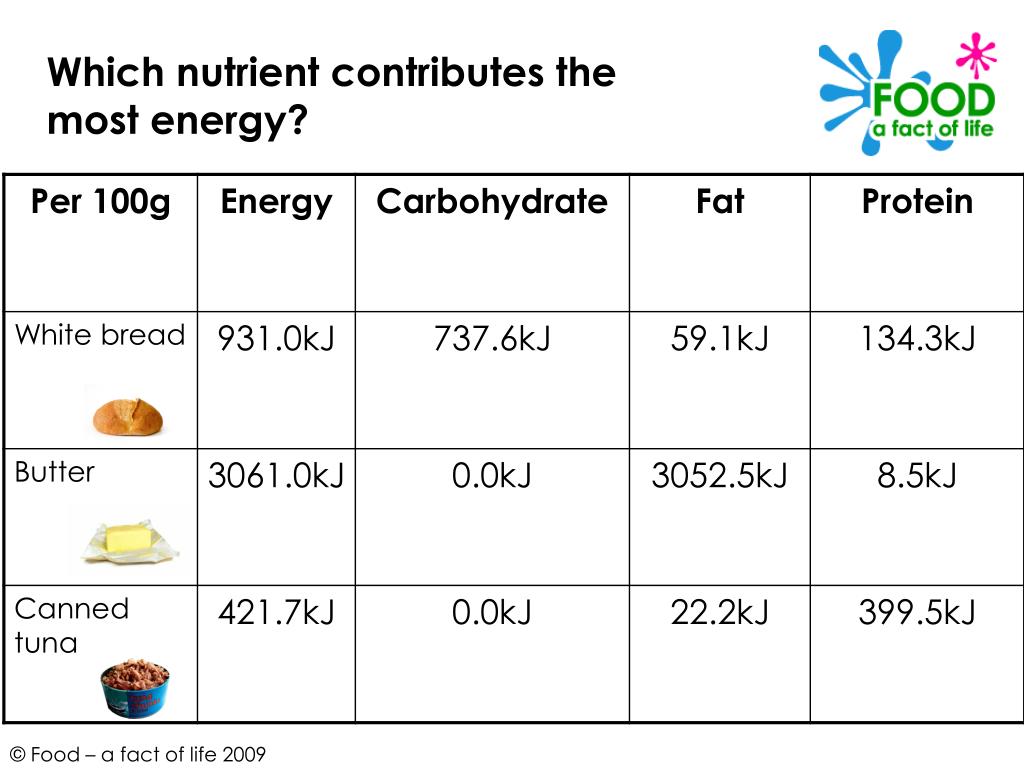
Which Nutrient Provides The Body With Quick Energy

Imagine a runner at the starting line, muscles coiled, anticipation hanging thick in the air like morning mist. With the crack of the starting gun, they explode forward, a burst of speed fueled by something far more immediate than last night's pasta. It's a cellular spark, a quick hit that bridges the gap between potential and kinetic energy.
The unsung hero of this immediate energy boost? It's carbohydrates, specifically the simple sugars that the body readily converts into fuel.
While fats and proteins also play crucial roles in energy production, carbohydrates are the body's go-to source for rapid power, enabling everything from sprinting to thinking.
The Carbohydrate Kingdom: A Quick Overview
Carbohydrates, often shortened to carbs, are organic compounds made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. They're broadly classified into simple and complex carbohydrates, each playing a distinct role in energy delivery.
Simple carbohydrates, like glucose, fructose, and sucrose, are found in fruits, honey, and refined sugars. These are the VIPs of quick energy because they're easily broken down and absorbed into the bloodstream.
Complex carbohydrates, on the other hand, consist of long chains of sugar molecules called starches and fibers. These are abundant in whole grains, vegetables, and legumes, providing a sustained energy release over time.
Glucose: The Body's Preferred Fuel
Glucose, often referred to as blood sugar, is the primary energy currency of the body. It's the form of sugar that our cells readily use to power their various functions.
When we consume carbohydrates, our digestive system breaks them down into glucose. This glucose is then absorbed into the bloodstream and transported to cells throughout the body.
Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, acts like a key, unlocking the doors of our cells to allow glucose to enter and be used for energy production.
Any excess glucose is stored in the liver and muscles in the form of glycogen, a readily available energy reserve for later use.
The Glycemic Index: Understanding Carbohydrate Impact
The glycemic index (GI) is a ranking system that measures how quickly a food raises blood glucose levels. Foods with a high GI are rapidly digested and absorbed, leading to a quick spike in blood sugar.
Examples of high-GI foods include white bread, sugary drinks, and processed snacks. While these foods can provide a quick energy boost, the subsequent crash can leave you feeling tired and sluggish.
Foods with a low GI, such as whole grains, legumes, and non-starchy vegetables, are digested and absorbed more slowly, resulting in a gradual and sustained rise in blood sugar. This provides a more stable and consistent energy supply.
Beyond the Sprint: Carbohydrates for Daily Life
The need for quick energy extends far beyond athletic performance. Our brains, in particular, rely heavily on glucose for optimal function.
Think about it: concentrating on a complex task, making a split-second decision, or even simply staying alert all require a steady supply of glucose to fuel neuronal activity.
A sudden drop in blood sugar can lead to brain fog, irritability, and difficulty concentrating. This is why maintaining stable blood sugar levels is crucial for cognitive function and overall well-being.
Moreover, quick energy from carbohydrates is essential for muscle function during everyday activities. Whether you're carrying groceries, climbing stairs, or simply walking, your muscles rely on glucose for fuel.
Even seemingly simple movements require a surprising amount of energy, highlighting the importance of carbohydrates in powering our daily lives.
Balancing Act: Healthy Carbohydrate Consumption
While carbohydrates are essential for quick energy, it's important to consume them in a balanced and healthy way. Not all carbohydrates are created equal, and the type and quantity you consume can significantly impact your health.
Prioritize whole, unprocessed carbohydrate sources like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. These foods are rich in nutrients and fiber, promoting sustained energy release and overall well-being.
Limit your intake of refined sugars, processed snacks, and sugary drinks. These foods provide empty calories and can contribute to weight gain, insulin resistance, and other health problems.
Consider incorporating complex carbohydrates into your meals and snacks for a sustained energy boost. Oatmeal with berries, a whole-wheat sandwich with vegetables, or a handful of nuts and seeds are all excellent choices.
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommend that carbohydrates make up 45-65% of your daily calorie intake. However, individual needs may vary depending on factors such as activity level and overall health.
The Takeaway: Carbs and Quick Energy
Carbohydrates, especially simple sugars, are undeniably the body's primary source of quick energy. They power everything from athletic feats to everyday activities, and even fuel our brains.
However, it's crucial to choose carbohydrates wisely, prioritizing whole, unprocessed sources over refined sugars and processed foods.
By understanding the role of carbohydrates in energy production and making informed dietary choices, we can optimize our physical and cognitive performance and enjoy a sustained and balanced energy supply throughout the day.
As the runner crosses the finish line, lungs burning, muscles aching, they've tapped into that immediate carbohydrate energy source, pushing their limits and achieving their goal. But even in our everyday lives, that same spark of quick energy, provided by carbohydrates, fuels our own journeys, big and small.