What Is The End Product Of Carbohydrate Digestion
Urgent health advisory: Millions are unaware of the critical final product of carbohydrate digestion, impacting energy levels and overall well-being.
This article cuts through the complex science to deliver the essential information you need to understand how your body fuels itself. Ignorance of this process can lead to dietary mismanagement and related health problems.
The Endpoint: Glucose
The final product of carbohydrate digestion is primarily glucose. This simple sugar is the body's preferred energy source.
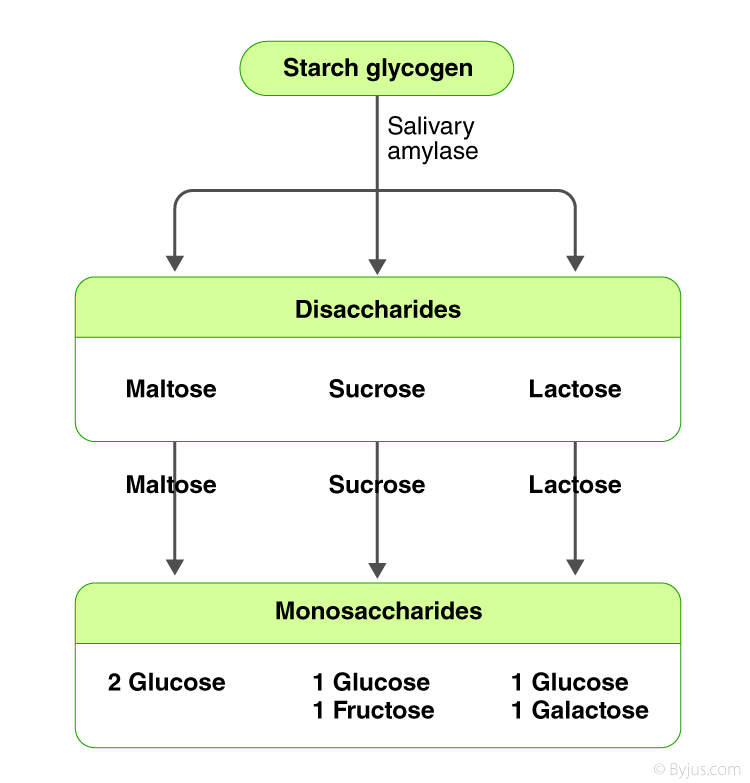
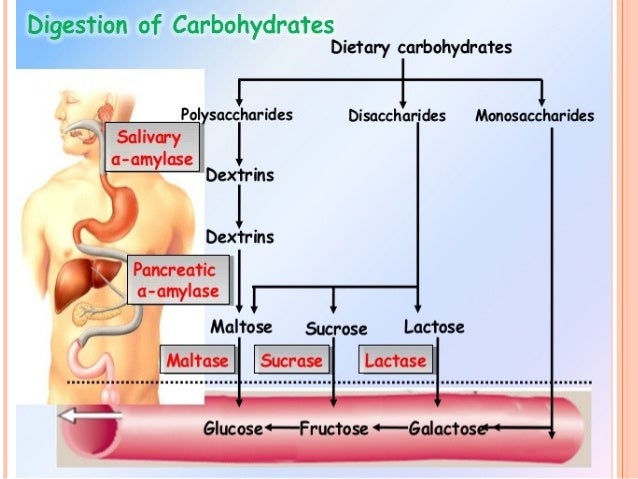
Carbohydrates, whether complex or simple, are broken down into smaller units during digestion. This process culminates in the formation of glucose, fructose, and galactose. However, fructose and galactose are converted to glucose in the liver.
Therefore, glucose is the key end product that fuels our cells.
