What Temperature Sensors Are Used With A Commercial Air Handler
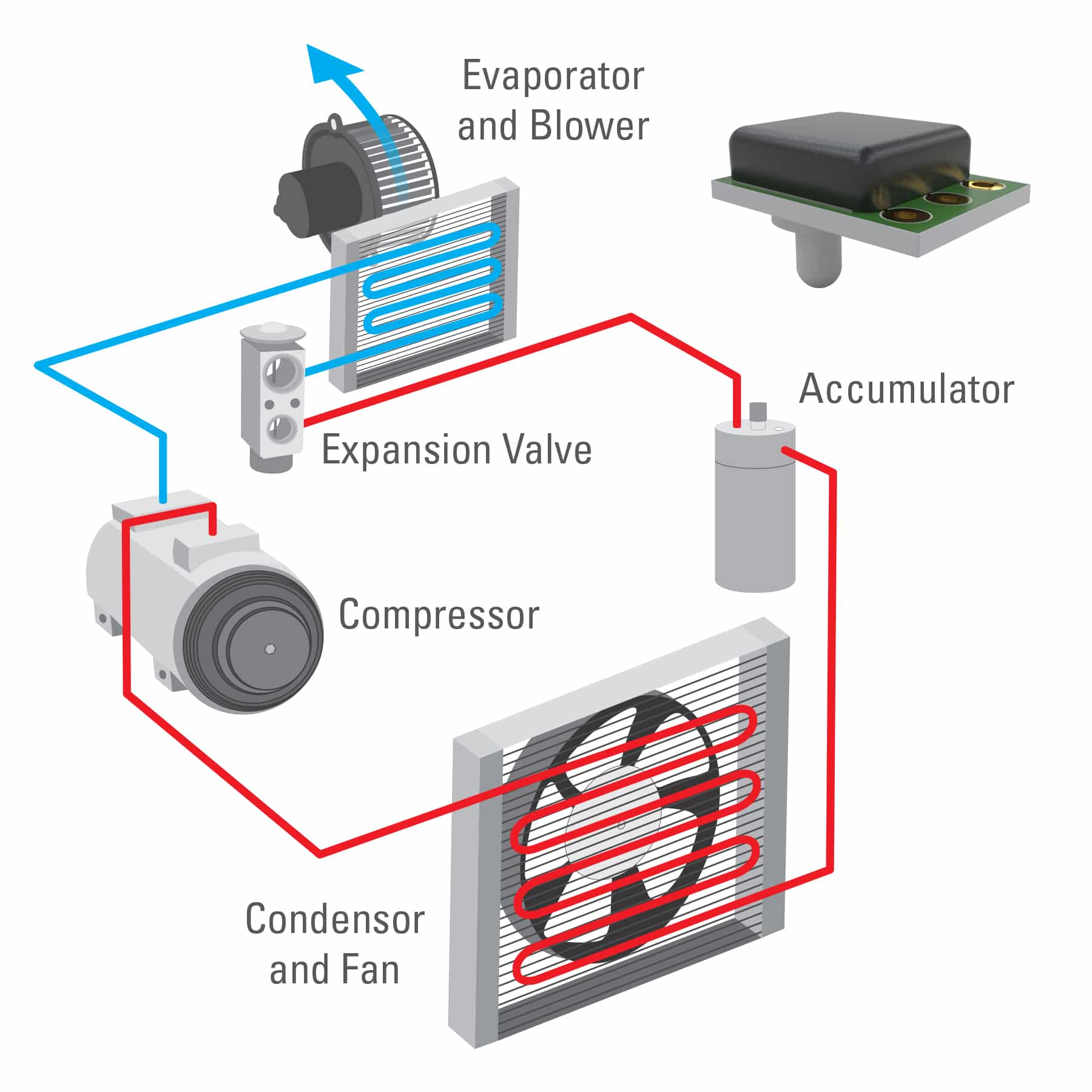
Imagine stepping into a bustling commercial building on a sweltering summer day. The air is crisp, cool, and perfectly comfortable, a stark contrast to the humid chaos outside. This oasis of comfort is no accident; it's the result of a sophisticated air handling system, silently working behind the scenes, constantly monitored and adjusted by an array of temperature sensors, the unsung heroes of indoor climate control.
