Which Of The Following Is An External User Of Data

The question of who constitutes an external user of data is a fundamental one in business, finance, and information security. Identifying these users is crucial for data governance, compliance, and strategic decision-making. The seemingly simple question has broad implications for data privacy, regulatory adherence, and competitive advantage.
Understanding the different types of data users – internal and external – is essential for implementing appropriate security measures and data-sharing policies. This distinction guides how organizations manage access control, data anonymization, and reporting obligations. Failing to correctly categorize users can lead to data breaches, regulatory penalties, and eroded stakeholder trust.
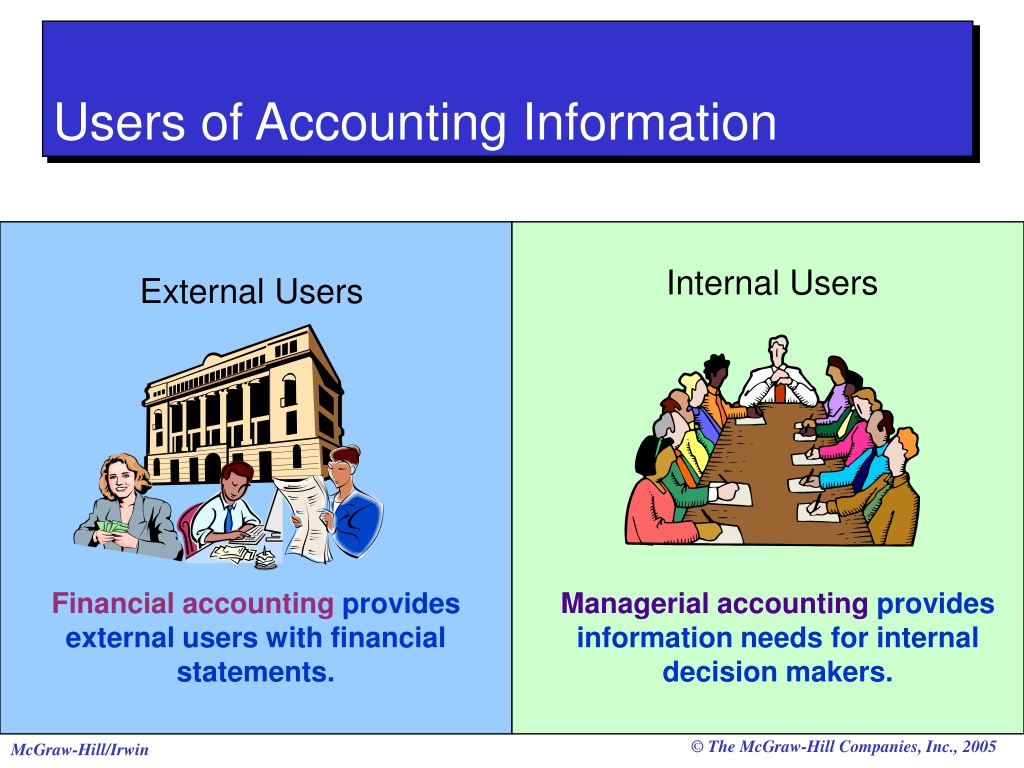
Defining Internal vs. External Data Users
The core distinction hinges on whether an individual or entity operates within the boundaries of the organization controlling the data. Internal users are typically employees, contractors, or board members with direct access to company resources and subject to internal policies. External users, conversely, exist outside of this defined organizational perimeter.
