Which Of The Following Are Stockholder Equity Accounts
The financial health of a corporation hinges on a clear understanding of its stockholder equity. Investors and stakeholders meticulously analyze these accounts to gauge a company's net worth and its ability to meet its obligations. Misinterpreting or misclassifying these accounts can lead to inaccurate financial reporting and potentially disastrous investment decisions.
This article delves into the essential components of stockholder equity, clarifying which accounts fall under this critical category. Understanding these accounts is crucial for investors, financial analysts, and anyone seeking to evaluate a company's financial stability and long-term prospects. We will explore common equity accounts, dissect their individual roles, and highlight their significance in financial analysis.
Understanding Stockholder Equity
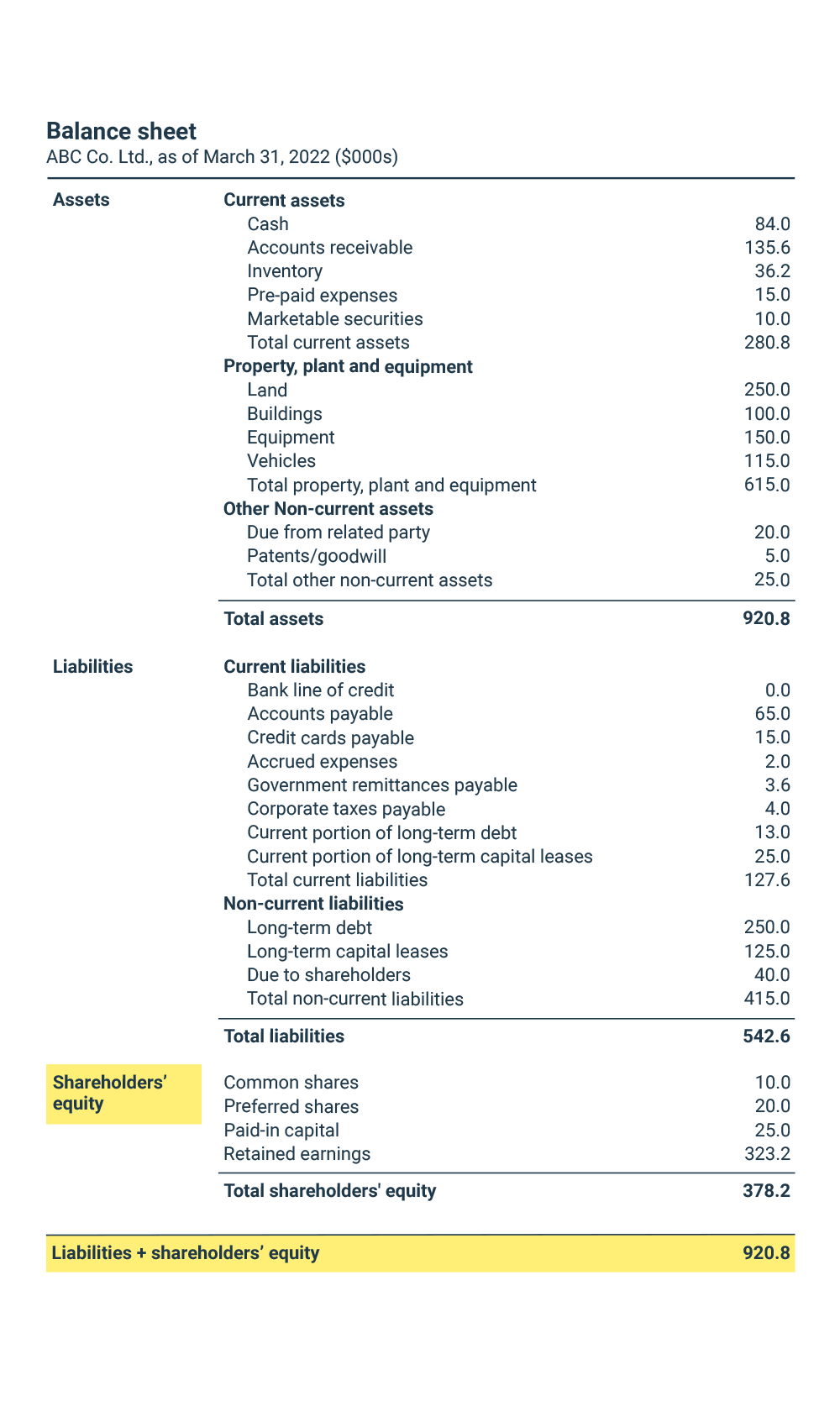
Stockholder equity, often called shareholders' equity or net worth, represents the owners' stake in a company's assets after deducting its liabilities. It is the residual interest in the assets of an entity that remains after deducting its liabilities. It's a crucial indicator of a company’s financial position and its ability to absorb losses.
