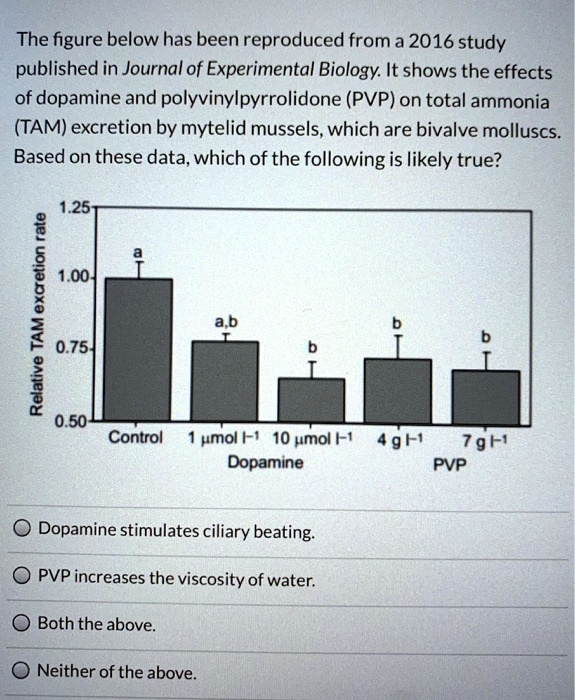
Which Of The Following Statements Is True About Dopamine
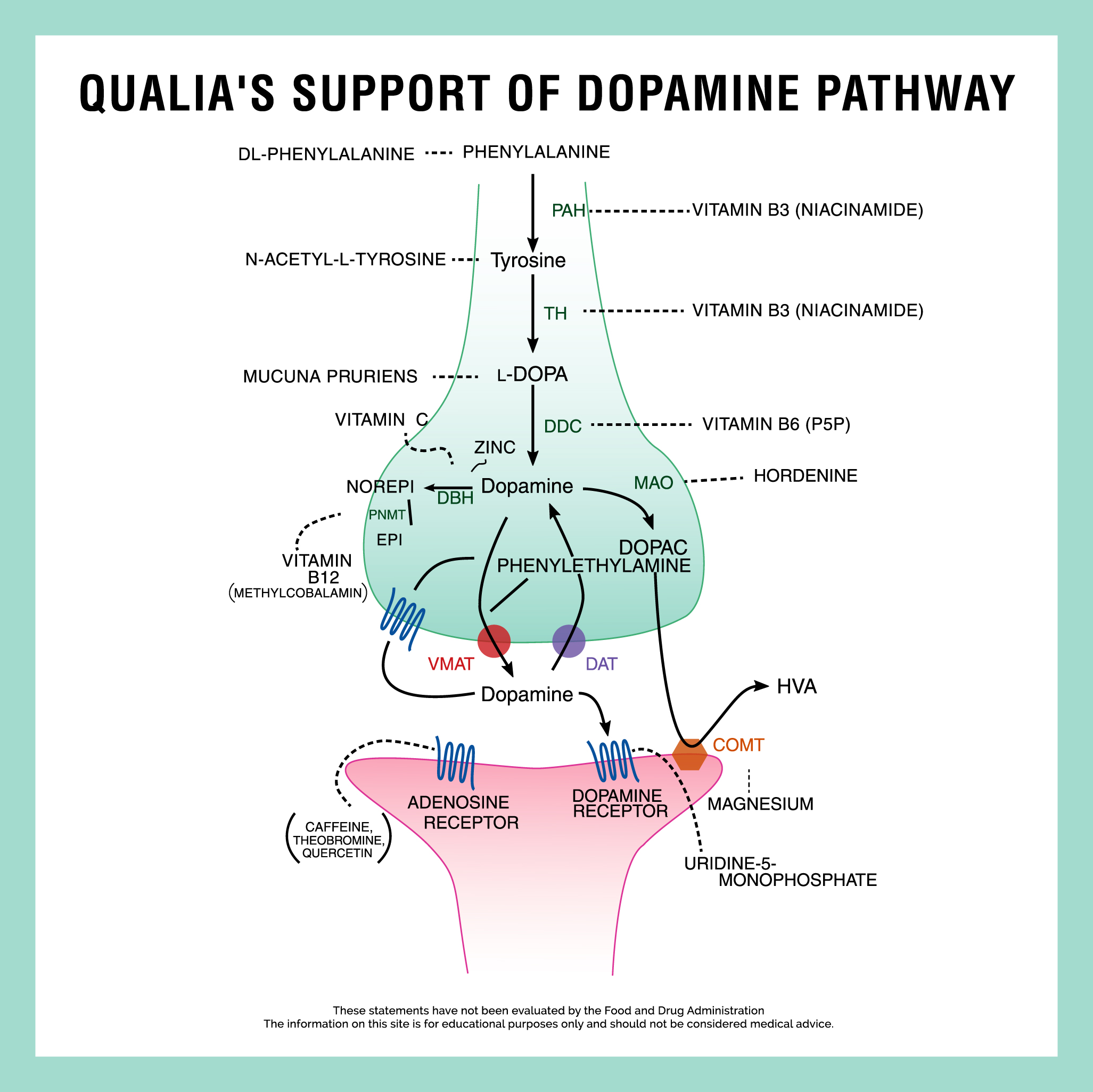
Dopamine, a neurotransmitter often associated with pleasure, is a complex chemical messenger playing a far more nuanced role in the brain than commonly understood. Misconceptions abound regarding its primary function, leading to simplified explanations that overshadow the intricate processes it governs.
