Which Of The Following Is An Example Of Vertical Integration
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Vertical-integration-7a31b884b9564a139c5ec2f7885ff3f0.jpg)
In today's rapidly evolving business landscape, companies are constantly seeking strategies to enhance efficiency, control costs, and gain a competitive edge. One such strategy, vertical integration, is frequently discussed yet often misunderstood. Understanding its various forms and practical examples is crucial for investors, business leaders, and anyone interested in the dynamics of modern industries.
This article will delve into the concept of vertical integration, providing a clear explanation of what it entails and, most importantly, illustrating it with concrete examples. The primary focus will be to answer the question: "Which of the following is an example of vertical integration?" through careful analysis of real-world scenarios and industry trends. By examining different business models, this piece aims to equip readers with the knowledge to confidently identify instances of vertical integration and understand their implications.
Understanding Vertical Integration
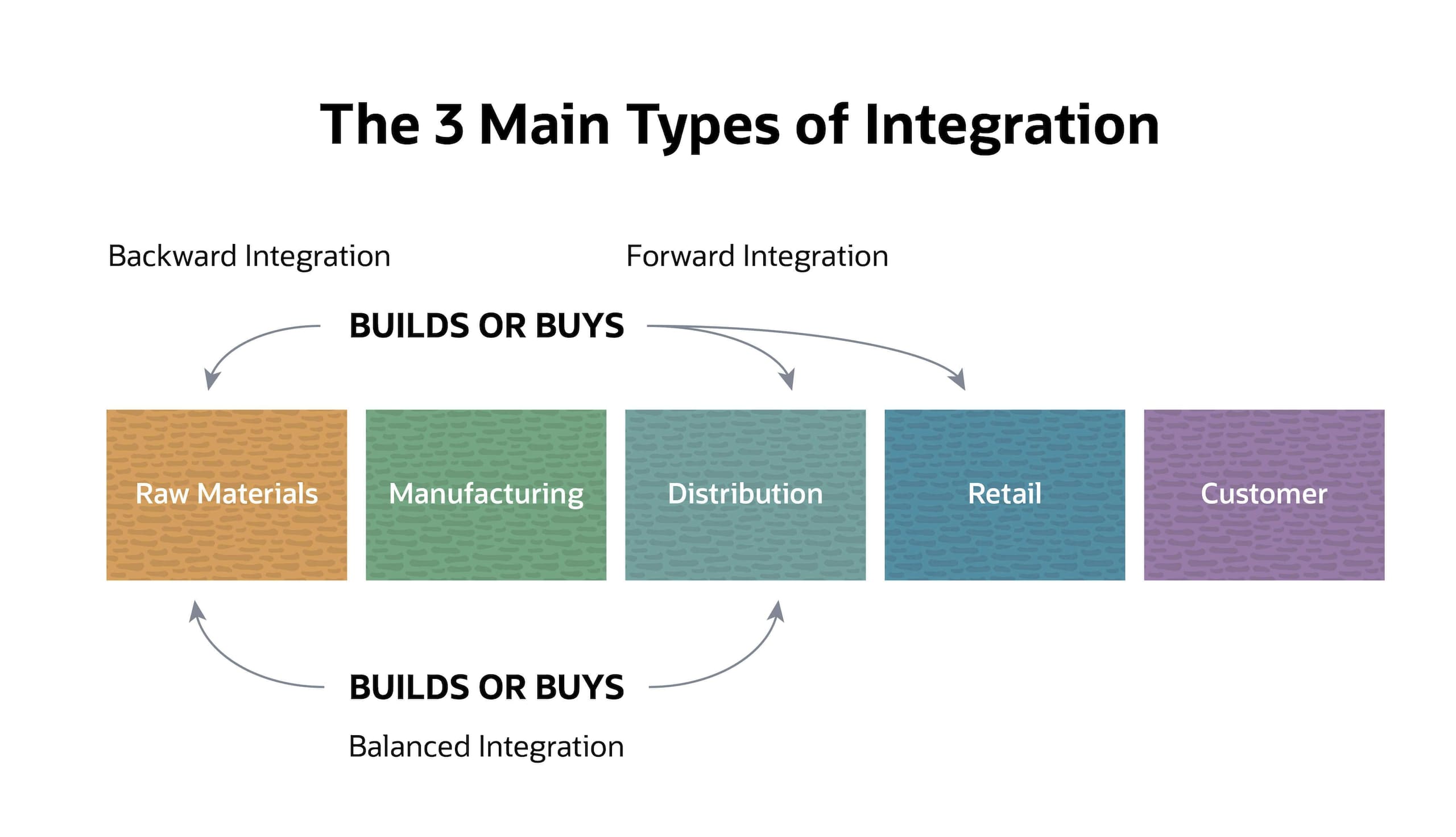
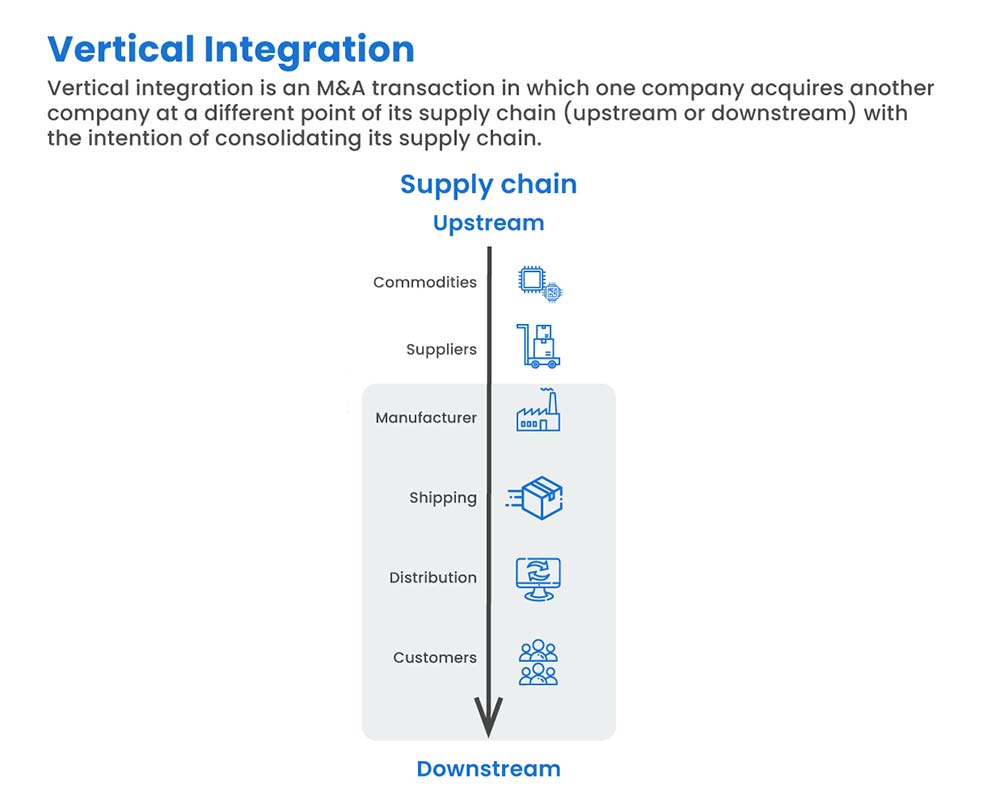
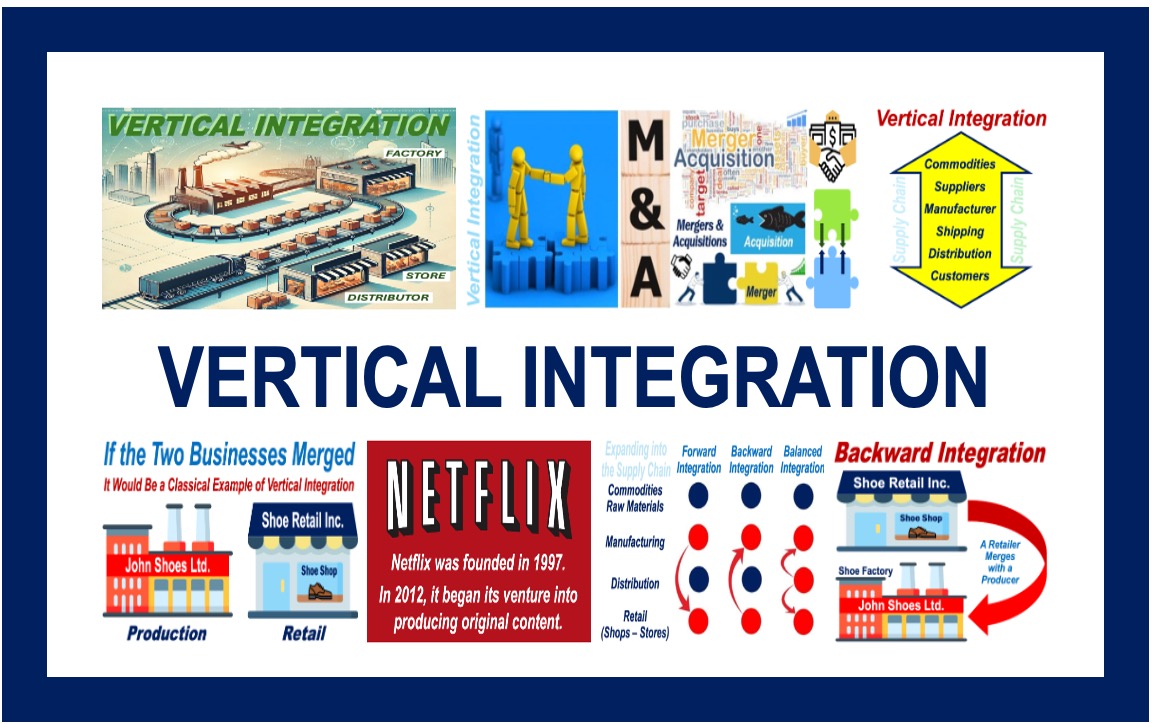
