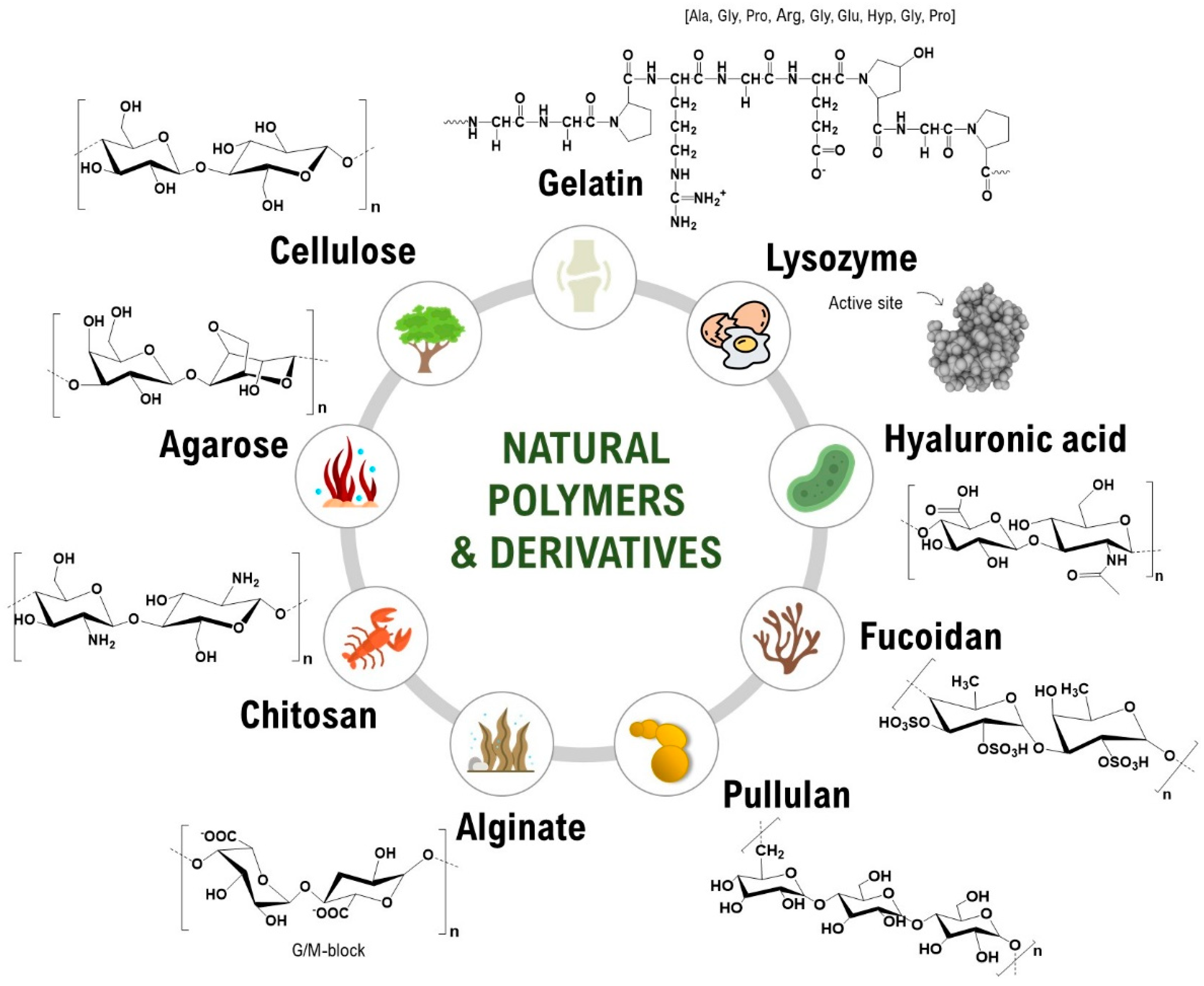
Which Of The Following Is A Natural Polymer

The question of identifying natural polymers has become increasingly relevant in various fields, from sustainable material science to biomedical engineering. Understanding the composition and source of these large molecules is crucial for developing eco-friendly alternatives and innovative technologies.
