Which Of The Following Are Parts Of An Ethernet Frame
In the digital age, the unsung hero of countless internet connections is the Ethernet frame. But what exactly comprises this crucial data packet? Understanding the components of an Ethernet frame is fundamental to grasping how local area networks (LANs) operate and how data traverses the internet.
This article delves into the anatomy of an Ethernet frame, identifying its key elements and explaining their roles in ensuring reliable data transmission. By examining the structure of this fundamental building block of network communication, we aim to provide clarity on a topic often shrouded in technical jargon, and its significance in modern networking.
The Structure of an Ethernet Frame
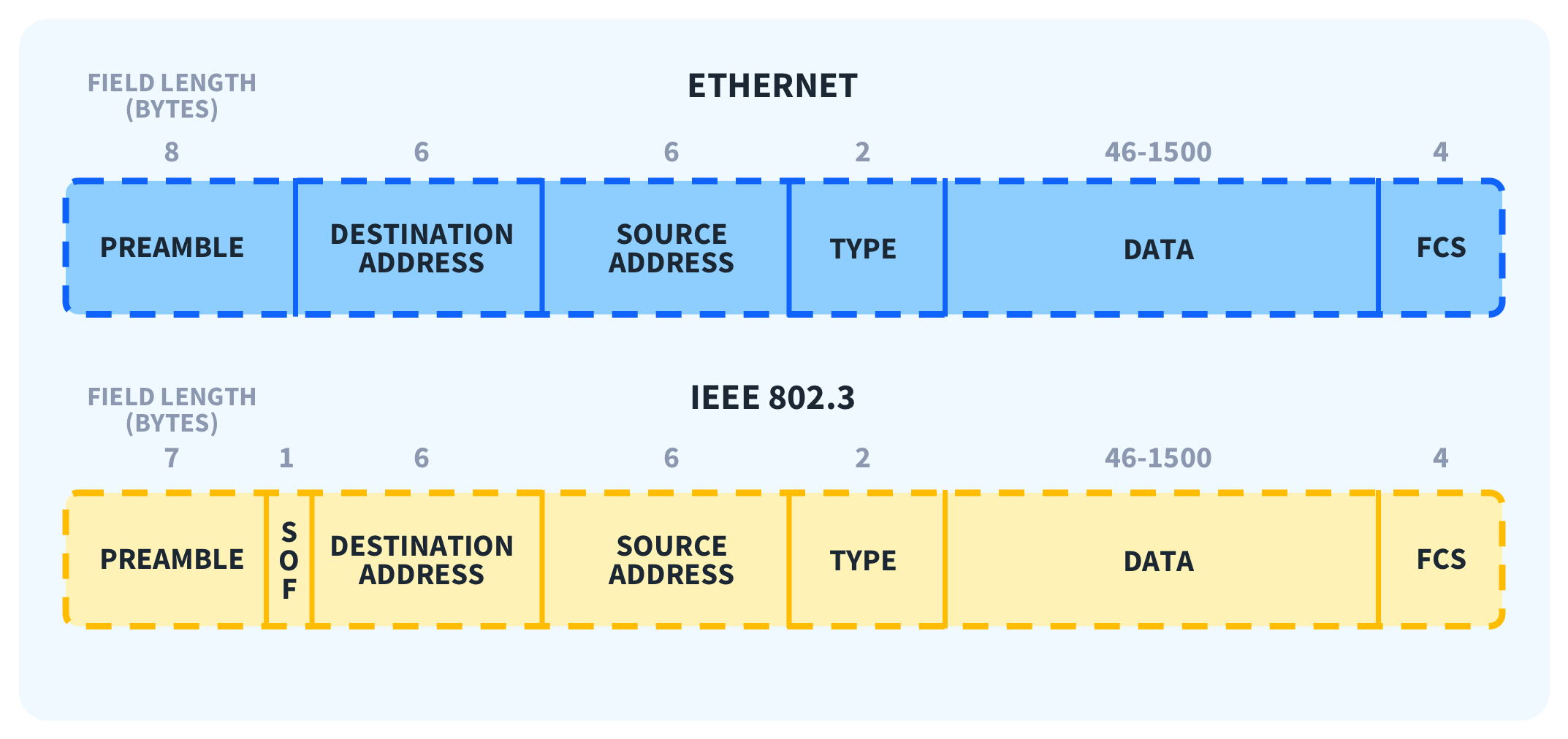
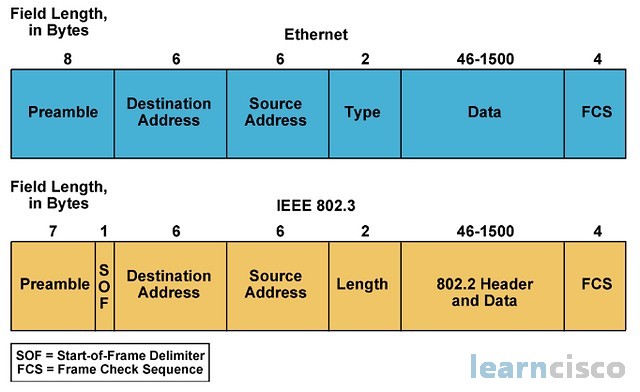
An Ethernet frame is a packet of data transmitted over a local area network. Its structure is defined by the IEEE 802.3 standard, which dictates the format and protocol for Ethernet communication. This standardized format ensures compatibility between different devices and networks.