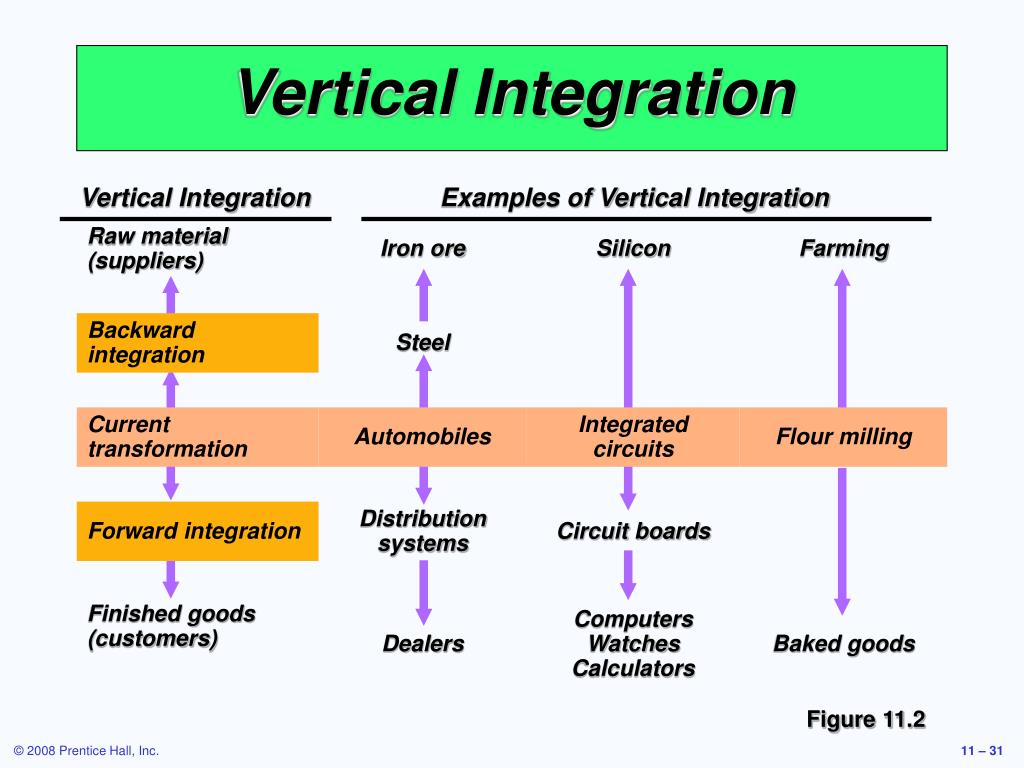
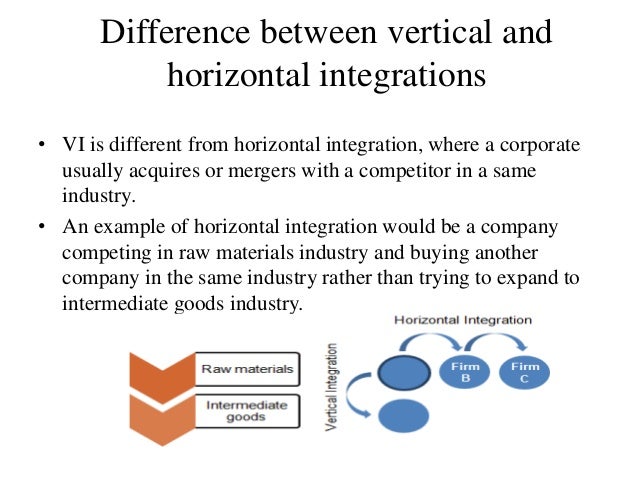
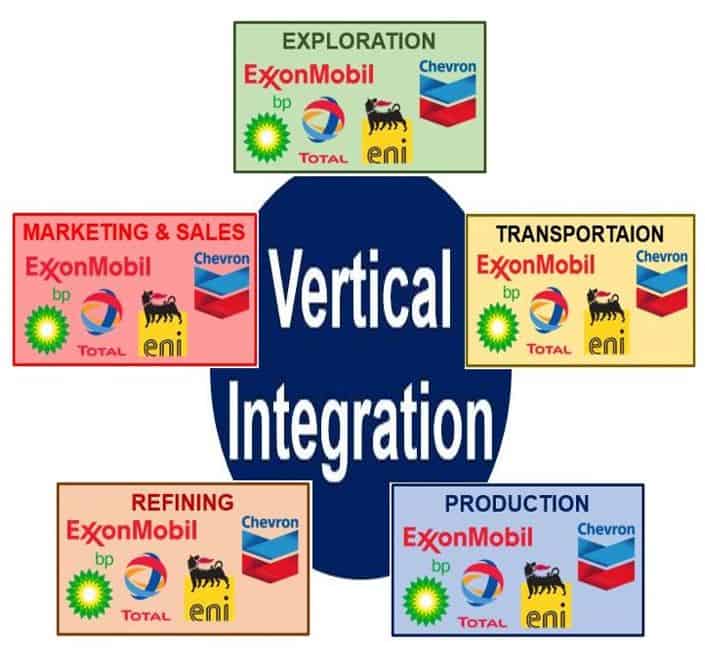
Vertical integration is a strategy where a company owns or controls multiple stages of its supply chain. Instead of relying on external suppliers or distributors, a vertically integrated company manages these processes internally. This can take two primary forms: backward integration and forward integration.
