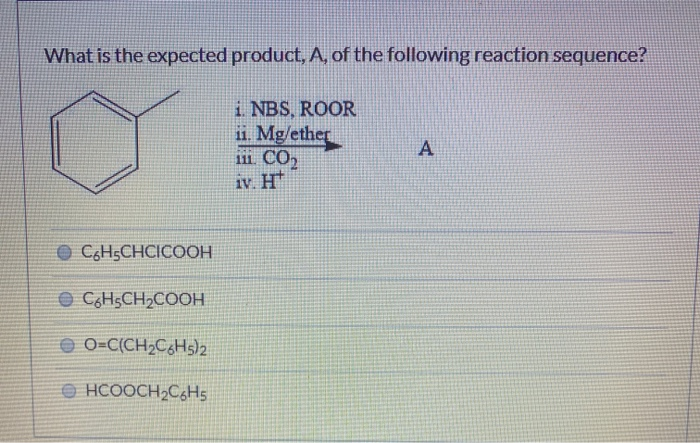
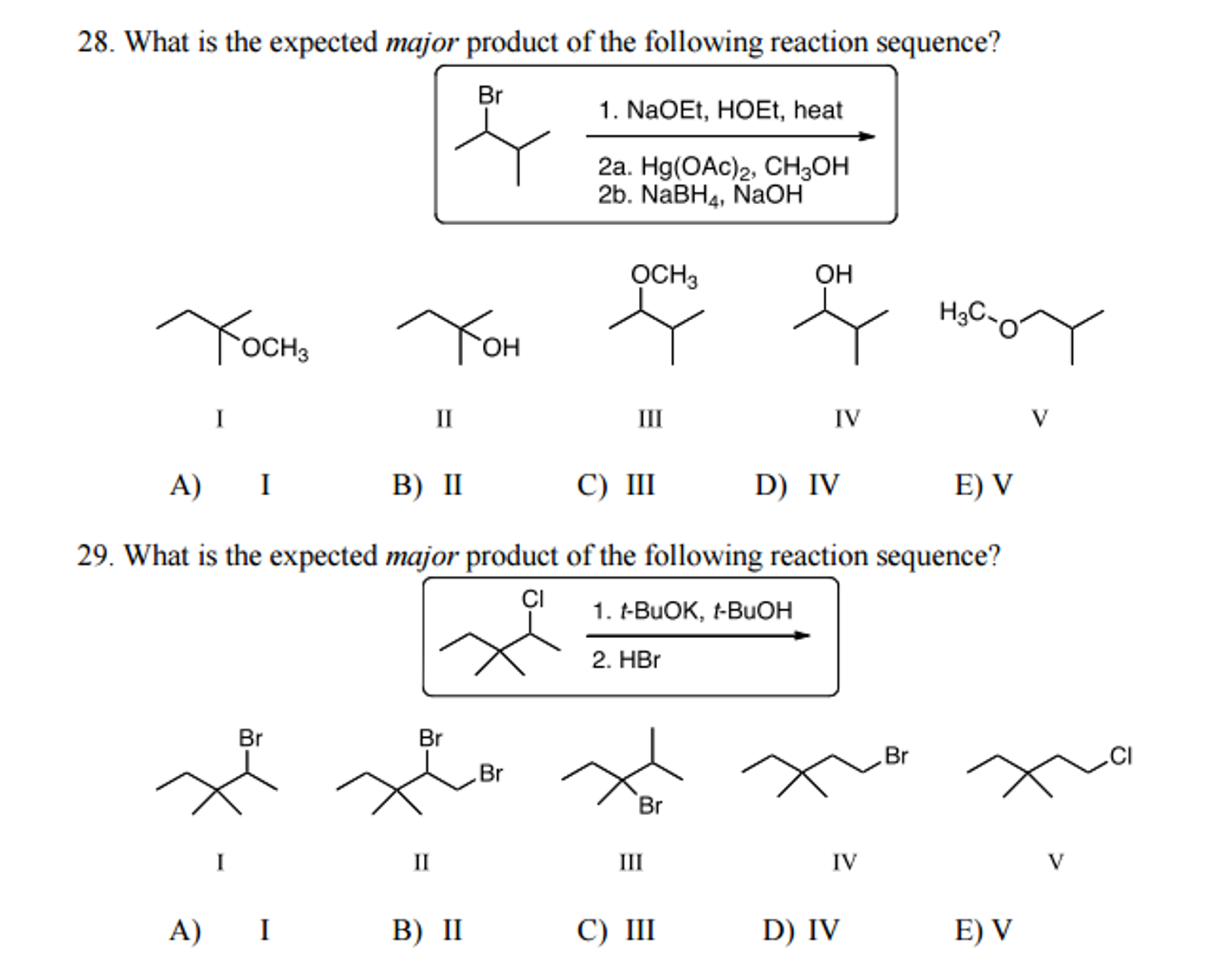
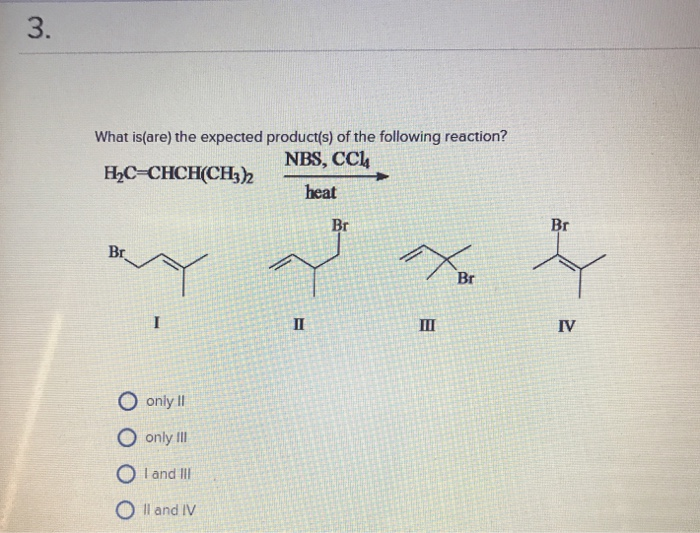
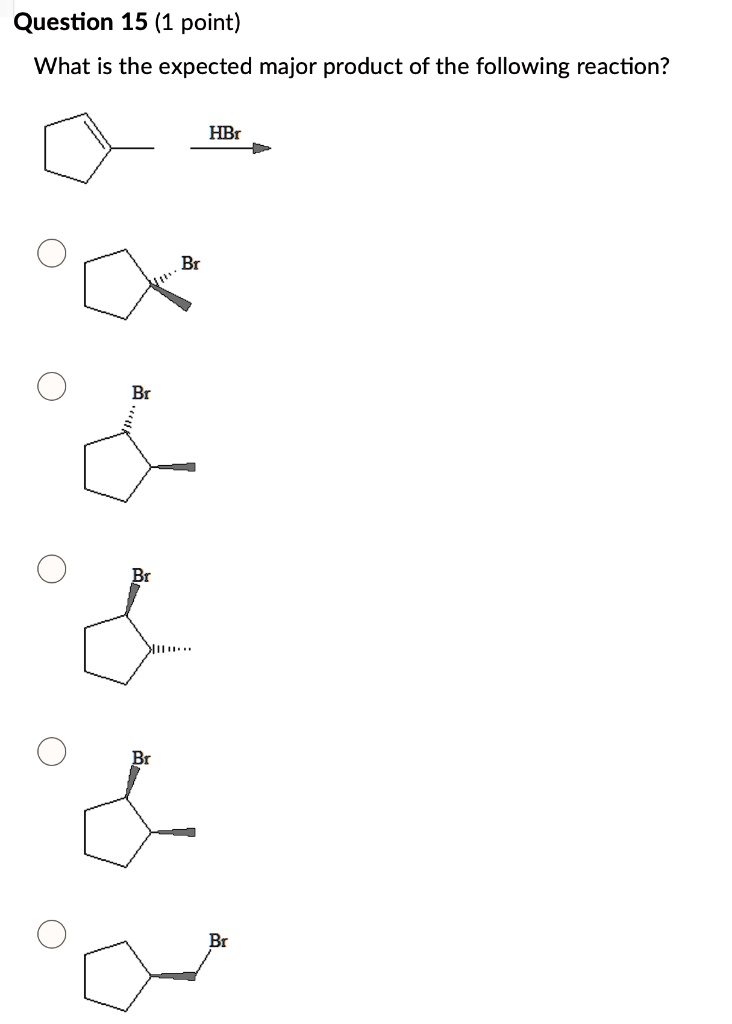
