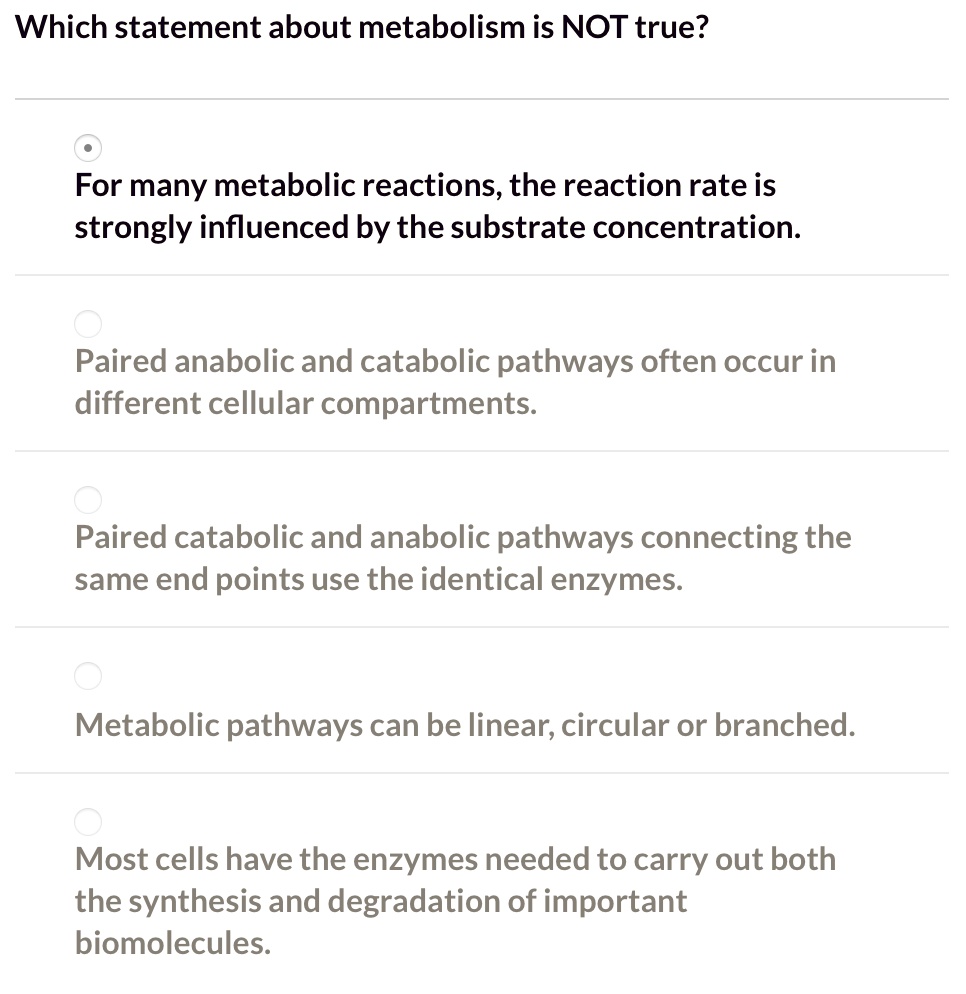
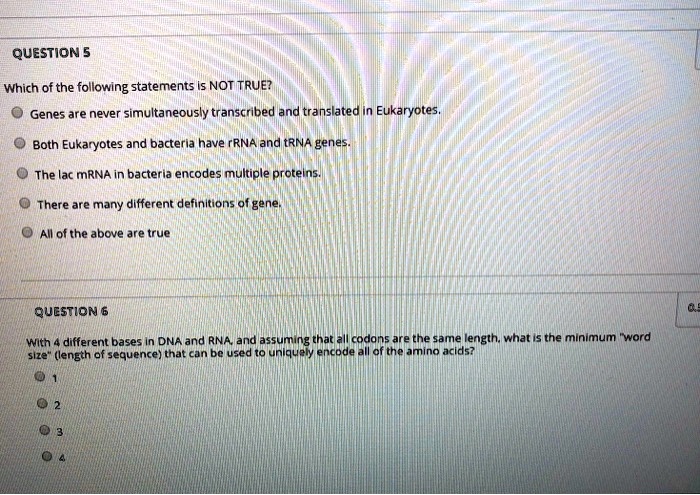
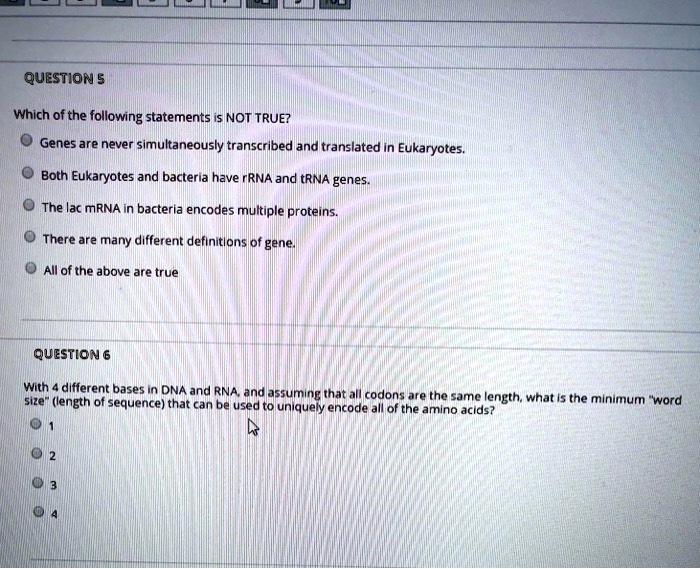
Which Of The Following Statements Is Not True About Metabolism
A widespread misunderstanding about metabolism is fueling ineffective weight management strategies. Experts are urgently clarifying common misconceptions to combat misinformation and promote evidence-based health practices.