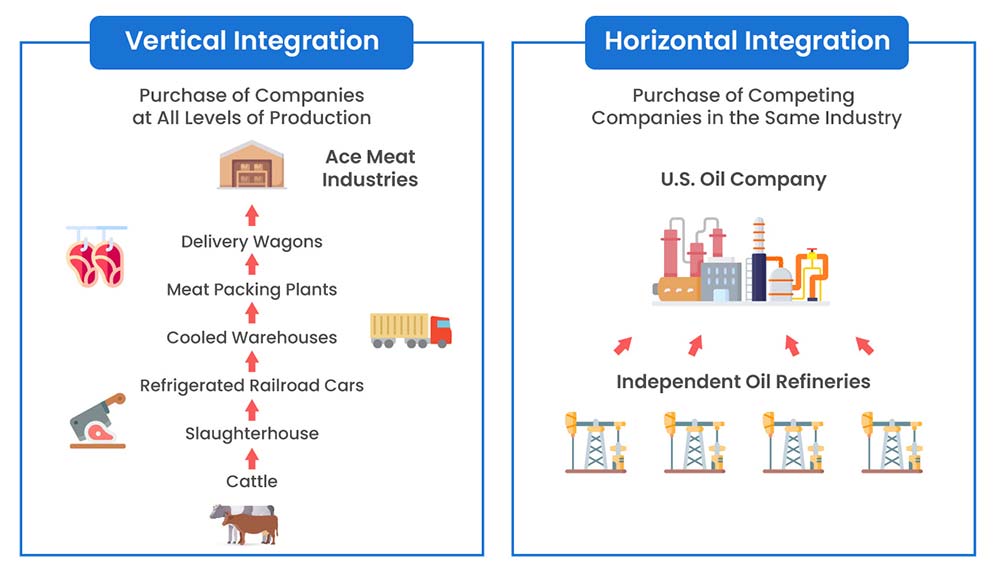
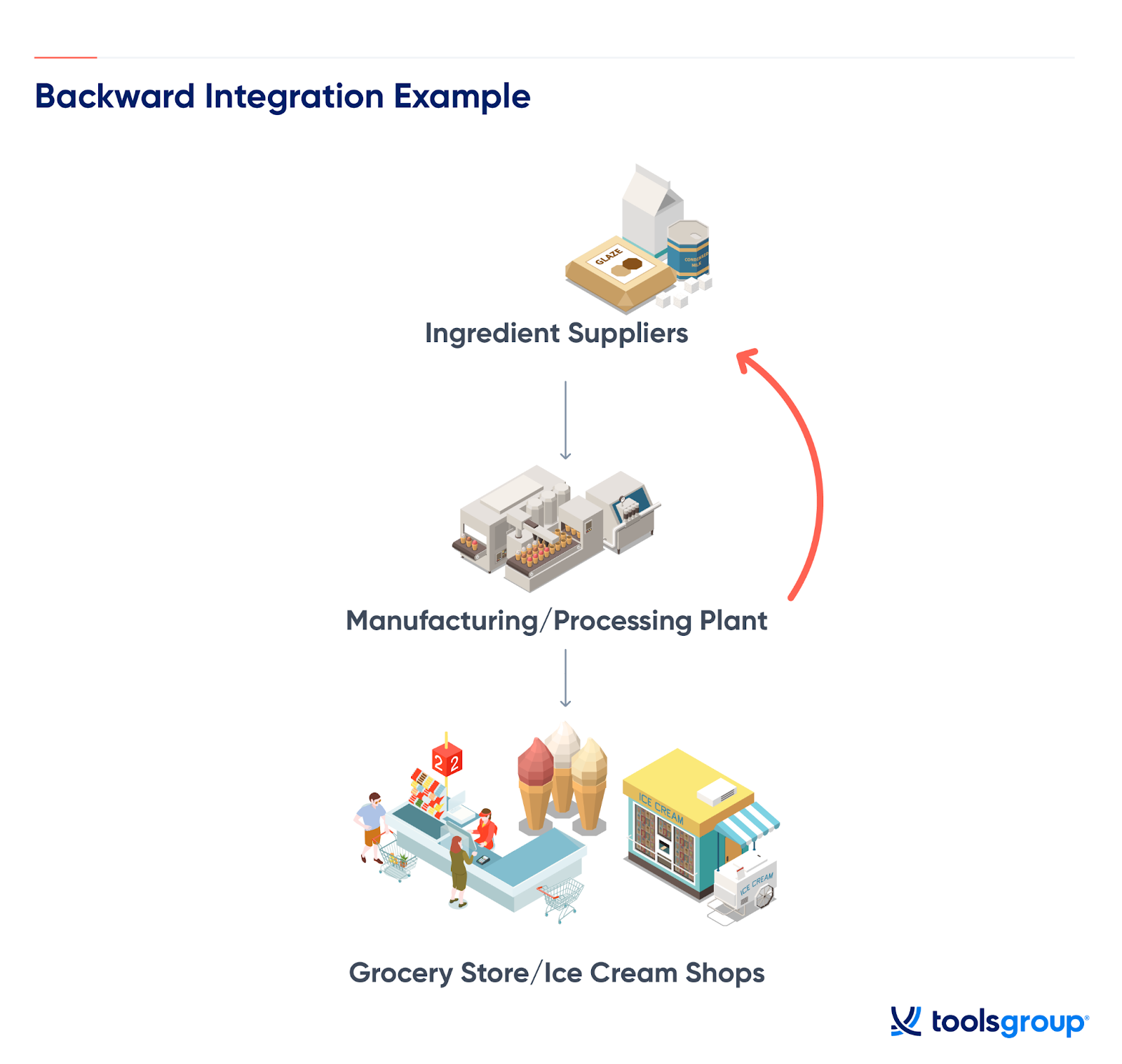
Backward integration involves a company acquiring or developing its own supply sources. For example, a car manufacturer buying a tire company would be an example of backward integration. This strategy aims to secure supply, reduce costs, and improve quality control over raw materials or components.
