What Is One Benefit To Measuring Your Body's Flexibility
In an era increasingly focused on holistic well-being, individuals are constantly seeking methods to enhance their physical and mental health. Among the various metrics people track, body flexibility often takes a back seat to strength and cardiovascular fitness. However, regularly assessing and improving your flexibility offers a significant, often overlooked benefit: enhanced injury prevention.
While flexibility might seem like a nice-to-have rather than a necessity, understanding its role in your physical health, particularly concerning injury risk, is critical. This article explores how measuring your flexibility contributes to proactive injury prevention and overall physical well-being.
Understanding Flexibility and Its Importance
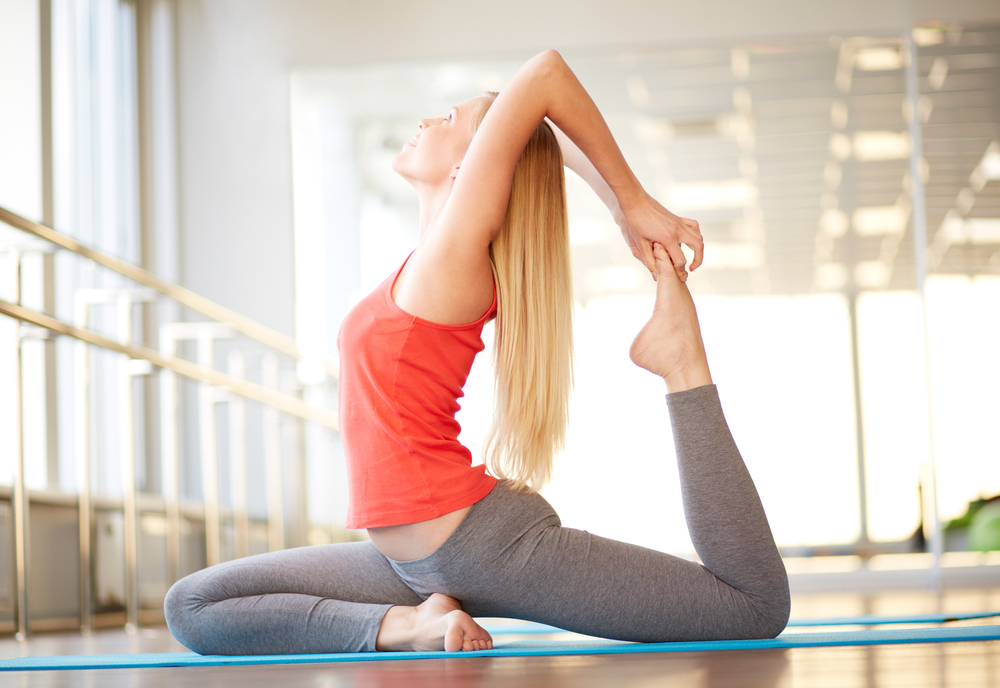
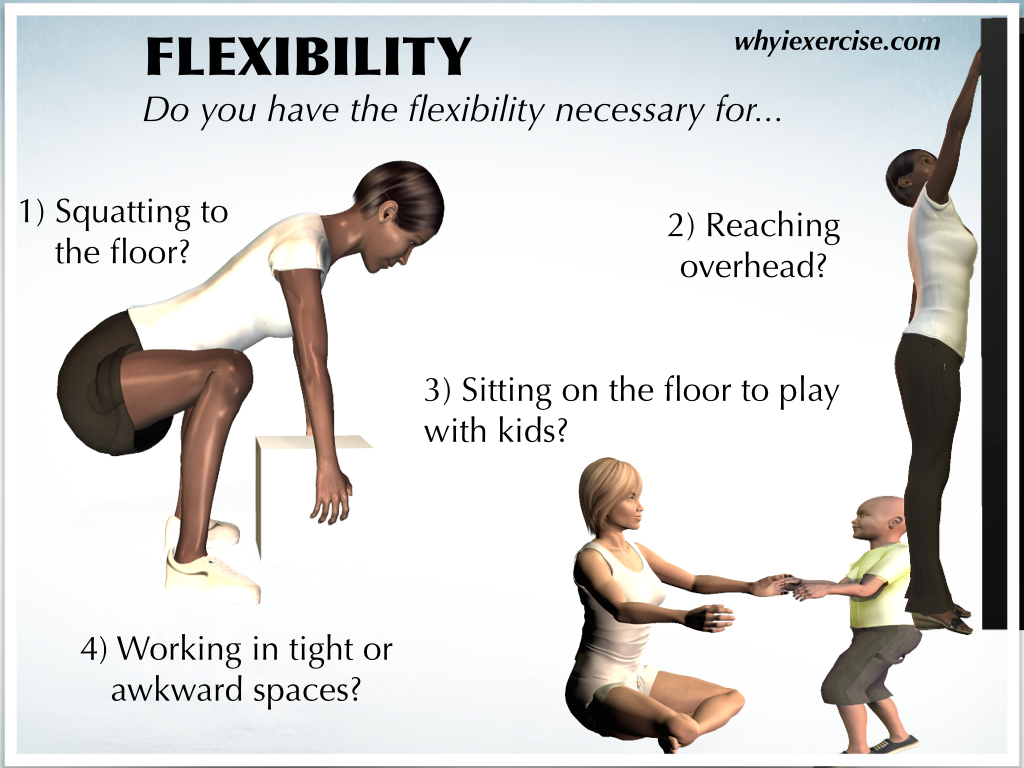
Flexibility refers to the range of motion available at a joint or series of joints. It's influenced by various factors, including muscle elasticity, joint structure, and nervous system activity. Improving flexibility involves stretching exercises that lengthen muscles and increase joint mobility.
Reduced flexibility can lead to muscle imbalances, restricted movement patterns, and increased stress on joints. This, in turn, elevates the risk of injuries, especially during physical activities and even in everyday movements.
The Link Between Flexibility and Injury Prevention
