Which Of The Following Can Be Characteristics Of Algae

Algae, often misunderstood and vastly diverse, exhibit a range of characteristics that are critical for understanding their role in our ecosystems. Confusion persists regarding which traits accurately define these vital organisms.
This article will pinpoint key characteristics of algae, clearing up misconceptions and providing a factual overview of their biology. Understanding these traits is crucial for addressing environmental challenges and harnessing algae's potential benefits.
Photosynthesis: The Core of Algal Life
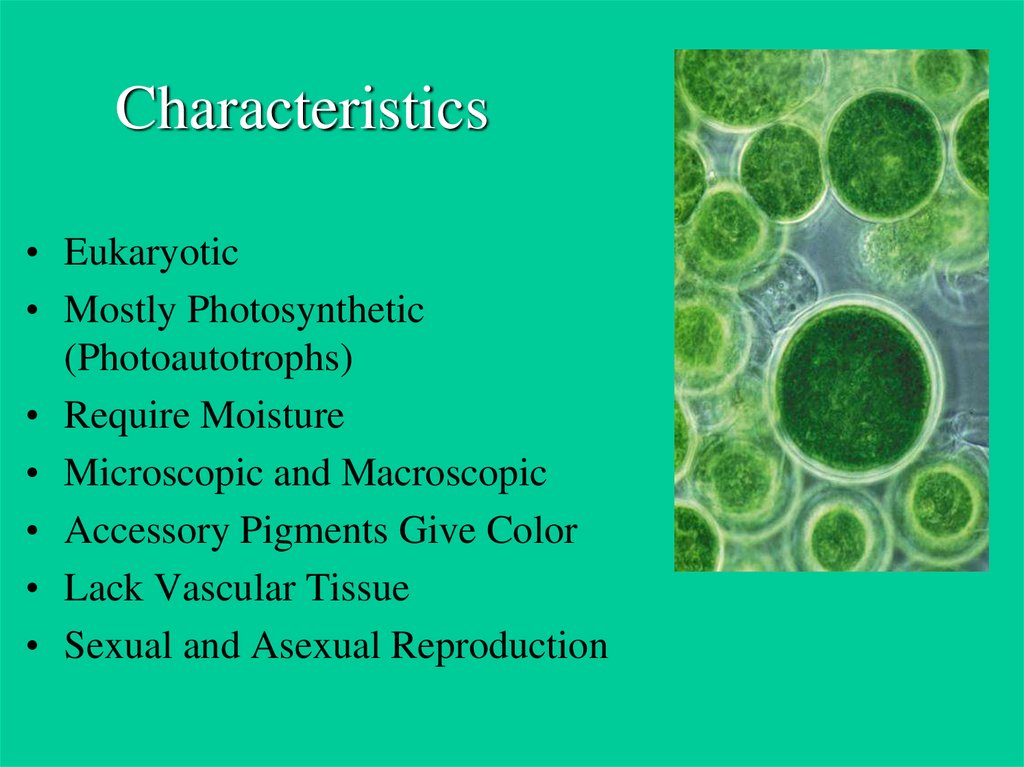
Algae are fundamentally photosynthetic organisms. Like plants, they possess chloroplasts and utilize chlorophyll to convert light energy into chemical energy. This process forms the basis of most aquatic food webs.
They consume carbon dioxide and release oxygen, contributing significantly to global oxygen production. Some studies indicate that algae produce at least 50% of the Earth's oxygen.