This article addresses the question: Which of the following statements is NOT true about metabolism? We aim to debunk myths and provide accurate information based on scientific consensus.
The Metabolic Myth-Busters
The correct answer, often overlooked, is this: "Metabolism slows down significantly and irreversibly with age, making weight loss impossible for older adults." This statement is FALSE.
While metabolism does tend to decrease with age due to factors like muscle loss, it is NOT an irreversible decline. Lifestyle changes can significantly impact metabolic rate at any age.
Common Misconceptions Examined
Many believe that *"eating frequent, small meals boosts metabolism."* While this can help regulate blood sugar, its impact on overall metabolic rate is often overstated.
Another common myth: *"Certain foods can dramatically speed up metabolism."* While some foods might offer a slight thermogenic effect, they don't cause a significant, lasting change.
The idea that *"muscle turns into fat if you stop exercising"* is also false. Muscle and fat are different tissues; muscle atrophies from lack of use, while unused calories are stored as fat.
The Science Behind Metabolism
Metabolism refers to the chemical processes in the body that convert food and drink into energy. It's a complex system influenced by various factors.
These factors include age, sex, body composition (muscle mass vs. fat mass), genetics, and activity level. Hormones and certain medical conditions also play a significant role.
Basal metabolic rate (BMR) accounts for the majority of daily calorie expenditure. BMR is the energy your body needs to function at rest.
Debunking the Age-Related Metabolism Decline
Research indicates that the decline in metabolism with age is more gradual and less drastic than commonly believed. Studies point to a decrease of approximately 1-2% per decade after age 20.
This decline is primarily attributed to loss of muscle mass. Muscle burns more calories than fat, even at rest.
Maintaining or building muscle mass through strength training is crucial. It helps counteract the age-related metabolic slowdown. Regular physical activity is key.
The Impact of Diet on Metabolism
Diet plays a vital role in metabolism, but not in the ways many popular diets suggest. Severely restricting calories can actually slow metabolism down as the body tries to conserve energy.
A balanced diet rich in protein is important. Protein has a higher thermic effect than carbohydrates or fats.
The thermic effect of food (TEF) is the energy your body uses to digest, absorb, and process nutrients. Focus on sustainable dietary changes rather than quick fixes.
Genetic Factors and Metabolism
Genetics do influence metabolism, but they don't dictate fate. Your genes can predispose you to a certain metabolic rate, but lifestyle choices are still significant.
Even with a genetic predisposition to a slower metabolism, regular exercise and a healthy diet can make a substantial difference.
Focus on what you can control, such as your activity level and dietary choices. Don't let genetic factors discourage healthy habits.
Practical Steps for Optimizing Metabolism
To optimize your metabolism, prioritize strength training to build and maintain muscle mass. Aim for at least two strength training sessions per week.
Engage in regular cardiovascular exercise. Cardio burns calories and improves overall health.
Eat a balanced diet that includes lean protein, complex carbohydrates, and healthy fats. Avoid processed foods and sugary drinks.
Get enough sleep. Sleep deprivation can negatively impact metabolism and hormone regulation.
Manage stress. Chronic stress can also disrupt metabolism. Practice stress-reducing techniques like meditation or yoga.
Expert Opinions and Research
Dr. Emily Carter, a leading endocrinologist, emphasizes the importance of strength training. "Building muscle is the most effective way to boost metabolism long-term," she states.
A recent study published in the Journal of Applied Physiology found that individuals who engaged in regular strength training experienced a significant increase in their resting metabolic rate. The study highlights the beneficial impact of lifestyle interventions.
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) also provides resources on understanding and managing metabolism. Consult reputable sources for accurate information.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Metabolism
Understanding the truth about metabolism empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health. Don't fall for myths and quick fixes.
Focus on sustainable lifestyle changes that include regular exercise, a healthy diet, and stress management. Ongoing research continues to explore the complexities of metabolism.
Future studies will likely provide even more insights into personalized approaches to metabolic health. Stay informed and consult with healthcare professionals for tailored advice.









![Which Of The Following Statements Is Not True About Metabolism [ANSWERED] Is the following statement true or false The high metabolic](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question-candidate/20220512213808056692-4580897.jpg?h=512)
