Which Of The Following Effects May Be Experienced With Overtraining

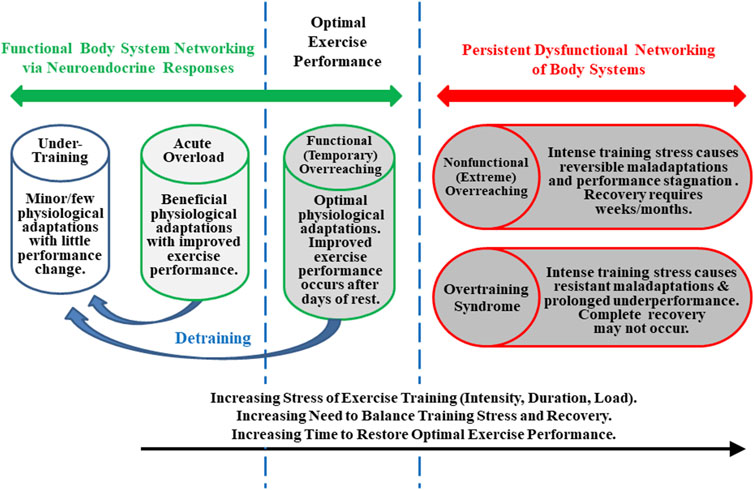
Athletes and fitness enthusiasts, heed this warning: pushing too hard can lead to serious consequences. Overtraining, a common pitfall for those striving for peak performance, manifests in a range of debilitating symptoms that can derail progress and harm health.
This article dissects the various effects of overtraining, providing critical information to help individuals recognize and address the warning signs before they escalate into chronic issues. Understanding these effects is paramount to maintaining a sustainable and healthy training regimen.
Performance Decline: The First Red Flag
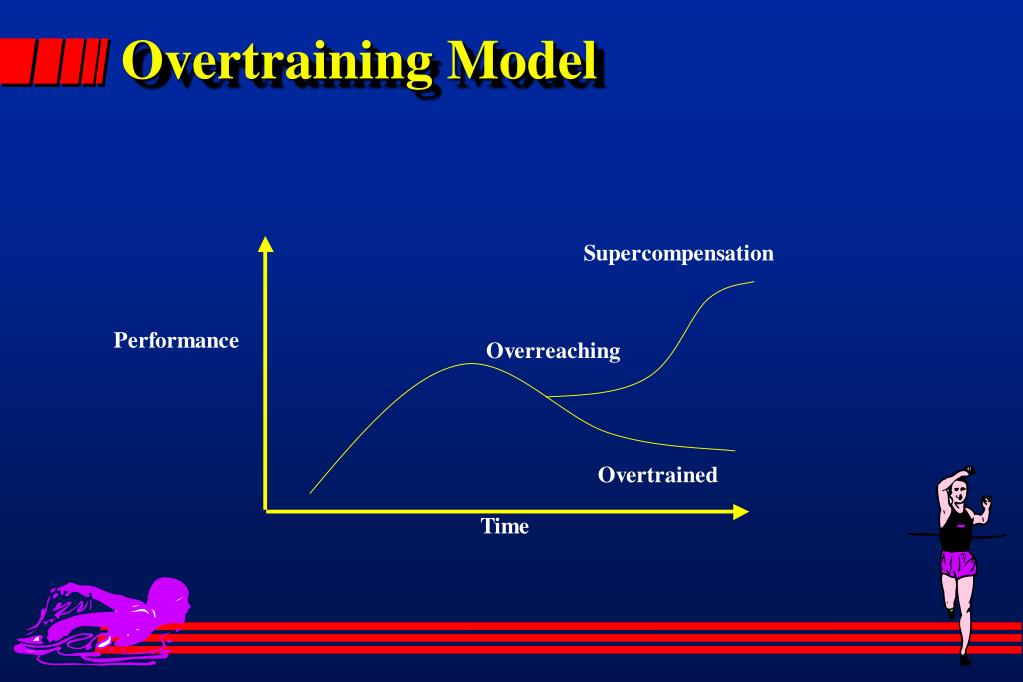
One of the earliest and most noticeable signs of overtraining is a paradoxical decrease in performance. Instead of improving with increased training volume and intensity, athletes find themselves struggling to maintain previous levels. This decline stems from the body's inability to adequately recover from the cumulative stress.
