Which Of The Following Statements Is True Of Iv Therapy

In an era defined by rapid medical advancements and increasing health consciousness, understanding the intricacies of medical procedures is paramount. Intravenous (IV) therapy, a cornerstone of modern healthcare, is no exception.
Misconceptions surrounding IV therapy are rife, leading to potentially dangerous situations where individuals are either overly reliant on it or unduly fearful of its application.
The critical question remains: which statements about IV therapy are actually true, and which are merely myths?
This article aims to dissect the complexities of IV therapy, clarifying its mechanisms, benefits, risks, and appropriate uses. We will explore verifiable information from reputable medical sources to distinguish fact from fiction.
This deep dive will serve as a guide for patients, caregivers, and anyone seeking a clear understanding of this crucial medical intervention.
What is IV Therapy and How Does it Work?
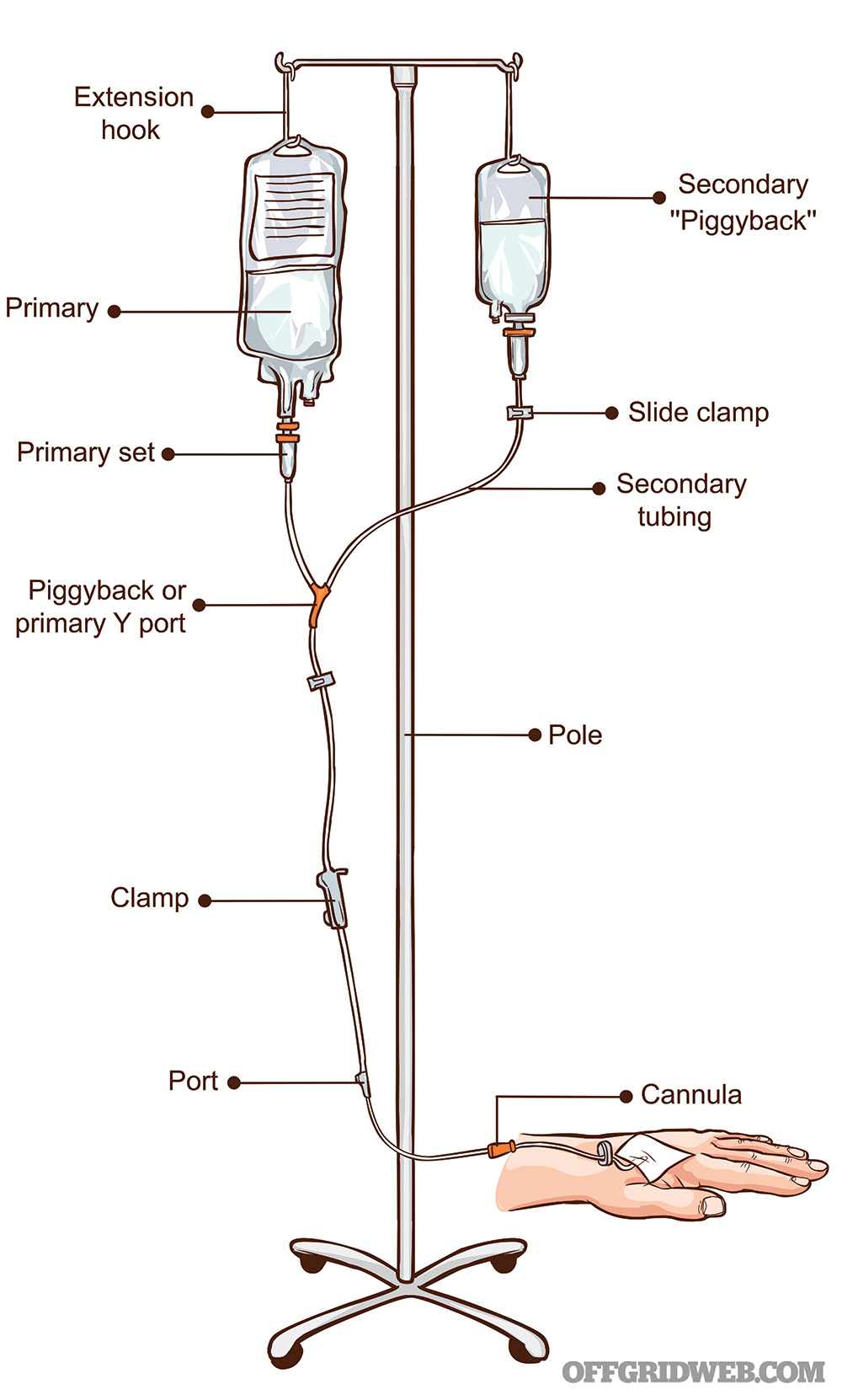
IV therapy involves administering fluids, medications, or nutrients directly into a patient's vein.