This article will explore what defines a natural polymer, highlight examples of commonly encountered natural polymers, and discuss their significance across diverse industries. We will delve into the characteristics that distinguish these materials from their synthetic counterparts, examining their sources, properties, and applications.
What Defines a Natural Polymer?
A polymer is a large molecule, or macromolecule, composed of many repeated subunits. Natural polymers are polymers that occur in nature, produced by living organisms.
They are typically created through a process called polymerization, where smaller molecules, known as monomers, combine to form the larger polymeric structure. Unlike synthetic polymers which are man-made, natural polymers originate from plant, animal, or microbial sources.
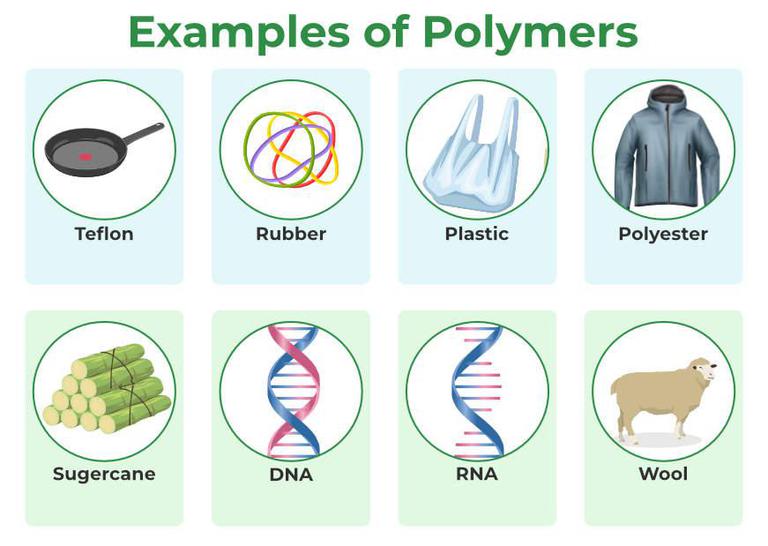
Key Examples of Natural Polymers
Several natural polymers are essential to life and play significant roles in various industries. These include polysaccharides, proteins, nucleic acids, and natural rubber.
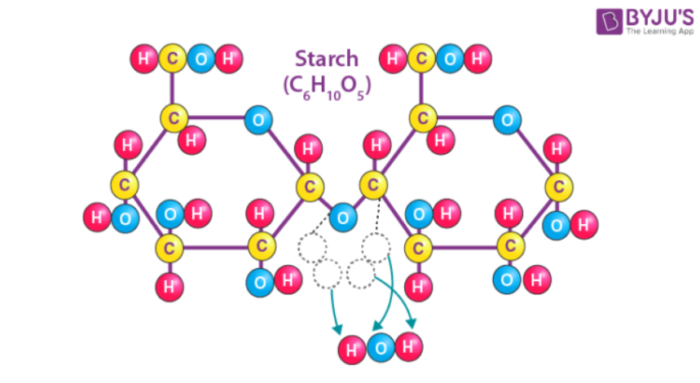
Polysaccharides, such as starch, cellulose, and chitin, are abundant carbohydrates. Starch, found in plants like potatoes and corn, serves as an energy storage molecule.
Cellulose, the primary structural component of plant cell walls, is the most abundant organic polymer on Earth. Chitin, found in the exoskeletons of insects and crustaceans, provides structural support and protection.