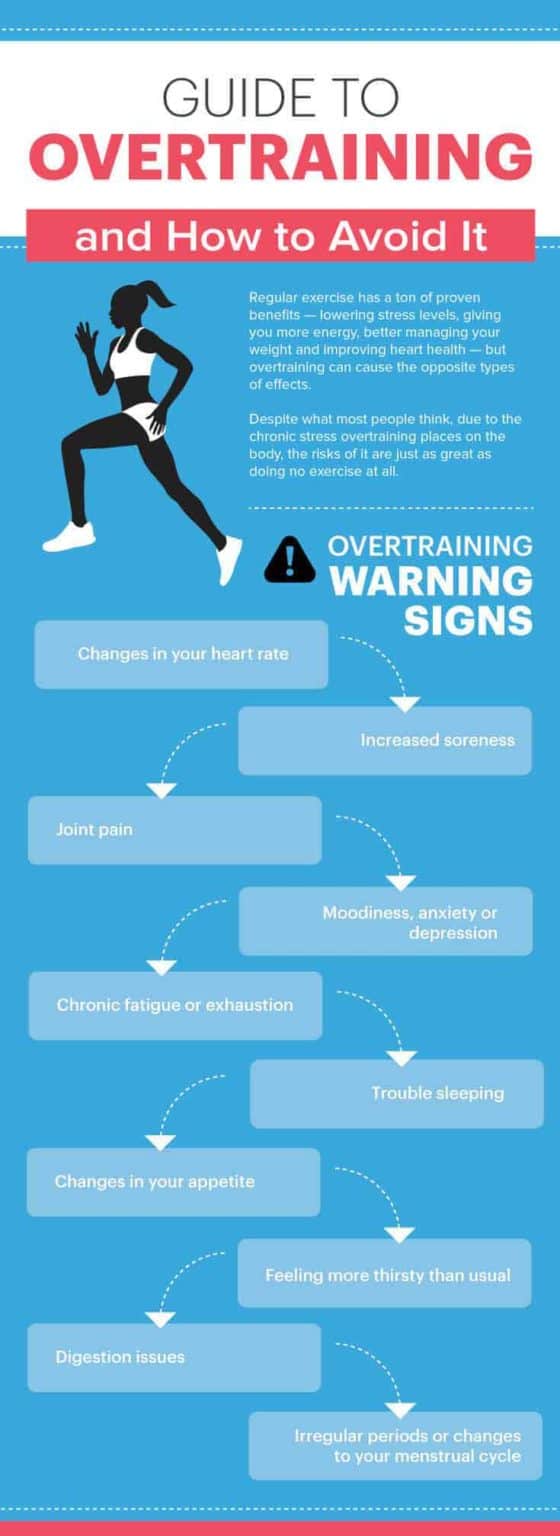
Decreased speed, reduced strength, and impaired endurance are all indicative of overtraining. Ignoring these initial symptoms can lead to more severe repercussions.
Physiological Effects: Body Under Siege
Overtraining significantly impacts various physiological systems. The body's hormonal balance is disrupted, impacting energy levels and overall well-being.
Elevated levels of cortisol, the stress hormone, coupled with decreased levels of testosterone, are common findings in overtrained individuals. These hormonal shifts contribute to fatigue, muscle loss, and mood disturbances.
Immune System Suppression: Opening the Door to Illness
The immune system, crucial for fighting off infections, becomes compromised under the strain of overtraining. Athletes become more susceptible to colds, flu, and other illnesses.
Studies have shown a direct correlation between intense training and a suppressed immune response. A weakened immune system hinders recovery and further exacerbates the effects of overtraining.
Sleep Disturbances: The Vicious Cycle
Sleep, essential for recovery and repair, is often disrupted by overtraining. Insomnia, restless sleep, and difficulty falling asleep are common complaints.
