Which Of The Following Is True About Fall Zones
Imagine a crisp autumn afternoon, leaves swirling in vibrant hues of red and gold, as children gleefully navigate a playground. But beyond the laughter and carefree play lies a critical, often unseen element: the fall zone. It’s the silent guardian, the soft landing spot designed to protect our little ones from the inevitable tumbles and stumbles that come with childhood exploration.
Understanding fall zones is crucial for anyone involved in child safety, from parents and caregivers to playground designers and school administrators. It's about proactively mitigating risks and ensuring that play areas are safe havens for exploration and development.
The essential truth about fall zones is that they are designated areas beneath and around playground equipment specifically designed to cushion falls and minimize injuries. This requires careful consideration of the surface material, the height of the equipment, and the anticipated patterns of children's movement.
The concept of fall zones emerged from a growing awareness of the potential for serious injuries on playgrounds. Prior to standardized safety guidelines, playgrounds often featured hard surfaces like asphalt or concrete, leading to a higher incidence of fractures, concussions, and other trauma.
Organizations like the Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) recognized the need for safer play environments and began developing guidelines to address these risks. Their work led to the publication of the Public Playground Safety Handbook, a comprehensive resource that outlines recommendations for fall zone design and maintenance.
One of the primary aspects of fall zone design is the selection of appropriate surfacing materials. Acceptable materials include engineered wood fiber (EWF), rubber mulch, poured-in-place rubber, and sand or pea gravel (when installed at sufficient depth).
