Which Of The Following Is True About Retained Earnings
URGENT: A critical misunderstanding about retained earnings is sweeping through the financial sector, impacting investment decisions and potentially misrepresenting company performance.
This article cuts through the confusion, providing a definitive answer to the question: Which of the following is true about retained earnings?
What Are Retained Earnings?
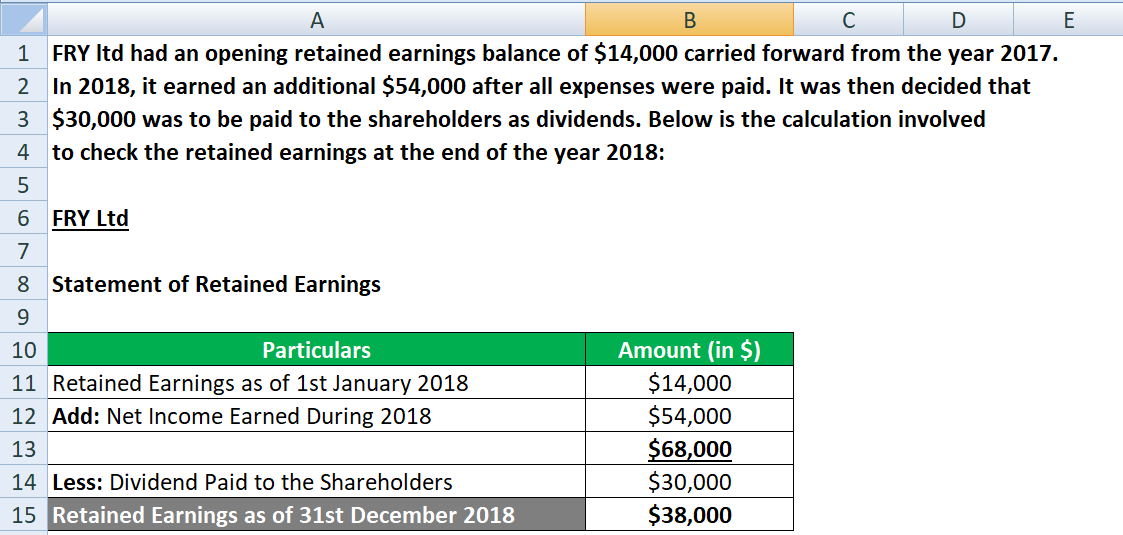
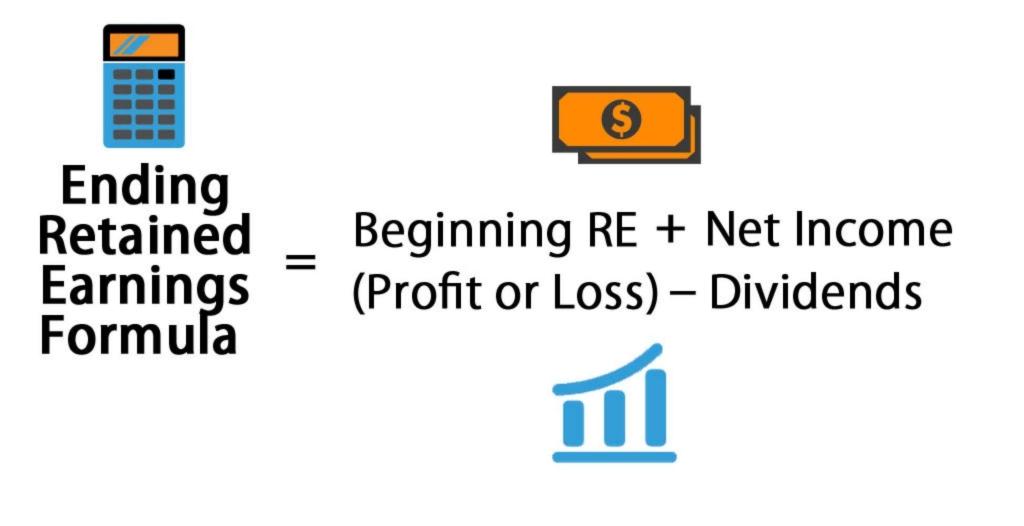
Retained earnings (RE) represent the cumulative net income of a company after dividends have been paid to shareholders.
They are essentially the profits that a company has kept and reinvested back into the business rather than distributing them to owners.
This is a key metric for assessing a company's financial health and future growth potential.
The Crucial Truth: Retained Earnings Are NOT Cash
The most prevalent and damaging misconception is that retained earnings represent a pile of readily available cash.
Retained earnings are an accounting entry, not a cash hoard.
They are recorded on the balance sheet and represent the accumulated profits that have been reinvested – likely in assets, inventory, or paying down debt.
Debunking False Statements
Several incorrect statements often circulate regarding retained earnings. One common myth is that higher retained earnings automatically equate to a stronger company.
While generally positive, high RE can also indicate a lack of investment opportunities or an unwillingness to distribute profits to shareholders.
Another fallacy is that retained earnings are always available for dividends. Dividend payouts are a board decision and depend on current cash flow and other financial considerations.