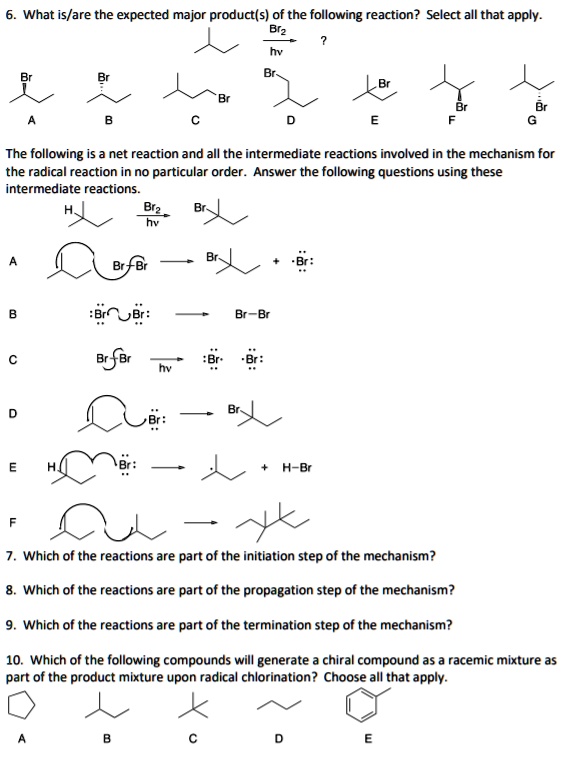
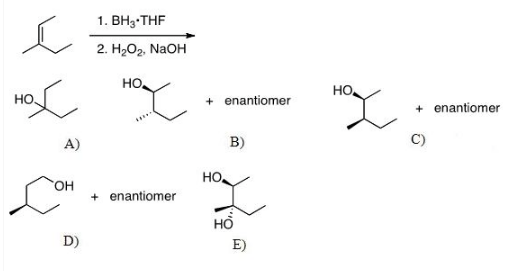
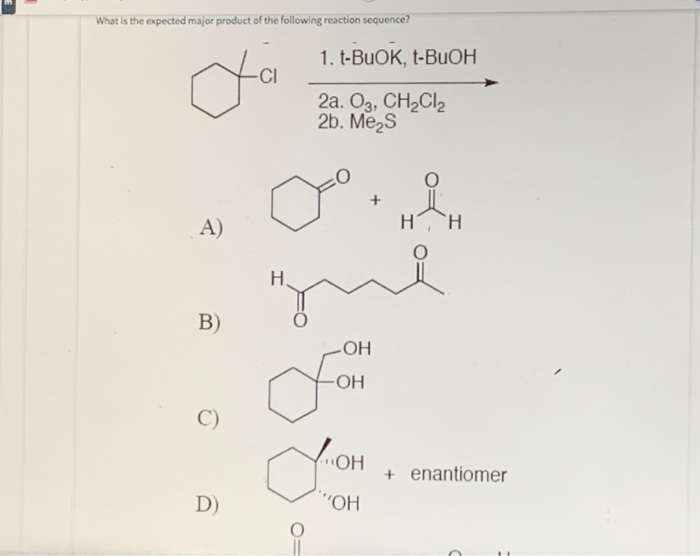
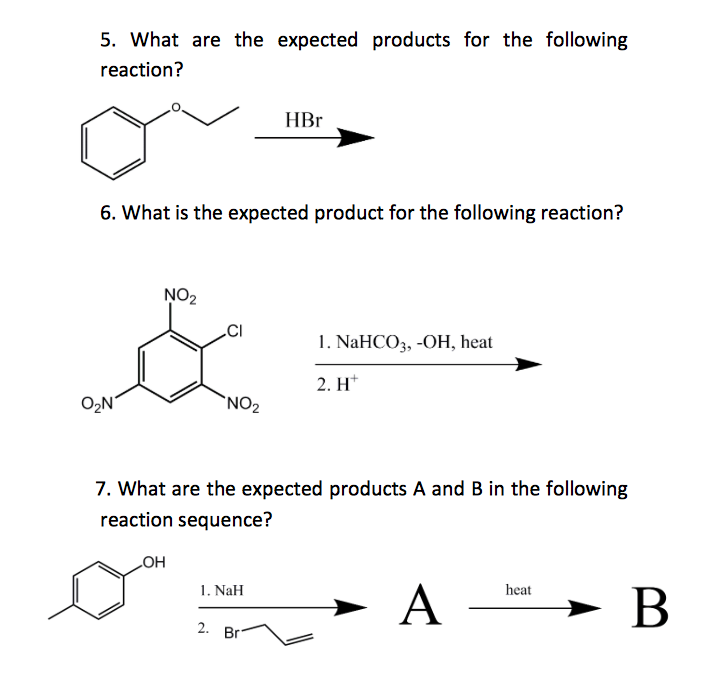
