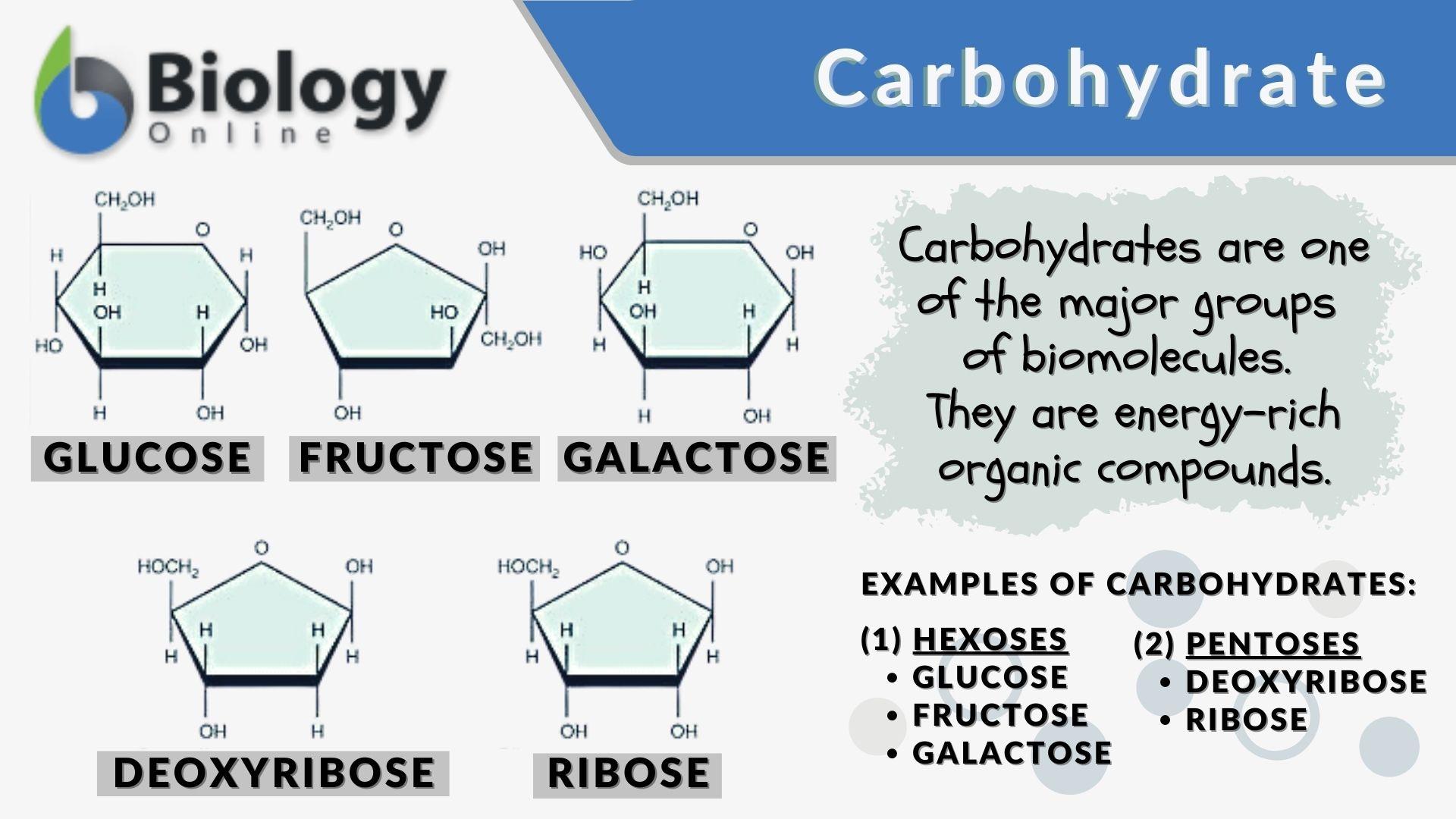
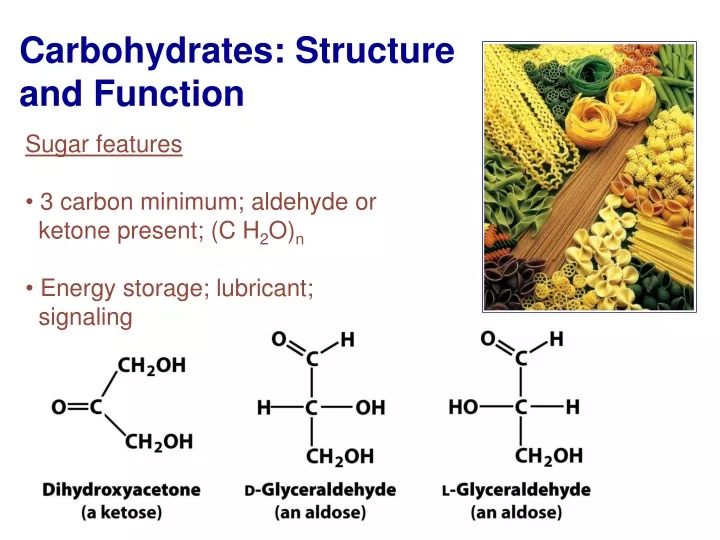
Which Of The Following Is A Primary Function Of Carbohydrates

Imagine a brisk morning, the sun barely peeking over the horizon. You’re reaching for that steaming cup of coffee and a slice of whole-wheat toast, the aroma filling your kitchen. What you might not consciously consider is the intricate dance happening within your body as it breaks down that simple carbohydrate, fueling your first steps into the day.