Key Facts About Retained Earnings
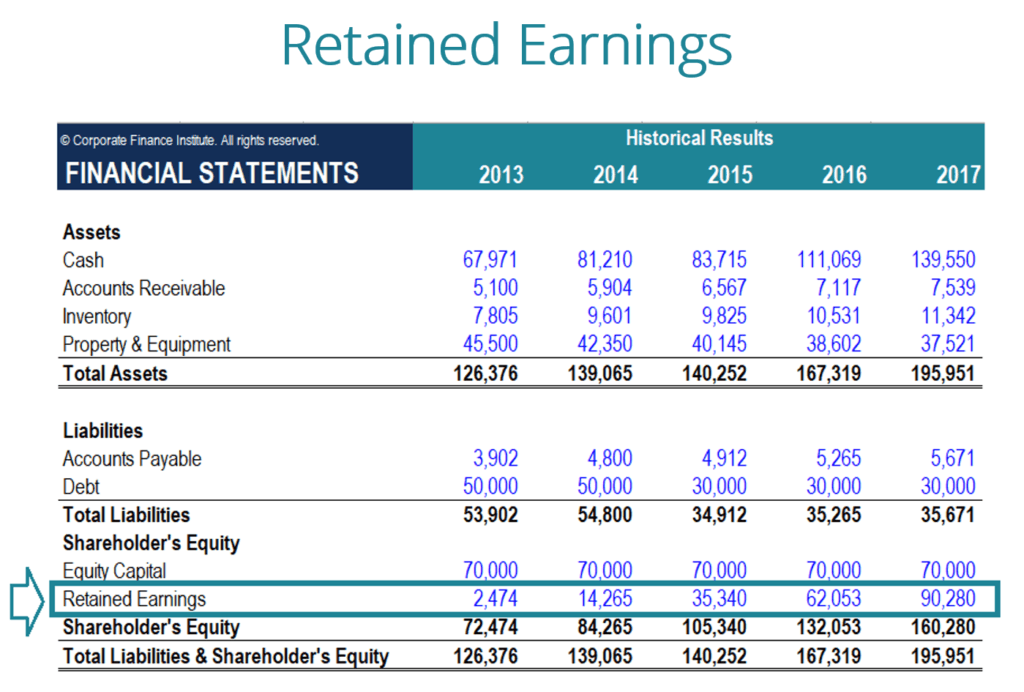
Retained earnings increase when a company generates a net profit and decrease when a company incurs a net loss or pays dividends.
They are reported in the equity section of the balance sheet.
A negative balance in retained earnings is called an accumulated deficit, indicating cumulative losses exceeding profits.
Why This Matters: Real-World Implications
Misunderstanding retained earnings can lead to flawed investment decisions.
Investors might overvalue a company believing its retained earnings represent accessible cash, leading to inflated stock prices.
Conversely, a company with high RE may be undervalued if investors fail to recognize the potential for future growth facilitated by those reinvested profits.
Expert Opinions
According to Dr. Anya Sharma, a leading financial analyst, "Investors must carefully analyze how retained earnings are being utilized. Simply looking at the balance sheet number is insufficient."
John Davies, CFO of GlobalTech Inc., emphasizes, "Retained earnings are a key indicator of our long-term strategy. We reinvest profits strategically to fuel innovation and market expansion."
These insights highlight the importance of understanding the context behind retained earnings.
The Correct Answer
Therefore, the TRUE statement about retained earnings is: Retained earnings represent the cumulative net income of a company after dividends have been paid and are reinvested in the business.
It's NOT a pool of cash and its implications require careful analysis.
This understanding is fundamental for sound financial analysis.
Looking Ahead: Ongoing Monitoring and Analysis
The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) is reportedly reviewing reporting requirements for retained earnings to enhance transparency and prevent misinterpretations.
Investors should consult with financial advisors and conduct thorough due diligence before making investment decisions based on retained earnings.
Stay tuned for updates as regulatory changes and expert analysis further refine our understanding of this critical financial metric.





