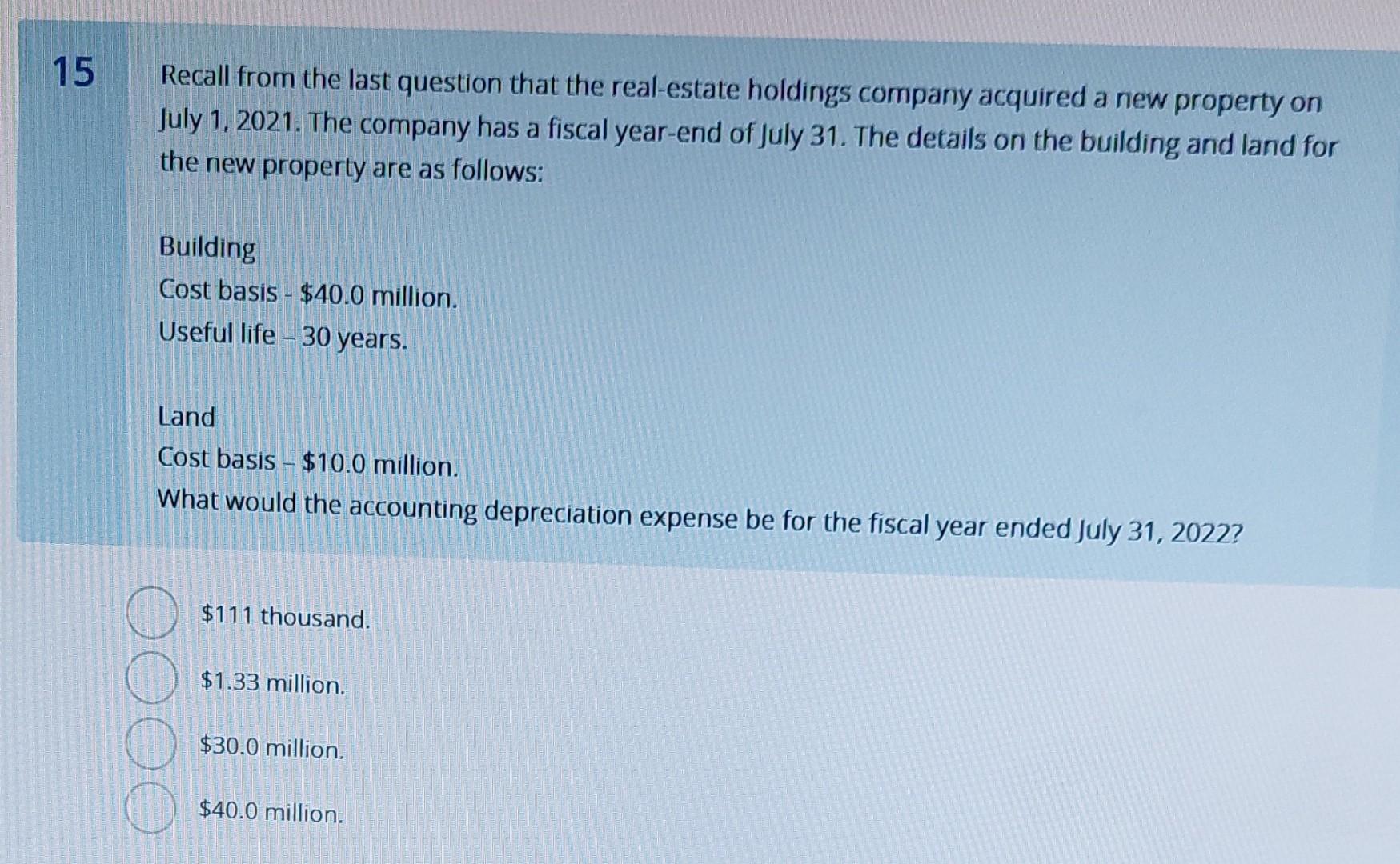
Which Of The Following Statements Regarding Gross Profit Is False
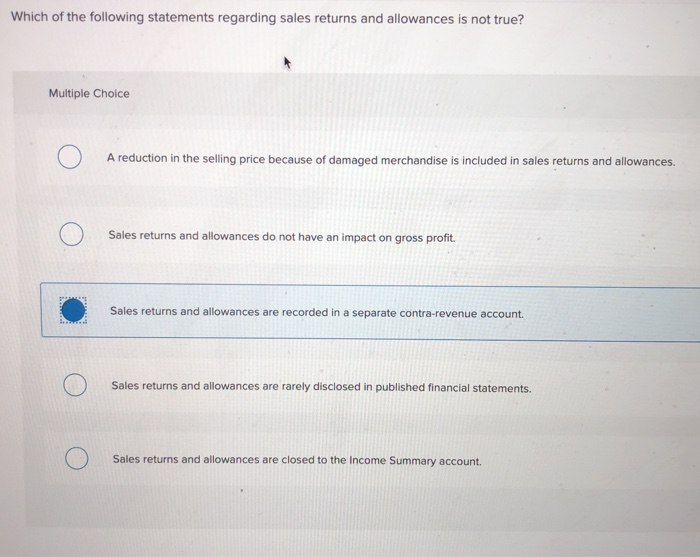
Imagine a bustling marketplace. Vendors hawk their wares, negotiating prices, balancing costs against the joy of a sale. Each transaction, a miniature equation: revenue in, expenses out, and what’s left? That "leftover," the gross profit, is the very lifeblood of any business, a simple concept masking a critical metric.
