Which Is A Component Of The Fossil Record
Imagine holding a piece of the past in your hand – a smooth, grey stone imprinted with the delicate fronds of a fern, or perhaps the spiraled shell of an ancient sea creature. The sun warms your face as you ponder the immense journey of time that this object has traveled, a silent witness to epochs long gone.
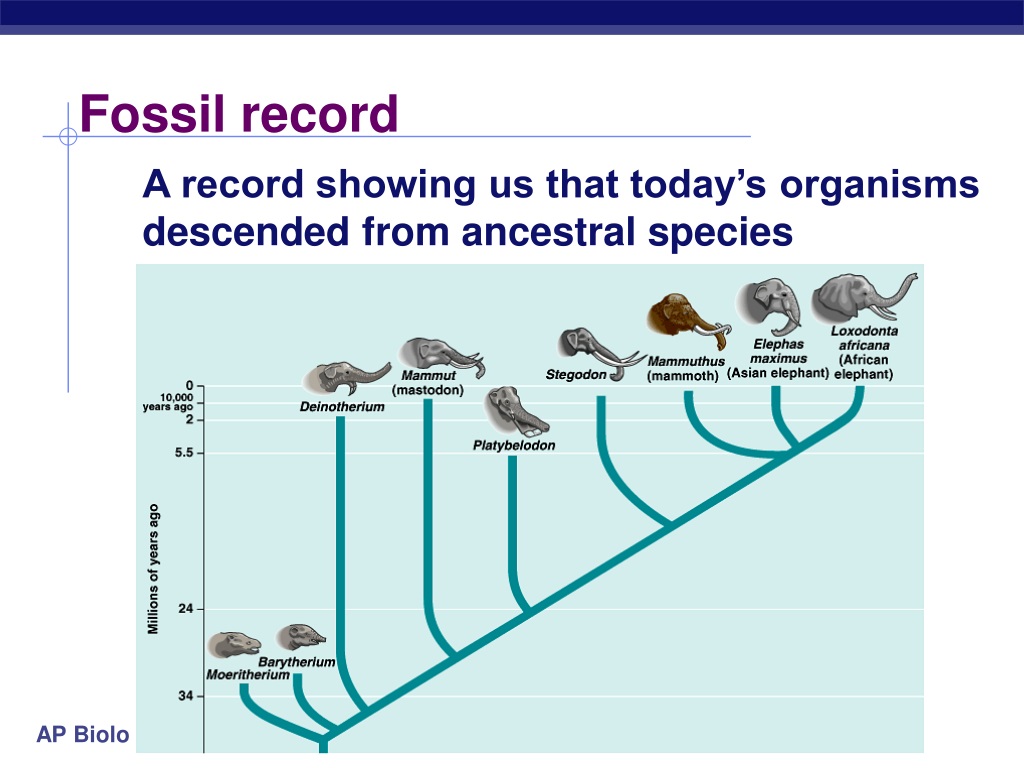
The fossil record, a vast and invaluable archive of life's history on Earth, is built upon more than just bones. While the dramatic skeletons of dinosaurs often steal the spotlight, a multitude of other components contribute to this rich tapestry of the past. This article explores the diverse elements that constitute the fossil record, shedding light on what we can learn from them.
Understanding the Fossil Record
The fossil record is essentially a collection of all discovered fossils. These fossils provide snapshots of organisms that lived at different times throughout Earth's history. It's an incomplete record, of course, because fossilization is a rare event, requiring specific conditions to preserve remains over millions of years.
But even with its gaps, the fossil record offers invaluable insights into evolution, climate change, and the history of life on our planet. It allows scientists to trace the ancestry of modern organisms and understand how species have adapted to changing environments.
Beyond the Bones: A Wider Perspective
While bones and teeth are often the most recognizable fossils, the fossil record encompasses a much wider range of materials. These include trace fossils, plant fossils, and even fossilized microorganisms.
Trace fossils are not the remains of the organism itself, but rather evidence of its activity. Think of footprints, burrows, and even fossilized feces (coprolites).
These traces provide invaluable clues about an organism's behavior, diet, and interactions with its environment. For example, a series of dinosaur footprints can reveal information about their gait, speed, and social behavior.
Plant Fossils: The Green History of Our Planet
Plant fossils are crucial for understanding the evolution of terrestrial ecosystems and past climates. These fossils can include preserved leaves, stems, roots, seeds, and even pollen grains.
Fossilized leaves, for example, can be analyzed to determine the type of vegetation that existed in a particular area. Scientists can estimate past temperatures and precipitation levels by examining the shape and structure of these leaves. Pollen grains, due to their durable outer coating, are often well-preserved and can provide a detailed picture of the plant communities that thrived in specific regions.
Microfossils: A World of Tiny Clues
Microfossils, as the name suggests, are microscopic fossils. This includes the remains of bacteria, algae, foraminifera, and other single-celled organisms.
They are abundant in sedimentary rocks and are especially useful for dating rock layers and reconstructing past environments. The study of microfossils is known as micropaleontology, a field that provides crucial information about the early evolution of life and the changing conditions of the oceans.
Chemical Fossils: Molecular Echoes of the Past
Chemical fossils, also known as biomarkers, are organic molecules that have been preserved in rocks for millions or even billions of years. These molecules are derived from the remains of ancient organisms and can provide insights into the types of organisms that lived in the past, even when no visible fossils are present.
For instance, certain lipids found in ancient rocks are unique to specific types of bacteria. Their presence indicates that these bacteria were thriving at that time. Analysis of chemical fossils requires sophisticated techniques, but it can offer a profound glimpse into the deep history of life on Earth. These molecular traces are the key to understanding the earliest forms of life.
The Significance of a Complete Record
The more complete the fossil record is, the better we can understand the history of life. Each type of fossil provides a different piece of the puzzle, revealing unique aspects of past organisms and environments.
For example, if we only had bone fossils, we would be missing vital information about the behavior and ecological interactions of extinct species. The inclusion of trace fossils, plant fossils, microfossils, and chemical fossils enriches our understanding and provides a more holistic view of the past.
The fossil record is a critical tool for understanding the current biodiversity crisis. By studying how organisms have responded to environmental changes in the past, we can gain insights into how species might respond to the current climate change. This knowledge is essential for developing effective conservation strategies and protecting the planet's biodiversity.
The Ongoing Discovery
The fossil record is constantly expanding as new discoveries are made around the world. Paleontologists are continually uncovering new fossils. These finds add to our knowledge of the history of life.
New technologies, such as high-resolution imaging and molecular analysis, are also providing new insights into existing fossils. These advances are allowing scientists to unlock new information from previously studied specimens and to understand the fossil record in greater detail.
Recently, researchers have been employing advanced imaging techniques to visualize the internal structures of fossils without damaging them.
This allows for non-destructive analysis.This provides valuable information about the anatomy and development of extinct organisms.
A Window to the Past, A Guide to the Future
The fossil record is more than just a collection of old bones and rocks. It is a vital resource for understanding the history of life on Earth and for addressing the challenges facing our planet today. By studying the fossils, we can learn about the evolution of organisms, the changing environments, and the impacts of past events.
It reminds us of the interconnectedness of all living things and the importance of preserving our planet's biodiversity. It is a story written in stone, a testament to the enduring power of life and the ever-evolving journey of our planet.
As we continue to explore the fossil record, we gain a deeper appreciation for the vastness of time and the intricate web of life that has shaped our world. It is a story that inspires awe, curiosity, and a profound sense of responsibility for the future of our planet.


















