Which Best Ensures That Pathogens Are Reduced To Safe Levels

The scent of chlorine hangs faintly in the air, a familiar aroma in countless swimming pools and water treatment plants. Sunlight glints off the surface of a freshly cleaned surgical instrument, ready to play its part in safeguarding health. In a bustling commercial kitchen, the rhythmic hiss of a sanitizing spray echoes, a silent guardian against unseen threats. But behind these everyday scenes lies a complex world of scientific inquiry: What truly best ensures that pathogens are reduced to safe levels, protecting us from the ever-present risks of disease?
At the heart of this question lies a critical understanding: no single solution reigns supreme. A multifaceted approach, carefully tailored to the specific context, is essential. This article explores the various methods employed to reduce pathogens, examining their strengths, weaknesses, and the critical role they play in safeguarding public health.
Understanding the Enemy: Pathogens and Their Persistence
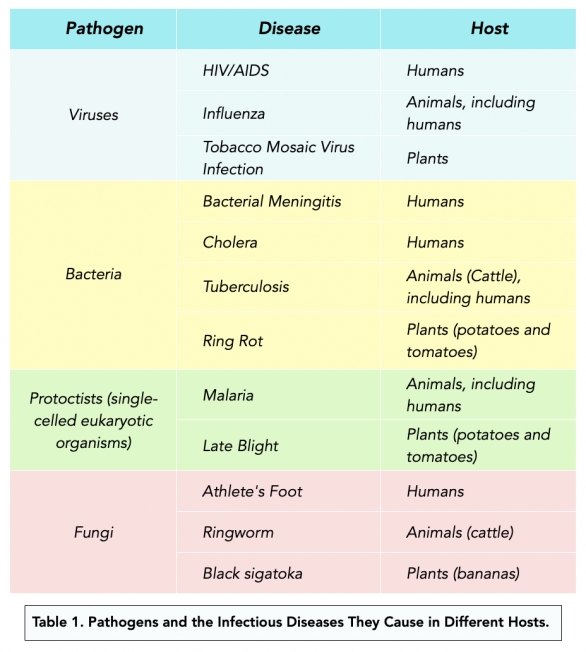
Pathogens, the microscopic agents of disease, are ubiquitous. Bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites – these invisible adversaries constantly surround us, seeking opportunities to thrive and multiply. Their persistence depends on various factors, including the environment, the type of pathogen, and the presence of organic matter that provides them sustenance.
Some pathogens, like Clostridium difficile (C. diff), can form resilient spores, making them exceptionally difficult to eradicate. Others, such as Norovirus, are highly contagious and can survive on surfaces for extended periods. Understanding these characteristics is paramount in selecting the most effective reduction strategies.
The Arsenal of Defense: Methods for Pathogen Reduction
The battle against pathogens is waged on many fronts, employing a diverse arsenal of methods. From the humble bar of soap to sophisticated sterilization technologies, each approach offers a unique set of advantages and limitations.
Physical Removal: The Foundation of Hygiene
Simple as it may seem, physical removal forms the bedrock of pathogen control. Washing hands with soap and water dislodges pathogens from the skin, effectively flushing them away. This seemingly elementary practice is one of the most powerful tools in preventing the spread of infection, a cornerstone of public health campaigns worldwide. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) emphasize hand hygiene as the single most effective way to prevent the spread of many infections.
Similarly, cleaning surfaces with detergents removes dirt, grime, and organic matter that can harbor pathogens. This step is crucial in preparing surfaces for subsequent disinfection or sanitization. Think of it as clearing the battlefield before deploying the heavy artillery.
Disinfection: Killing the Unseen
Disinfection goes beyond mere cleaning, aiming to kill or inactivate pathogens on surfaces or in liquids. Chemical disinfectants, such as bleach, alcohol, and quaternary ammonium compounds, are widely used in healthcare settings, food processing plants, and homes.
The effectiveness of disinfectants depends on several factors, including the concentration of the active ingredient, the contact time, and the presence of organic matter. Some disinfectants are broad-spectrum, effective against a wide range of pathogens, while others are more specific. For example, hospitals frequently use disinfectants with proven efficacy against C. diff spores to combat the spread of this tenacious infection.
Sanitization: Reducing to Safe Levels
Sanitization focuses on reducing the number of pathogens to a safe level, as defined by public health standards. This approach is commonly used in food service establishments, where the goal is to minimize the risk of foodborne illness. Sanitizers, often less potent than disinfectants, are typically used on food contact surfaces.
Heat sanitization, using hot water or steam, is a popular method in commercial dishwashers. Chemical sanitizers, such as chlorine-based solutions, are also widely employed. Regular sanitization practices are essential in preventing the proliferation of harmful bacteria, such as Salmonella and E. coli, which can cause serious foodborne illnesses.
Sterilization: The Ultimate Defense
Sterilization represents the highest level of pathogen control, aiming to eliminate all microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and spores. This rigorous process is critical in healthcare settings for surgical instruments, medical devices, and other items that come into contact with sterile tissues.
Sterilization methods include autoclaving (using high-pressure steam), dry heat sterilization, and chemical sterilization. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on the nature of the item being sterilized. Sterilization protocols are meticulously followed to ensure the complete elimination of pathogens, safeguarding patients from potentially life-threatening infections.
Emerging Technologies: The Future of Pathogen Control
Innovation continues to drive advancements in pathogen reduction. Ultraviolet (UV) light disinfection, for example, is gaining popularity for air and surface disinfection. UV-C light, a specific wavelength of UV light, disrupts the DNA of microorganisms, rendering them unable to replicate.
Other emerging technologies include antimicrobial coatings, which can be applied to surfaces to inhibit the growth of pathogens, and advanced filtration systems that remove airborne pathogens. These innovations hold promise for enhancing pathogen control in various settings, from hospitals to schools to public transportation.
Context is Key: Tailoring the Approach
The most effective approach to pathogen reduction is highly dependent on the specific context. A hospital operating room requires a vastly different approach than a daycare center. Factors to consider include the type of pathogens present, the potential for exposure, the surfaces or items being treated, and the resources available.
In healthcare settings, strict adherence to infection control protocols is paramount. This includes rigorous hand hygiene, proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE), and meticulous cleaning and disinfection of surfaces and equipment. In food service establishments, food safety plans that address proper cooking temperatures, hand hygiene, and surface sanitization are essential.
The Importance of Training and Education
Even the most effective methods are useless without proper training and education. Healthcare workers, food handlers, and the general public all play a vital role in preventing the spread of pathogens. Training programs should emphasize the importance of hand hygiene, proper cleaning and disinfection techniques, and the appropriate use of PPE.
Public health campaigns can also play a crucial role in raising awareness about pathogen transmission and prevention. By empowering individuals with knowledge and skills, we can collectively reduce the burden of infectious diseases.
A Collective Responsibility: Protecting Public Health
The quest to effectively reduce pathogens is an ongoing endeavor, demanding continuous vigilance and adaptation. There is no single "best" method; rather, a comprehensive strategy that integrates multiple approaches, tailored to the specific context, is essential. This necessitates a collective commitment from healthcare professionals, food service workers, policymakers, and the public. From the simple act of washing our hands to the implementation of advanced sterilization technologies, each action contributes to a safer and healthier world.
Ultimately, protecting ourselves and our communities from the threat of pathogens requires a profound understanding of the microscopic world and a unwavering commitment to evidence-based practices. Only through such diligent effort can we ensure that pathogens are reduced to safe levels, safeguarding the well-being of all.