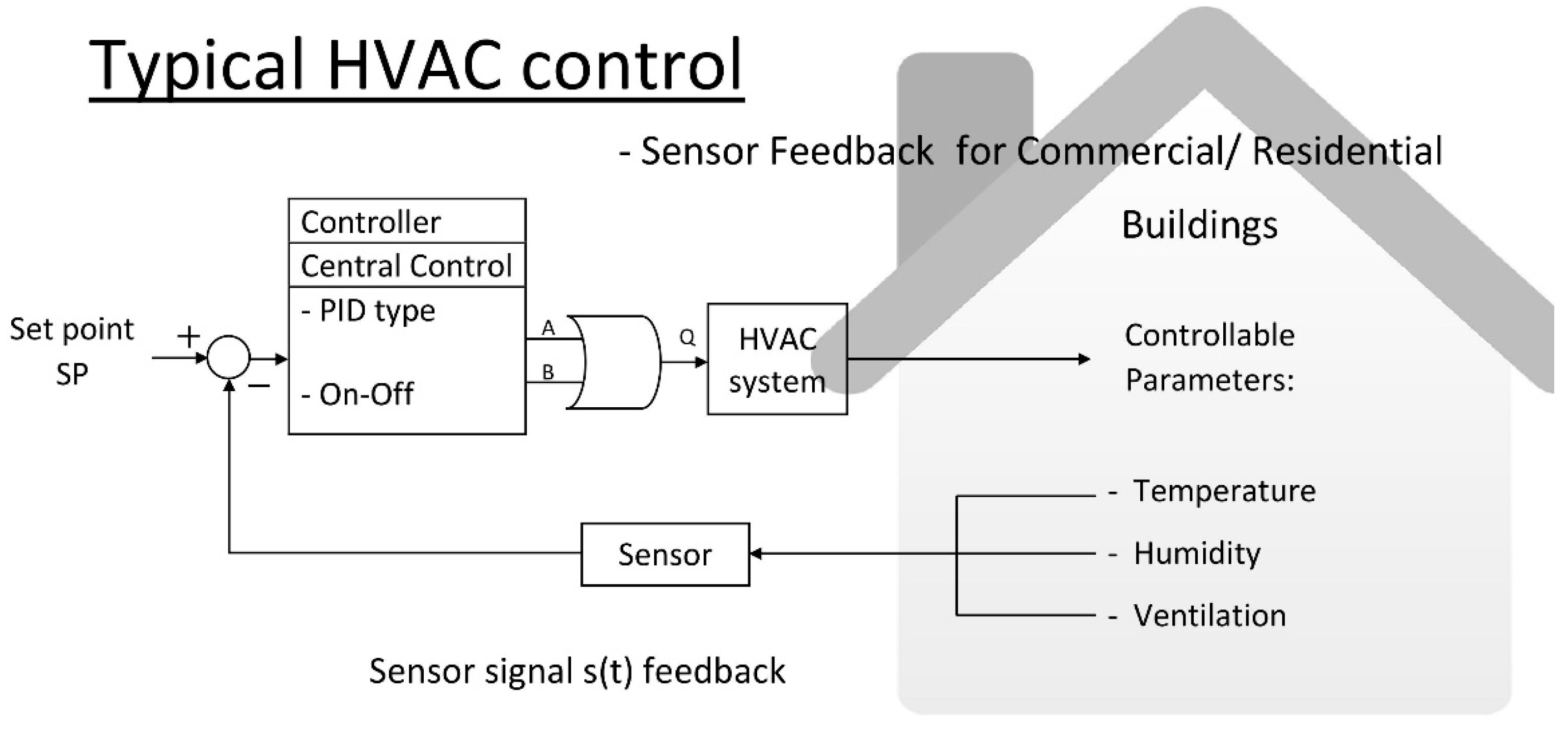
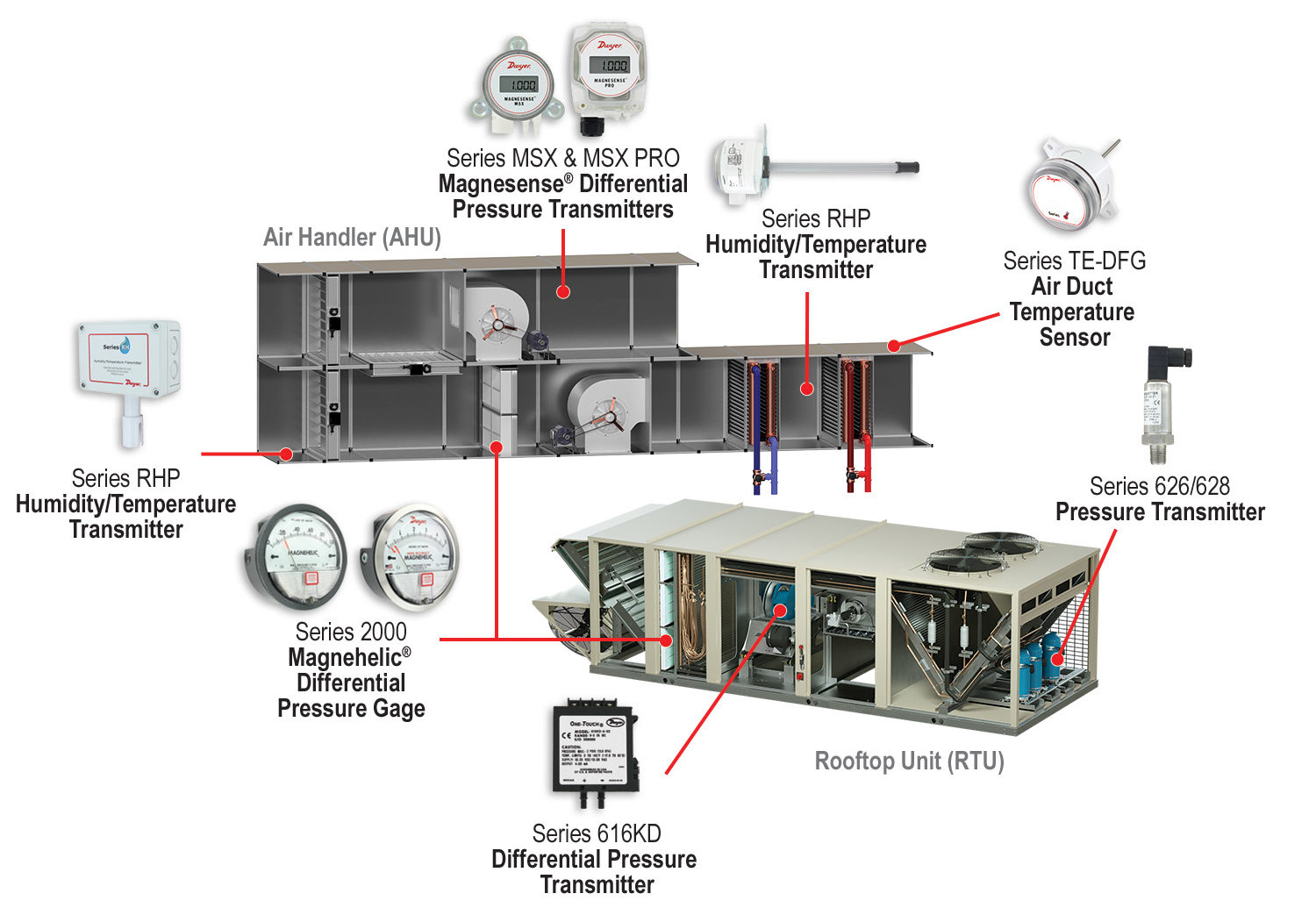
Commercial air handlers rely on a network of temperature sensors to maintain optimal indoor environments. These sensors are critical for energy efficiency, occupant comfort, and the overall performance of the