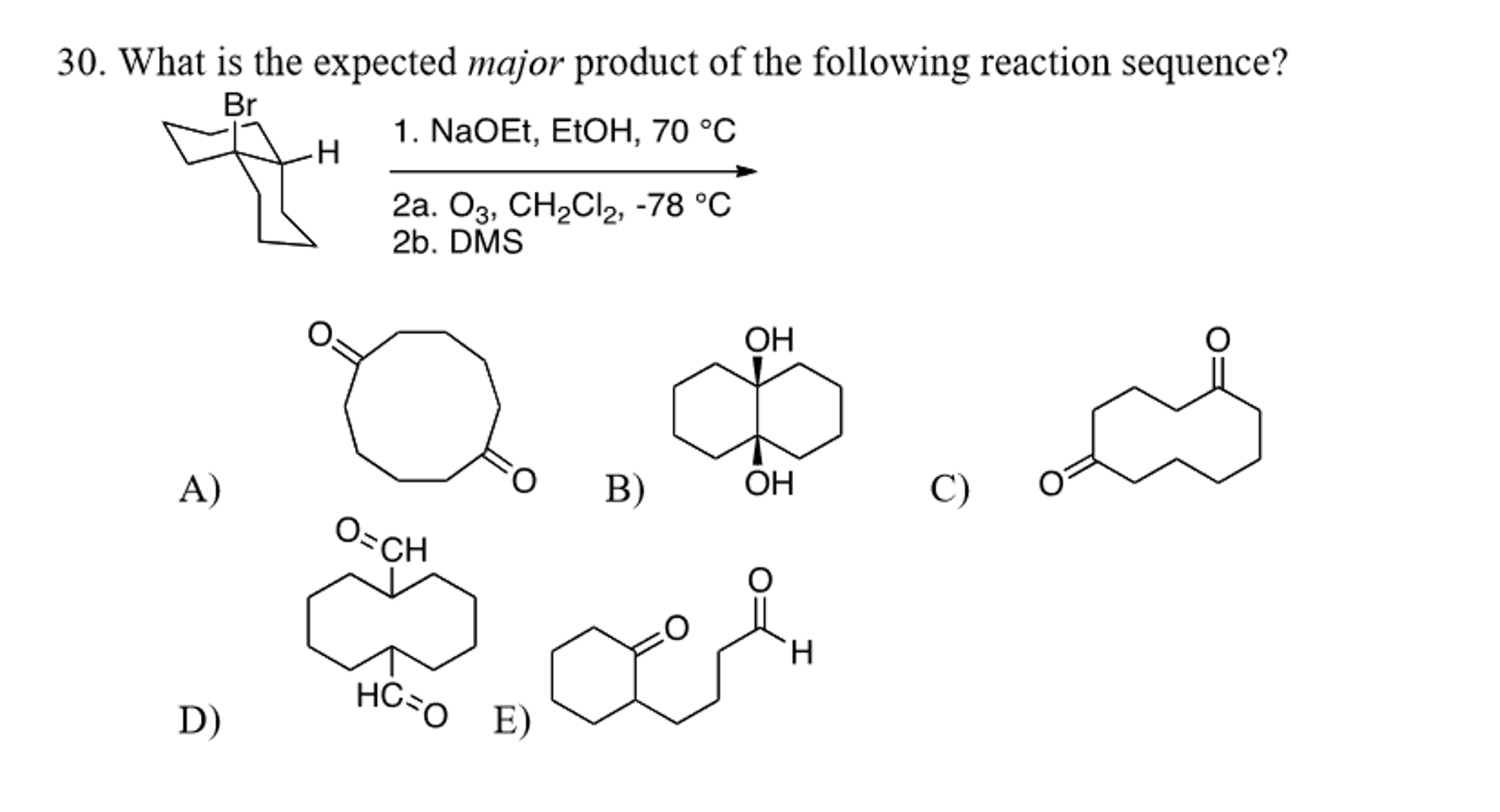
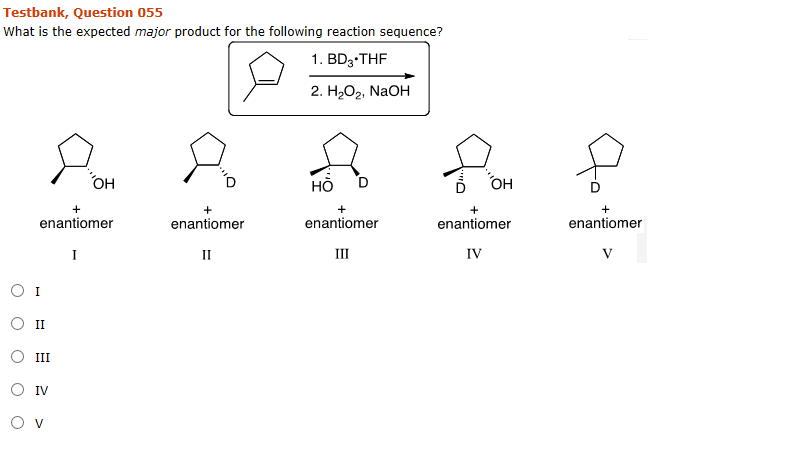
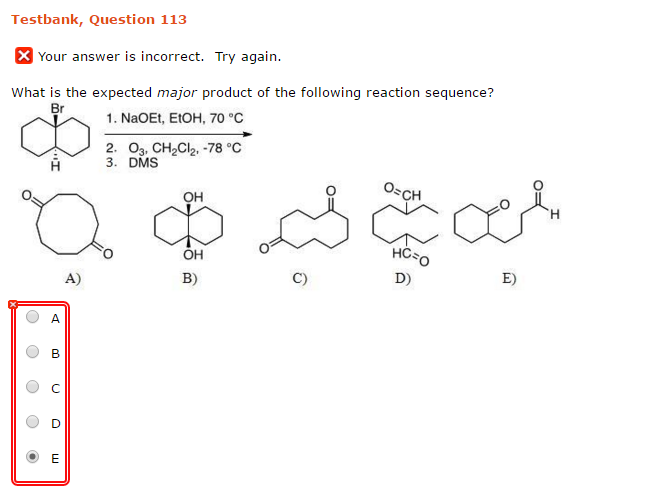