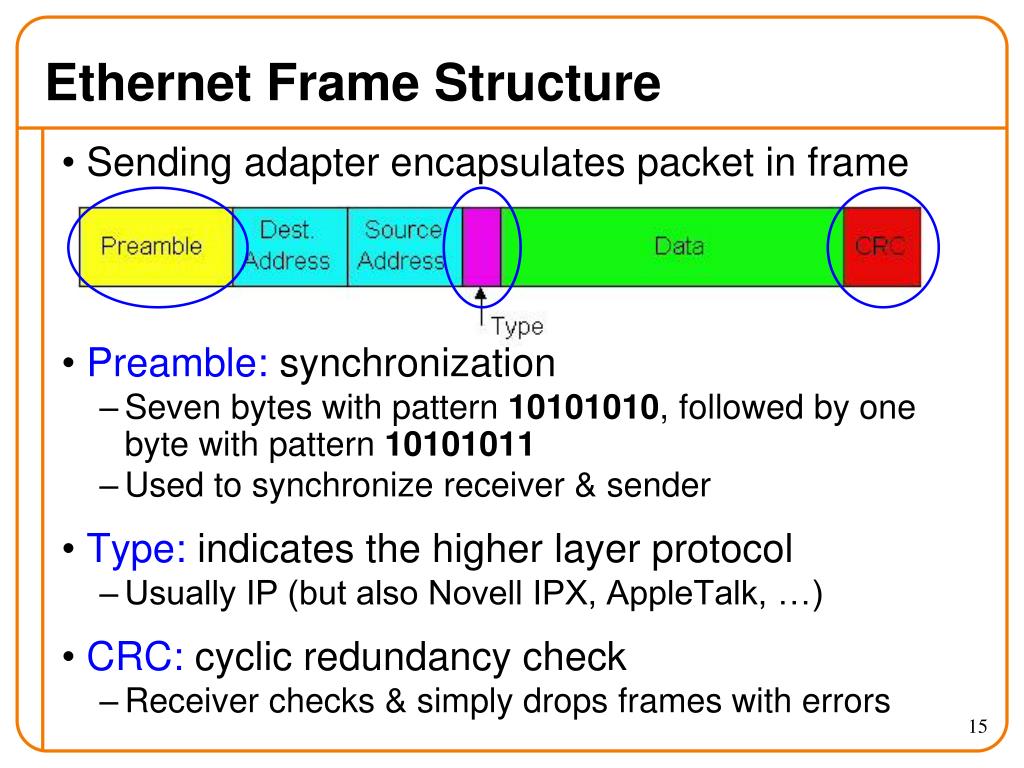
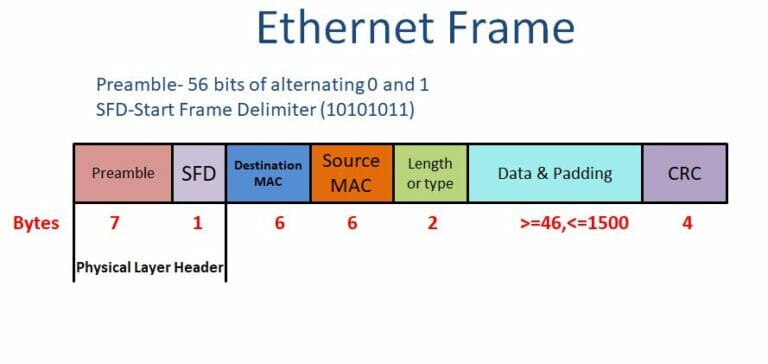
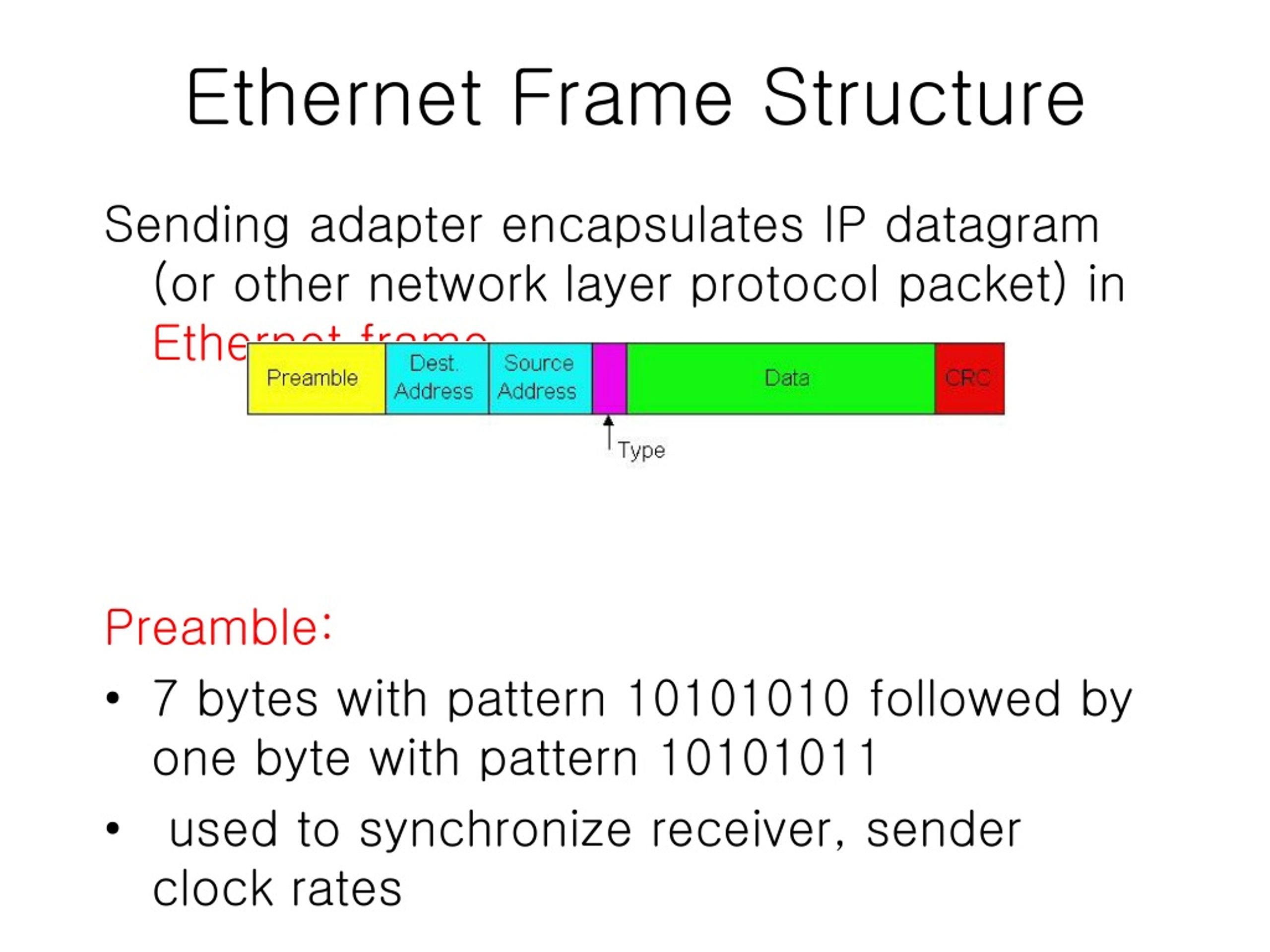
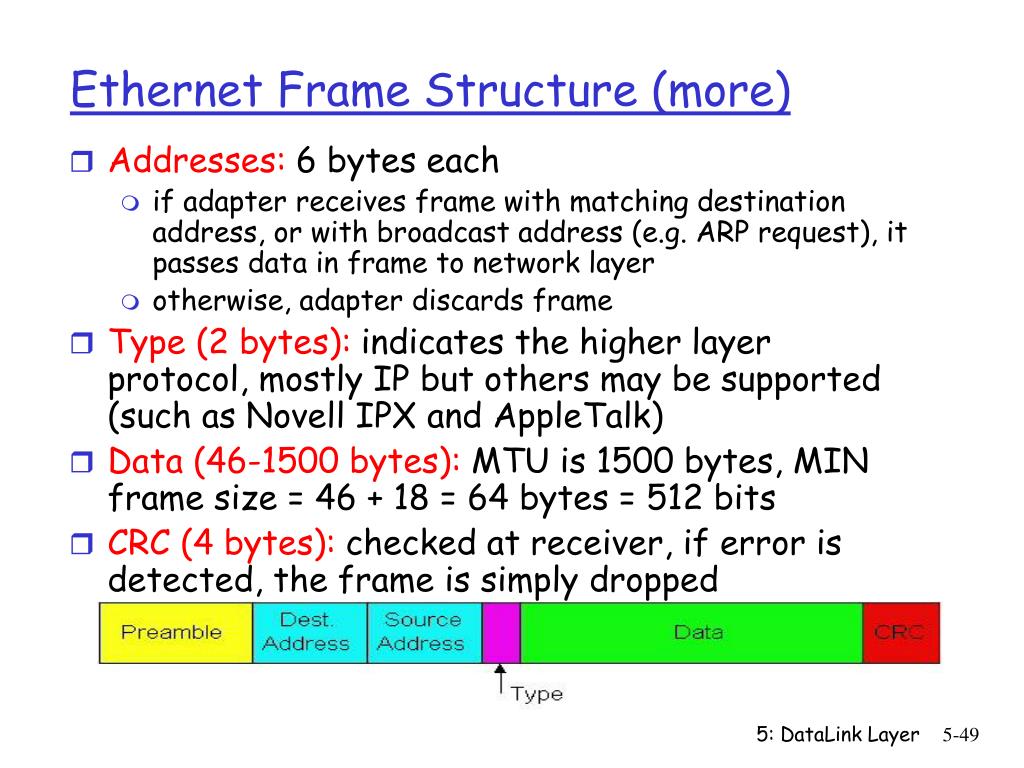
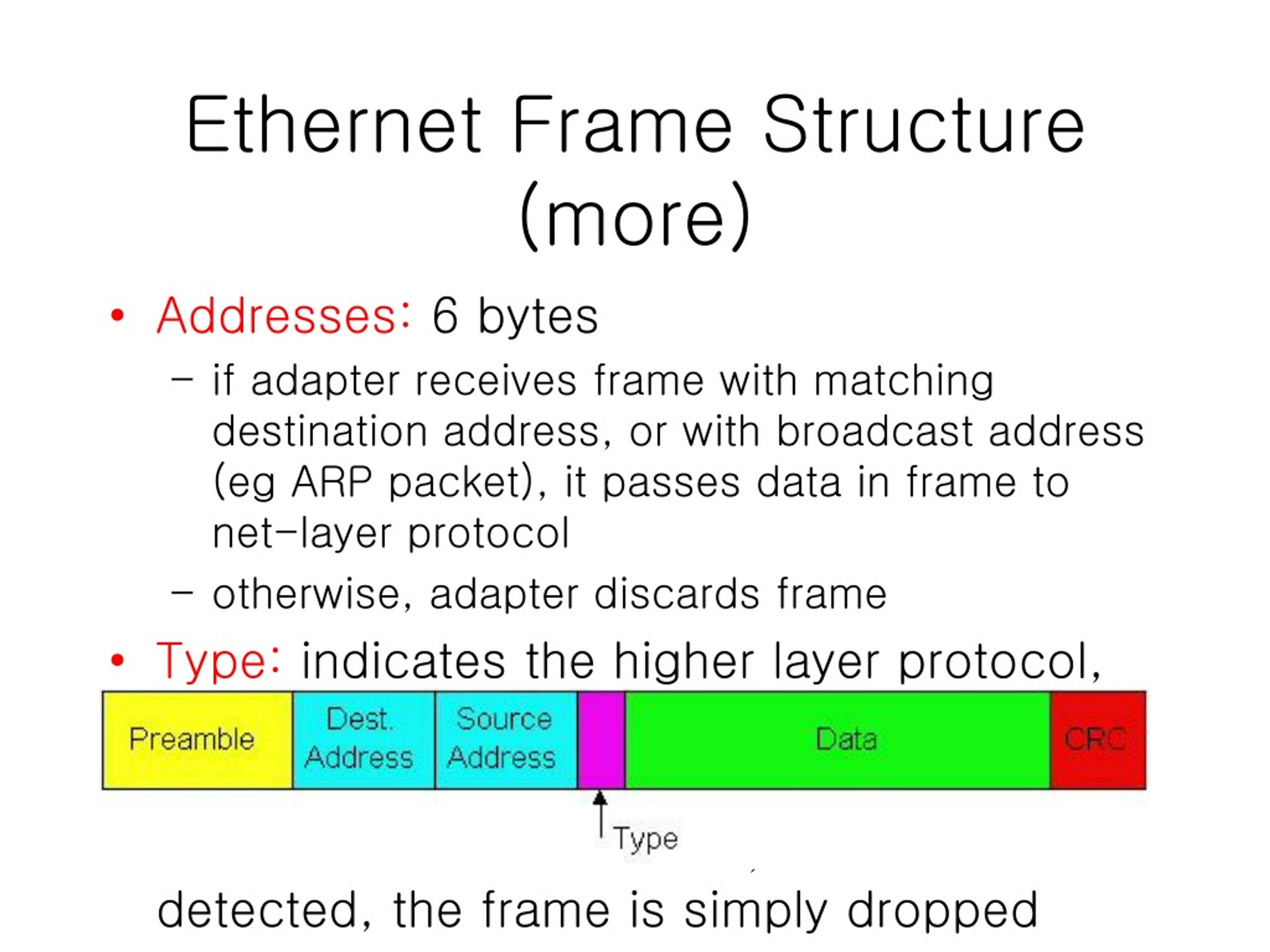
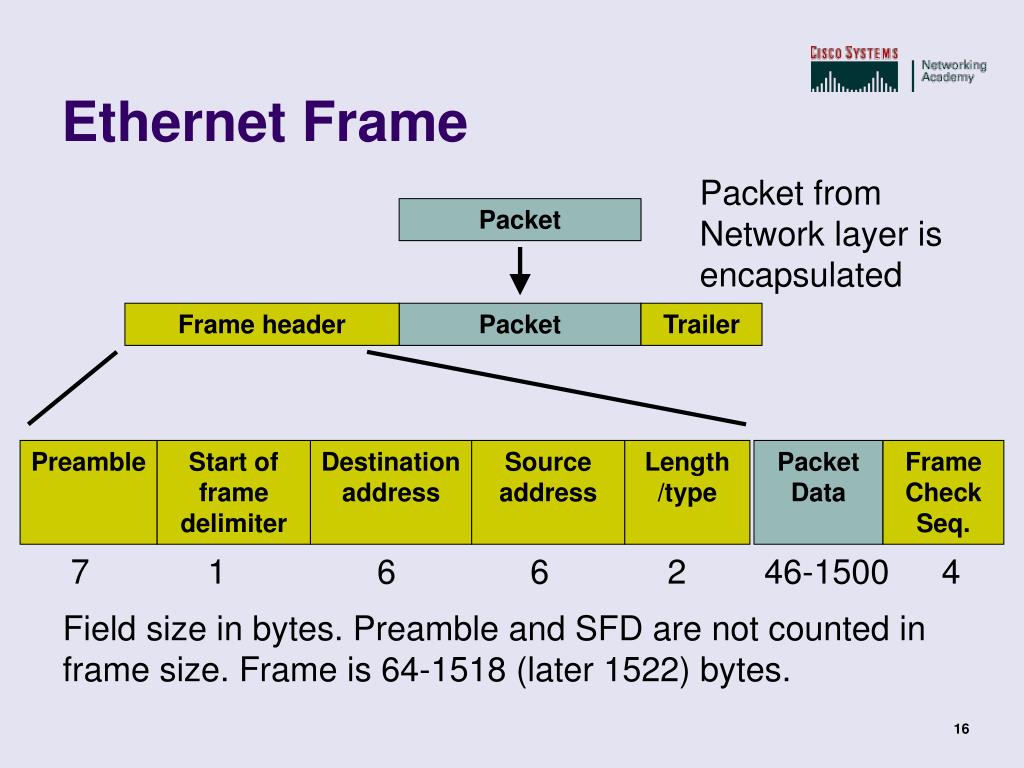
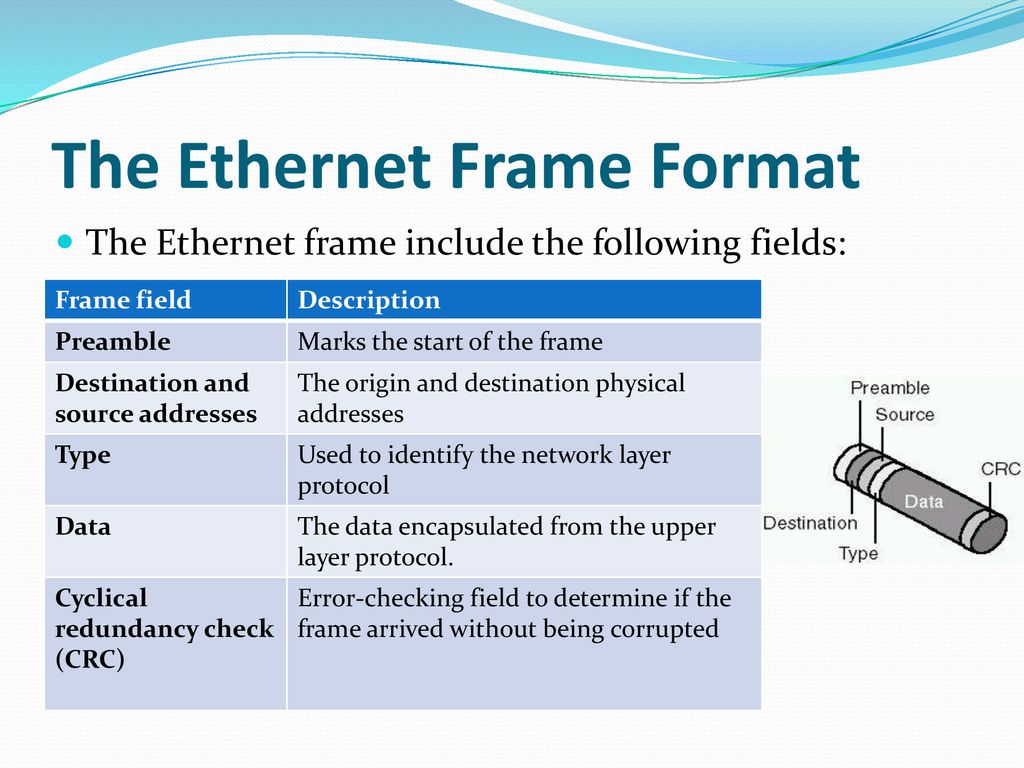
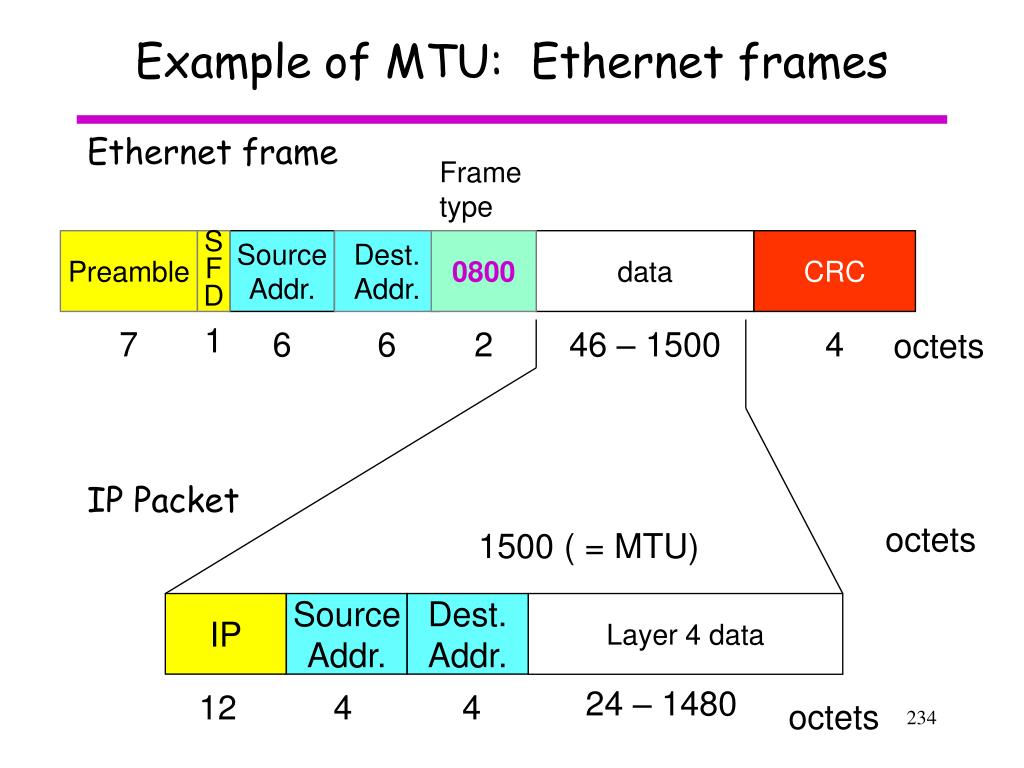
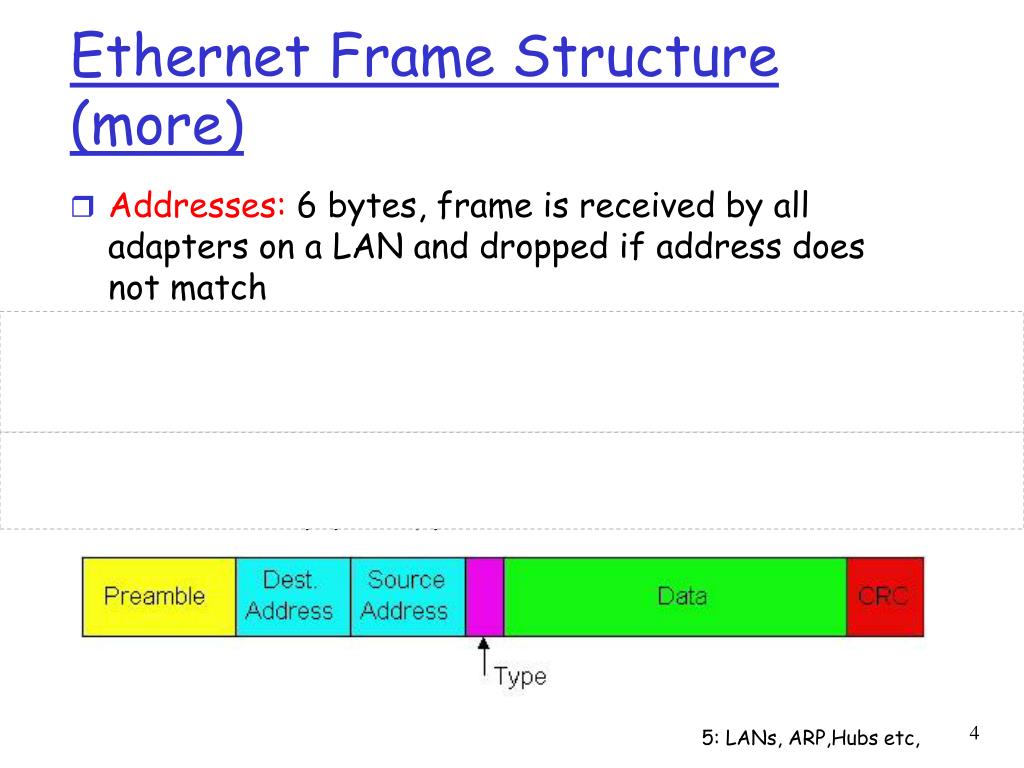
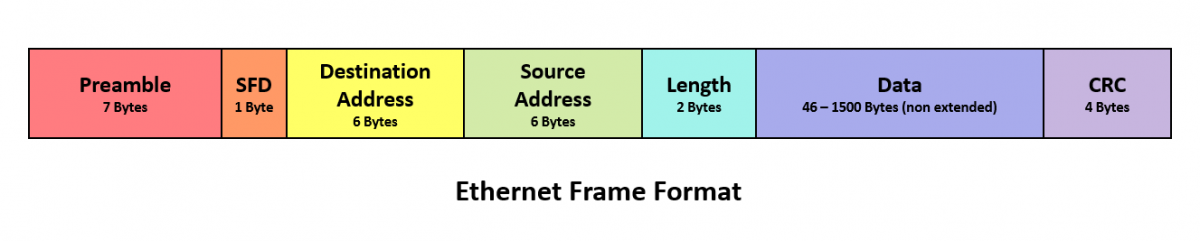
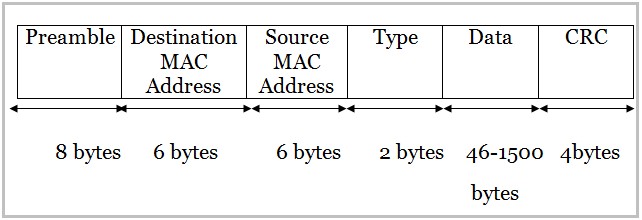
The basic parts of an Ethernet frame are the preamble, start-of-frame delimiter (SFD), destination MAC address, source MAC address, EtherType/Length, data payload, and frame check sequence (FCS).
