What Is The Primary Source Of Fuel For The Brain

The human brain, a complex and energy-demanding organ, powers our thoughts, emotions, and actions. Understanding its primary fuel source is crucial for optimizing cognitive function and overall health. This article delves into the science behind brain energy, examining the role of glucose and other potential fuel sources.
The brain's reliance on a consistent energy supply makes understanding its fuel requirements paramount. Cognitive performance, neurological health, and even mood are significantly affected by the brain's access to its preferred fuel. This article explores the scientific consensus on the primary fuel and investigates alternative energy sources.
The Brain's Sweet Tooth: Glucose as the Primary Fuel
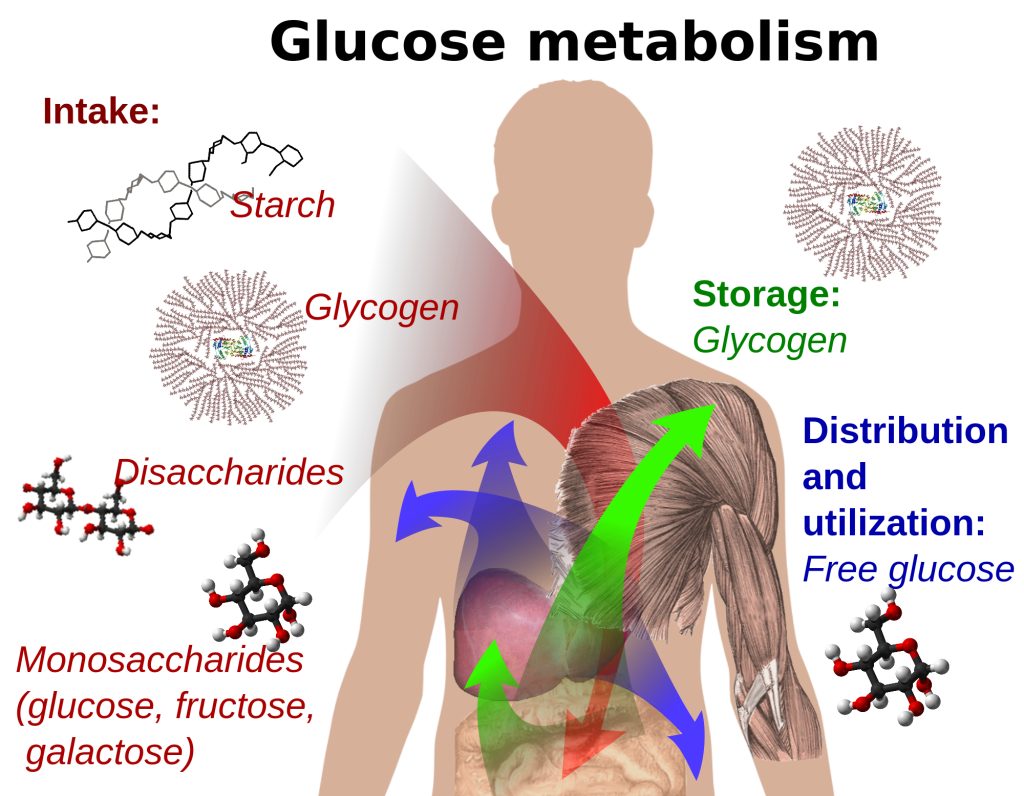
For decades, the scientific community has recognized glucose as the brain's primary fuel source. Glucose, a simple sugar derived from the carbohydrates we consume, is readily transported across the blood-brain barrier.
This barrier, a highly selective membrane, protects the brain from harmful substances while allowing essential nutrients to pass through. Once inside, glucose is metabolized to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the energy currency of cells.
ATP powers neuronal activity, enabling communication between brain cells and supporting various cognitive processes. The brain consumes a disproportionately large amount of energy relative to its size.
Why Glucose Reigns Supreme
Several factors contribute to glucose's dominance as the brain's preferred fuel. Glucose can be metabolized relatively easily and efficiently.
The brain possesses specialized transporters that facilitate the uptake of glucose, ensuring a constant supply even when blood glucose levels fluctuate. While the brain can utilize other fuel sources, glucose remains the most readily available and efficiently used.
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) extensively funds research on glucose metabolism in the brain. Their studies consistently highlight its importance in maintaining optimal brain function.
Alternative Fuel Sources: When Glucose is Scarce
Although glucose is the primary fuel, the brain can adapt and utilize alternative energy sources under certain circumstances. During prolonged fasting or periods of carbohydrate restriction, the body begins to break down fat into fatty acids.
These fatty acids are then converted into ketone bodies in the liver. Ketones, such as beta-hydroxybutyrate, acetoacetate, and acetone, can cross the blood-brain barrier and be used as fuel by brain cells.
This metabolic adaptation is known as ketogenesis, and it provides the brain with an alternative energy source when glucose availability is limited. This is the basis for ketogenic diets which have been investigated for neurological conditions such as epilepsy and Alzheimer's disease.
The Role of Ketones in Brain Health
Research suggests that ketone bodies may offer neuroprotective benefits. Some studies indicate that ketones can improve mitochondrial function, reduce oxidative stress, and enhance neuronal survival.
However, the long-term effects of relying heavily on ketones as the primary brain fuel are still under investigation. The American Academy of Neurology is continuously evaluating the evidence related to ketogenic diets and neurological disorders.
Therefore, while ketones can serve as an alternative fuel, glucose remains the brain's preferred and most efficient energy source under normal circumstances.
Implications for Diet and Cognitive Function
Understanding the brain's fuel preferences has significant implications for dietary choices and cognitive performance. Maintaining stable blood glucose levels is crucial for optimal brain function.
Consuming a balanced diet that includes complex carbohydrates, fiber, and protein helps regulate blood sugar and provides a steady supply of glucose to the brain. Avoiding excessive sugar intake and refined carbohydrates can prevent rapid spikes and crashes in blood glucose, which can negatively impact cognitive function.
The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends limiting added sugar intake to promote overall health and well-being, including brain health. They emphasize the importance of a balanced and nutritious diet.
The Future of Brain Fuel Research
Ongoing research continues to explore the intricacies of brain energy metabolism and the potential benefits of alternative fuel sources. Scientists are investigating the role of specific nutrients and dietary interventions in optimizing brain function and preventing neurodegenerative diseases.
Studies are also examining the interplay between glucose, ketones, and other metabolic pathways in the brain. The goal is to develop targeted strategies to enhance cognitive performance and promote brain health throughout the lifespan.
Ultimately, understanding the brain's fuel preferences is essential for making informed dietary choices and supporting optimal cognitive function.