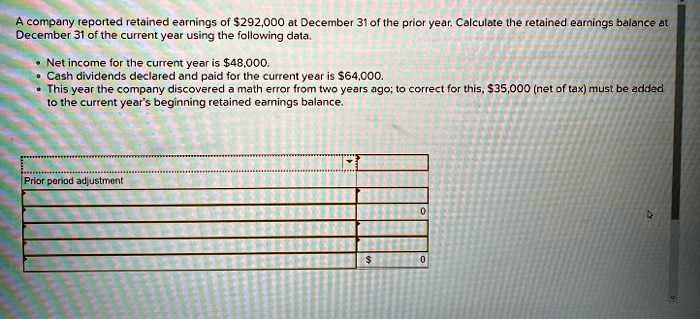
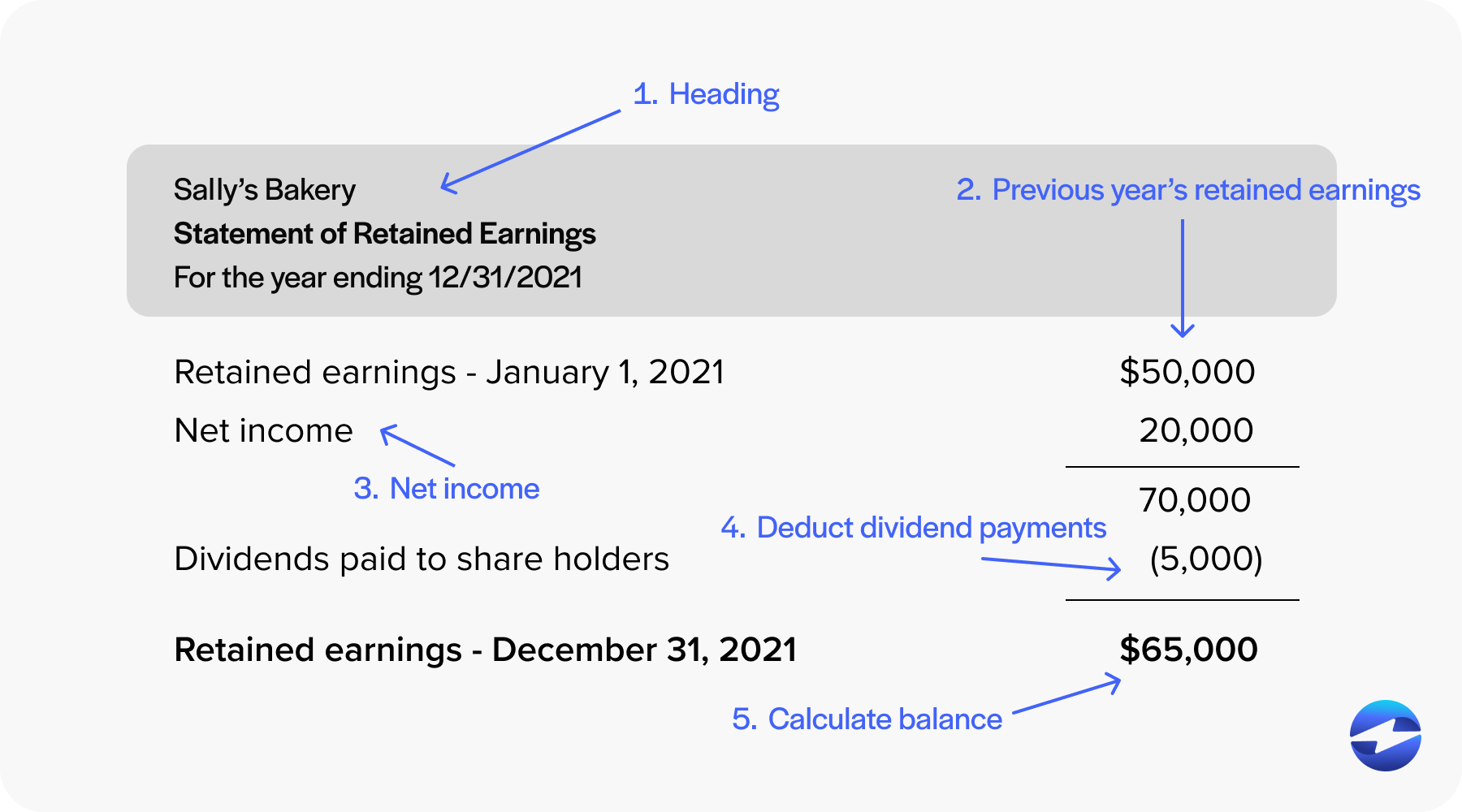
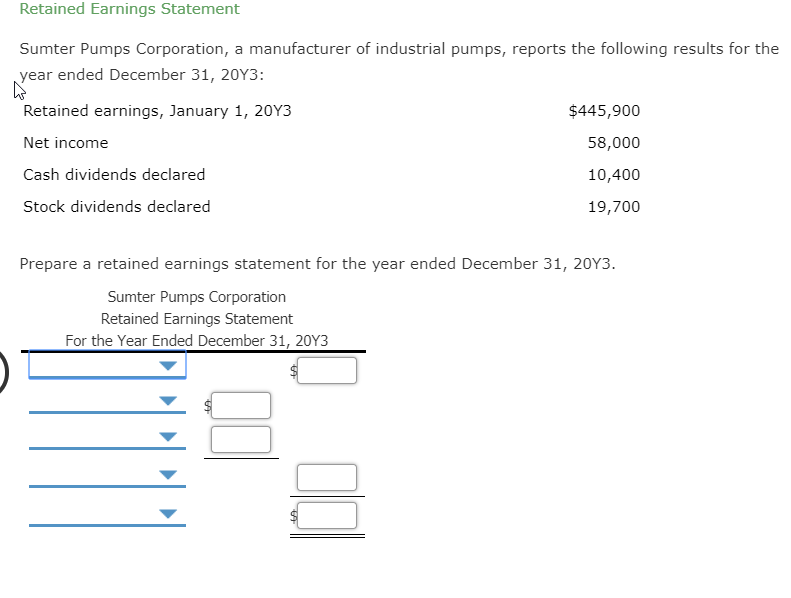

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Term-Definitions_Retained-earnings-f74f8d96dc3447179d35a3f74b86913f.jpg)
