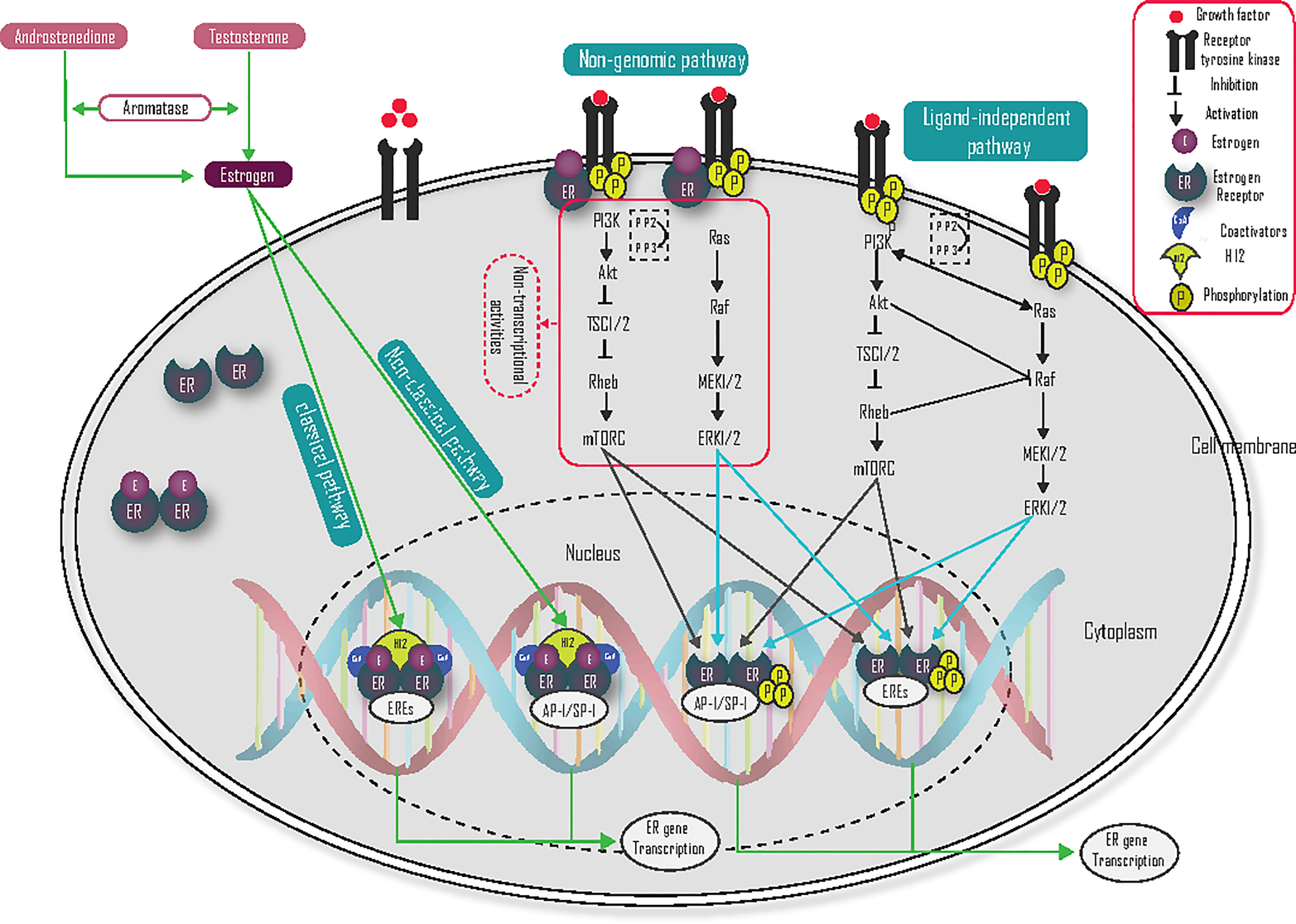
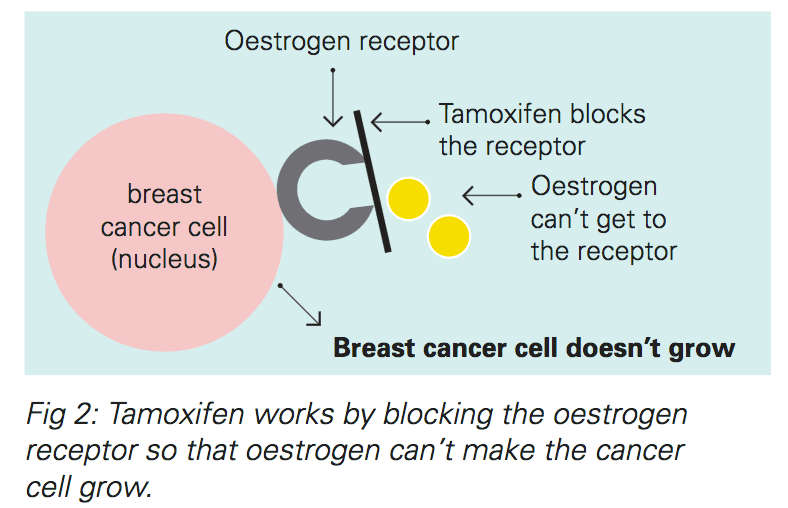
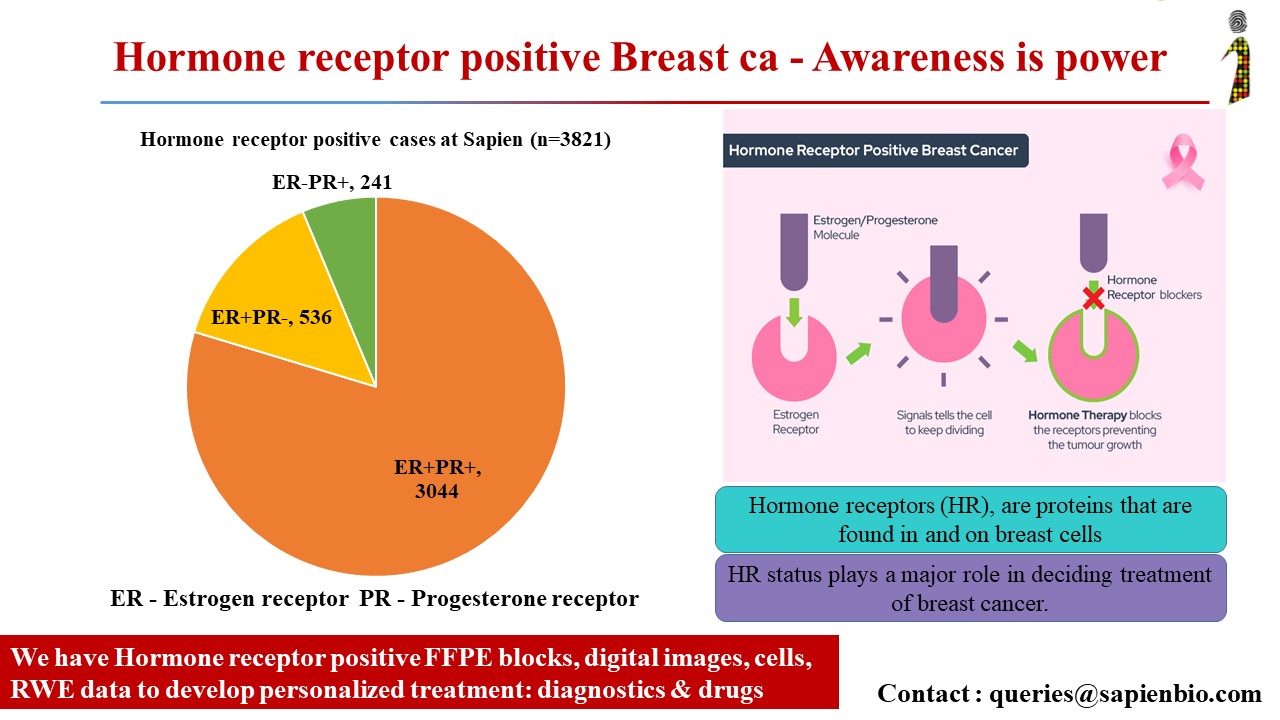
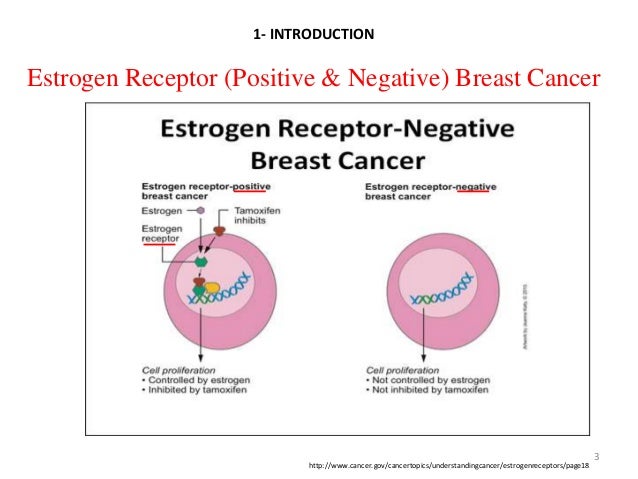
Whey Protein And Estrogen Positive Breast Cancer
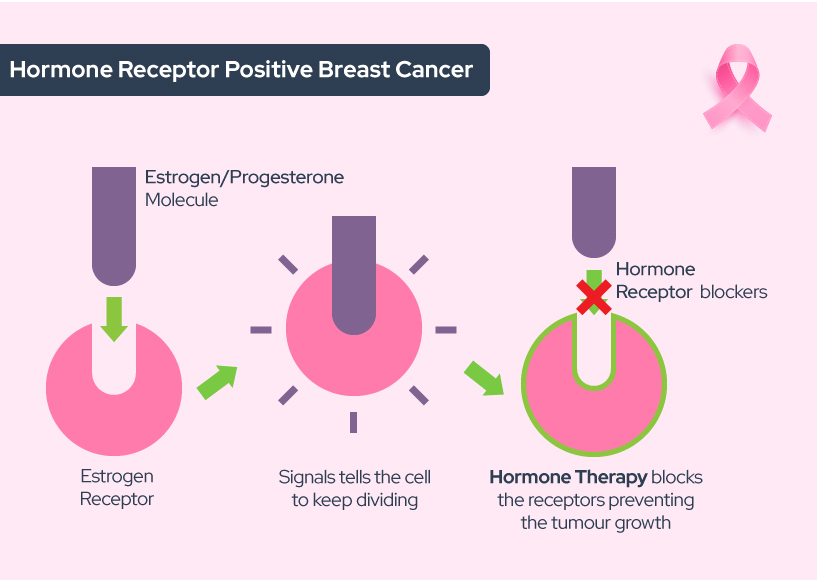
Breaking research raises concerns about potential links between whey protein consumption and increased risk in estrogen-positive breast cancer patients. Emerging data suggests a possible correlation, prompting calls for further investigation and caution.
This article dissects recent findings suggesting that whey protein, a popular dietary supplement, may influence estrogen levels and potentially stimulate the growth of estrogen-positive breast cancer cells. We explore the evidence, expert opinions, and what this means for individuals at risk.
Understanding the Link: What the Research Shows
A recent study, presented at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, explored the effects of whey protein on breast cancer cells in vitro. The findings indicate that certain components within whey protein may mimic or amplify estrogen's effect, stimulating the growth of estrogen-positive breast cancer cells. This research, while preliminary, highlights a potential area of concern that demands further examination.
The study examined the response of several breast cancer cell lines to varying concentrations of whey protein. Researchers found a significant increase in cell proliferation in estrogen-positive lines, suggesting a hormonal influence.
In vitro studies are valuable tools, but these findings need to be validated through in vivo research and human clinical trials.
