Which Of The Following Is An Example Of Secondary Prevention

Imagine a bustling community health fair, sunlight streaming through the windows, illuminating tables overflowing with pamphlets and smiling faces. A nurse diligently measures blood pressure, a nutritionist offers healthy snack samples, and a doctor patiently answers questions about managing diabetes. The air buzzes with a sense of proactive wellness, a shared commitment to catching potential health issues before they truly take hold. What brings all these people together? It's the power of secondary prevention, a crucial strategy in public health.
At its core, secondary prevention aims to detect and address diseases in their early stages, before they cause significant harm or disability. This article will explore what constitutes secondary prevention, providing concrete examples and highlighting its vital role in improving community health and individual well-being.
Understanding the Layers of Prevention
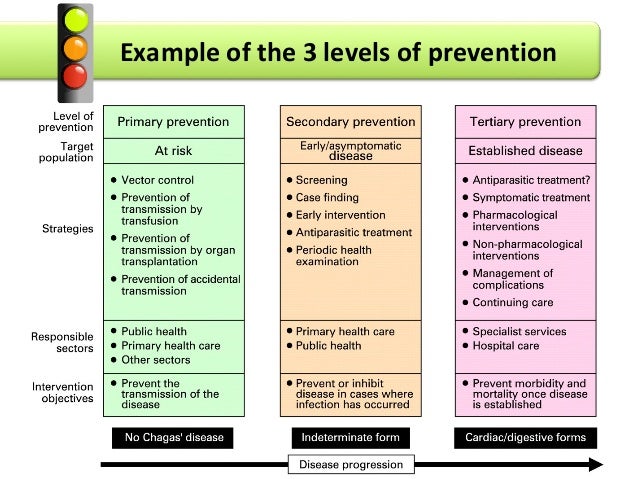
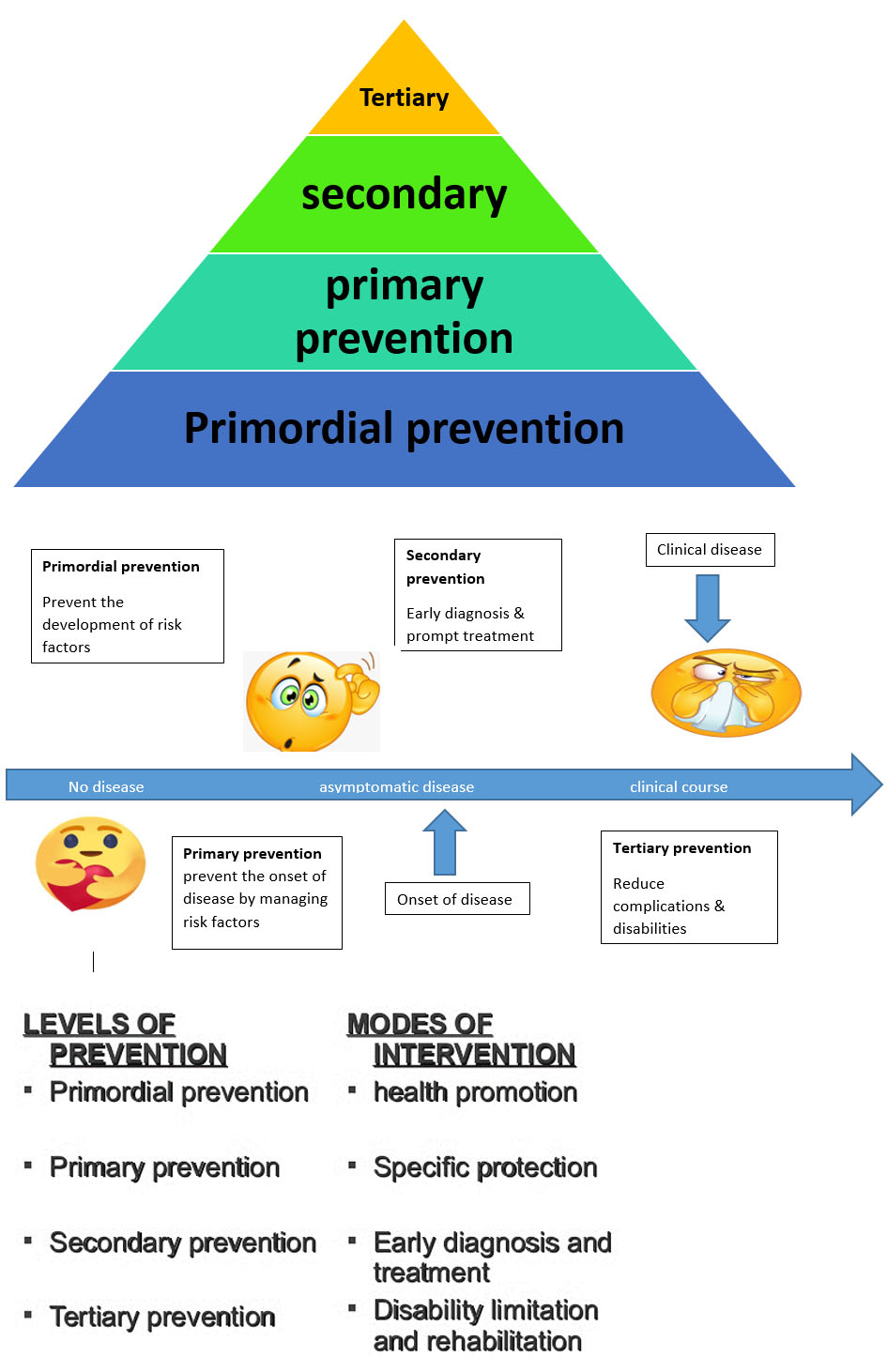
To fully grasp the significance of secondary prevention, it's essential to understand its place within the broader spectrum of preventive healthcare. Public health professionals often categorize prevention efforts into three main levels: primary, secondary, and tertiary.