This article delves into the heart of gross profit, unpacking its meaning, its importance, and common misconceptions surrounding it. We’ll explore the concept through the lens of a deceptively simple question: Which of the following statements regarding gross profit is false? By dissecting the nuances of this financial yardstick, we aim to provide clarity and dispel confusion, empowering you to better understand the financial health of your own business, or any business you encounter. Let’s clarify what it is, how to calculate it and its true importance.
The Essence of Gross Profit
Gross profit, at its core, represents the profit a company makes after deducting the costs associated with producing and selling its goods or services. It’s the initial profit a company earns before accounting for operating expenses, interest, taxes, and other overhead costs. In essence, it's the profit derived from its primary business activities.
The formula for calculating gross profit is straightforward: Gross Profit = Revenue - Cost of Goods Sold (COGS). Revenue represents the total income generated from sales, while COGS encompasses the direct costs tied to producing those goods or services.
Understanding Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
COGS typically includes raw materials, direct labor, and any other expenses directly attributable to the production or purchase of goods sold. Think of a bakery: flour, sugar, eggs, and the baker's wages would all be included in COGS. It excludes indirect costs like rent, utilities, and marketing expenses, these are considered overhead.
For service-based businesses, COGS might include the direct labor costs of providing the service. For example, a landscaping company's COGS might include the wages of the crew and the cost of plants and materials used for a specific job.
The Significance of Gross Profit
Gross profit offers a crucial snapshot of a company's efficiency in managing its production costs. A high gross profit margin suggests that a company is efficiently producing its goods or services and effectively controlling its costs. Conversely, a low gross profit margin can signal problems with pricing, production costs, or both.
Investors and analysts closely monitor gross profit margins to assess a company's profitability and competitiveness within its industry. Trends in gross profit margin can reveal valuable insights into a company's performance over time.
Dissecting Common Misconceptions
Now, let's address the question posed earlier: Which of the following statements regarding gross profit is false? To answer this, we need to examine some common misconceptions surrounding gross profit.
Misconception 1: Gross profit equals net profit. This is perhaps the most common error. Net profit, also known as net income, is the profit remaining after all expenses (including operating expenses, interest, and taxes) have been deducted from revenue. Gross profit is simply an intermediary step in calculating net profit. It is the profit before these expenses.
Misconception 2: A high gross profit guarantees overall profitability. A high gross profit is certainly a positive sign, but it doesn't guarantee that a company is profitable overall. If a company has excessively high operating expenses, it can still incur a net loss despite a healthy gross profit. A significant amount of revenue needs to convert to net profit.
Misconception 3: Gross profit is the same as cash flow. Gross profit is an accounting measure of profitability, while cash flow represents the actual movement of cash in and out of a business. A company can have a healthy gross profit but still struggle with cash flow problems if it doesn't manage its receivables and payables effectively. Think of a business with a high amount of accounts receivable.
Misconception 4: Gross profit is irrelevant for service-based businesses. While the calculation might be slightly different, gross profit is equally important for service-based businesses. It helps them understand the profitability of their services and identify areas for cost optimization. Service business need to measure the labor, etc.
Identifying the False Statement
Based on these clarifications, we can now confidently identify a potentially false statement. Consider the following examples:
A. Gross profit is calculated as revenue minus cost of goods sold.
B. A high gross profit margin always indicates strong overall profitability.
C. Gross profit is useful for assessing the efficiency of production costs.
D. Service-based businesses do not need to calculate gross profit.
The false statements is B and D. B is false because a high gross profit margin can be offset by high operating expenses and D is false because service-based business need to calculate gross profit.
The Bigger Picture
Understanding gross profit goes beyond just memorizing a formula. It's about grasping the underlying dynamics of a business and its ability to generate value. By analyzing gross profit and its related metrics, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the challenges and opportunities that businesses face. Gross profit is one of the most basic financial statements that must be understood.
Gross profit is just one piece of the puzzle, a crucial indicator of a company's financial health, but not the entire picture. It needs to be considered in conjunction with other financial metrics to gain a comprehensive understanding of a business's overall performance. Gross profit is something that is useful and that should be understood.
In Conclusion
The journey through the world of gross profit reveals its significance as a fundamental measure of business performance. By dispelling common misconceptions, we've gained a clearer perspective on its limitations and its role within the broader financial landscape. Let us remember the value of asking the right questions and seeking a deeper understanding of the numbers that shape our economic world. It is important to know how to calculate and use the gross profit.








![Which Of The Following Statements Regarding Gross Profit Is False [ANSWERED] 22 Which of the following statements is FALSE regarding the](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question-candidate/20230920150204894475-4569668.jpg?h=512)