Which Of The Following Are Included In Marketing Research

In today's competitive business landscape, marketing research serves as a critical compass guiding companies towards informed decisions and successful strategies. But what exactly constitutes marketing research, and which activities fall under its expansive umbrella? This question is pivotal for both seasoned professionals and those new to the field.
At its core, marketing research encompasses a systematic and objective process of gathering, analyzing, and interpreting information about a specific market, product, or service. The goal is to understand customer needs, preferences, and behaviors to make better strategic decisions.
Defining the Scope of Marketing Research
Marketing research is not a single activity, but rather a collection of methodologies and techniques. Understanding the components is crucial for effective implementation.
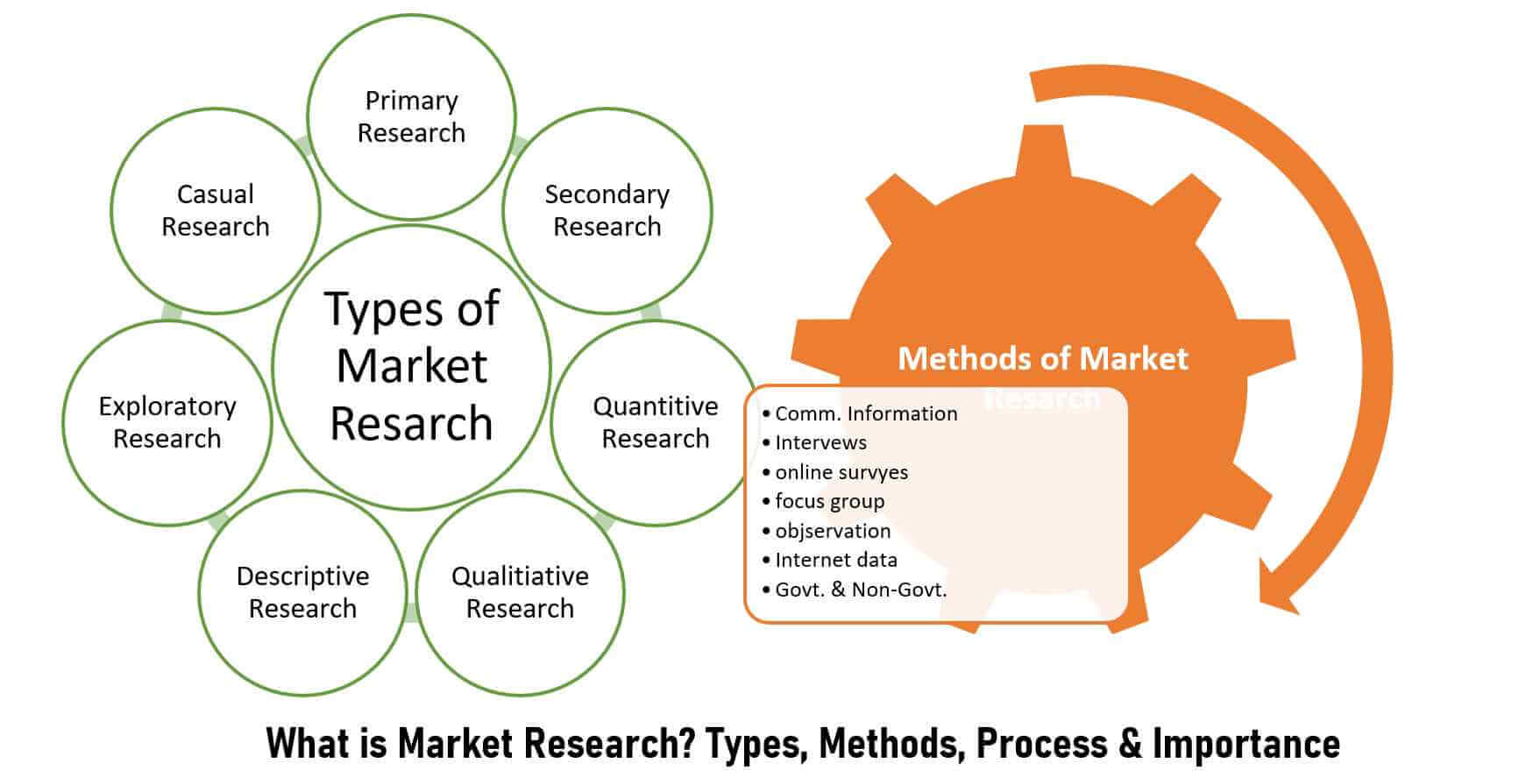
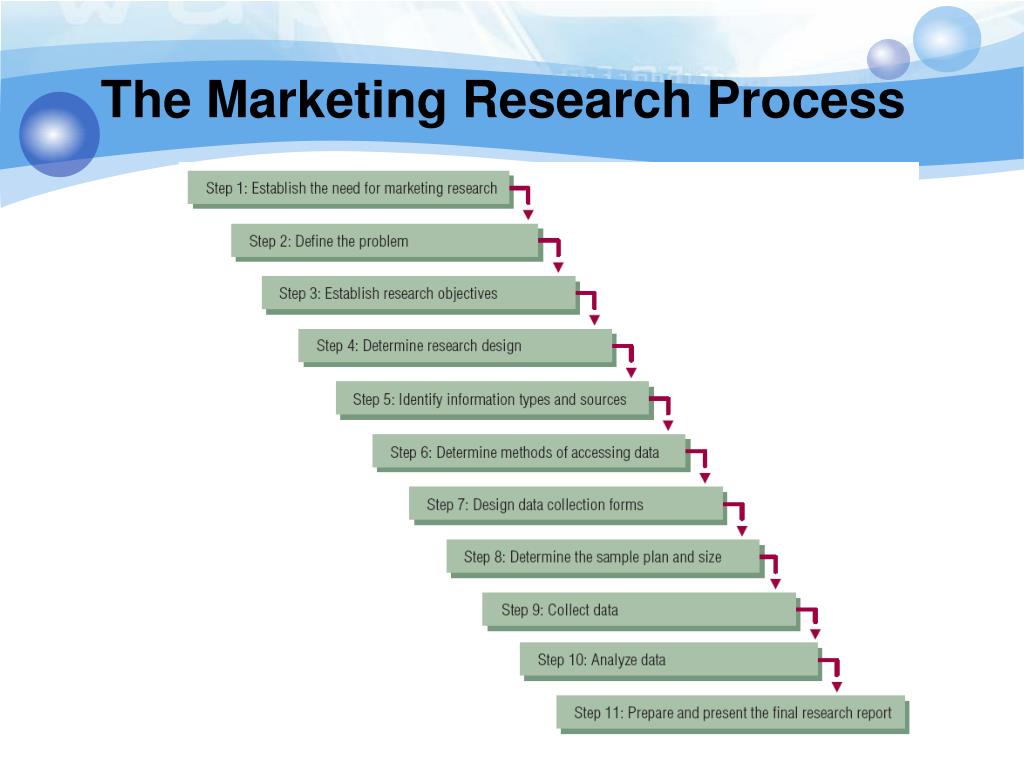
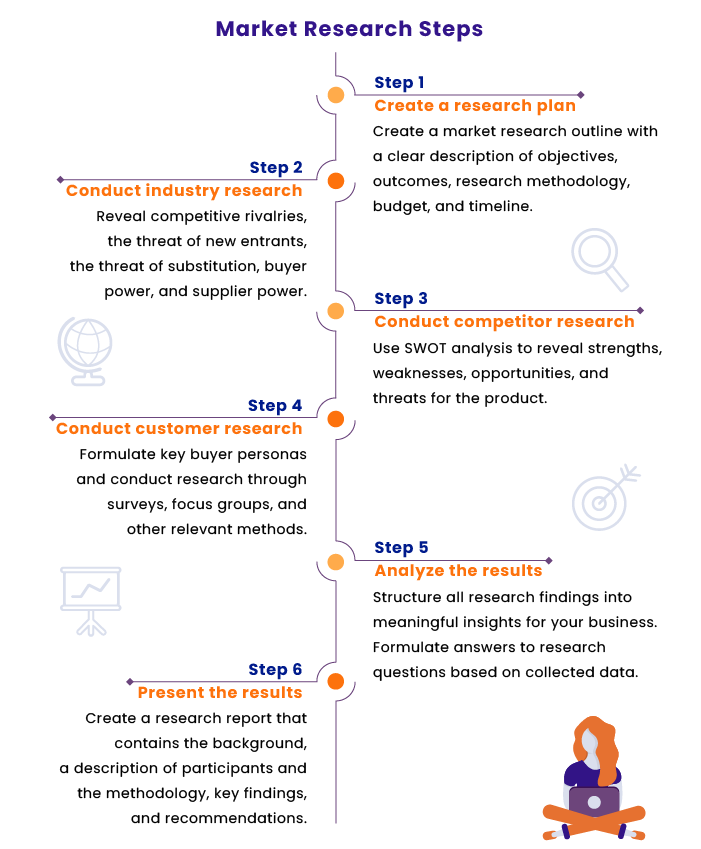