Primary prevention focuses on preventing diseases from occurring in the first place. Think of childhood vaccinations, promoting healthy diets, or implementing seatbelt laws. These actions aim to reduce the incidence of new cases of a disease or condition.
In contrast, tertiary prevention focuses on managing established diseases to minimize their complications and improve the quality of life for those already affected. This might include rehabilitation programs for stroke survivors, chronic pain management clinics, or support groups for individuals with mental health conditions.
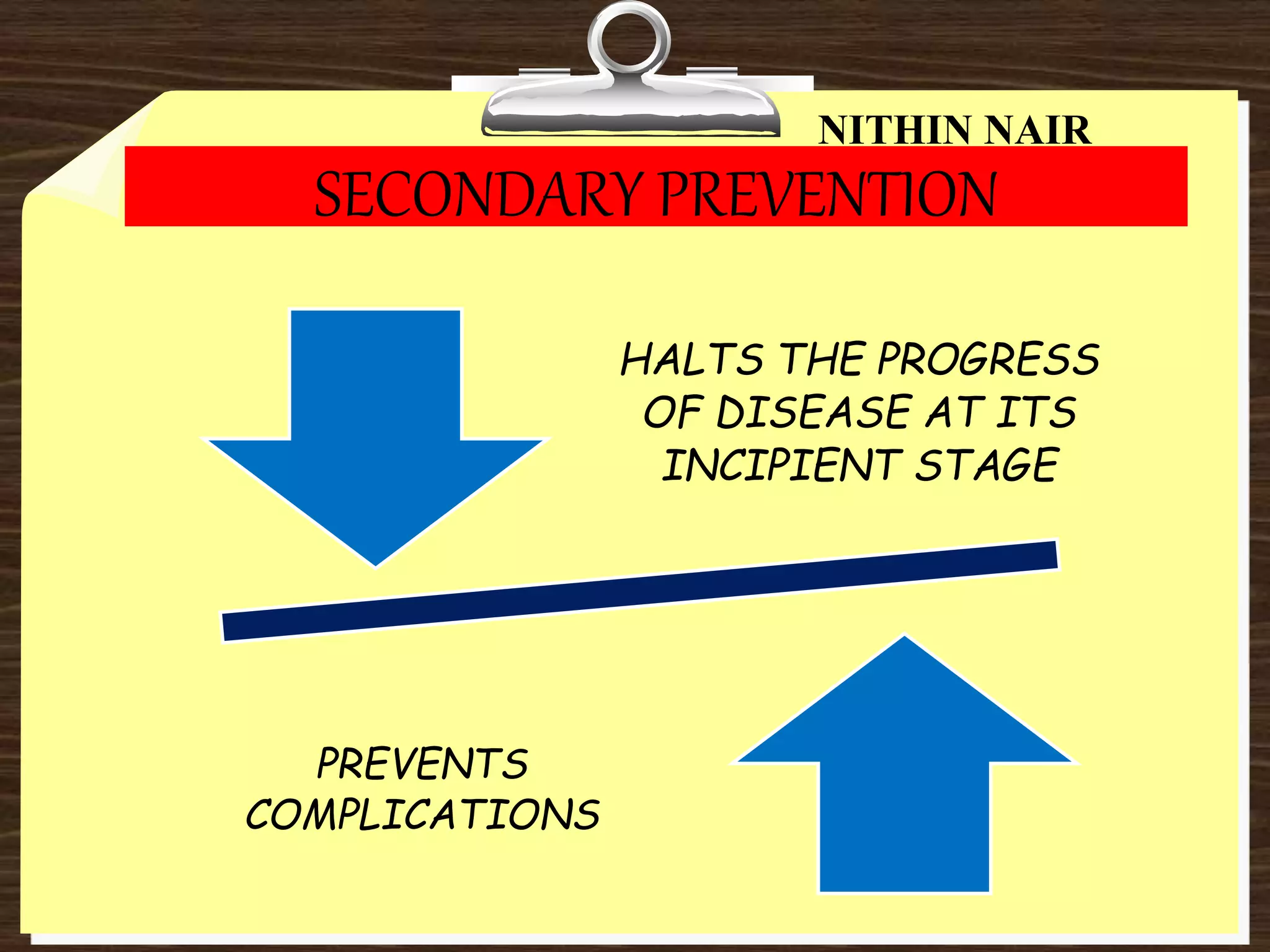
Secondary prevention bridges the gap between these two, acting as an early detection and intervention system. It targets individuals who have already developed a disease but may not yet be experiencing severe symptoms or complications.
