Which Of The Following Statements About Cells Is True

In classrooms and laboratories worldwide, a fundamental question echoes: "Which of the following statements about cells is true?" This seemingly simple query unlocks a vast and complex world, the very foundation of life itself. However, misconceptions and oversimplifications often cloud understanding, leading to confusion and hindering deeper scientific exploration.
This article delves into common statements about cells, rigorously examining their accuracy based on established scientific principles. It aims to clarify key concepts in cell biology, addressing potential misunderstandings, and providing a solid foundation for further learning. We will explore various facets of cellular structure and function, separating fact from fiction in this critical area of biological science.
The Cellular Landscape: Truths and Misconceptions
The cell, the basic unit of life, is a marvel of biological engineering. Its intricate structure and function are subjects of continuous study, revealing new insights regularly. Let's dissect some prevalent statements and ascertain their veracity.
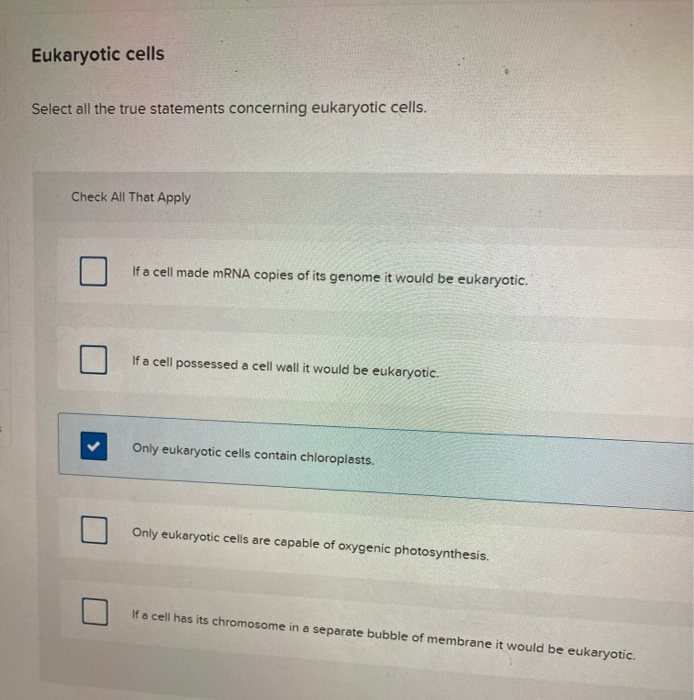
Statement 1: All cells have a nucleus.
This statement is false. While eukaryotic cells, like those found in animals, plants, fungi, and protists, possess a defined nucleus enclosed within a membrane, prokaryotic cells do not. Bacteria and Archaea, for example, are prokaryotes, their genetic material residing in the cytoplasm without a nuclear envelope.
The presence or absence of a nucleus is a defining characteristic differentiating these two major cell types. Understanding this distinction is fundamental to grasping the diversity of life.
Statement 2: All cells are the same size.
Absolutely not. The size of cells varies dramatically, depending on their function and the organism they belong to. Some bacterial cells are less than a micrometer in diameter, while certain nerve cells in animals can extend for meters.
This size disparity is directly related to the cell's role. Red blood cells are small for efficient oxygen transport, whereas nerve cells require length for rapid signal transmission.
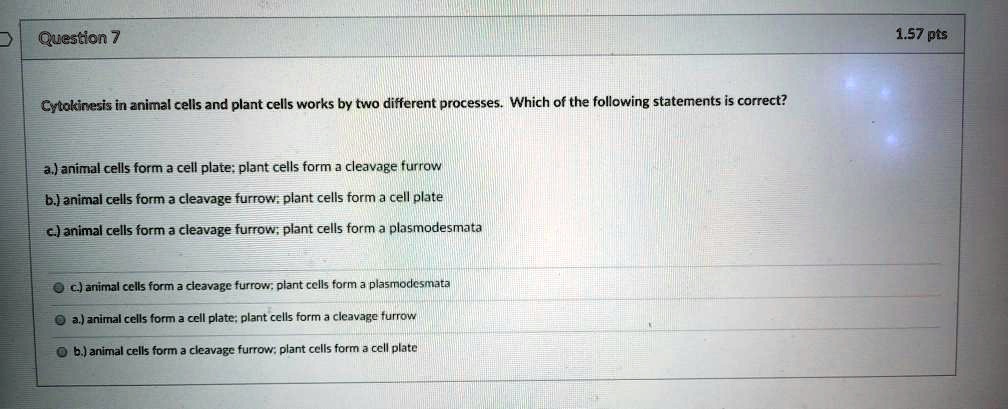
Statement 3: The cell membrane is rigid and impermeable.
This is a significant misconception. The cell membrane is a dynamic, fluid structure composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. It is selectively permeable, controlling which substances can enter or exit the cell.
This selective permeability is crucial for maintaining cellular homeostasis. The membrane allows essential nutrients to enter while preventing harmful substances from gaining access.
Statement 4: Mitochondria are only found in animal cells.
This is demonstrably false. Mitochondria, the powerhouses of the cell, are present in nearly all eukaryotic cells, including those of plants, fungi, and protists, in addition to animal cells. They are responsible for generating energy through cellular respiration.
The endosymbiotic theory proposes that mitochondria were once free-living bacteria that were engulfed by early eukaryotic cells. This theory has strong supporting evidence.
Statement 5: All cells can perform photosynthesis.
Clearly untrue. Photosynthesis, the process of converting light energy into chemical energy, is primarily carried out by plant cells and some bacteria and algae. Animal cells lack the necessary structures, like chloroplasts, to perform photosynthesis.
The ability to perform photosynthesis is what makes plants autotrophs, meaning they can produce their own food. Animals, being heterotrophs, rely on consuming other organisms for sustenance.
Expert Opinions and Scientific Consensus
Leading cell biologists emphasize the importance of accurate foundational knowledge. Dr. Emily Carter, a renowned cell biologist at the University of California, Berkeley, states, "A solid understanding of basic cell biology is crucial for advancements in medicine, biotechnology, and environmental science."
She further added: "Misconceptions can lead to flawed research and misguided approaches." This underscores the need for clear and precise education in cell biology.
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the National Science Foundation (NSF) actively support research aimed at enhancing our understanding of cellular processes. Their initiatives highlight the continuous efforts to refine and expand our knowledge of cell biology.
Future Directions in Cell Biology Education
The field of cell biology is constantly evolving, with new discoveries emerging regularly. Educational approaches must adapt to incorporate these advancements, ensuring that students receive the most up-to-date and accurate information.
Interactive simulations, virtual reality experiences, and inquiry-based learning are increasingly being used to enhance cell biology education. These methods foster deeper understanding and critical thinking skills.
Conclusion
Understanding the fundamental principles of cell biology is essential for comprehending the complexity of life. By addressing common misconceptions and providing accurate information, we empower students and researchers to explore the cellular world with greater confidence and precision. Continuous learning and critical evaluation of information are crucial for navigating the ever-evolving landscape of cell biology. Further investigation and inquiry are strongly encouraged.