1. Identifying and Defining Marketing Opportunities and Problems
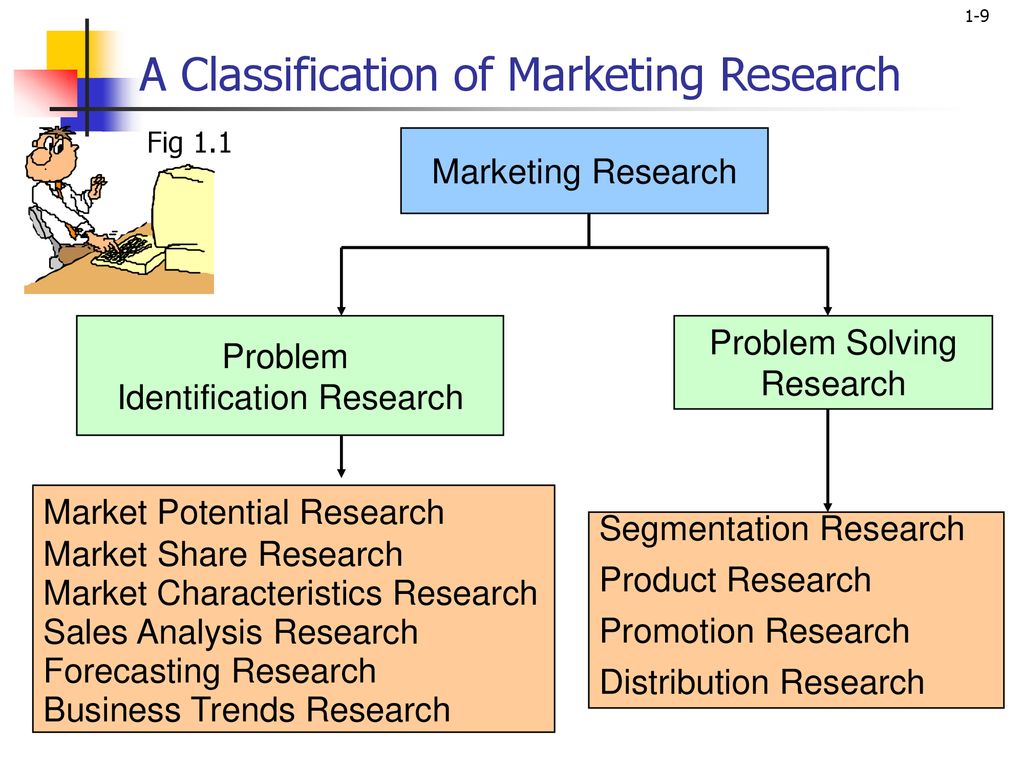
The first step often involves recognizing a potential market opportunity or identifying an existing problem. This includes analyzing market trends, competitor activities, and internal company data to pinpoint areas that require further investigation.
For instance, a decline in sales might trigger research to uncover the root causes. A successful venture often needs to understand the market's potential.