Examples of Secondary Prevention in Action
So, what are some practical examples of secondary prevention? Here are a few common scenarios:
Screening Programs
Screening programs are a cornerstone of secondary prevention. These involve testing large populations to identify individuals who may have a particular disease or condition, even if they don't have any obvious symptoms.
Mammograms to detect breast cancer are a prime example. According to the American Cancer Society, regular mammograms can help find breast cancer early, when it is most treatable.
Similarly, colonoscopies are used to screen for colorectal cancer. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends regular screening for colorectal cancer starting at age 45.
Other common screening programs include Pap smears for cervical cancer, prostate-specific antigen (PSA) tests for prostate cancer, and blood pressure checks for hypertension.
Early Intervention Programs
Once a disease or condition has been detected through screening or other means, early intervention programs come into play. These programs aim to provide prompt treatment and support to prevent the condition from worsening.
For example, individuals diagnosed with pre-diabetes may be enrolled in lifestyle modification programs that focus on diet and exercise. Studies have shown that these programs can significantly reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Another example is early intervention services for children with developmental delays. These services can help children reach their full potential and prevent long-term disabilities.
Self-exams and Awareness Campaigns
Empowering individuals to take charge of their own health is another important aspect of secondary prevention. This can involve teaching people how to perform self-exams, such as breast self-exams or skin self-exams, to detect potential problems early.
Public awareness campaigns also play a crucial role in promoting secondary prevention. These campaigns can educate people about the importance of screening, the early warning signs of certain diseases, and the steps they can take to protect their health.
For instance, campaigns promoting the "Know Your Numbers" initiative encourage individuals to regularly check their blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and blood sugar levels. These numbers can provide valuable insights into their overall health and help identify potential risks early on.
The Significance of Secondary Prevention
The benefits of secondary prevention are numerous and far-reaching. By detecting diseases early, it can lead to more effective treatment, reduced healthcare costs, and improved quality of life.
Early detection often means that less aggressive and less expensive treatments can be used. For example, a breast cancer detected through a mammogram at an early stage may be treatable with a lumpectomy and radiation, while a later-stage cancer may require a mastectomy and chemotherapy.
Moreover, secondary prevention can prevent or delay the onset of complications and disabilities associated with chronic diseases. This can significantly improve individuals' ability to live full and productive lives.
From a public health perspective, secondary prevention can also help to reduce the burden of disease on communities. By identifying and treating diseases early, it can help to control outbreaks and prevent the spread of infectious diseases.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its many benefits, secondary prevention also faces several challenges. One of the main challenges is ensuring equitable access to screening and early intervention services. Individuals from marginalized communities, particularly those with low incomes or limited access to healthcare, may be less likely to receive these services.
Another challenge is the potential for over-diagnosis and over-treatment. Screening tests can sometimes detect abnormalities that would never have caused any harm, leading to unnecessary anxiety and potentially harmful treatments. This is a particular concern with screening for certain types of cancer.
To address these challenges, public health professionals are working to improve the accuracy and effectiveness of screening tests, develop more targeted interventions, and ensure that all individuals have access to the care they need.
Future directions in secondary prevention include the development of new technologies, such as genetic testing and personalized medicine, that can help to identify individuals at high risk for certain diseases and tailor interventions accordingly. There is also growing interest in using data analytics and artificial intelligence to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of screening programs.
Conclusion
As we reflect on the bustling scene at the community health fair, the importance of secondary prevention becomes clear. It is a proactive and powerful approach to healthcare that can significantly improve individual and community well-being.
By embracing screening programs, early intervention services, and self-awareness initiatives, we can work together to detect diseases early, prevent complications, and promote healthier lives for all. It's not just about finding disease, it's about building a healthier future.