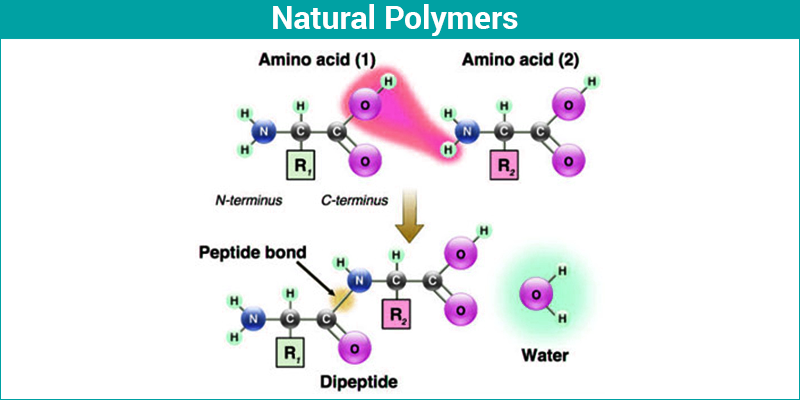
Proteins are another crucial class of natural polymers. These complex molecules are composed of amino acid monomers and perform a wide range of functions in living organisms, from catalyzing biochemical reactions to transporting molecules.
Examples of proteins include enzymes, antibodies, and structural proteins like collagen and keratin. Collagen provides structural support in connective tissues, while keratin is the main component of hair, skin, and nails.
Nucleic acids, including DNA and RNA, are responsible for storing and transmitting genetic information. These polymers are composed of nucleotide monomers, each consisting of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
DNA carries the genetic code that determines the characteristics of an organism, while RNA plays a role in protein synthesis. These natural polymers are fundamental to life as we know it.
Natural rubber, derived from the sap of rubber trees, is another important example. This polymer, composed of isoprene monomers, possesses unique elastic properties, making it valuable in various applications, including tires and sealants.
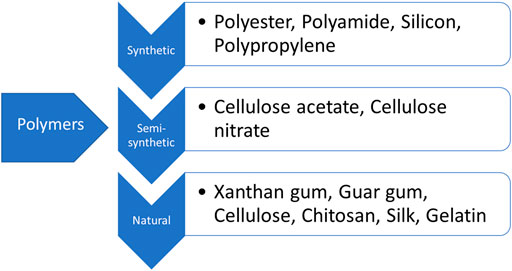
Distinguishing Natural Polymers from Synthetic Polymers
The primary difference between natural and synthetic polymers lies in their origin. Natural polymers are derived from living organisms, while synthetic polymers are created through chemical processes in laboratories or industrial settings.
Synthetic polymers, such as polyethylene, polypropylene, and PVC, are often derived from petroleum-based resources. The properties of natural polymers are often dependent on their natural source and processing methods.
Another key distinction is biodegradability. Many natural polymers are biodegradable, meaning they can be broken down by microorganisms in the environment. This makes them attractive for environmentally friendly applications.
Significance and Applications
Natural polymers are significant due to their renewability, biodegradability, and biocompatibility. These properties make them attractive alternatives to synthetic polymers in various applications.
In the food industry, starch and cellulose are used as thickeners, stabilizers, and packaging materials. Proteins are essential nutrients and functional ingredients in various food products.
In the biomedical field, natural polymers like collagen and chitosan are used in tissue engineering, drug delivery, and wound healing applications. Their biocompatibility and biodegradability make them ideal for these purposes.
The textile industry utilizes natural polymers like cotton, wool, and silk. These fibers provide comfort, breathability, and aesthetic appeal in clothing and other textile products.
Moreover, ongoing research focuses on modifying natural polymers to enhance their properties and expand their applications. This includes developing new bio-based plastics, adhesives, and coatings.
Future Trends and Developments
The demand for sustainable materials is driving innovation in the field of natural polymers. Researchers are exploring new sources of natural polymers and developing more efficient extraction and processing methods.
Genetic engineering is also being used to modify organisms to produce natural polymers with enhanced properties. This approach holds promise for creating customized materials with specific functionalities.
The development of bio-based polymers and composites is expected to continue to grow in the coming years. This trend will be driven by increasing environmental awareness and stricter regulations on the use of petroleum-based materials.
In conclusion, understanding which materials are natural polymers is essential for developing sustainable and innovative solutions across various industries. From the food we eat to the medical treatments we receive, these remarkable molecules play a vital role in our lives.
As research and development continue, we can expect to see even greater utilization of natural polymers in the future, contributing to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly world. Identifying these materials is just the first step in unlocking their full potential.

+Which+of+the+following+is+not+an+example+of+a+natural+polymer.jpg)