HVAC system, ensuring that spaces remain consistently comfortable, regardless of external conditions.
The Crucial Role of Temperature Sensors
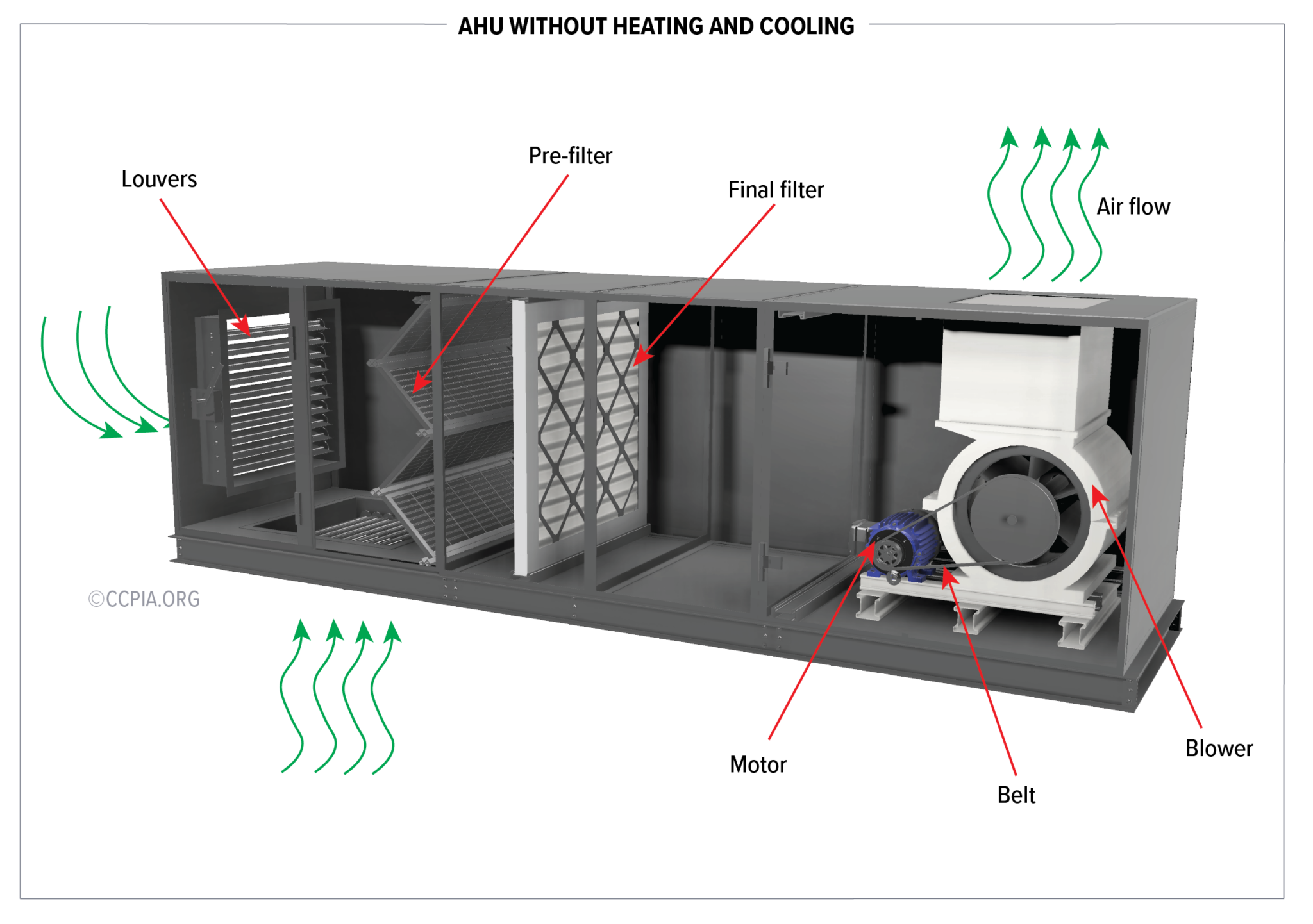
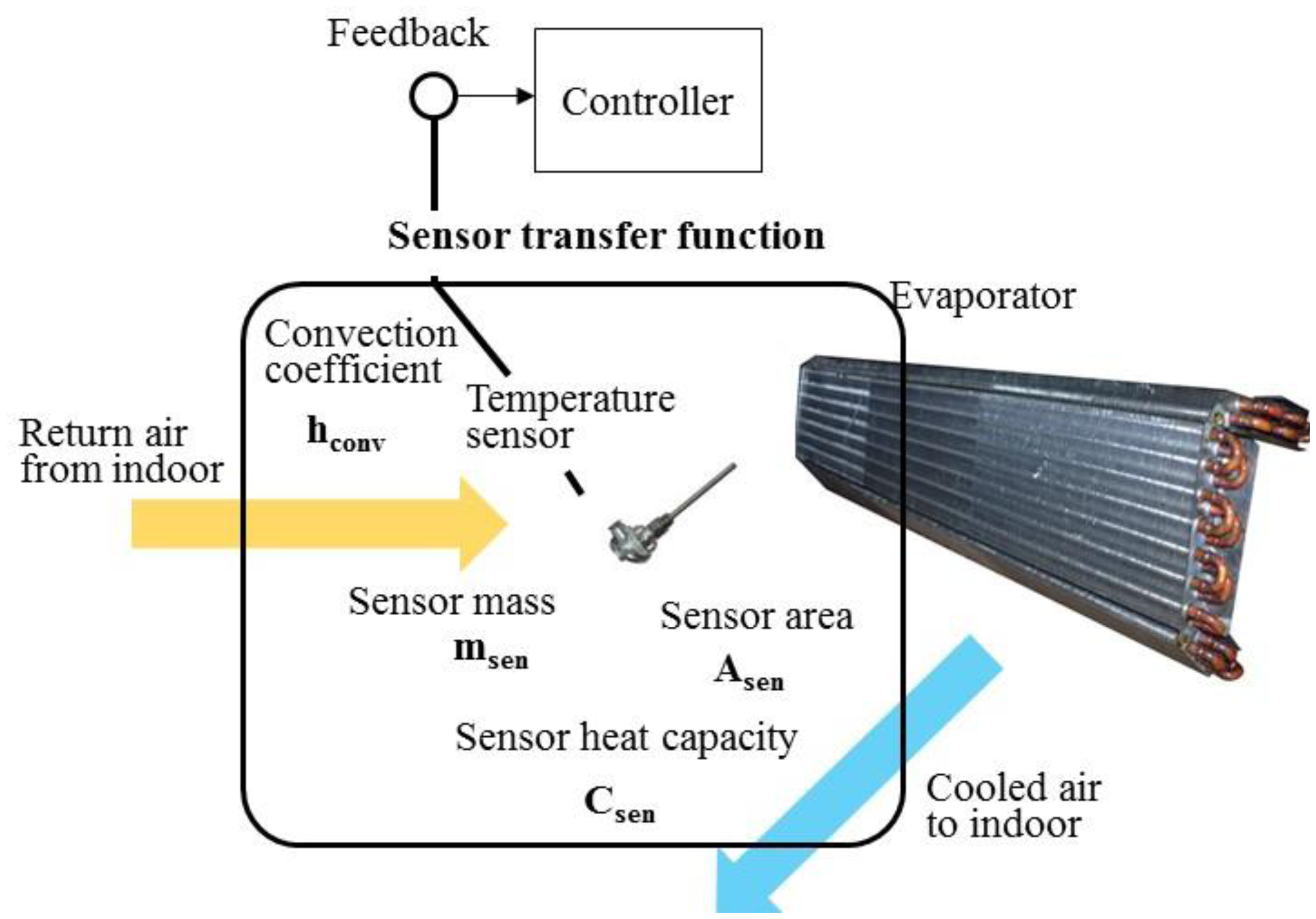
Temperature sensors within a commercial air handler act as the eyes and ears of the system. They provide real-time data that enables the air handler to adjust its operations, ensuring consistent and efficient climate control. This data allows the system to react to changing conditions, such as fluctuating occupancy levels or external temperature shifts.