At its core, the primary function of carbohydrates is to provide energy. This article delves into the multifaceted role of carbohydrates, exploring how they power our bodies, their different forms, and why understanding their function is essential for maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
The Energy Currency of Life
Carbohydrates are one of the three macronutrients – the others being fats and proteins – that our bodies need to function properly. They are the body’s preferred and most readily available source of energy.
Think of them as the fuel in your car, allowing you to move, think, and perform all the vital functions that keep you alive. This energy is crucial for everything from breathing to running a marathon.
Glucose: The Star Player
The magic behind carbohydrate energy lies in a simple sugar called glucose. When you consume carbohydrates, your body breaks them down into glucose, which is then transported through the bloodstream to cells throughout your body.
Inside the cells, glucose undergoes a process called cellular respiration, where it's converted into ATP (adenosine triphosphate). ATP is often described as the "energy currency" of the cell.
It's the primary source of energy for most cellular functions, including muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and protein synthesis, according to the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
Different Forms, Different Functions
Not all carbohydrates are created equal. They come in various forms, each with its unique structure and impact on the body.
The main types of carbohydrates are simple sugars, complex carbohydrates (starches), and fiber.
Simple Sugars: Quick Energy Bursts
Simple sugars, also known as monosaccharides and disaccharides, are found in foods like fruits, honey, and table sugar. They are easily digested and provide a quick burst of energy.
However, because they are rapidly absorbed, they can lead to spikes in blood sugar levels followed by a crash, making them less ideal for sustained energy.
Complex Carbohydrates: Sustained Release
Complex carbohydrates, or starches, are found in foods like whole grains, legumes, and starchy vegetables. They are made up of long chains of glucose molecules.
These long chains take longer to digest, resulting in a more gradual and sustained release of energy. This is why foods rich in complex carbohydrates are often recommended for maintaining stable blood sugar levels and providing lasting energy.
Fiber: The Unsung Hero
Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that the body cannot digest. While it doesn't directly provide energy, it plays a vital role in maintaining digestive health and overall well-being.
Fiber adds bulk to the diet, promotes regular bowel movements, and helps regulate blood sugar levels. It's also been linked to a reduced risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer, as noted by the American Heart Association.
Beyond Energy: Other Roles of Carbohydrates
While energy provision is the primary function of carbohydrates, they also contribute to other important bodily processes.
Carbohydrates, specifically glucose, are crucial for brain function. The brain relies almost exclusively on glucose for energy. When glucose levels drop too low, it can lead to impaired cognitive function.
Carbohydrates also play a role in protein sparing. If carbohydrate intake is insufficient, the body will break down protein to use as energy. Adequate carbohydrate intake helps prevent this, preserving protein for its essential functions like building and repairing tissues.
The Importance of Balanced Carbohydrate Intake
Understanding the role of carbohydrates is crucial for making informed dietary choices. A balanced intake of carbohydrates, particularly complex carbohydrates and fiber, is essential for maintaining optimal health.
Choosing whole grains over refined grains, incorporating plenty of fruits and vegetables, and limiting added sugars can help ensure that you are getting the right type and amount of carbohydrates.
According to the Dietary Guidelines for Americans, carbohydrates should make up 45-65% of your daily calorie intake. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine your specific carbohydrate needs based on individual factors such as activity level, health conditions, and personal preferences.
Reflecting on the Power of Carbs
From the simple act of breathing to the complex task of solving a problem, carbohydrates fuel every aspect of our lives. Understanding their primary function as an energy source, and appreciating the nuances of their different forms, empowers us to make healthier choices and optimize our well-being.
So, the next time you reach for that slice of toast or a bowl of oatmeal, remember the remarkable role these macronutrients play in keeping you energized and thriving. It's not just food; it's fuel for life's journey.