Key Components of Stockholder Equity
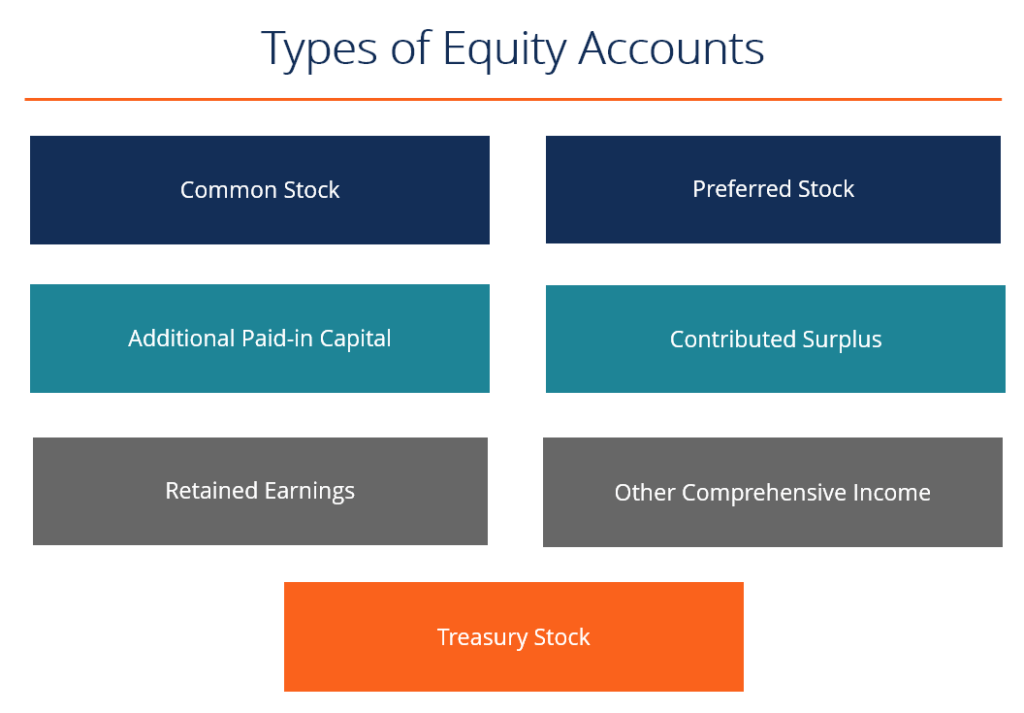
Several accounts typically comprise stockholder equity. These accounts provide a detailed breakdown of the company's ownership structure and accumulated profits. We will examine these individually.
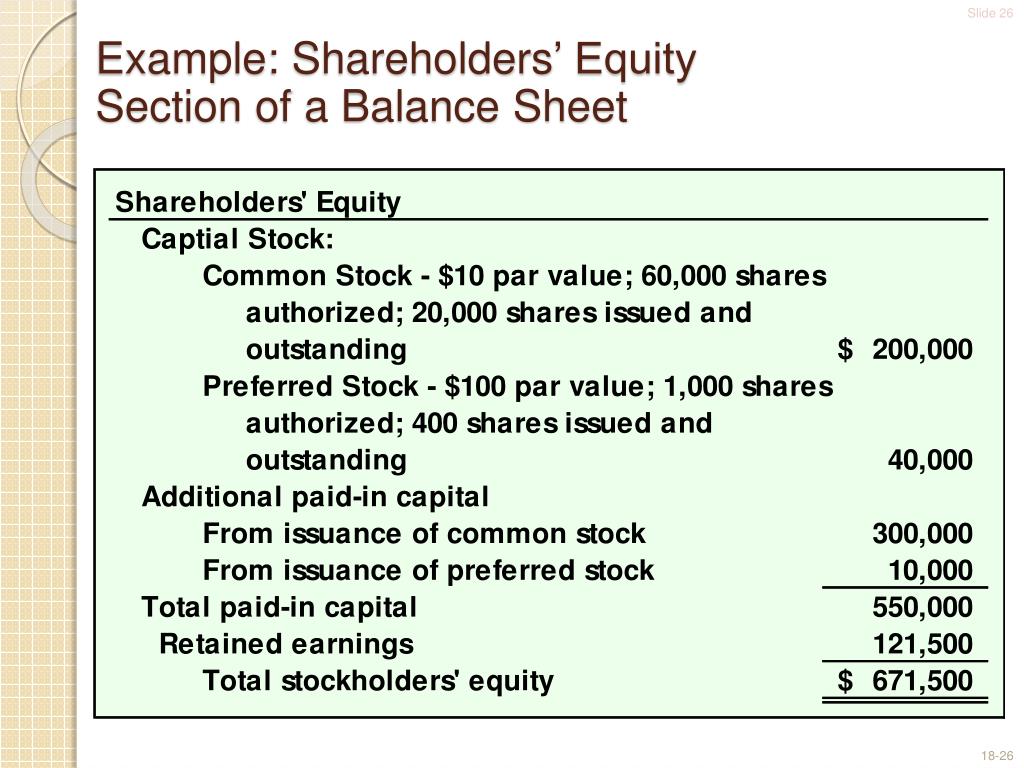
Common Stock
Common stock represents the basic ownership in a corporation. Common stockholders typically have voting rights, allowing them to participate in company decisions. The par value of common stock is usually a nominal amount.