Without these sensors, an air handler would be essentially blind, unable to respond to the dynamic needs of a building. This leads to energy waste, inconsistent temperatures, and ultimately, unhappy occupants.
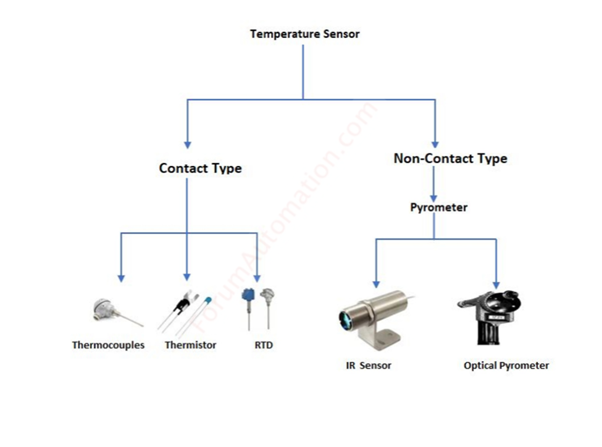
Types of Temperature Sensors Used
Several types of temperature sensors are commonly employed in commercial air handling systems, each with its own strengths and applications. Understanding these different types is crucial for optimizing HVAC performance.
Thermocouples
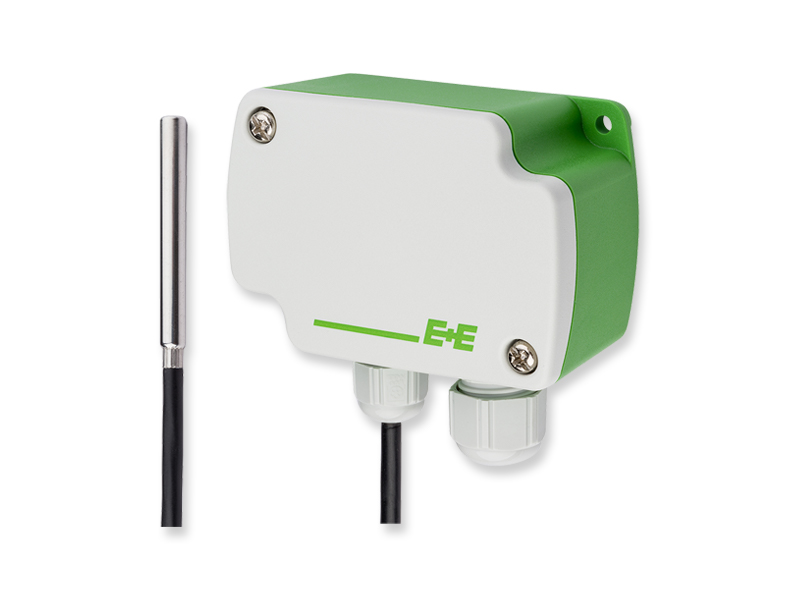
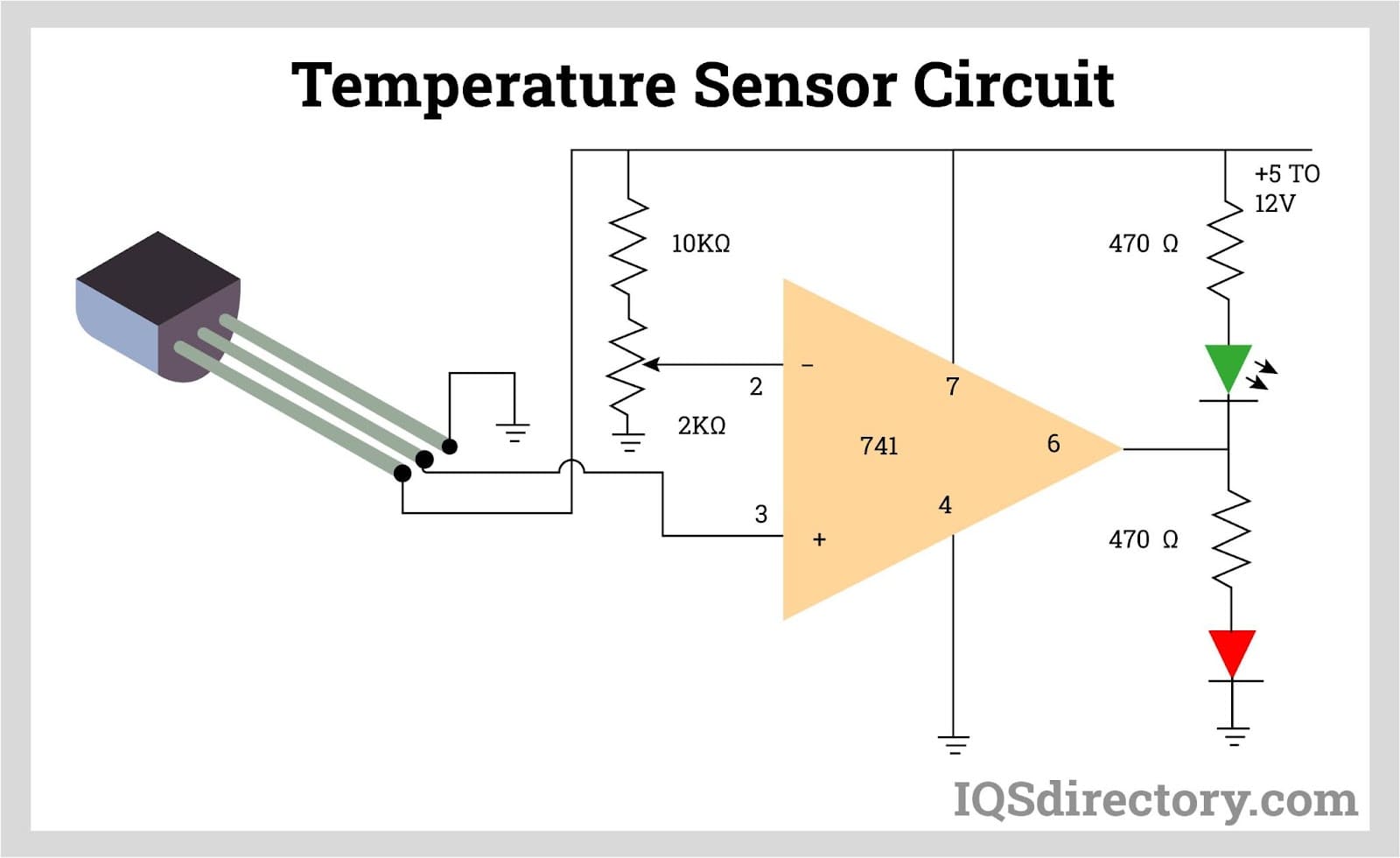
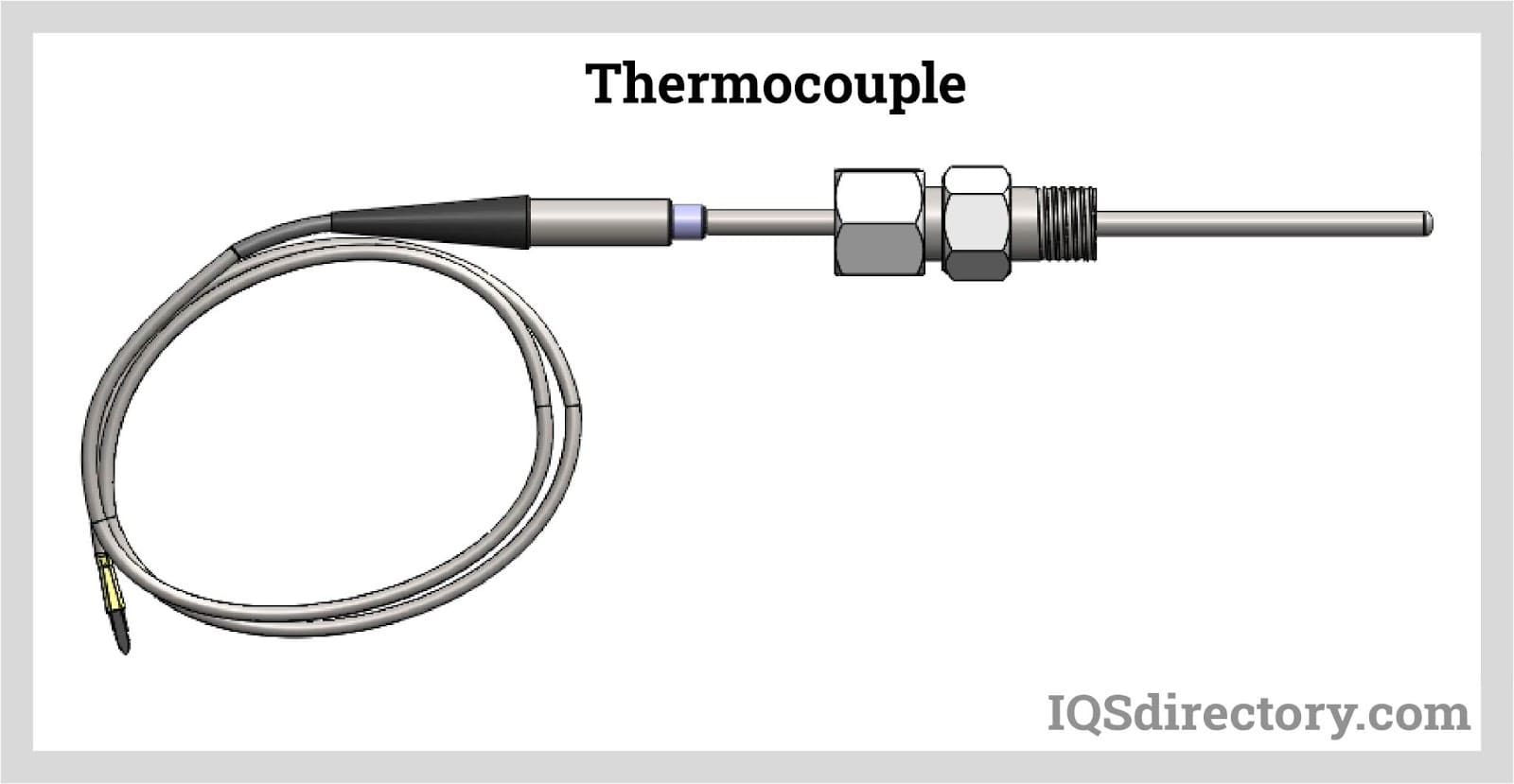
Thermocouples are among the most versatile and widely used temperature sensors. They consist of two dissimilar metal wires joined at one end, creating a junction where temperature is measured. The temperature difference between this junction and a reference point produces a voltage that correlates to the temperature.