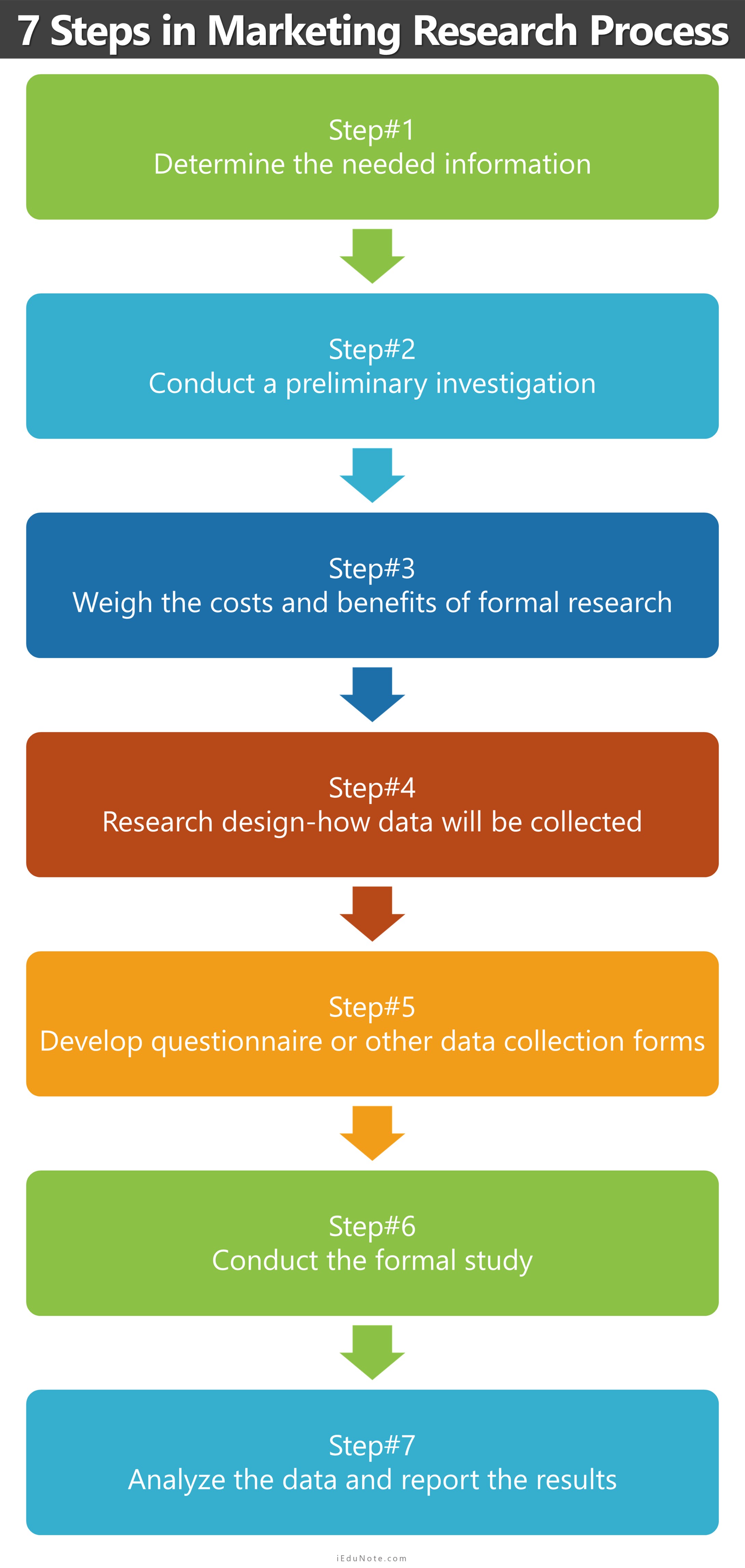
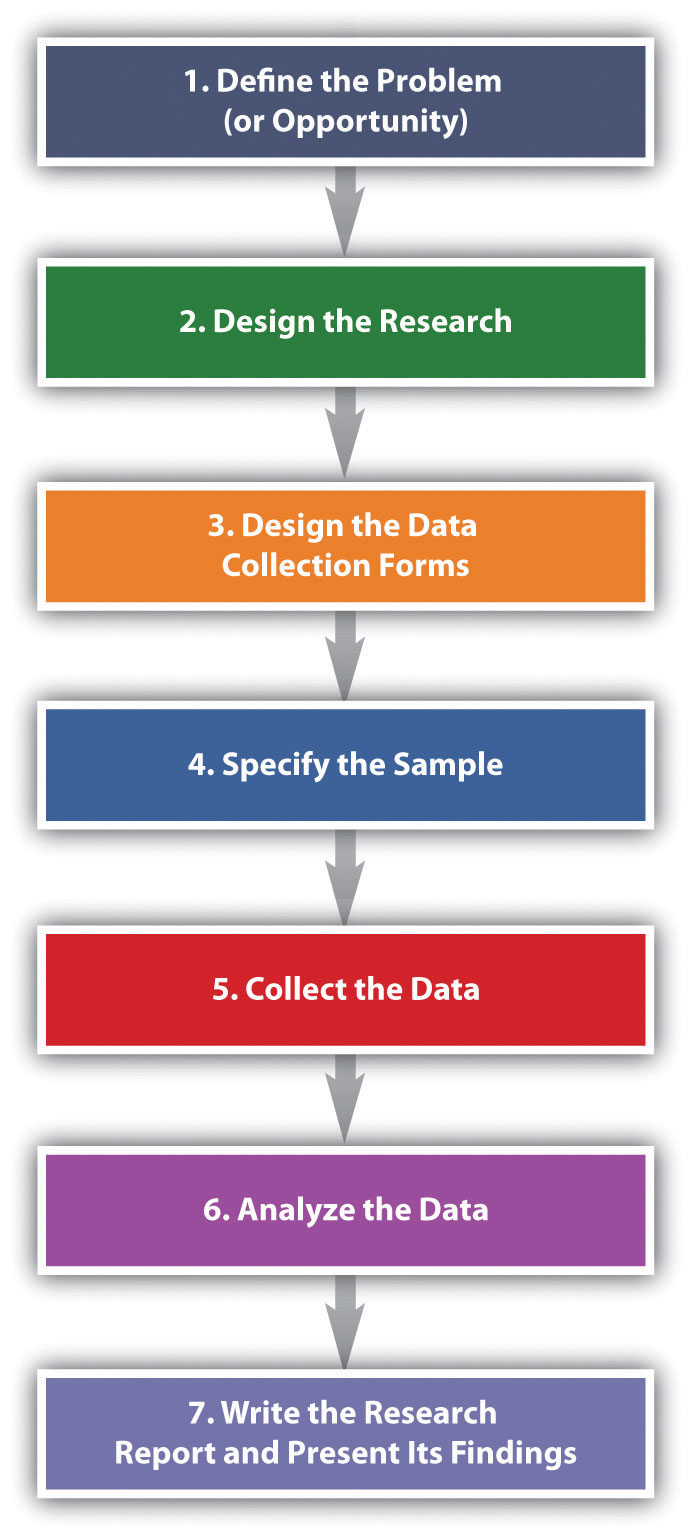
2. Planning and Conducting Research
Once a problem or opportunity is defined, a detailed research plan is developed. This includes determining the research objectives, identifying the target audience, and selecting the appropriate research methods.
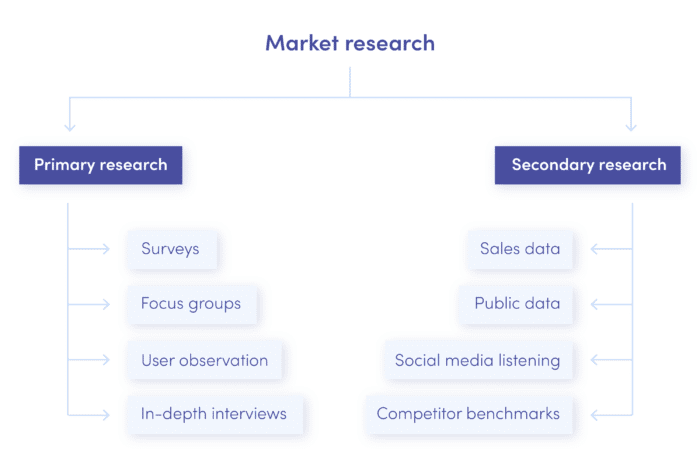
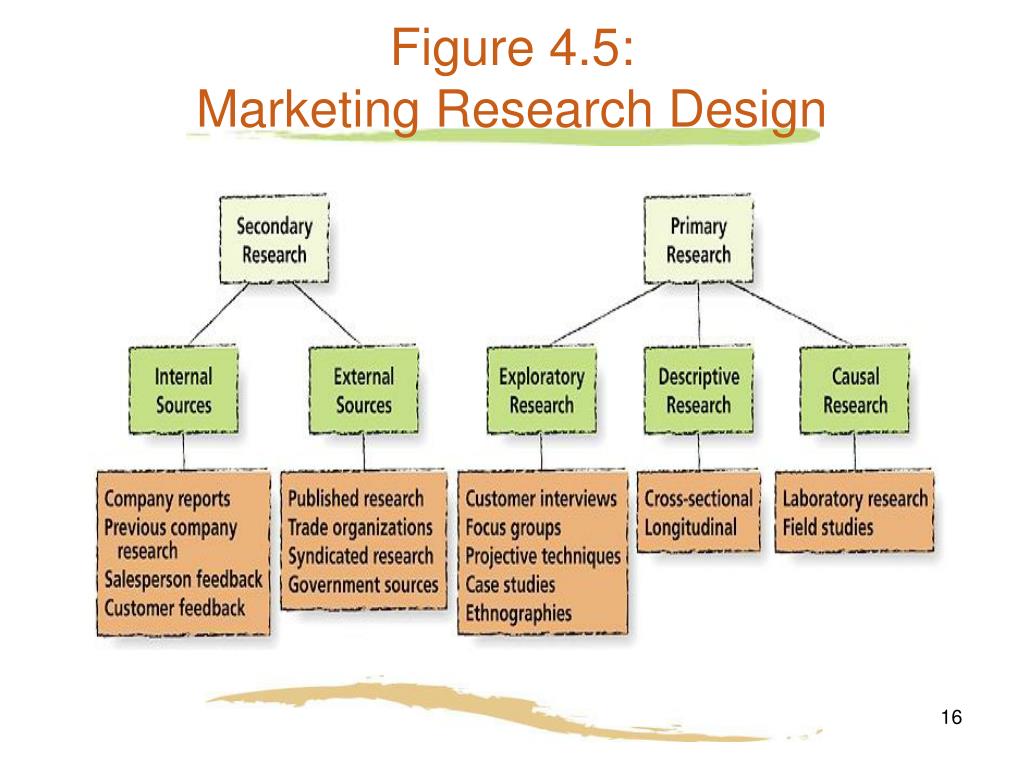
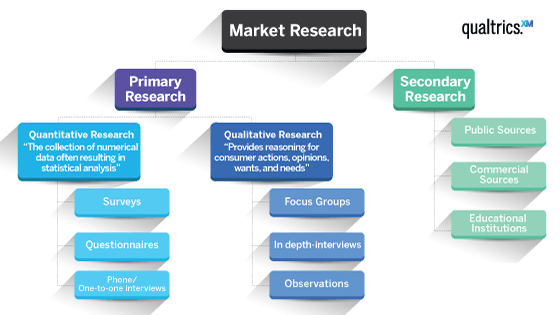
Research methods can be broadly categorized into qualitative and quantitative approaches. Qualitative research, such as focus groups and in-depth interviews, seeks to understand the 'why' behind consumer behavior, while quantitative research, such as surveys and experiments, uses numerical data to measure and analyze patterns.
3. Data Collection Methods
Effective marketing research relies on diverse data collection methods. Surveys, a staple in quantitative research, involve structured questionnaires distributed to a sample of the target population. Surveys can be administered online, by mail, or in person.
Focus groups bring together a small group of participants to discuss a specific topic, moderated by a trained facilitator. Observations involve directly observing consumer behavior in a natural setting, such as a retail store or online platform.
Experiments are often used to test cause-and-effect relationships, such as the impact of different advertising campaigns on sales. Data mining involves analyzing large datasets to uncover hidden patterns and insights.