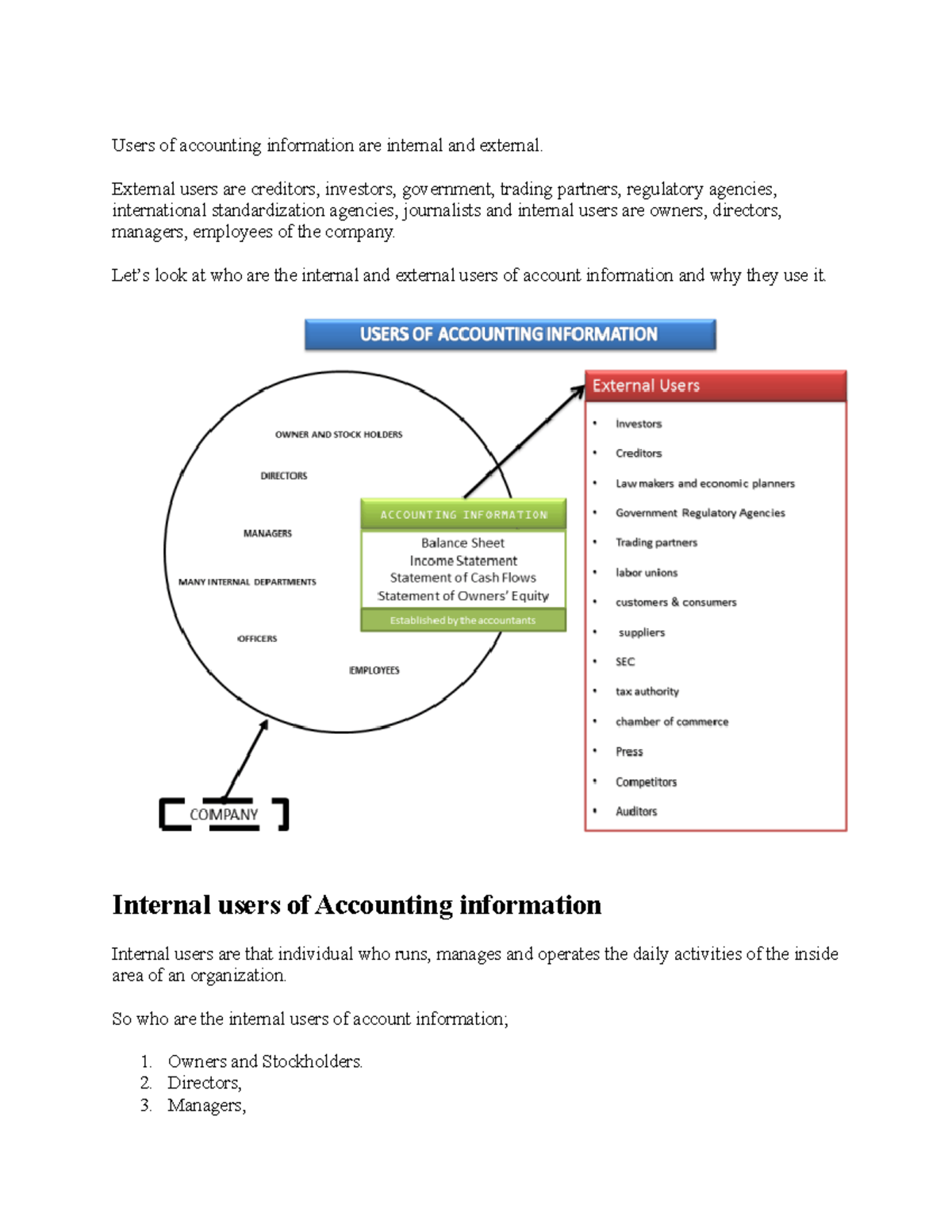
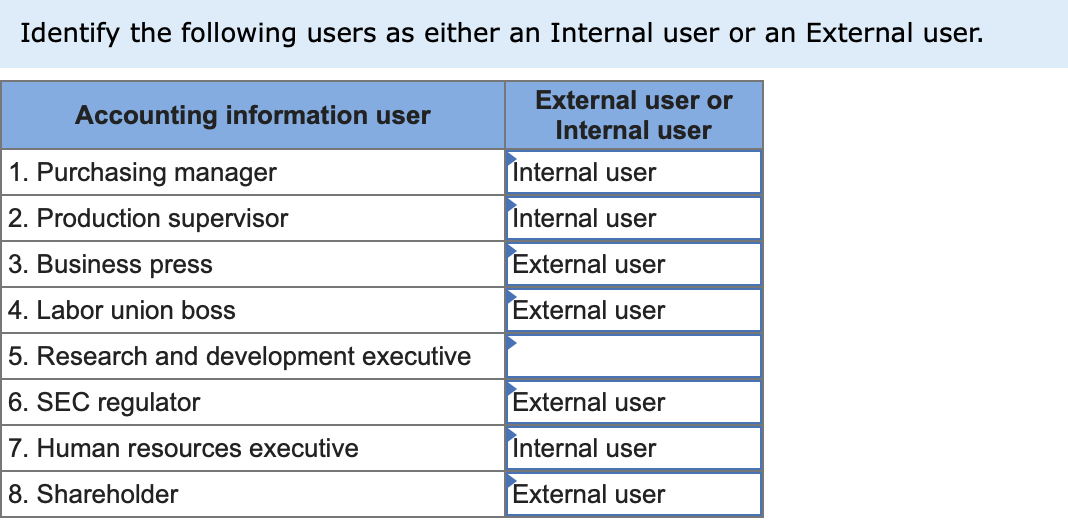
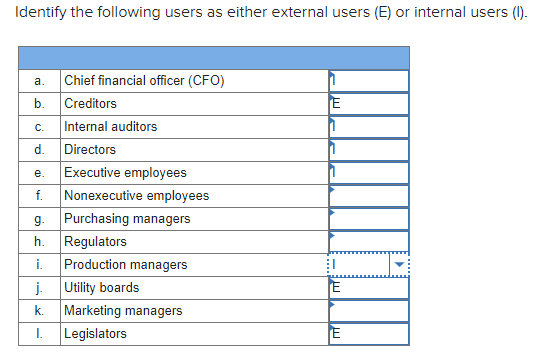
External users encompass a wide range of individuals and entities. This includes customers, suppliers, investors, regulators, auditors, and even competitors in certain contexts. Each group accesses and utilizes data for different purposes, requiring tailored approaches to data sharing and protection.
Common Examples of External Data Users
Customers are perhaps the most obvious example of external data users. They provide data through transactions, interactions with customer service, and participation in loyalty programs.
Suppliers also represent a significant category. They often require access to inventory data, sales forecasts, and other information to effectively manage supply chains.
Investors, including shareholders and potential buyers, need financial data and performance metrics to assess the organization's value and future prospects. Regulators require access to various data sets to ensure compliance with laws and regulations.
Auditors, both internal and external, require access to financial records and internal controls data to verify the accuracy and integrity of financial statements. Competitors may access publicly available data about the organization to understand market share, pricing strategies, and product development plans.
The Significance of Data User Classification
Proper classification of data users is not merely a technical exercise; it's a strategic imperative. It directly influences data governance frameworks, security protocols, and compliance strategies.
For instance, data shared with customers often falls under privacy regulations like GDPR or CCPA, requiring specific consent mechanisms and data minimization practices. Data provided to regulators must adhere to strict reporting formats and timelines.