Forward integration occurs when a company expands its operations to include activities closer to the end consumer. A brewery that owns and operates its own chain of pubs is an example of forward integration. This gives the company greater control over distribution and customer experience.
Identifying Examples of Vertical Integration
To answer the question "Which of the following is an example of vertical integration?", we need to look at scenarios that demonstrate a company consolidating different stages of its value chain under common ownership.
Consider a hypothetical scenario: Company A, a clothing retailer, decides to purchase a textile factory. This is a clear example of backward vertical integration. Company A is moving upstream in its supply chain, taking control of a key raw material source.
Alternatively, consider Company B, a software developer, opens its own chain of retail stores to sell its products directly to consumers. This represents forward vertical integration. Company B is expanding downstream, taking control of its distribution channel and customer interaction.
In contrast, a company that simply negotiates a better price with its existing supplier or outsources its customer service operations would not be engaging in vertical integration. These actions only represent contractual agreements or operational adjustments, not a fundamental change in ownership or control of the supply chain.
Real-World Examples
Several well-known companies employ vertical integration strategies to varying degrees. For instance, Netflix started as a DVD rental service, then moved into content distribution via streaming, and now produces its own original programming. This is a form of forward integration as Netflix moved from being a distributor to becoming a content creator.
Another classic example is Ford Motor Company's historical strategy of owning rubber plantations, iron ore mines, and even glass factories. This comprehensive control over its supply chain allowed Ford to reduce costs and ensure the quality of its vehicles – a prime example of backward integration.
However, it's important to note that vertical integration is not always the best strategy. It can lead to increased complexity, higher capital expenditures, and reduced flexibility. Many companies today prefer to focus on their core competencies and outsource non-core activities to specialized suppliers.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Vertical Integration
The benefits of vertical integration can be significant. It can lead to reduced costs by eliminating the profit margins of suppliers or distributors. It can also provide greater control over quality, ensuring that materials and components meet specific standards. Further, it offers improved coordination between different stages of the supply chain, leading to greater efficiency and responsiveness to market changes.
However, vertical integration also has its drawbacks. It can require substantial capital investment, which may strain a company's resources. It can also lead to a lack of flexibility, as the company becomes less able to adapt to changing market conditions or technological advancements. Moreover, it can create organizational complexity, making it more difficult to manage the different stages of the value chain effectively.
Ultimately, the decision of whether or not to pursue vertical integration depends on a careful assessment of the costs and benefits in a specific context. Factors such as industry structure, market dynamics, and the company's own capabilities and resources all play a role.
Conclusion: Identifying Vertical Integration in Practice
In summary, vertical integration involves a company taking ownership or control of multiple stages of its supply chain, either moving upstream (backward integration) or downstream (forward integration). The key element is the consolidation of ownership and control, not simply contractual relationships or outsourcing agreements.
Examples like Netflix producing original content or Ford's historical ownership of raw material sources clearly illustrate this strategy. While vertical integration can offer advantages such as cost reduction and quality control, it also presents challenges related to capital investment and organizational complexity.
Therefore, when considering the question "Which of the following is an example of vertical integration?", look for scenarios where a company is actively expanding its operations to encompass different stages of its value chain through acquisition or internal development. Understanding this distinction is crucial for navigating the complexities of modern business strategy.