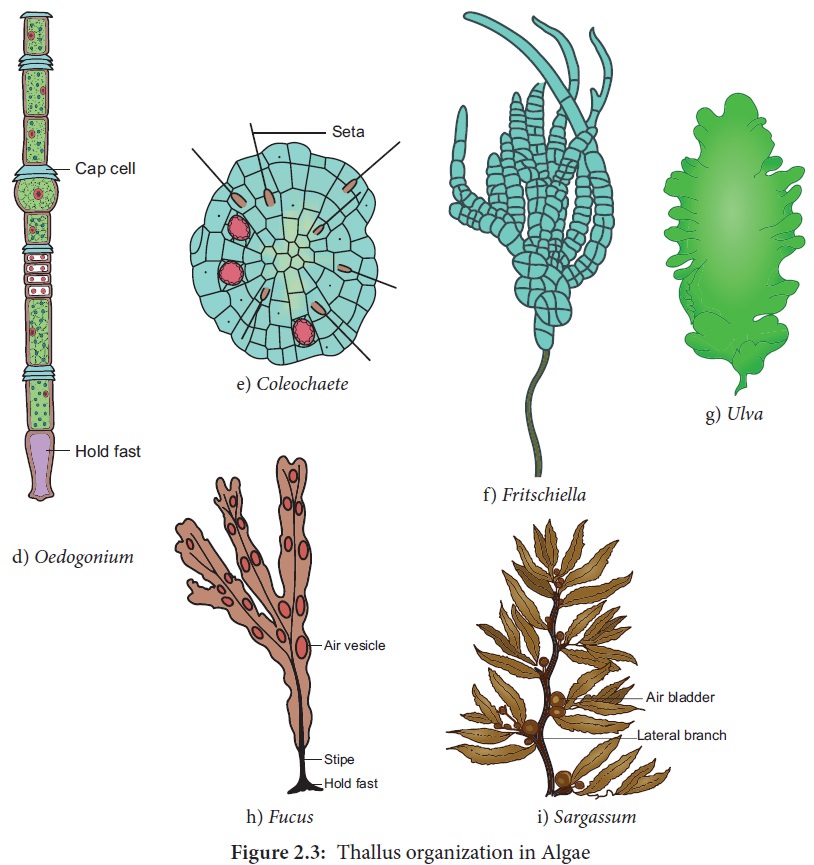
Cellular Structure: From Unicellular to Multicellular
Algae display a remarkable diversity in cellular organization. They range from single-celled, microscopic organisms to complex, multicellular seaweeds.
Unicellular algae, such as diatoms and dinoflagellates, are crucial components of phytoplankton. Multicellular algae, like kelp, can form vast underwater forests.
Habitat: Thriving in Diverse Environments
Algae inhabit a wide array of environments. They are found in oceans, lakes, rivers, and even terrestrial habitats like soil and snow.
Some algae are extremophiles, thriving in harsh conditions such as hot springs or highly saline environments. Their adaptability is a key factor in their ecological success.
Pigments: Beyond Chlorophyll
While chlorophyll is essential for photosynthesis, algae often contain other pigments. These pigments, such as carotenoids and phycobilins, give algae their distinctive colors.
Different algal groups have varying combinations of pigments, resulting in green, brown, red, and even golden-colored species. These pigments also play a role in light absorption at different depths in aquatic environments.
Reproduction: A Variety of Strategies
Algae reproduce through diverse methods, including both sexual and asexual reproduction. Asexual reproduction, such as fragmentation and spore formation, allows for rapid population growth.
Sexual reproduction, involving the fusion of gametes, increases genetic diversity. Some species exhibit complex life cycles involving alternating generations with different reproductive strategies.
Nutrient Uptake: Absorbing from the Environment
Algae absorb nutrients directly from their surrounding environment. They lack the complex vascular systems found in plants, relying on diffusion to obtain essential elements.
Nitrogen, phosphorus, and iron are particularly important for algal growth. Excess nutrients can lead to algal blooms, which can have detrimental effects on aquatic ecosystems.
Cell Walls: Structure and Protection
Algae possess cell walls that provide structural support and protection. The composition of the cell wall varies among different algal groups.
Diatoms, for example, have cell walls made of silica, forming intricate and beautiful structures. Other algae may have cell walls composed of cellulose or other polysaccharides.
Storage Products: Energy Reserves
Algae store energy in various forms, including starch, oils, and other carbohydrates. These storage products serve as reserves for periods of nutrient limitation or darkness.
The high oil content of some algae makes them promising candidates for biofuel production. Research is ongoing to optimize algal lipid production for sustainable energy applications.
Ecological Roles: Keystone Species
Algae play critical roles in aquatic ecosystems. They are primary producers, forming the base of the food web and supporting a vast array of organisms.
They also contribute to nutrient cycling and help regulate water quality. Disruptions to algal populations can have cascading effects on the entire ecosystem.
What Are Not Universal Characteristics of Algae
While many consider them plants, algae are not true plants. They lack the complex structures found in vascular plants, such as roots, stems, and leaves.
Not all algae are microscopic. Giant kelp, for instance, can grow to be over 100 feet long.
Ongoing Research and Future Directions
Researchers continue to explore the diverse world of algae. Studies focus on understanding their physiology, ecology, and potential applications in various fields.
Efforts are underway to develop sustainable methods for cultivating algae for food, fuel, and other valuable products. Further research is needed to fully unlock the potential of these remarkable organisms. Monitoring and mitigation strategies are crucial to address harmful algal blooms and protect aquatic ecosystems.