This method bypasses the digestive system, allowing for rapid absorption and immediate effect, crucial in emergency situations or when oral administration is not possible.
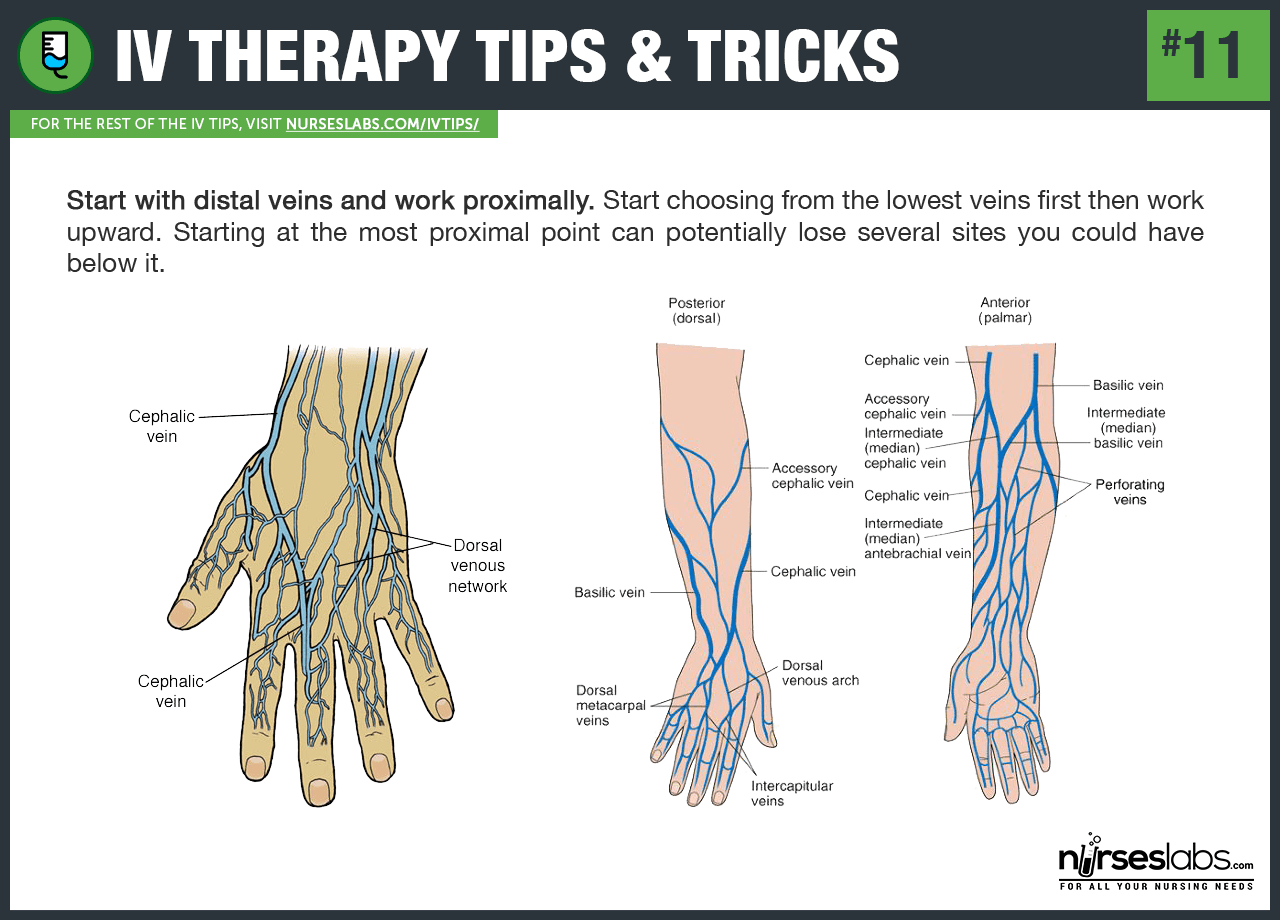
The procedure typically involves inserting a small catheter into a vein, usually in the arm, through which the necessary substances are delivered.