The Digestive Process Unpacked
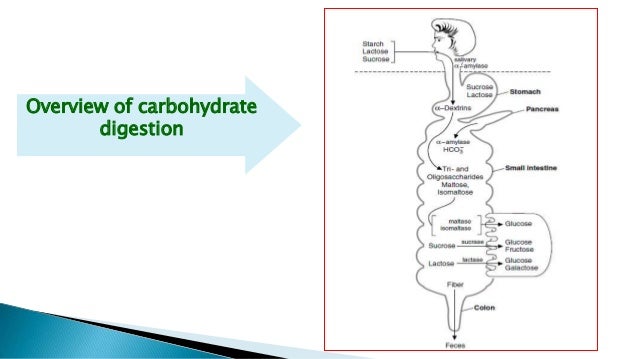
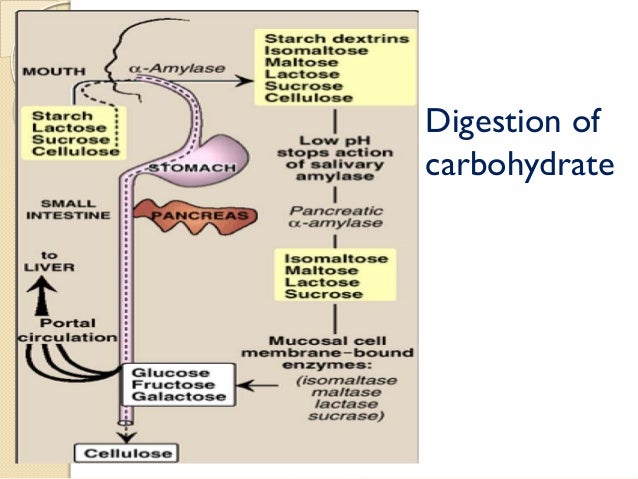
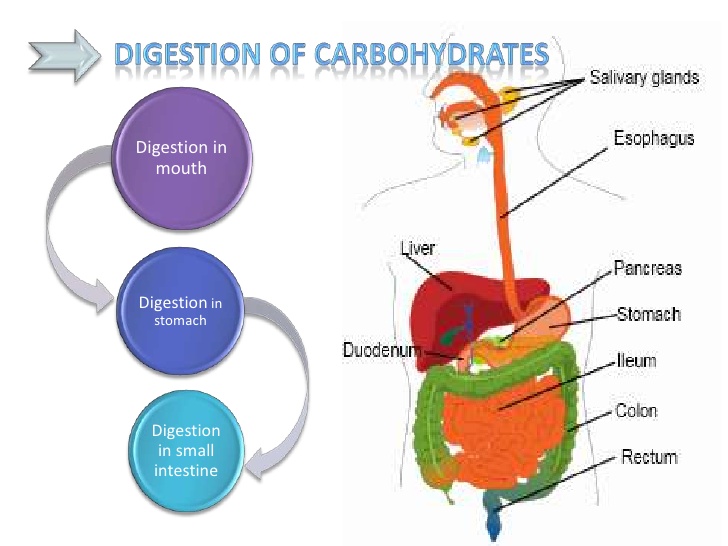
The breakdown of carbohydrates begins in the mouth. Salivary amylase starts the initial digestion of starches.
The process continues in the small intestine. Pancreatic amylase further breaks down carbohydrates into disaccharides.
Enzymes like sucrase, lactase, and maltase then convert disaccharides into glucose, fructose, and galactose. These are absorbed into the bloodstream.
Where Does Absorption Occur?
Carbohydrate absorption primarily occurs in the small intestine, specifically the jejunum and ileum. Specialized cells lining the intestinal wall facilitate this process.
Once absorbed, glucose enters the bloodstream. It's then transported to cells throughout the body.
The liver plays a vital role in regulating glucose levels. It converts fructose and galactose into glucose.
How is Glucose Utilized?
Cells use glucose for immediate energy. This energy powers various bodily functions.
Excess glucose is stored as glycogen in the liver and muscles. This serves as a readily available energy reserve.
When glycogen stores are full, excess glucose is converted into fat. This fat is stored for long-term energy needs.
Who Needs to Know This?
Everyone needs to understand this process. Knowledge empowers informed dietary choices.
Individuals with diabetes must closely monitor their glucose levels. It helps to control blood sugar.
Athletes can optimize carbohydrate intake. They will need it for enhanced performance and recovery.
Impact of Understanding Glucose Metabolism
Understanding glucose metabolism helps prevent dietary imbalances. This may include excessive sugar consumption.
It allows for better management of chronic conditions. This includes diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
Informed dietary choices can improve overall health. This includes weight management and energy levels.
Potential Problems and Solutions
Consuming too many simple carbohydrates can lead to rapid spikes in glucose. This could result in energy crashes and insulin resistance.
Prioritize complex carbohydrates and fiber-rich foods. They provide a steady release of glucose.
Regular exercise improves glucose utilization. It helps maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
The Role of Fiber
Fiber slows down the absorption of glucose. This leads to a more gradual rise in blood sugar.
Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains in your diet. This ensures adequate fiber intake.
Fiber also promotes gut health. A healthy gut can improve carbohydrate metabolism.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Consult a healthcare professional if you experience persistent symptoms. These symptoms include fatigue, excessive thirst, or frequent urination.
These symptoms may indicate issues with glucose metabolism. Early intervention is crucial.
Regular blood sugar testing is recommended. Especially for individuals at risk of diabetes.
Dr. Emily Carter, a leading endocrinologist, emphasizes the importance of understanding carbohydrate digestion. She states that “A basic knowledge of how our bodies process carbohydrates is crucial for maintaining optimal health.”
According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), proper carbohydrate management is essential for preventing chronic diseases. These include type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
Next Steps
Monitor your carbohydrate intake and prioritize complex carbohydrates. Maintain a balanced diet with adequate fiber.
Stay informed about ongoing research into carbohydrate metabolism and related health conditions. Consult with healthcare professionals for personalized dietary advice.
Further research is underway to optimize carbohydrate intake. It aims to improve health outcomes and manage chronic diseases.