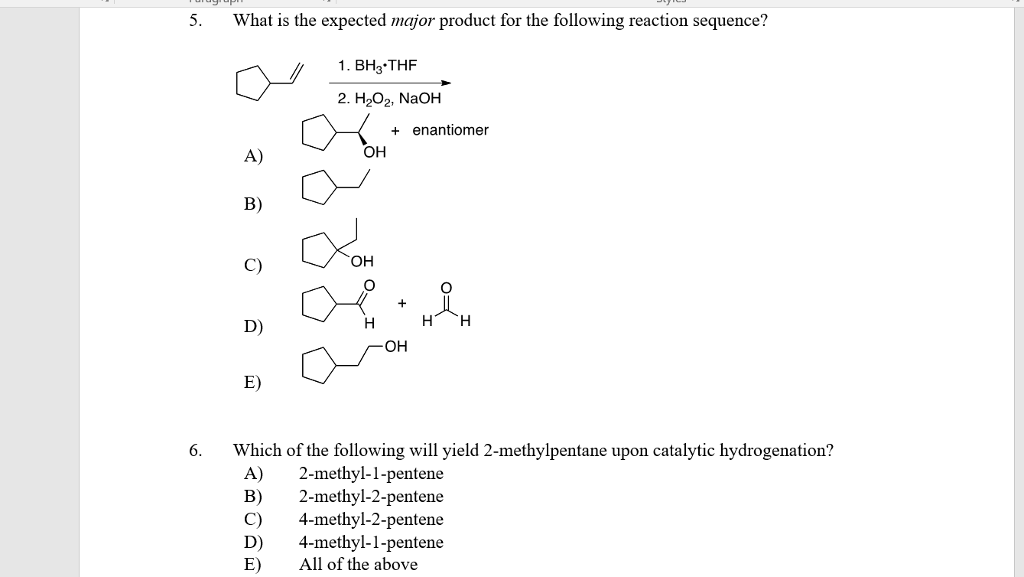
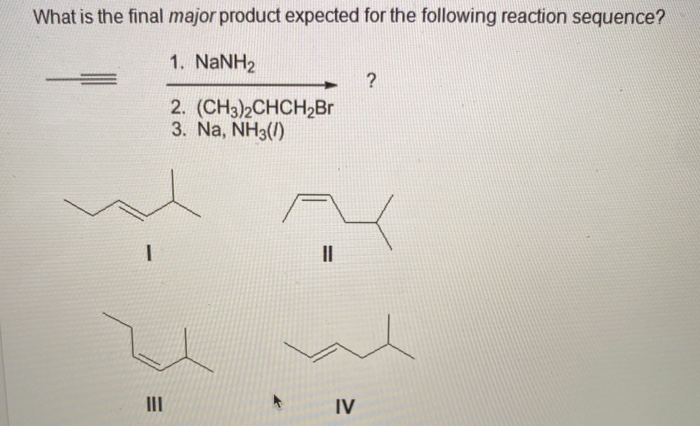
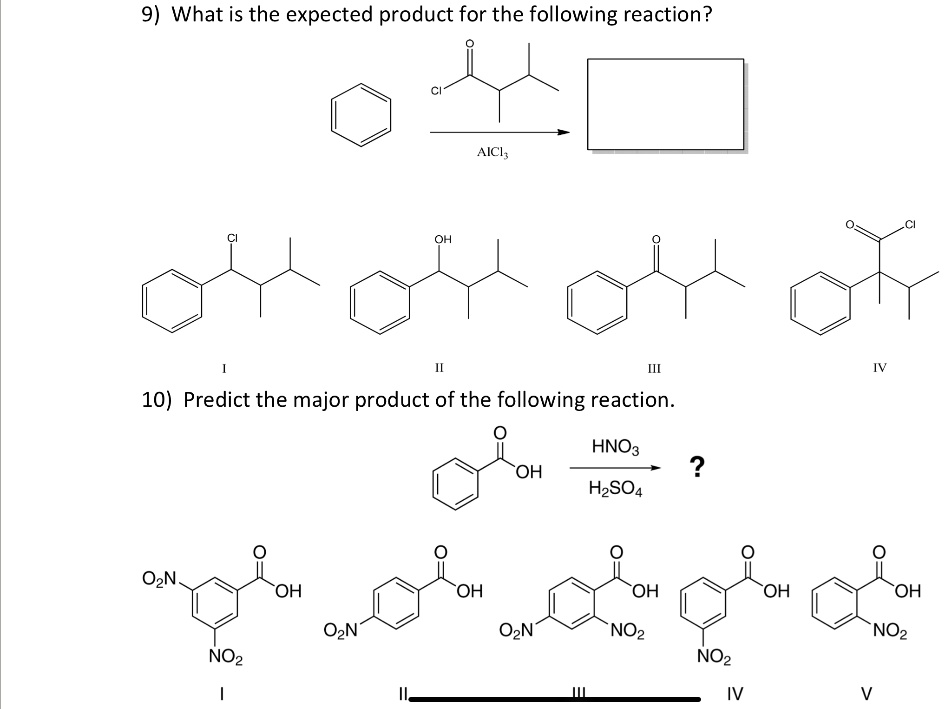
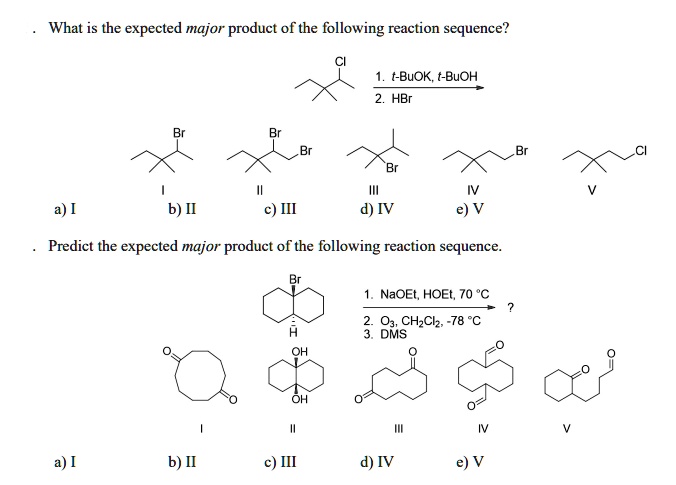
What Is The Expected Product Of The Following Reaction
The chemical reaction between sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and hydrochloric acid (HCl) is a cornerstone of introductory chemistry, but understanding the nuanced implications of its product remains vital across scientific disciplines.