Key Components of IV Fluids
IV fluids are not simply water. They are often carefully formulated solutions designed to address specific needs.
Common examples include saline solutions (various concentrations of sodium chloride), dextrose solutions (sugar solutions), and lactated Ringer's solution (containing electrolytes).
These solutions help restore fluid balance, correct electrolyte imbalances, and deliver essential nutrients.
Medications and Nutrients Administered via IV
A wide range of medications, from antibiotics to pain relievers, can be administered intravenously.
Similarly, nutrients like vitamins and minerals can be delivered directly into the bloodstream, particularly beneficial for patients with malabsorption issues or severe nutritional deficiencies.
This route ensures 100% bioavailability, meaning the entire dose reaches the systemic circulation.
Common Misconceptions and Realities
One common misconception is that IV therapy is only for critically ill patients in hospitals.
While it is essential in emergency rooms and intensive care units, IV therapy is also used in outpatient settings for hydration, vitamin supplementation, and certain medication infusions.
Another misconception is that IV therapy is risk-free.
Risks Associated with IV Therapy
Like any medical procedure, IV therapy carries potential risks.
These can include infection at the insertion site, infiltration (fluid leaking into surrounding tissues), phlebitis (inflammation of the vein), and, in rare cases, more serious complications like air embolism or allergic reactions.
Proper technique and sterile equipment are crucial to minimizing these risks.
The "Cure-All" Myth and the Importance of Evidence-Based Practice
The rise of IV hydration clinics has fueled the misconception that IV therapy is a universal remedy for everything from hangovers to fatigue.
While IV hydration can provide temporary relief from dehydration, it is not a substitute for healthy lifestyle choices or appropriate medical treatment for underlying conditions.
It is crucial to seek advice from qualified medical professionals and rely on evidence-based practices rather than succumbing to unsubstantiated claims.
When is IV Therapy Medically Necessary?
IV therapy is essential in several medical scenarios.
Severe dehydration due to vomiting, diarrhea, or heatstroke necessitates IV fluid replacement.
Patients undergoing surgery often require IV fluids and medications to maintain hydration and manage pain.
IV Therapy for Specific Conditions
Certain medical conditions, such as severe infections, malnutrition, or electrolyte imbalances, often require IV therapy for effective management.
It is also a critical tool in delivering chemotherapy drugs directly to cancer cells.
In cases where patients are unable to take medications orally, IV administration provides a vital alternative.
Alternatives to IV Therapy
While IV therapy can be life-saving in certain situations, it's not always the only option.
Oral rehydration solutions are often sufficient for mild to moderate dehydration.
Whenever possible, oral medications are preferred over IV administration due to the lower risk of complications and greater convenience for the patient.
The Role of Qualified Medical Professionals
Administering IV therapy should always be performed by trained and qualified medical professionals, such as nurses, paramedics, or physicians.
They are responsible for assessing the patient's needs, selecting the appropriate IV fluids and medications, and monitoring for potential complications.
Self-administration of IV therapy can be dangerous and is strongly discouraged.
Regulation and Oversight of IV Therapy Clinics
The regulation of IV therapy clinics varies by jurisdiction.
It is essential to ensure that these clinics adhere to strict safety protocols and are staffed by qualified medical personnel.
Patients should always research the credentials and reputation of any IV therapy provider before undergoing treatment.
The Future of IV Therapy
Advancements in technology are leading to the development of more sophisticated IV infusion pumps and delivery systems.
These innovations allow for more precise control over fluid and medication administration, reducing the risk of errors and improving patient safety.
Research is also exploring the use of IV therapy for novel applications, such as delivering targeted therapies for specific diseases.
Personalized IV Therapy
The future may hold personalized IV therapy regimens tailored to individual patient needs.
Genetic testing and other diagnostic tools could help identify specific deficiencies or imbalances, allowing for more targeted and effective treatment.
This approach could optimize outcomes and minimize the risk of adverse effects.
In conclusion, IV therapy is a powerful medical tool that, when used appropriately under the guidance of qualified professionals, can be life-saving and improve health outcomes.
It's vital to dispel myths and rely on evidence-based information to make informed decisions about its use.
By understanding its benefits, risks, and limitations, we can harness the power of IV therapy safely and effectively.