The hormonal imbalances and heightened nervous system activity associated with overtraining interfere with normal sleep patterns. Lack of quality sleep further impairs recovery, creating a vicious cycle of fatigue and declining performance.
Psychological Effects: Mental Fatigue and Burnout
Overtraining not only affects the body but also takes a toll on mental well-being. Athletes experiencing overtraining often report increased irritability, anxiety, and depression.
Loss of motivation, decreased focus, and a general sense of burnout are also characteristic of overtraining. These psychological effects can be as debilitating as the physical symptoms.
Mood Swings and Irritability: Emotional Rollercoaster
The hormonal imbalances associated with overtraining can lead to significant mood swings. Athletes may experience sudden bouts of anger, sadness, or frustration.
Increased irritability and a decreased tolerance for stress are also common. These emotional fluctuations can strain relationships and further hinder performance.
Decreased Appetite: Fueling the Fire With Less
Overtraining can disrupt appetite regulation, leading to a decrease in appetite. This can further compound the problem by depriving the body of the nutrients it needs to recover.
Reduced calorie intake, combined with increased energy expenditure, creates a deficit that further exacerbates the symptoms of overtraining. Proper nutrition is crucial for recovery and preventing overtraining.
Musculoskeletal Issues: Aches and Pains Beyond Normal Soreness
Chronic muscle soreness, joint pain, and an increased risk of injuries are common musculoskeletal manifestations of overtraining. The body simply cannot repair itself adequately under constant stress.
Stress fractures, tendonitis, and other overuse injuries are more likely to occur in overtrained individuals. Ignoring these warning signs can lead to chronic pain and long-term disability.