Each material has its own set of advantages and disadvantages. EWF offers good shock absorption and is relatively affordable, while rubber mulch is durable and long-lasting. Poured-in-place rubber provides a seamless, accessible surface, and sand or pea gravel can be a cost-effective option for some settings.
The key is ensuring that the chosen material meets the critical fall height requirements for the playground equipment. The critical fall height is the maximum height from which a child could be expected to fall onto the surface.
The CPSC guidelines provide specific recommendations for the depth of surfacing materials needed to protect against falls from different heights. For example, a playground structure with a fall height of 8 feet might require 12 inches of EWF or 9 inches of rubber mulch.
Another critical element of fall zone design is the extent of the area covered. The fall zone should extend a minimum distance beyond the perimeter of the equipment, accounting for the potential for children to fall in various directions.
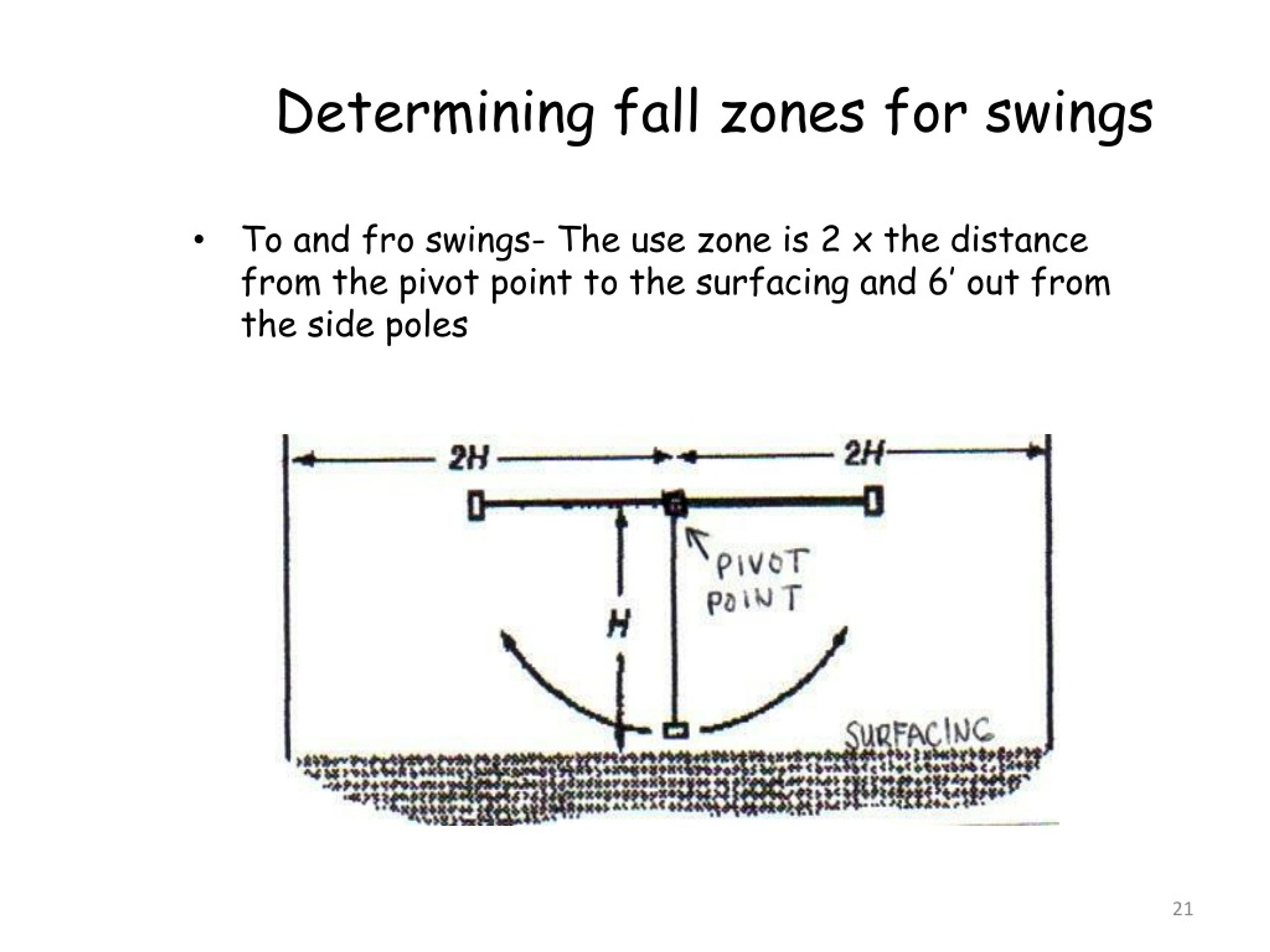
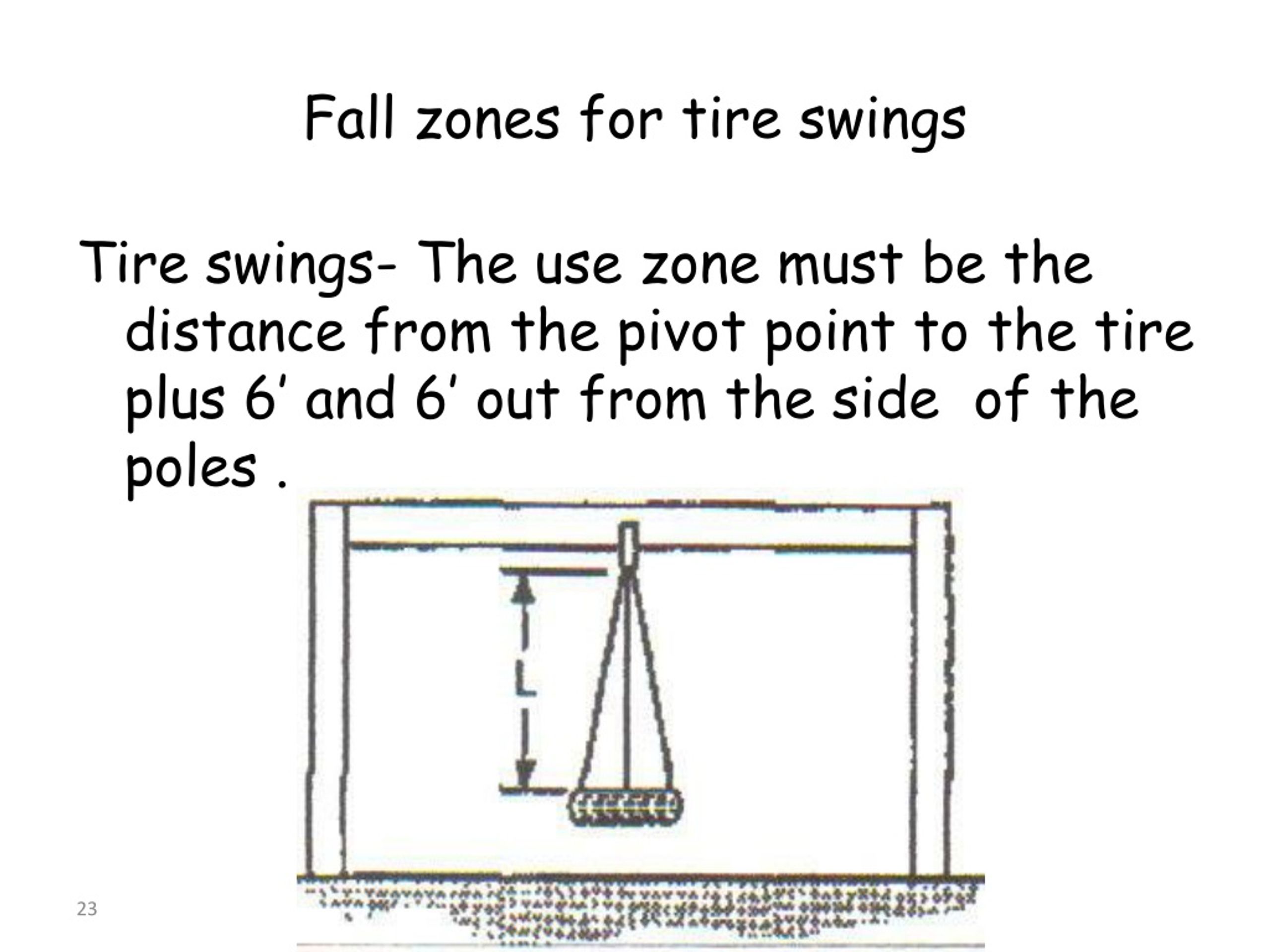
For stationary equipment like slides and climbers, the fall zone should extend at least 6 feet in all directions. For swinging equipment, such as swings and seesaws, the fall zone needs to be larger, extending at least twice the height of the suspending bar both front and back.
The installation and maintenance of fall zone surfacing materials are also paramount. Improper installation, such as inadequate depth or compaction, can significantly reduce the effectiveness of the fall zone. Regular maintenance, including raking, leveling, and replenishing materials, is essential to ensure that the surfacing remains safe and effective over time.
Beyond the physical characteristics of the fall zone, it's important to consider the surrounding environment. Obstacles such as rocks, tree roots, and sharp edges should be removed from the fall zone area.