This seemingly simple acid-base neutralization reaction carries significant weight in fields ranging from industrial manufacturing to environmental science. This article delves into the expected products of this reaction, its implications, and why it continues to be a critical concept in various sectors.
Understanding the Basics
The reaction involves NaOH, a strong base, and HCl, a strong acid. When these two substances are mixed in a solution, a chemical reaction occurs. The fundamental process involves the hydrogen ions (H+) from HCl reacting with the hydroxide ions (OH-) from NaOH.
This leads to the formation of water (H2O) and sodium chloride (NaCl), commonly known as table salt. The balanced chemical equation for the reaction is: NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O.
Key Components and Their Roles
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is a highly caustic metallic base and alkali metal hydroxide. It is used in many industries, mostly as a strong chemical base in the manufacturing of pulp and paper, textiles, drinking water, soaps and detergents and as a drain cleaner.
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) is a clear, colorless, highly pungent solution of hydrogen chloride (HCl) in water. It is a highly corrosive strong acid with many industrial uses. It's found naturally in gastric acid.
The Expected Products: Sodium Chloride and Water
The reaction produces sodium chloride (NaCl), a neutral salt formed from the cation of the base (Na+) and the anion of the acid (Cl-). Water (H2O) is the other product, resulting from the combination of hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions.
The resulting solution will be neutral if the acid and base are present in stoichiometric amounts. This means the moles of NaOH and HCl are equal.
Implications of the Reaction
The neutralization reaction has significant implications across various sectors. It's a fundamental process in chemical synthesis, waste water treatment, and pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Understanding this reaction is crucial for controlling pH levels in industrial processes and ensuring the safety and efficacy of various products. In environmental remediation, this reaction is utilized to neutralize acidic or alkaline spills to prevent harm to ecosystems.
Applications Across Industries
In the pharmaceutical industry, the precise control of pH using this reaction is vital for drug formulation and stability. Waste water treatment plants employ neutralization techniques to ensure that effluent meets regulatory standards before being released into the environment.
The food industry also uses this reaction in controlled settings. For example, it can be used in the production of certain food additives and preservatives.
Quantifying the Reaction: Titration
The reaction is also a key part of acid-base titration experiments. Titration is a quantitative chemical analysis used to determine the concentration of an unknown acid or base by neutralizing it with a known concentration of another acid or base.
The reaction between NaOH and HCl is commonly used as a standard for demonstrating and teaching titration techniques. Students and researchers use indicators or pH meters to identify the equivalence point, where the acid and base have completely neutralized each other.
Potential Impact and Considerations
The products, NaCl and H2O, are generally considered safe when produced in controlled conditions. However, the reaction itself can generate heat and, if not properly managed, could lead to dangerous situations.
Handling concentrated solutions of NaOH and HCl requires appropriate safety measures, including wearing protective gear and working in well-ventilated areas. Improper handling can result in chemical burns and other health hazards.
Environmental Concerns
While the products themselves are relatively benign, the process can have environmental implications if not managed properly. The disposal of large volumes of the resulting solution, especially if it contains impurities, must adhere to environmental regulations.
Industries are required to implement waste management practices to minimize environmental impact. This includes proper neutralization, treatment, and disposal of by-products.
Conclusion
The reaction between sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and hydrochloric acid (HCl) produces sodium chloride (NaCl) and water (H2O). This seemingly simple reaction is a fundamental concept with widespread applications in diverse fields.
Its significance ranges from industrial manufacturing and pharmaceutical production to environmental science and waste water treatment. A thorough understanding of this reaction remains crucial for ensuring safety, efficiency, and environmental stewardship in various processes.
By recognizing its key components, implications, and potential impacts, professionals and students alike can contribute to the responsible and effective application of this chemical reaction in numerous aspects of modern life.