Who is at Risk? Everyone From Weekend Warriors to Elite Athletes
While often associated with elite athletes, overtraining can affect anyone who pushes their body too hard without adequate rest and recovery. Beginners, intermediate exercisers, and seasoned athletes are all susceptible.
Factors such as poor training planning, inadequate nutrition, insufficient sleep, and chronic stress can increase the risk of overtraining. Being aware of these risk factors is crucial for prevention.
When to Seek Help? Recognizing the Point of No Return
Recognizing the early signs of overtraining is crucial for preventing long-term consequences. If you experience a combination of the symptoms described above, it's essential to seek professional help.
Consult with a physician, sports medicine specialist, or qualified coach to assess your condition and develop a recovery plan. Early intervention is key to avoiding chronic overtraining.
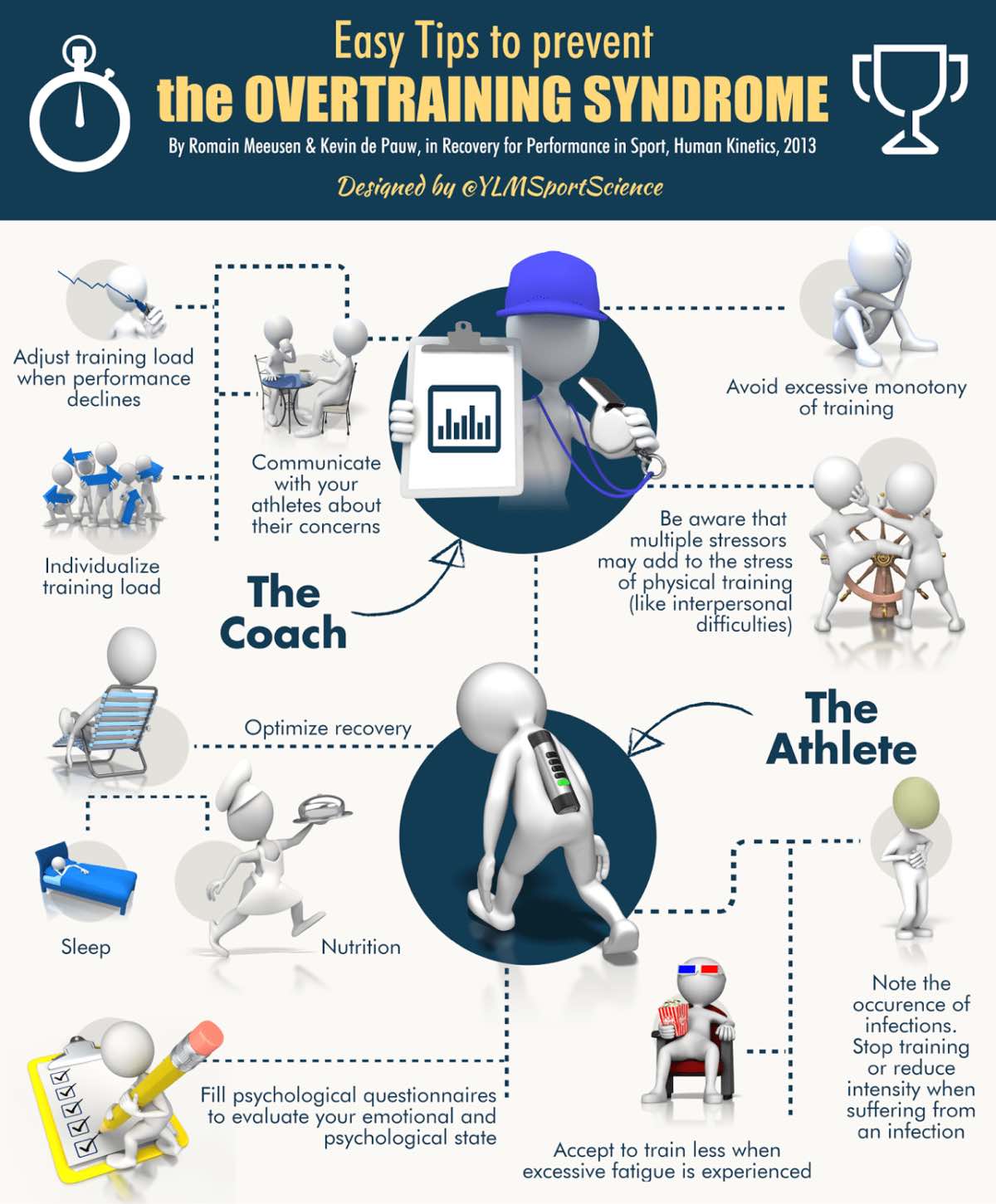
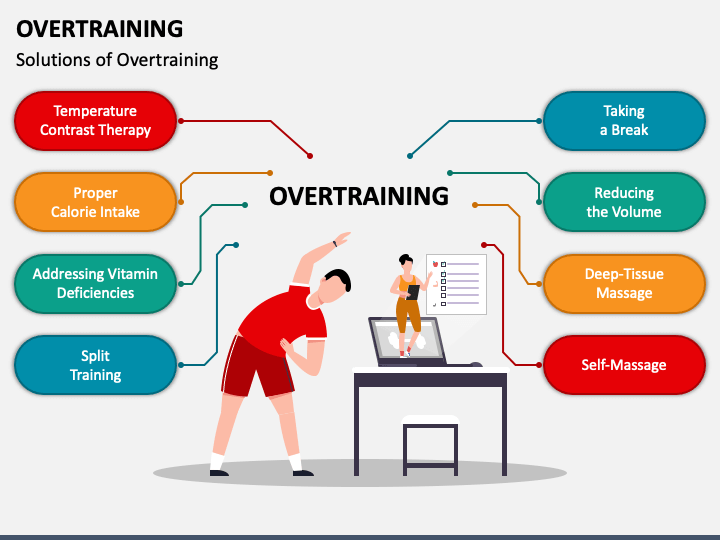
How to Prevent Overtraining? Smart Training is Key
Preventing overtraining involves implementing a smart training plan that prioritizes rest and recovery. Gradual increases in training volume and intensity, along with adequate sleep and proper nutrition, are essential.
Listen to your body, and don't hesitate to take rest days when needed. Consider incorporating cross-training and active recovery into your routine to reduce stress on specific muscle groups.
Next steps: If you suspect you are experiencing overtraining, immediately reduce your training load. Consult with a healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation and personalized recovery plan. Further research is ongoing to refine our understanding of overtraining and develop more effective prevention and treatment strategies. Stay tuned for updates.