Their robust nature makes them suitable for harsh environments and high-temperature applications. Thermocouples are cost-effective and can measure a wide range of temperatures.
Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs)
RTDs, particularly Platinum RTDs (Pt100, Pt1000), offer excellent accuracy and stability. These sensors rely on the principle that the electrical resistance of a metal changes predictably with temperature.
They are highly accurate and stable, but generally more expensive than thermocouples. RTDs are often used in critical applications where precise temperature readings are essential.
Thermistors
Thermistors are semiconductor-based sensors that exhibit a significant change in resistance with temperature. They are available in two types: Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) and Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC).
NTC thermistors are more commonly used in HVAC systems, as their resistance decreases with increasing temperature. Thermistors are compact, sensitive, and relatively inexpensive.
Digital Temperature Sensors
Digital temperature sensors integrate the sensing element, signal conditioning, and digital interface into a single device. They offer advantages such as high accuracy, digital output, and easy integration with control systems.
These sensors can transmit temperature data directly to a building management system (BMS) or controller. This simplifies wiring and improves data integrity.
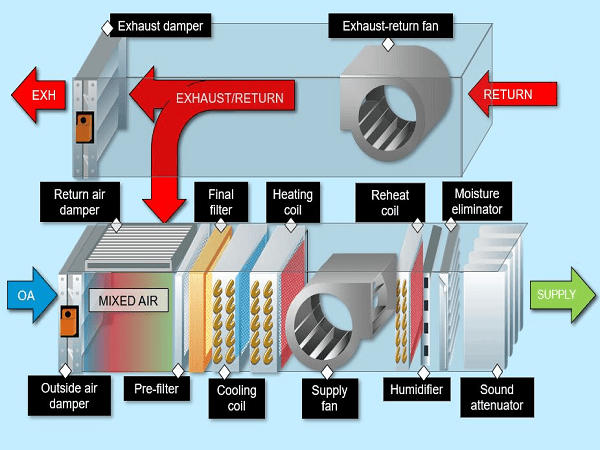
Sensor Placement and Application
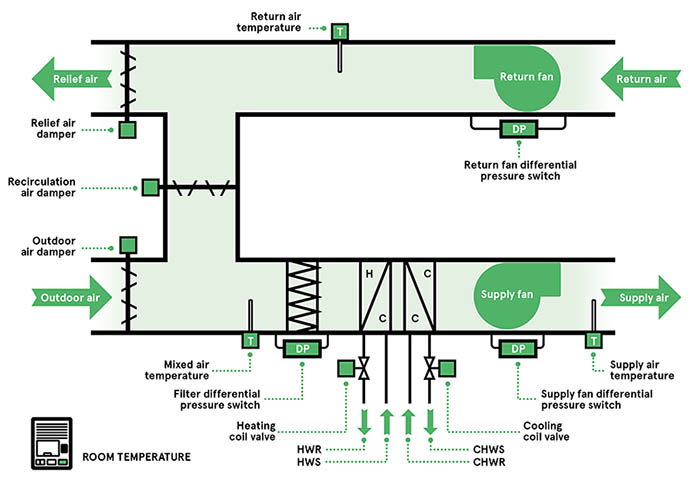
The placement of temperature sensors within an air handler is critical for accurate and effective control. Sensors are strategically positioned to monitor various aspects of the air handling process.
