Which Of The Following Is True Regarding Series Circuits

Electrical engineers and students are scrambling to understand critical principles of series circuits after widespread confusion on recent online assessments. Understanding these core concepts is vital for ensuring electrical safety and proper circuit design.
This article provides a clear, concise breakdown of series circuit characteristics, focusing on identifying the accurate statements regarding their functionality. Incorrect assumptions can lead to dangerous practices; therefore, accurate knowledge is paramount.
Key Characteristics of Series Circuits
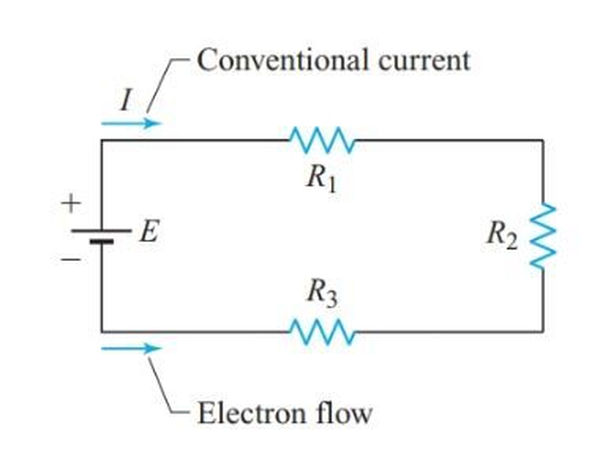
A series circuit is defined as a circuit where components are connected end-to-end along a single path. This means the current has only one route to flow.
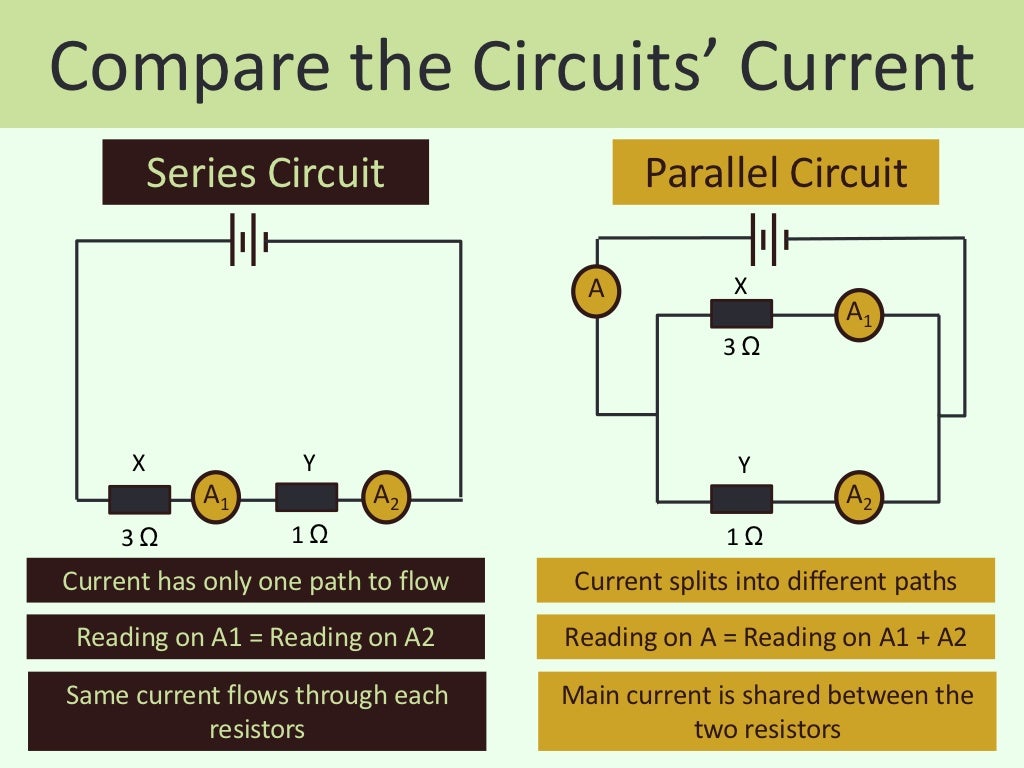
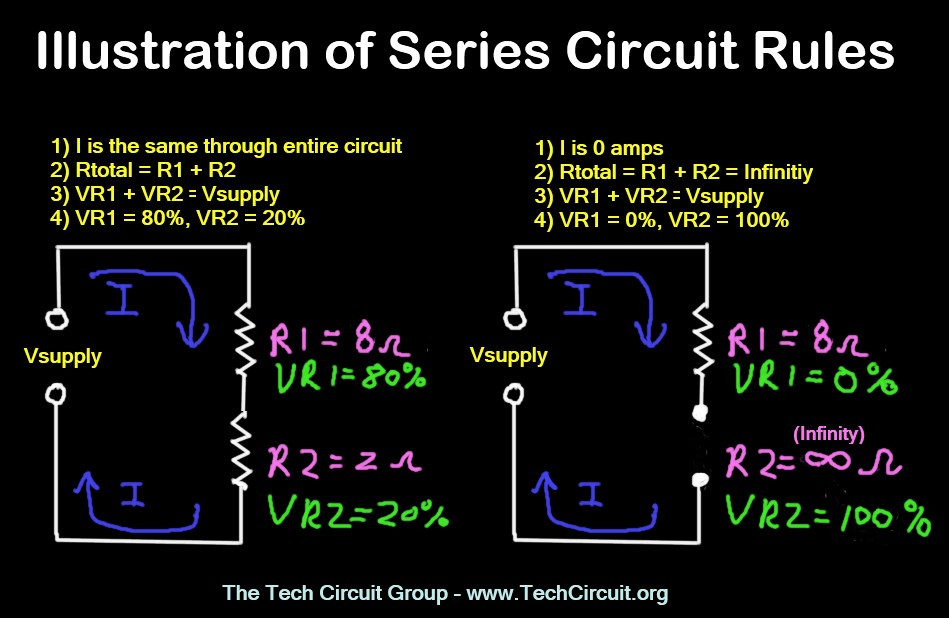
Current is Constant: In a series circuit, the current is the same at every point throughout the circuit. This is a fundamental characteristic.
This constant current flow is independent of the resistance of individual components.
Voltage Division
Voltage Drops: The voltage supplied by the source is divided among the components in the series circuit. This division is proportional to the resistance of each component.
