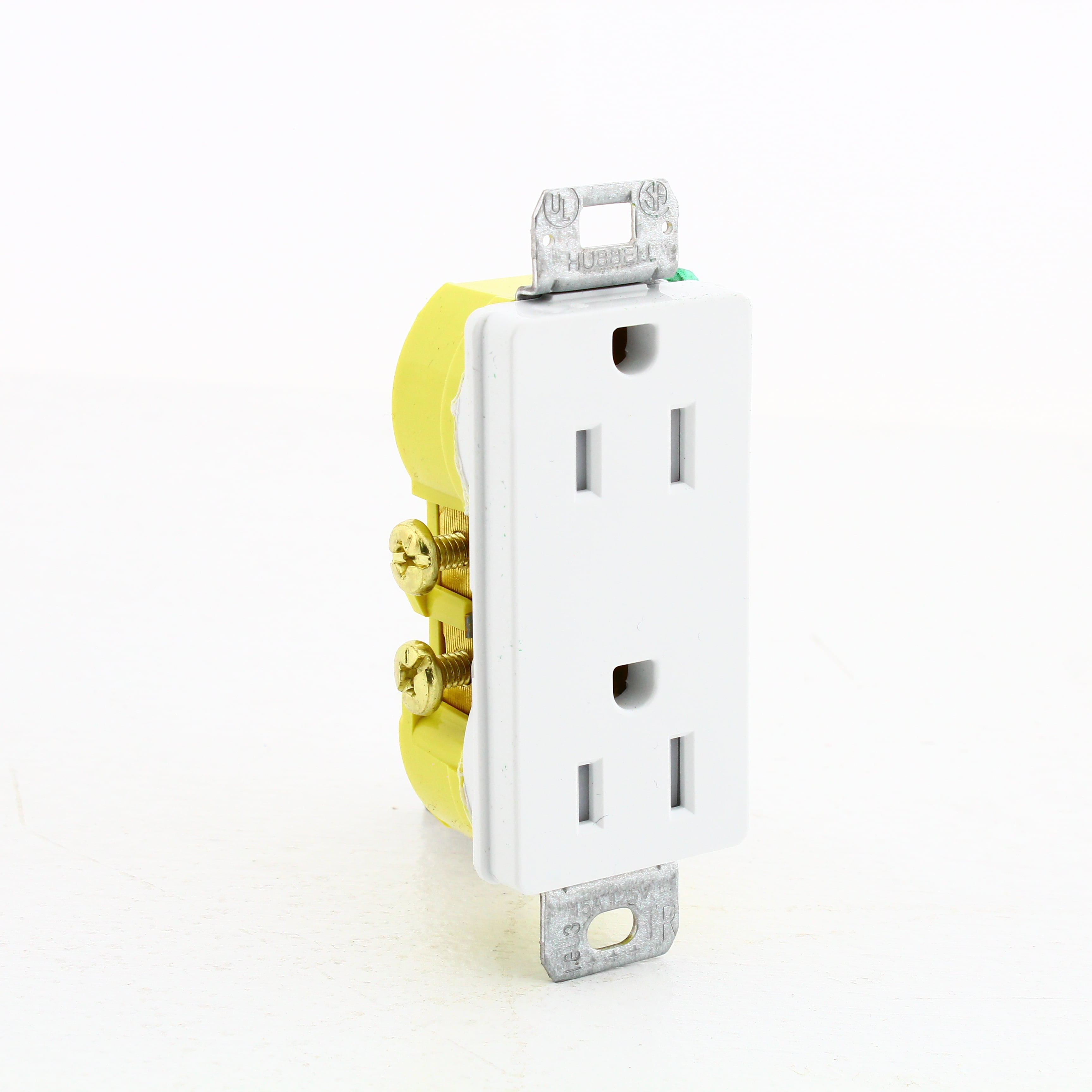
Self-grounding outlets typically feature a metal clip or spring mechanism. This clip ensures consistent and firm contact between the outlet's grounding terminal and the metal mounting bracket. This bracket is connected to the grounded electrical box.
The key is the reliable electrical connection to the grounded box.
Standard non-self-grounding outlets rely solely on the physical contact between the outlet's metal strap and the box, which can be less reliable over time.
How Self-Grounding Outlets Work
When a self-grounding outlet is installed in a properly grounded metal box, the metal clip or spring mechanism on the outlet creates a direct electrical path between the outlet's grounding terminal and the box.
This grounded metal box becomes part of the overall grounding system of the building.
Therefore, if a fault occurs, the current can flow through the outlet to the box and back to the electrical panel.
Benefits of Self-Grounding Outlets
Improved Grounding Reliability: The primary advantage of self-grounding outlets is their ability to provide a more reliable grounding connection compared to standard outlets, especially in situations where the electrical box might not be perfectly grounded.
Enhanced Safety: By ensuring a more reliable ground, these outlets reduce the risk of electrical shock in the event of a fault.
Easier Installation: Some electricians find self-grounding outlets easier to install, as they eliminate the need for separate grounding pigtails in some cases.
Important Considerations
It is crucial to remember that self-grounding outlets only function correctly if the electrical box is itself properly grounded. If the box is not grounded, the self-grounding feature is ineffective, and a shock hazard can still exist.
Wiring errors can also negate the benefits of self-grounding outlets. Always consult with a qualified electrician for any electrical work.
Self-grounding outlets are not a substitute for proper grounding practices throughout the entire electrical system.
Code Compliance and Standards
The National Electrical Code (NEC) outlines specific requirements for grounding electrical systems. While self-grounding outlets can contribute to code compliance, they must be installed according to the NEC and local electrical codes.
Local jurisdictions may have specific interpretations and amendments to the NEC.
Consult with local building inspectors or qualified electricians to ensure compliance with all applicable regulations.
Potential Impact and Significance
Self-grounding outlets represent a relatively small but important advancement in electrical safety. While not a revolutionary technology, their ability to enhance grounding reliability contributes to a safer electrical environment in both residential and commercial buildings.
Their use can reduce the risk of electrical shock and equipment damage.
By understanding the function and limitations of self-grounding outlets, homeowners and electricians can make informed decisions about their use in electrical installations.
Conclusion
Self-grounding outlets offer a valuable feature for improving the reliability of grounding connections in electrical systems. While they do not replace the need for a properly grounded electrical system, they can enhance safety and simplify installation in certain situations.
Understanding their purpose and limitations is crucial for ensuring electrical safety and code compliance.
Always prioritize safety and consult with a qualified electrician for any electrical work. Never compromise on safety when dealing with electricity.