Expert Opinions and Concerns
Leading oncologists are urging caution, emphasizing that while the link isn't definitively proven, the possibility warrants attention. Dr. Emily Carter, a breast cancer specialist at the Mayo Clinic, stated, "This preliminary data is concerning and highlights the need for more research into the potential impact of whey protein on estrogen-positive breast cancer."
Dr. Carter added that patients with a history of, or predisposition to, estrogen-positive breast cancer should consult with their healthcare provider before using whey protein supplements. This is crucial to assess individual risk factors and make informed decisions.
Who is at Risk?
The primary concern revolves around individuals with a history of estrogen-positive breast cancer or those at increased risk due to family history or genetic predisposition. These individuals might be more susceptible to the potential estrogen-mimicking effects of whey protein.
Women undergoing hormone replacement therapy (HRT) should also exercise caution and discuss the use of whey protein with their doctor. The combined effect of HRT and potential estrogenic components in whey protein needs careful consideration.
Navigating the Information: What You Need to Know
While awaiting more conclusive research, experts advise a balanced approach. This includes prioritizing whole foods and consulting healthcare professionals for personalized dietary guidance.
Individuals using whey protein for muscle building or weight management should consider alternative protein sources, such as plant-based options. Examples of alternative protein include soy, pea, and rice protein.
Pay close attention to your body and report any unusual symptoms or changes to your doctor promptly. Early detection remains the best defense against breast cancer.
Next Steps: Ongoing Research and Future Directions
Researchers are planning larger-scale studies to further investigate the effects of whey protein on estrogen levels and breast cancer risk. These studies will involve in vivo animal models and, eventually, human clinical trials.
The goal is to determine the precise mechanisms by which whey protein may influence estrogen-positive breast cancer cells and to identify specific components responsible for the observed effects. Further studies will help refine dietary recommendations for at-risk populations.
This is a developing situation, and we will continue to provide updates as more information becomes available. Stay informed and consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice.


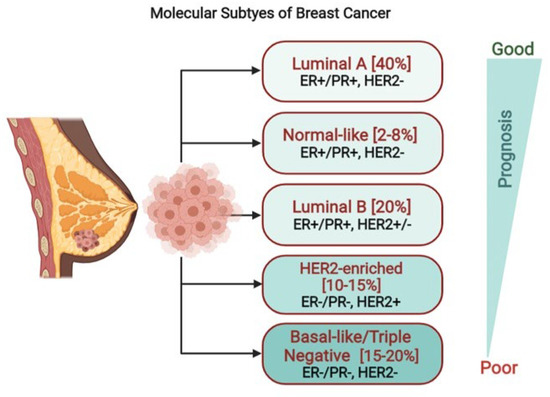
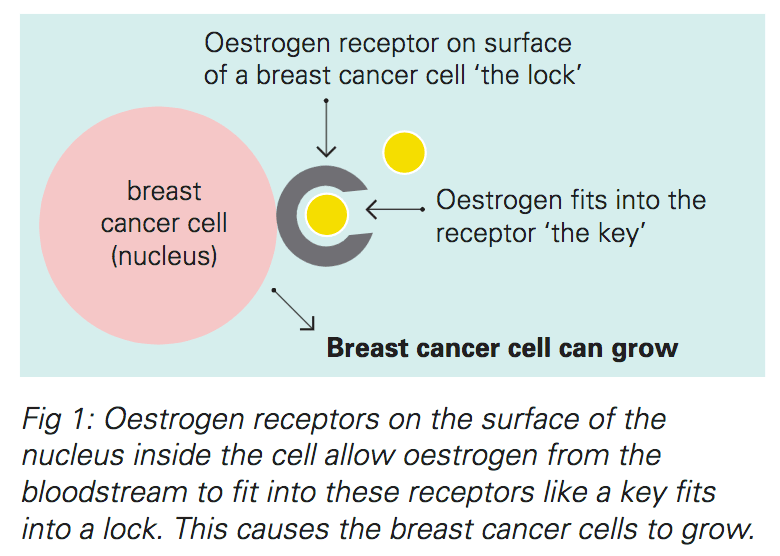
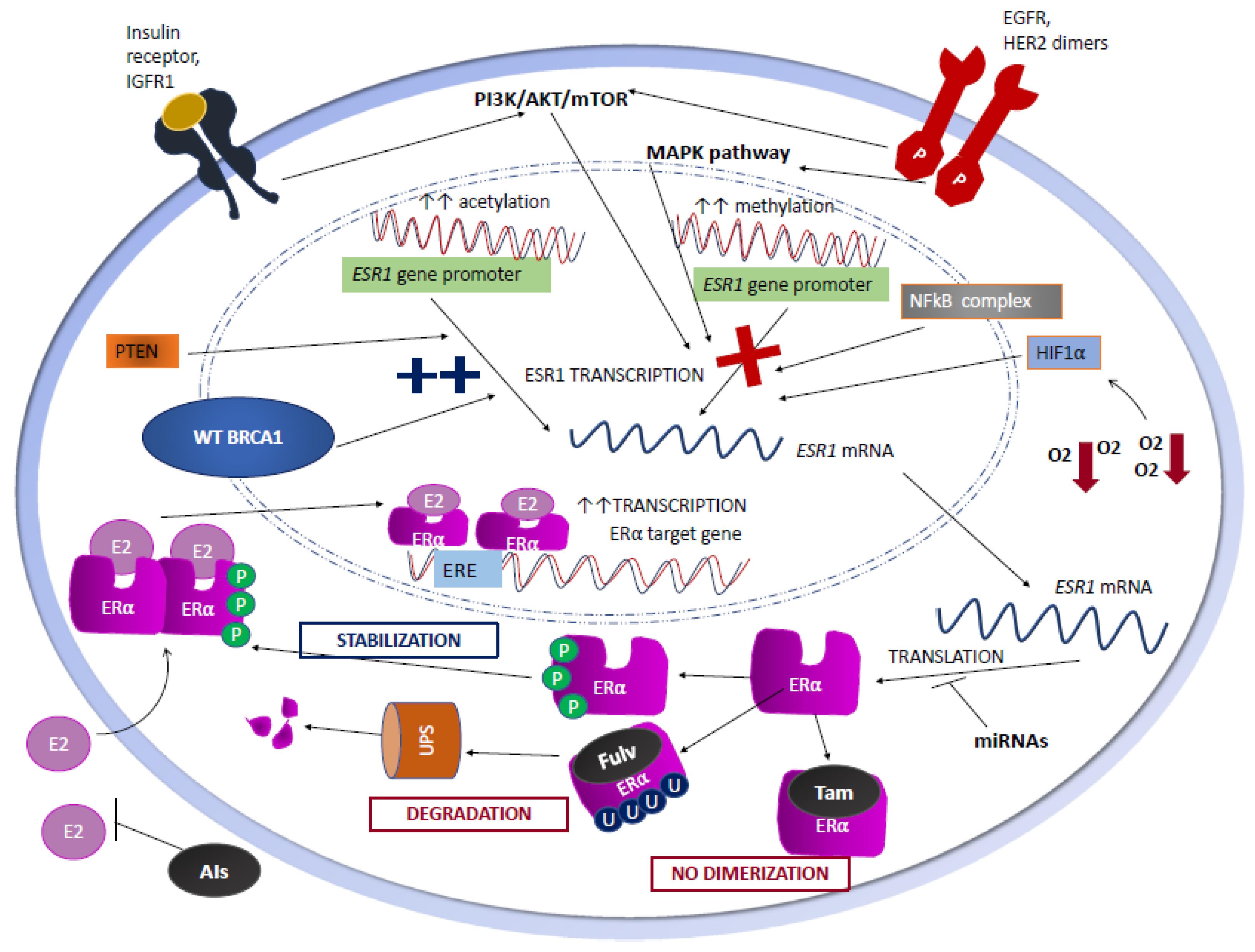



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/hormone-receptor-status-and-diagnosis-430106-color-V12-c330f4d3c9d043aa8b081d2021f3623e.png)