4. Data Analysis and Interpretation
Once data is collected, it must be analyzed and interpreted. This involves using statistical techniques to identify trends, patterns, and relationships within the data. Sophisticated software and tools are used for this purpose.
Qualitative data, such as transcripts from interviews or focus groups, requires thematic analysis to identify key themes and insights. The goal is to translate raw data into actionable information that can inform marketing decisions.
5. Reporting and Dissemination of Findings
The final stage of marketing research involves preparing a comprehensive report that summarizes the findings and provides recommendations. This report should be clear, concise, and tailored to the needs of the intended audience.
The findings can be disseminated through various channels, such as presentations, webinars, or written reports. Actionable insights must reach the decision-makers.
6. Monitoring and Evaluation
Marketing research doesn't end with the initial report. It also includes monitoring the effectiveness of marketing strategies and evaluating the impact of research findings. This feedback loop helps to refine future research efforts and improve marketing performance.
Tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) and conducting follow-up studies is crucial for measuring the success of marketing initiatives. Businesses should adapt to changing market dynamics and customer needs.
Exclusions from Marketing Research
While marketing research encompasses a wide range of activities, it's important to distinguish it from other related fields. For example, sales analysis, while valuable for tracking sales performance, is generally considered a separate function from marketing research.
Similarly, customer service activities, such as handling complaints and providing support, are not typically classified as marketing research. They are integral to customer relationship management, but have a different focus and purpose.
The Impact and Significance
The impact of marketing research is far-reaching. It empowers companies to make informed decisions about product development, pricing, promotion, and distribution.
By understanding customer needs and preferences, businesses can create products and services that resonate with their target audience. The result is increased customer satisfaction, brand loyalty, and ultimately, improved financial performance.
In conclusion, marketing research is a multifaceted process that encompasses identifying opportunities, planning research, collecting data, analyzing findings, and reporting insights. It is an essential tool for businesses seeking to understand their markets, customers, and competitors, and to make informed decisions that drive success.