Larger resistors will have a larger voltage drop across them. Smaller resistors will exhibit smaller voltage drops.
The sum of all the voltage drops across each component must equal the total voltage supplied by the source. Kirchhoff's Voltage Law is at play here.
Resistance in Series Circuits
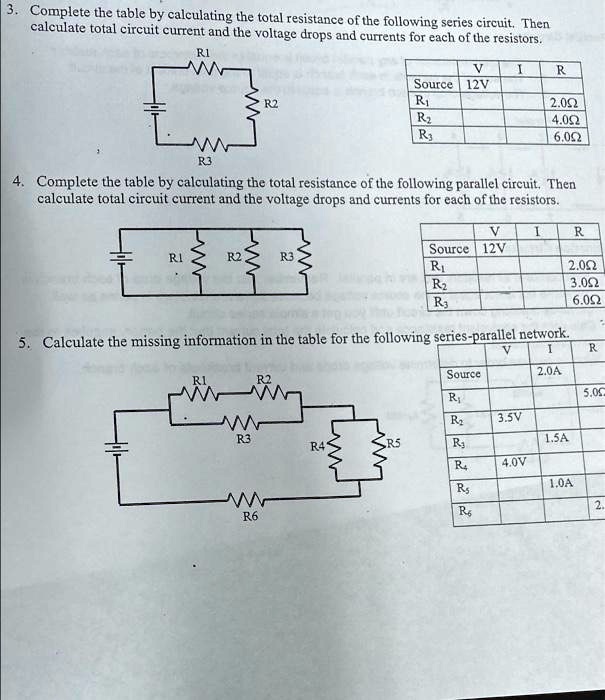
Total Resistance: The total resistance in a series circuit is the sum of all individual resistances. Simply add each resistance value together.
If you have three resistors with values of 10 ohms, 20 ohms, and 30 ohms in series, the total resistance is 60 ohms. This is a straightforward calculation.
Increasing the number of resistors in a series circuit will always increase the total resistance. This consequently affects the current flowing through the circuit.
Implications for Circuit Behavior
Open Circuit: If any component in a series circuit fails open (breaks the circuit), the entire circuit ceases to function. The current flow stops completely.
This "all or nothing" behavior is a key disadvantage of series circuits in certain applications. One failure can disable the entire system.
Consider a string of Christmas lights wired in series. If one bulb burns out, the entire string goes dark.