Proper drainage is also essential to prevent the accumulation of water, which can create slippery conditions and reduce the effectiveness of the surfacing material. Regular inspections should be conducted to identify and address any potential hazards.
The impact of well-designed and maintained fall zones extends beyond immediate injury prevention. Safe play environments encourage children to engage in active play, promoting physical activity, social interaction, and cognitive development.
When children feel safe and secure, they are more likely to take risks, explore their surroundings, and develop important skills. This, in turn, contributes to their overall health and well-being.
The principles of fall zone safety aren't limited to public playgrounds. They can and should be applied to residential play areas as well. Parents who install swing sets, slides, or other play equipment in their backyards should take the same precautions to ensure that their children have a safe place to play.
Choosing appropriate surfacing materials, providing adequate fall zones, and regularly inspecting the equipment are all essential steps in creating a safe and enjoyable play environment at home.
Ultimately, understanding fall zones is about prioritizing the safety and well-being of children. It's about recognizing that play is an essential part of childhood development and that we have a responsibility to create environments where children can explore, learn, and grow without unnecessary risk.
By embracing the principles of fall zone safety, we can help ensure that playgrounds remain places of joy, laughter, and endless possibilities.
So, the next time you see children playing on a playground, take a moment to appreciate the often-unseen safety measures that are in place. Remember that the soft landing beneath their feet is more than just a surface; it’s a testament to our commitment to protecting and nurturing the next generation.






+for+Outdoor+Play.jpg)
+%3D+11+feet.jpg)