The primary benefit of measuring flexibility lies in its ability to identify potential risk areas before an injury occurs. By assessing the range of motion in key joints like the shoulders, hips, and hamstrings, individuals can pinpoint areas of tightness or limitation.
For example, tight hamstrings can contribute to lower back pain and increase the likelihood of hamstring strains during exercise. Measuring hamstring flexibility can alert individuals to this issue, allowing them to implement targeted stretching exercises to address the imbalance.
Furthermore, improved flexibility allows for more efficient and controlled movements. When muscles are flexible and joints have a full range of motion, the body can move with greater ease and coordination. This reduces the likelihood of awkward movements or compensations that can lead to injuries.
How to Measure Your Flexibility
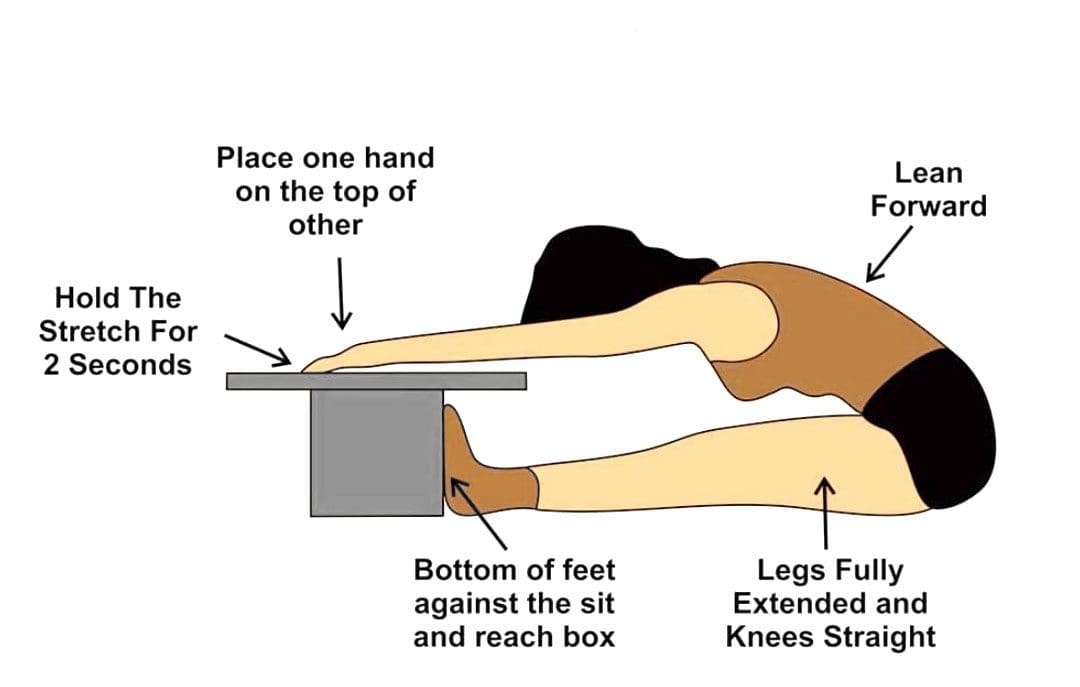
Several methods exist for measuring flexibility, ranging from simple self-assessments to more sophisticated techniques performed by professionals. The sit-and-reach test, a common measure of hamstring and lower back flexibility, is easily performed at home with a ruler or measuring tape.
Other assessments include shoulder flexibility tests, which evaluate the range of motion in the shoulder joint, and hip flexibility tests, which assess the mobility of the hip flexors and surrounding muscles. These assessments often involve simple movements and observations of range of motion.
For a more comprehensive evaluation, consulting a physical therapist or certified athletic trainer is advisable. These professionals can perform a detailed assessment of flexibility and identify specific areas of concern.