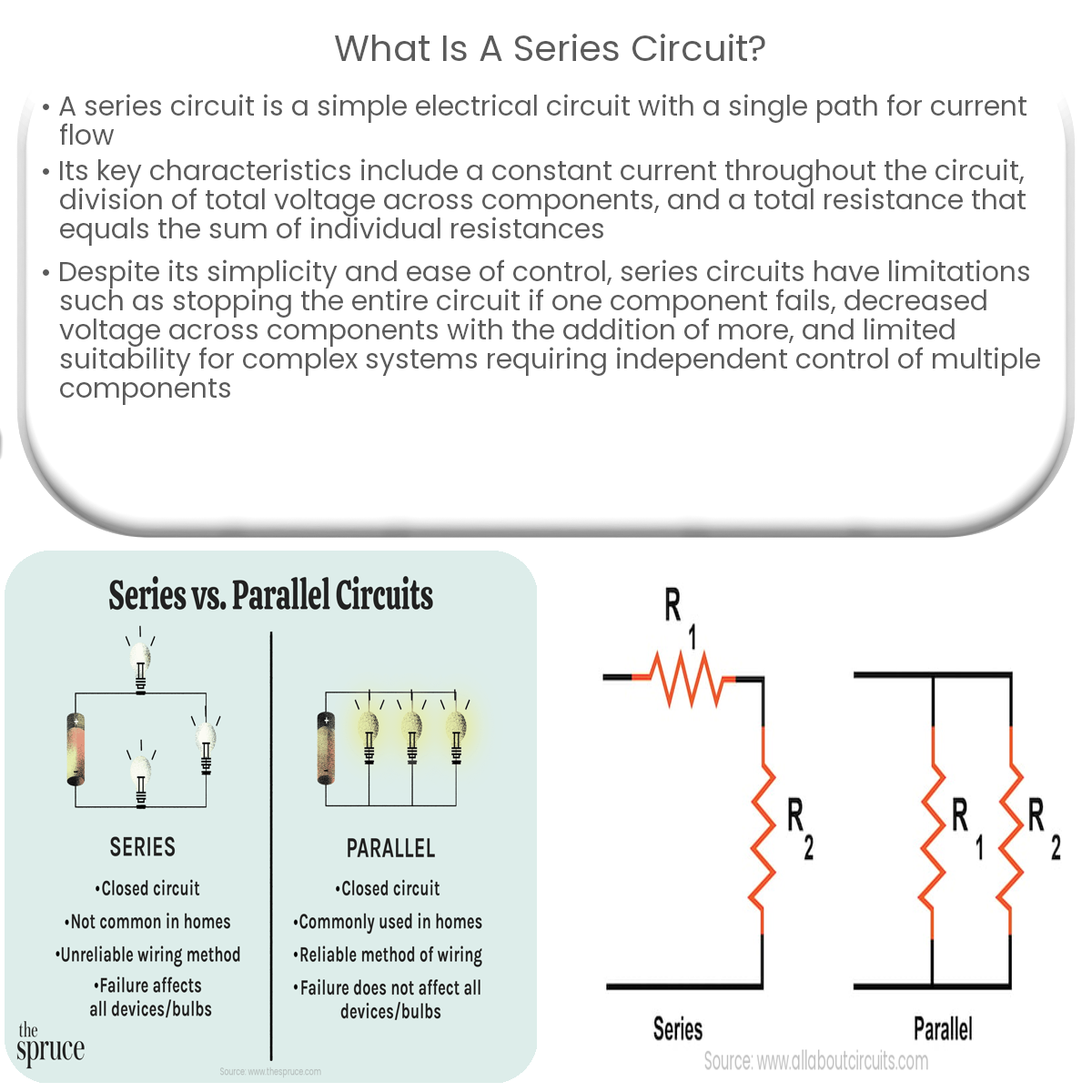
Differentiating Series from Parallel Circuits
It is crucial to distinguish series circuits from parallel circuits. In a parallel circuit, components are connected across each other, providing multiple paths for current.
In parallel circuits, voltage remains constant across all branches, while current divides. This is the opposite of series circuits.
Misunderstanding the difference between series and parallel circuits can have serious consequences. In design, diagnosis, and repair, accurate identification is necessary.
Correct Statements Regarding Series Circuits
Based on the explanations above, the following statements are true regarding series circuits:
- The current is the same at all points in the circuit.
- The voltage drops across each component add up to the total voltage supplied.
- The total resistance is the sum of all individual resistances.
- If one component fails open, the entire circuit stops working.
Next Steps and Ongoing Learning
Students and professionals are urged to review these principles regularly. Practice problems and hands-on experiments can reinforce understanding.
Further study of circuit analysis techniques, such as Ohm's Law and Kirchhoff's Laws, is highly recommended. These tools are essential for effectively working with series circuits.
Stay informed about new developments in electrical engineering and circuit design. Continuous learning is critical in this rapidly evolving field. Understanding the basics of series circuits is foundational knowledge.