This article aims to clarify the true nature of dopamine, debunking popular myths and highlighting its critical involvement in motivation, learning, and motor control. Understanding dopamine's multifaceted role is crucial for comprehending neurological disorders and developing effective treatments.
The Multifaceted Role of Dopamine
Dopamine, a neurotransmitter, is a chemical substance that transmits signals between nerve cells, or neurons, in the brain. It is synthesized in specific brain regions, including the substantia nigra and the ventral tegmental area (VTA).
These regions are integral to the brain's reward system and motor pathways. Dopamine's influence extends far beyond simple pleasure signaling.
Reward and Motivation
The common misconception is that dopamine directly causes pleasure. Rather, dopamine plays a critical role in motivation and reinforcement learning.
It signals the predictive value of rewards. This means dopamine release increases when we experience something better than expected, prompting us to repeat those behaviors.
According to a study published in the Journal of Neuroscience, dopamine neurons are most active when an unexpected reward is received.
Learning and Memory
Dopamine is also intricately involved in learning and memory processes. It strengthens synaptic connections, making it easier for neurons to communicate in the future.
This process, known as synaptic plasticity, is essential for acquiring new skills and forming memories. Dopamine facilitates the association between actions and their consequences, allowing us to learn from experience.
Researchers at MIT have demonstrated that dopamine is crucial for reinforcement learning tasks, where individuals learn to associate specific actions with rewards.
Motor Control
Beyond reward and learning, dopamine is crucial for motor control. The substantia nigra, a dopamine-producing region, is particularly important for coordinating movement.
Degeneration of dopamine-producing neurons in this area leads to Parkinson's disease, a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by tremors, rigidity, and difficulty with movement.
Medications that increase dopamine levels in the brain, such as L-DOPA, are used to manage Parkinson's symptoms.
Debunking Dopamine Myths
One pervasive myth is that dopamine is solely responsible for pleasure. This is a gross oversimplification. While dopamine is involved in the reward system, it's more accurate to say it mediates motivation and anticipation.
Opioids, such as endorphins, are more directly associated with feelings of euphoria. Another myth is that increasing dopamine levels is always beneficial.
Elevated dopamine levels can contribute to addiction and compulsive behaviors. Furthermore, imbalances in dopamine signaling are implicated in various psychiatric disorders, including schizophrenia.
"Dopamine is not simply a 'pleasure chemical'; it is a crucial neurotransmitter that shapes our behavior, learning, and motor control," said Dr. Emily Carter, a neuroscientist at Stanford University, in a recent interview.
Implications for Health and Well-being
Understanding dopamine's role is crucial for understanding and treating neurological and psychiatric disorders. Medications targeting dopamine pathways are used to manage Parkinson's disease, schizophrenia, and ADHD.
Lifestyle factors, such as diet, exercise, and sleep, can also influence dopamine levels and overall brain health. Engaging in activities that promote dopamine release, such as exercise and social interaction, can improve mood and cognitive function.
However, it's essential to avoid activities that lead to excessive dopamine release, as this can contribute to addiction and compulsive behaviors. A balanced approach is key to maintaining healthy dopamine levels.
The Future of Dopamine Research
Ongoing research continues to unravel the complexities of dopamine signaling. Scientists are exploring new ways to modulate dopamine activity for therapeutic purposes.
This includes developing more targeted medications with fewer side effects and exploring non-pharmacological interventions, such as brain stimulation techniques. A deeper understanding of dopamine will pave the way for more effective treatments for a wide range of neurological and psychiatric disorders.
Ultimately, recognizing the nuanced role of dopamine is essential for promoting brain health and well-being. It's a complex neurotransmitter with far-reaching implications for our behavior, learning, and motor control.