Preamble and Start-of-Frame Delimiter (SFD)
The preamble is a 7-byte sequence of alternating 1s and 0s (10101010) used for synchronization. It allows receiving devices to synchronize their clocks with the incoming signal. Following the preamble is the SFD (start-of-frame delimiter), a 1-byte sequence (10101011) that signals the beginning of the actual frame data.
These elements work together to prepare the receiving network card for data reception. Without them, the rest of the frame could be misinterpreted.
Destination and Source MAC Addresses
The destination MAC address is a 6-byte field specifying the hardware address of the intended recipient of the frame. This address is unique to each network interface card (NIC). Similarly, the source MAC address is a 6-byte field that indicates the hardware address of the sending device.
These addresses enable devices on the network to identify the sender and receiver of data. They are essential for ensuring that data reaches the correct destination within the LAN. The MAC address is a 48-bit hexadecimal address.
EtherType/Length Field
This 2-byte field serves a dual purpose. If the value is less than or equal to 1500 (0x05DC), it represents the length of the data payload in bytes. If it is greater than 1536 (0x0600), it indicates the EtherType, specifying the protocol of the data carried within the frame, such as IP (Internet Protocol).
This duality allows the Ethernet frame to carry data from various higher-layer protocols. The EtherType enables the receiving device to correctly interpret the contents of the data payload.
Data Payload
The data payload is the actual information being transmitted. The size of this field can vary depending on the network