Misclassifying an external user as internal can lead to inadequate security measures, increasing the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. Conversely, overly restrictive access controls for legitimate external users can hinder collaboration and efficiency.
Impact on Data Security and Privacy
The rise of data breaches and privacy concerns has heightened the importance of controlling access to sensitive information. Organizations must implement robust authentication and authorization mechanisms to verify the identity of users and restrict access based on their role and the sensitivity of the data.
This includes multi-factor authentication, role-based access control (RBAC), and data encryption. Regular audits of user access privileges are also essential to identify and mitigate potential security vulnerabilities.
Furthermore, organizations must comply with relevant data privacy regulations when sharing data with external users. This requires obtaining explicit consent, providing transparency about data usage, and offering individuals the right to access, correct, and delete their personal data.
The Future of Data User Management
The landscape of data user management is constantly evolving with the emergence of new technologies and regulatory requirements. Cloud computing, big data analytics, and artificial intelligence are transforming how organizations collect, process, and share data.
Organizations need to adopt a proactive and adaptive approach to data user management. This includes investing in advanced security tools, implementing comprehensive data governance policies, and providing ongoing training to employees and stakeholders.
By prioritizing data security and privacy, organizations can build trust with their customers, partners, and regulators. This, in turn, fosters innovation, drives business growth, and enhances their overall reputation.





![Which Of The Following Is An External User Of Data Top 16 Users of Accounting Information [With PDF] - Accounting Share](https://accountingshare.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/Users-of-Accounting-Information-1-1024x536.png)