Implementing Flexibility Training
Once you've identified areas where your flexibility is limited, implementing a regular stretching routine is crucial. Static stretching, which involves holding a stretch for a period of time (typically 15-30 seconds), is an effective way to improve muscle length and joint mobility.
Dynamic stretching, which involves controlled movements through a full range of motion, is also beneficial. Dynamic stretches prepare the body for activity by increasing blood flow to the muscles and improving joint lubrication.
Yoga and Pilates are excellent modalities for enhancing flexibility and overall body awareness. These practices incorporate a variety of stretches and movements that promote flexibility, strength, and balance.
The Broader Impact of Improved Flexibility
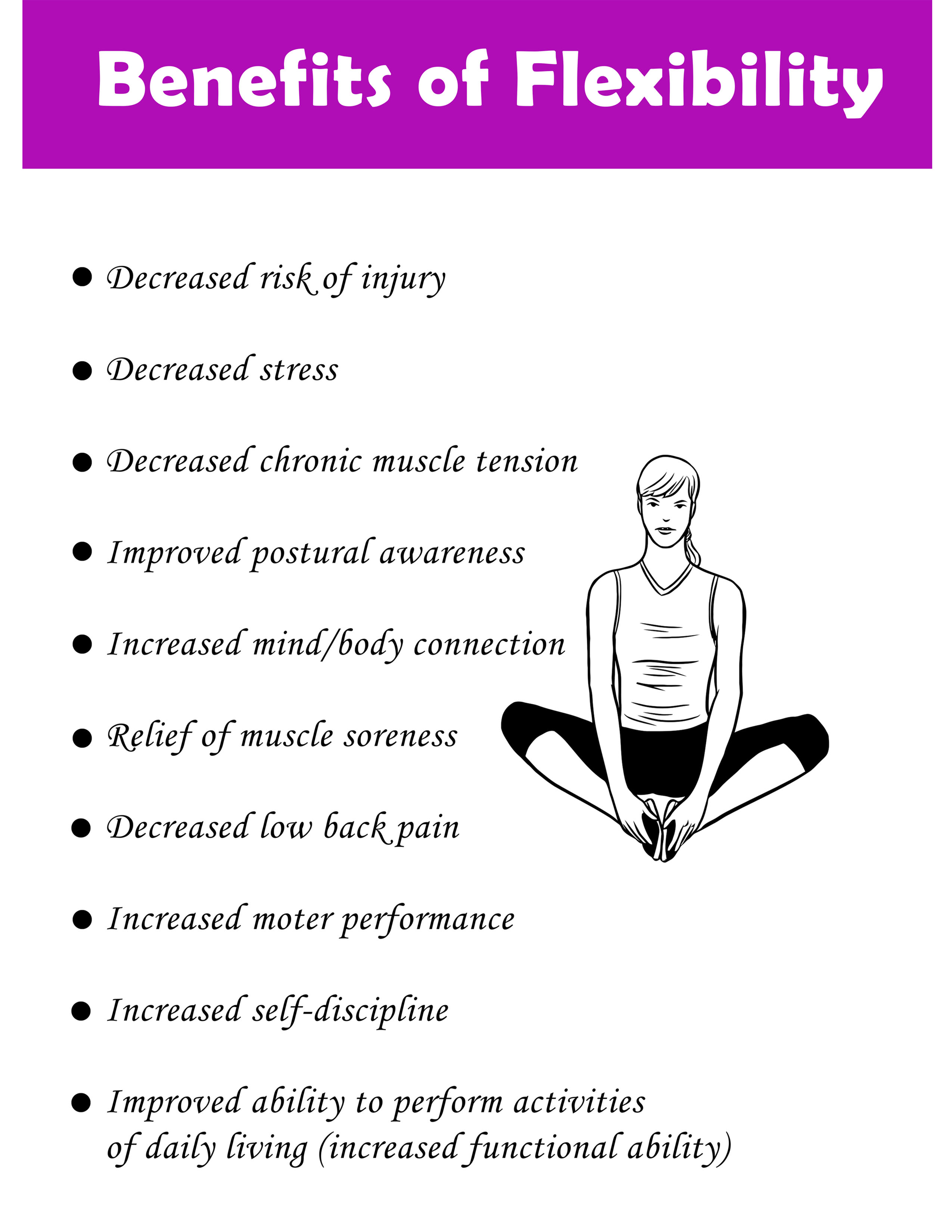
The benefits of measuring and improving flexibility extend beyond injury prevention. Enhanced flexibility can also improve posture, reduce muscle soreness, and enhance athletic performance. It can also contribute to a greater sense of body awareness and overall well-being.
According to the American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM), regular stretching is an important component of a well-rounded fitness program. The ACSM recommends performing flexibility exercises at least two to three times per week.
For older adults, maintaining flexibility is particularly important for preserving mobility and independence. Reduced flexibility can make everyday tasks, such as bending over or reaching for objects, more difficult and increase the risk of falls.
A Personal Perspective
Sarah Miller, a 45-year-old avid runner, shared her experience: "I used to dismiss stretching as unnecessary, until I developed a persistent knee pain. After seeing a physical therapist, I realized my tight hamstrings were contributing to the problem. Now, I regularly measure my flexibility and incorporate stretching into my routine. My knee pain has significantly improved, and I feel much more comfortable running."
Miller's experience highlights the importance of proactive flexibility management. By identifying and addressing flexibility limitations, individuals can prevent injuries and maintain an active lifestyle.
Conclusion
Measuring your body's flexibility offers a tangible pathway to injury prevention and improved physical well-being. By identifying areas of tightness or limitation, individuals can implement targeted stretching exercises to restore balance and reduce the risk of injuries.
Incorporating flexibility assessments and training into a regular fitness routine is a proactive step towards a healthier, more resilient body. Don't underestimate the power of flexibility – it's a key ingredient for a long and active life.
Remember to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new exercise program. Their guidance can ensure that your flexibility routine is safe and effective for your individual needs.