configuration, but it typically ranges from 46 to 1500 bytes. This data can include everything from text and images to video and audio.
The payload contains the actual data that the sender wishes to transmit to the receiver. It's the core of the Ethernet frame.
Frame Check Sequence (FCS)
The FCS is a 4-byte field containing a cyclic redundancy check (CRC) value. This CRC is calculated based on the contents of the frame, excluding the preamble and SFD. The receiving device recalculates the CRC and compares it to the FCS value.
If the values match, it indicates that the frame was transmitted without errors. If the values differ, it indicates that the frame has been corrupted during transmission and is discarded, ensuring data integrity on the network. This process of error detection is critical for reliable communication.
Significance and Impact
The Ethernet frame, with its carefully structured components, plays a pivotal role in the functioning of modern networks. Its standardized format allows devices from different manufacturers to communicate seamlessly, forming the backbone of countless LANs and contributing to the internet's overall infrastructure.
Understanding the components of an Ethernet frame is crucial for network administrators, developers, and anyone seeking to deepen their knowledge of how networks operate. This knowledge enables better troubleshooting, network design, and overall network management.
The efficiency and reliability of Ethernet communication, underpinned by the structure of the Ethernet frame, have facilitated the growth of the internet and the proliferation of networked devices. This is a testament to the importance of standardized protocols in ensuring interoperability and seamless data exchange in the digital age.