Here are a few key locations:
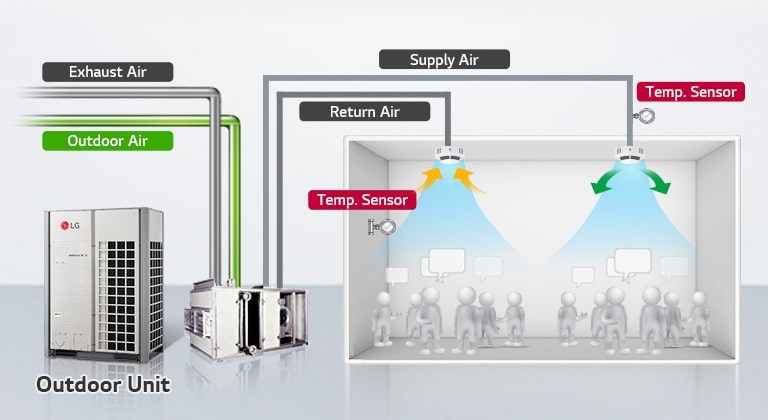
- Mixed Air Temperature Sensor: Measures the temperature of the air after outdoor air and return air are mixed.
- Supply Air Temperature Sensor: Monitors the temperature of the air being delivered to the conditioned space.
- Return Air Temperature Sensor: Measures the temperature of the air returning from the conditioned space.
- Chilled/Hot Water Temperature Sensors: Monitors the temperature of the water entering and leaving the cooling or heating coils.
These sensors are used for different stages of air conditioning. The precise location and type of sensor can vary depending on the specific design of the air handling system and the requirements of the building.
Integration with Building Management Systems (BMS)
Temperature sensors are integral to the operation of a Building Management System (BMS). The BMS collects data from these sensors and uses it to control the air handler and other HVAC components.
By continuously monitoring temperatures, the BMS can optimize energy consumption, maintain consistent comfort levels, and detect potential issues before they escalate. The data provided by temperature sensors enables the BMS to make informed decisions about heating, cooling, and ventilation.
Importance of Calibration and Maintenance
Regular calibration and maintenance of temperature sensors are crucial for ensuring accuracy and reliability. Over time, sensors can drift or become damaged, leading to inaccurate readings and suboptimal system performance.
Calibration involves comparing the sensor's output to a known standard and adjusting it to ensure accuracy. Routine maintenance includes cleaning sensors, checking wiring connections, and replacing any damaged components. According to ASHRAE (American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers), a well-maintained sensor network can significantly improve energy efficiency and indoor air quality.
Impact on Energy Efficiency and Comfort
The proper use of temperature sensors in commercial air handlers has a significant impact on both energy efficiency and occupant comfort. By accurately monitoring and controlling temperatures, air handlers can minimize energy waste and maintain consistent comfort levels throughout a building.
Accurate temperature control prevents overheating or overcooling, which can lead to wasted energy and uncomfortable conditions. A well-optimized HVAC system, powered by reliable temperature sensors, contributes to a more sustainable and productive indoor environment.
The Future of Temperature Sensing
The field of temperature sensing is constantly evolving, with new technologies and innovations emerging regularly. Wireless sensors, for example, are becoming increasingly popular due to their ease of installation and flexibility.
Advancements in sensor technology are leading to more accurate, reliable, and energy-efficient HVAC systems. Furthermore, the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) algorithms is enabling smarter and more predictive control of air handlers, based on data from temperature sensors.
Conclusion
Temperature sensors are the silent guardians of comfort and efficiency in commercial buildings. These small but mighty devices provide the crucial data needed to control air handlers, ensuring optimal indoor environments. From thermocouples to digital sensors, each type plays a vital role in maintaining consistent temperatures, reducing energy waste, and enhancing the well-being of occupants.
As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more sophisticated temperature sensing solutions to emerge, further optimizing HVAC performance and creating healthier, more sustainable indoor spaces. The next time you enjoy a comfortable indoor environment, remember the unsung heroes working diligently behind the scenes – the temperature sensors, ensuring your comfort, one degree at a time.