Which Of The Following Statements Regarding Economic Resources Is True:

Imagine a bustling farmer's market on a crisp autumn morning. Baskets overflow with vibrant tomatoes, golden corn, and earthy potatoes. Each item represents not just food, but a culmination of land, labor, and ingenuity. These seemingly simple resources are the bedrock of our economy, shaping livelihoods and fueling progress.
At the heart of understanding how economies function lies a crucial question: Which of the following statements regarding economic resources is true? Understanding this principle is vital for anyone seeking to grasp the complexities of economic systems, from individual businesses to global markets.
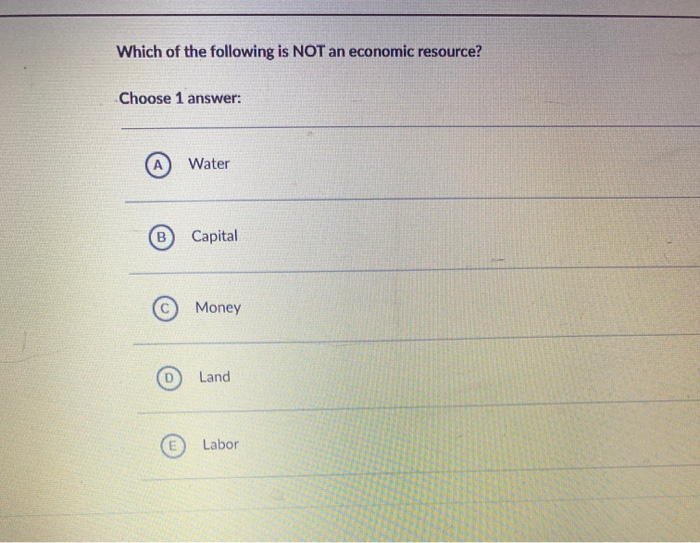
Economic resources, often called factors of production, are the inputs used to produce goods and services. These resources are fundamentally limited, creating the economic problem of scarcity.
Understanding Economic Resources
Let's delve deeper into the components of these fundamental resources.
Land: More Than Just Territory
Land encompasses all natural resources, not just physical acreage. It includes minerals, forests, water, and even the air we breathe.
The availability and quality of land resources heavily influence a nation's potential for agriculture, manufacturing, and overall economic growth.
For example, countries rich in oil reserves, like Saudi Arabia, possess a significant economic advantage due to this natural resource.
Labor: The Human Element
Labor refers to the human effort, both physical and mental, used in production. It's the skills, knowledge, and experience that workers bring to the table.
The quality of labor, often referred to as human capital, is enhanced through education, training, and healthcare.
A highly skilled workforce is a magnet for investment and innovation, driving economic prosperity.
Capital: Tools of the Trade
Capital encompasses all the manufactured aids to production. Think of machinery, equipment, factories, and infrastructure.
Unlike natural resources, capital is created by humans through investment. It's crucial to remember that in economics, 'capital' does not refer to money; money is a medium of exchange.
A nation with a robust capital stock can produce goods and services more efficiently and on a larger scale.
Entrepreneurship: The Spark of Innovation
Entrepreneurship is the driving force behind economic activity. It's the ability to combine land, labor, and capital in innovative ways to create new goods and services.
Entrepreneurs are risk-takers who identify opportunities, organize resources, and manage businesses.
They are the engine of job creation and economic growth, constantly pushing the boundaries of what's possible.
The Correct Statement and Its Significance
The statement that is definitively true regarding economic resources is that they are limited in supply. This fundamental concept of scarcity is the cornerstone of economics.
Because resources are finite, societies must make choices about how to allocate them. This leads to trade-offs and opportunity costs, where choosing one use of a resource means forgoing another.
Understanding this limitation is crucial for making informed decisions in all aspects of economic life, from personal budgeting to government policy.
Consider a farmer with a limited amount of land. They must decide whether to grow corn or soybeans, weighing the potential profits of each crop against the resources required.
Similarly, a government must decide how to allocate its budget between education, healthcare, and defense, recognizing that spending on one area may mean less funding available for others.
These choices, driven by scarcity, shape the economic landscape and determine the well-being of individuals and societies.
The Implications of Scarcity
The scarcity of economic resources has far-reaching implications.
It necessitates efficiency in production, encourages innovation, and drives the market mechanism of supply and demand.
When resources are scarce, businesses are incentivized to find ways to produce more with less, leading to technological advancements and productivity gains.
The price mechanism, driven by supply and demand, helps to allocate scarce resources to their most valued uses. Goods and services that are in high demand and limited supply command higher prices.
This signals to producers where resources should be directed.
Furthermore, the distribution of scarce resources can be a source of inequality.
Those who control or have access to valuable resources often enjoy greater economic power. This highlights the importance of policies aimed at promoting equitable access to resources and opportunities.
Consider the global debate surrounding access to clean water, a vital but increasingly scarce resource. The unequal distribution of water resources can lead to conflict and hinder development in certain regions.
Addressing these inequalities requires international cooperation and sustainable resource management practices.
Looking Ahead: Sustainable Resource Management
As the global population continues to grow and economies expand, the pressure on economic resources will only intensify. Sustainable resource management is therefore crucial for ensuring long-term economic prosperity and environmental sustainability.
This involves using resources more efficiently, reducing waste, and investing in renewable alternatives. Policies that promote conservation, incentivize recycling, and encourage the development of clean energy technologies are essential.
For example, promoting the use of solar and wind power can reduce our reliance on fossil fuels, a finite resource with significant environmental consequences.
Moreover, fostering innovation and technological advancements can help us find new ways to extract, process, and utilize resources more efficiently. The development of precision agriculture techniques, for instance, can help farmers optimize their use of water, fertilizers, and pesticides, leading to higher yields and reduced environmental impact.
Education and awareness are also vital for promoting sustainable resource management. By educating individuals and communities about the importance of conservation and responsible consumption, we can encourage more sustainable behaviors.
Ultimately, ensuring the long-term availability of economic resources requires a collective effort from individuals, businesses, and governments.
In Conclusion
Understanding that economic resources are inherently limited is more than just an academic exercise; it's a fundamental truth that shapes our economic reality. From the farmer's field to the global marketplace, scarcity dictates choices and drives innovation.
By embracing sustainable practices and fostering a greater awareness of resource constraints, we can strive towards a more equitable and prosperous future. It's about recognizing the value of every resource and making informed decisions that benefit both present and future generations.
The vibrant tomatoes at the farmer's market serve as a reminder of the precious resources that sustain us. Let us use them wisely.




+Which+of+the+following+statements+concerning+unsaturated+fats+is+true..jpg)