Preferred Stock
Preferred stock is another type of ownership, often carrying preferential rights over common stock. These rights may include priority in dividend payments or asset distribution during liquidation. Preferred stockholders generally do not have voting rights.
Additional Paid-In Capital (APIC)
APIC represents the amount of money received from investors for stock exceeding its par value. It reflects the premium investors are willing to pay for a company's shares. This is an important metric showing investor confidence.
Retained Earnings
Retained earnings are the accumulated profits of a company that have not been distributed to shareholders as dividends. It is a key indicator of a company's profitability over time. A healthy balance of retained earnings is usually a sign of financial strength.
Treasury Stock
Treasury stock refers to shares of a company's own stock that it has repurchased from the open market. This reduces the number of outstanding shares. Treasury stock is a contra-equity account, meaning it reduces the overall stockholder equity.
Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (AOCI)
AOCI includes items such as unrealized gains and losses on available-for-sale securities and foreign currency translation adjustments. These items are not reported on the income statement but are included in stockholder equity. It provides a more comprehensive view of a company's financial performance.
Accounts That Are Not Stockholder Equity
It is essential to distinguish stockholder equity accounts from other financial statement items. Misclassification can lead to misleading financial analysis. Here are some examples of accounts that are not part of stockholder equity.
Liabilities
Liabilities represent obligations to external parties. Examples include accounts payable, salaries payable, and debt. Liabilities are completely separate from owner's equity.
Assets
Assets are resources controlled by the company as a result of past events and from which future economic benefits are expected to flow to the company. Examples include cash, accounts receivable, and property, plant, and equipment (PP&E). Assets are distinct from owner's equity.
Revenue and Expenses
Revenue and expenses are income statement accounts that reflect a company's performance over a specific period. These accounts ultimately impact retained earnings but are not direct components of stockholder equity. They are key to calculating net income, which flows into retained earnings.
The Importance of Accurate Stockholder Equity Reporting
Accurate reporting of stockholder equity is paramount for transparency and investor confidence. Financial statements, particularly the balance sheet, must accurately reflect the composition of equity. Any misrepresentation or omission can significantly impact investment decisions.
The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) closely monitors financial reporting. Companies must adhere to Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) or International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) to ensure accuracy. Failure to comply can result in severe penalties.
Analyzing Stockholder Equity
Analysts use stockholder equity to calculate various financial ratios, such as return on equity (ROE). ROE measures a company's profitability relative to its shareholder equity. These ratios are vital for assessing a company's financial performance and investment potential.
A declining equity balance can signal financial distress. An increasing balance usually signifies growth and profitability.
The Future of Stockholder Equity Accounting
The landscape of financial accounting is constantly evolving. New accounting standards and interpretations may affect how stockholder equity is reported. Staying abreast of these changes is critical for financial professionals.
Furthermore, the increasing use of technology, such as blockchain, could revolutionize equity management and reporting. This could lead to greater transparency and efficiency.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of stockholder equity accounts is essential for navigating the complexities of financial analysis. By accurately identifying and interpreting these accounts, investors and stakeholders can make informed decisions and assess a company's true financial standing. Continued vigilance and adaptation to evolving accounting standards will be crucial for maintaining accurate and reliable financial reporting in the years to come.